GCSE DT | Quizlet
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Hardwood
Timbers from deciduous trees e.g. oak, mahogany, beech, ash
Softwood
Timbers from coniferous trees
Oak
Hardwood. Hard, tough, durable, high density. Used in high-quality furniture and boat building. Finishes well, but contains an acid that corrodes steel
Mahogany
Hardwood. Durable, medium density. Used in indoor furniture, window frames. Finishes well, but is prone to warping.
Beech
Hardwood. Hard, tough. Used in workshop benches, children's toys. Turns and finishes well, but is prone to warping.
Ash
Hardwood. Tough, flexible, good elasticity. Used for ladders, sports equipment. Is flexible, but can splinter
Pine
Softwood. Lightweight. Used in garden decking, floorboards, children's toys. Has a nice colour and grain pattern, but is prone to warping and knots can fall out and leave holes.
Plywood
Manufactured board. Very strong, resistant to splintering. Used in boat building, drawers etc. Available in large sheets, thick sheets will not warp, can be laminated. Thin sheets v. felxibile and will warp
Chipboard
Manufactured board. Not v. resistant to water, strong in all directions. Used for large floor boards and decking, and flatpack furniture etc. Makes good use of waste materials. Not v. good around water, will chip and flake on edges
Medium Density Fibreboard (MDF)
Manufactured board. V. dense, stable and not affected by changing humidity levels. used for flatpack furniture, drawers etc. Thin sheets can make 2D shapes. Not v. good with water.
Hardboard
Manufactured board. Used for drawer bottoms, cabinets etc. Cheapest manufacture board. Not v. strong
Ferrous Metal
Composed mainly of ferrite or iron. Is likely to be magnetic.
Non-Ferrous Metal
Contains no iron, and consists almost entirely of pure metals
Alloy
A metal formed by mixing two or more metals or elements together.
Mild Steel
Ferrous metal. Tough, malleable, magnetic. Used for structural girders, car body panels. Easily worked and joined, cheap, can be recycled. Will rust, can only be case hardened.
Stainless Steel
Ferrous metal. Hard, tough, corrosion resistant. Used in cutlery, kitchen sinks, pots and pans etc. Easily cleaned, can be recycled, high lustre finish. Difficult to use and join - specialist welding equipment required.
Carbon Steel
Ferrous metal. Ductile. Used for nails, screws, nuts etc. Can be recycled. Will rust, can easily be heat treated
Aluminium
Non-ferrous metal. Lightweight, soft, ductile, malleable, good conductor, good corrosion resistance. Used for cans, window frames, kitchen foil. Easily drawn into wires and sheets, easily cast, can be recycled. Expensive, difficult to weld.
Copper
Non-ferrous metal. Malleable, ductile, good conductor, corrosion resistant. Used in electrical cables, plumbing fittings and pipes etc. Easily drawn into wires, can be recycled, easily soldered. Exspensive, will tarnosh over time
Zinc
Non-ferrous metal. Corrosion resistant. Used in protective coverings, negative battery terminals. Can be recycled. Brittle
Brass
Non-ferrous metal. Corrosion resistant, casts well, good conductor. Used in marine fittings. High lustre finish, can be recycled. Exspensive
Mild Steel (Alloy)
99.8% iron. 0.2% carbon
Brass (Alloy)
65% copper. 35% zinc
Ductility
The ability to be drawn or stretched into smaller, thinner sections
Malleability
The abilty to be deformed or compressed without tearing or cracking
Hardness
The ability to withstand abrasive wear and indentation
Toughness
The ability to withstand sudden and shock loading without fracture
Elasticity
The ability to return to its original shape once the deforming force is removed
Tension Strength
The ability of a material to withstand being pulled apart
Compression Strength
The ability of a material to withstand being squashed
Shear Strength
The ability of a material or joint, to withstand being slid or pulled apart.
Thermoplastic
Long chains of molecules that are tangled together and have no fixed pattern. Can be reheated and reshaped many times. Have a plastic memory
Acrylic
Polymer. Good impact strength, lightweight, good electrical insulator, durable. Used in fish tanks, furniture, car indicator covers. Can be recycled, finished well, available in numerous colours. Scratches easily, soft.
Polyethene
Polymer. Tough, resistant to chemicals, soft and flexible, electrical insulator. Used for carrier bags, toys plastic bottles etc. Can be recycled. A lot of waste ends up in landfills
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polymer. Weather resistance, weather resistant, lightweight, stiff, hard, tough. Used for pipes, shoe soles, bottles etc. Can be recylced, cheap to manufacture. V. expensive to recycle, dangerous fumes given off when burnt
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)
Polymer. Tough, high impact strength, rigid, good electrical insulator. used for food appliances, toys cutlery, DVD/CD cases. Available in numerous colours, can be machined and painted, can be recycled. Expensive, limited flexibility, will not biodegrade
Acrylonitrile Butadienestyrene (ABS)
Polymer. High impact strength, tough, scratch-resistance, lightweight, durable. Used for kitchenware, camera cases, toys etc. Available in numerous colours. relatively expensive
Polyester Resin
Thermosetting plastic. Good electrical insulator, hard, brittle, resists UV radiation. Used in boat hulls, adhesives, casting etc., Can be mixed to achieve a range of colours. Water resistant. Contracts on curing. Can cause excess heat
Urea Formaldehyde
Thermosetting plastic. Stiff, hard, brittle, scratch/stain resistant, high tensile strength Used in tableware, worktop laminates etc. Can be coloured. Gives off toxiv fumes when it cures
Plasticity
The ability to withstand weathering deterioration or corrosion
Durability
The ability to withstand weathering deterioration or corrosion
Carbon Fibre
Composite. High tensile strength. Aesthetically pleasing. V. exspensive
Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP)
Composite. Lightweight, low maintenance, an endless range of colours, durable etc. Difficult to repair, time-consuming to manufacture. Produces a fine dust
Shape Memory Alloys (SMA)
Smart Material. A collection of metal alloys that remember their original cold form shape. Common SMAs are nitinol (titanium/nickel alloy) Used for glasses frames, braces etc. Realtively exspensive
Photochromic paint
Smart Material. A pain that changes colour when exposed directly to a UV light source. The base colour is white. Used in clothing and textiles. Over time the ability to chnge colour will decay (natural fatigue)
Reactive Glass
Smart Material. Glass that changes colour when exposed to UV light, or when a voltage is passed through it. Used in windows etc. Expensive to install and manufacture
Carbon Nanotubes
Smart Material. Cylindrical nanostructure made from carbon molecules. Join together to form long 'ropes'. have many forms like Single-Wall Nanotubes (SWNT) and Multi-Wall Nanotubes (MWNT). Six times lighter than steel, flexible, conductor, inert, good tensile strength. Expensive.
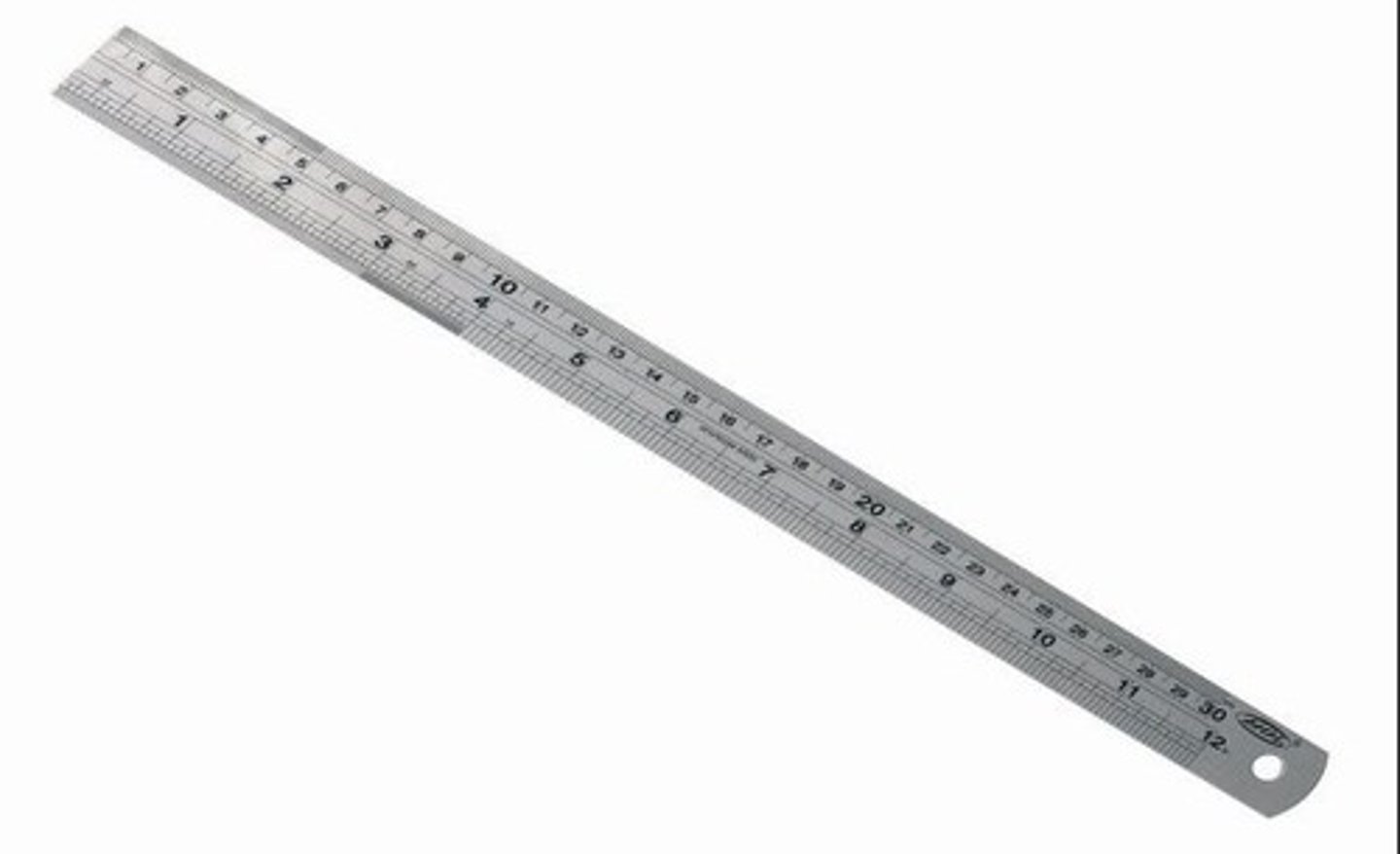
Steel Rule
Tool. For measuring up to 300mm in length

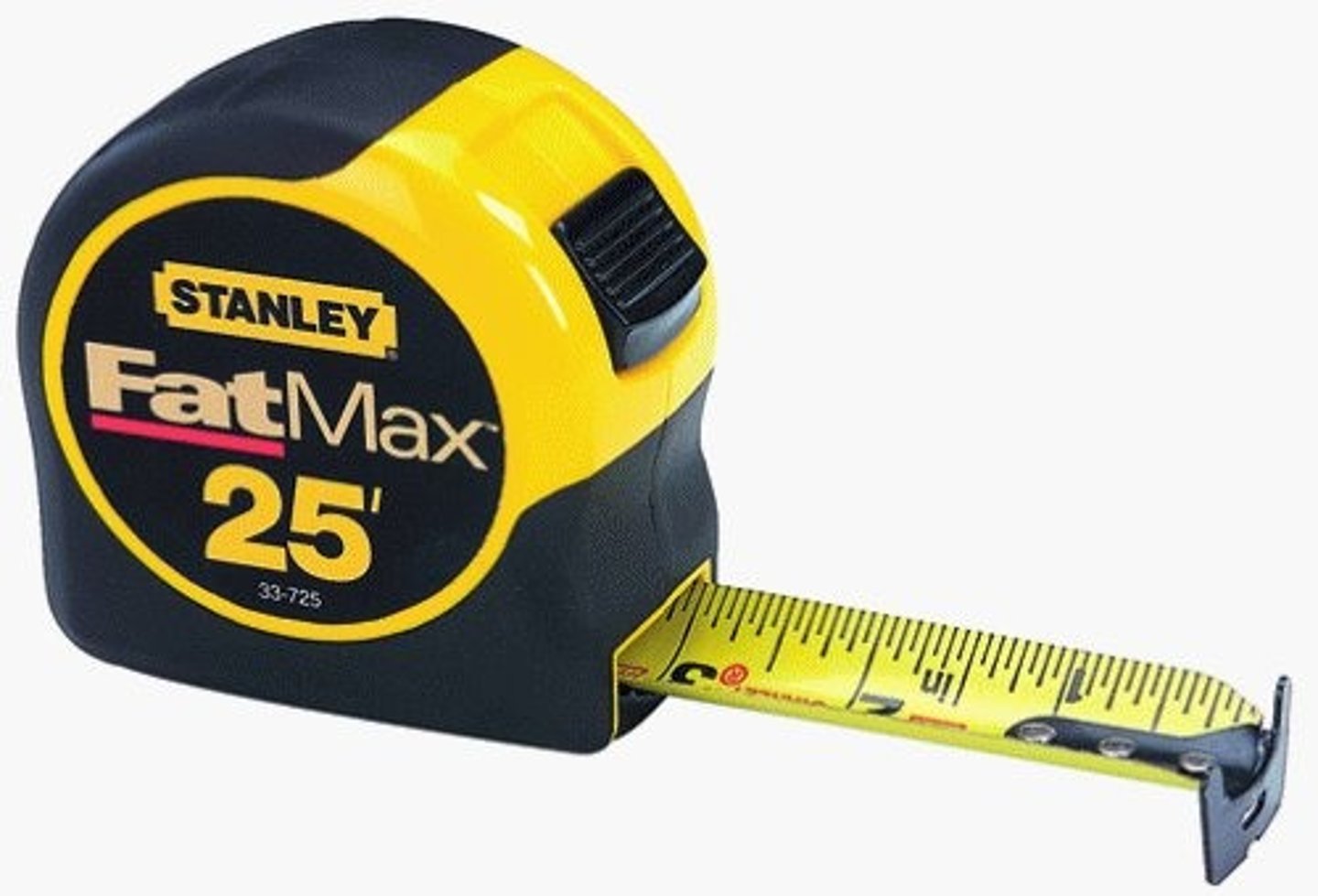
Measuring Tape
Tool. For making longer measurements up to 5m

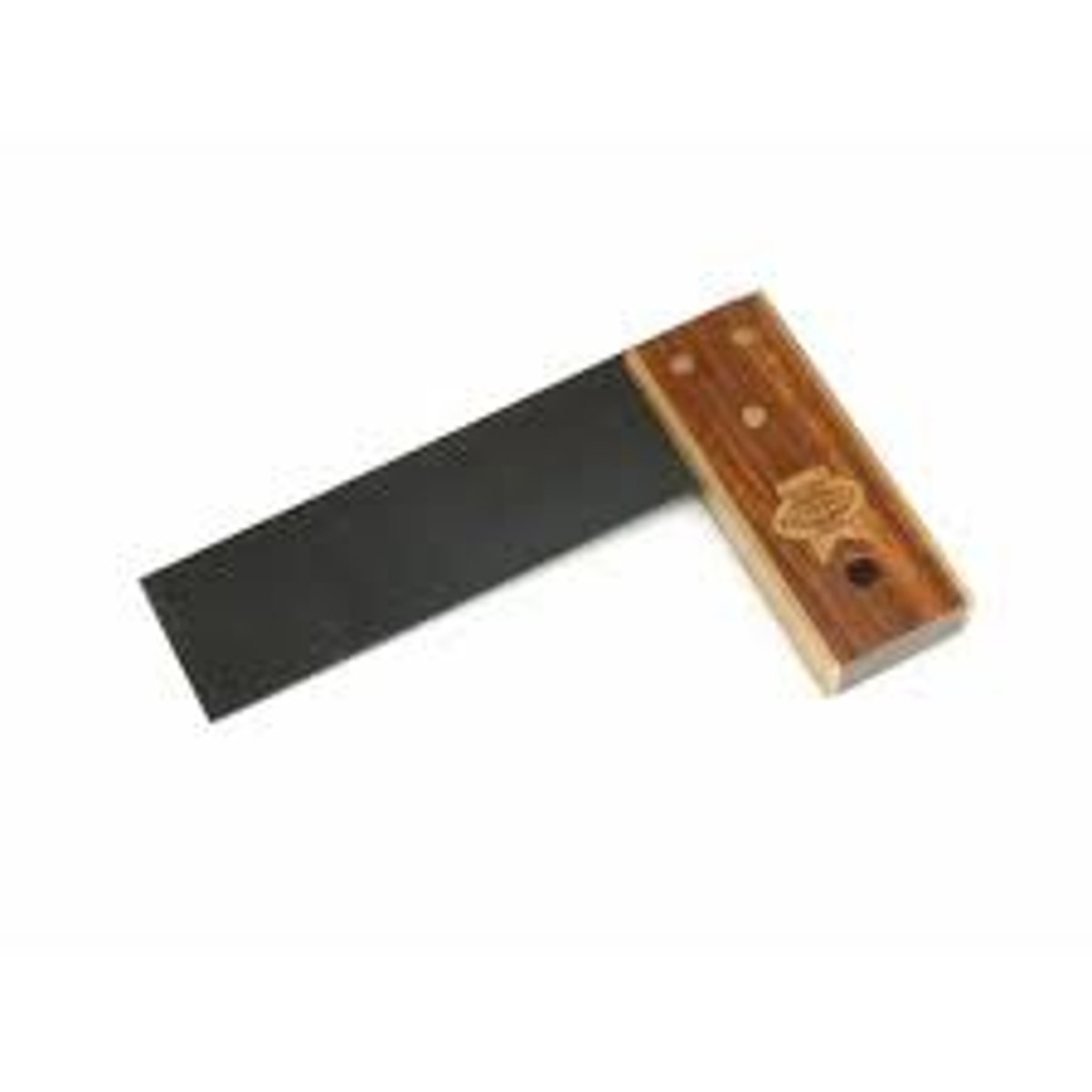
Try Square
Tool. Marking out or checking right angles on wood or plastic

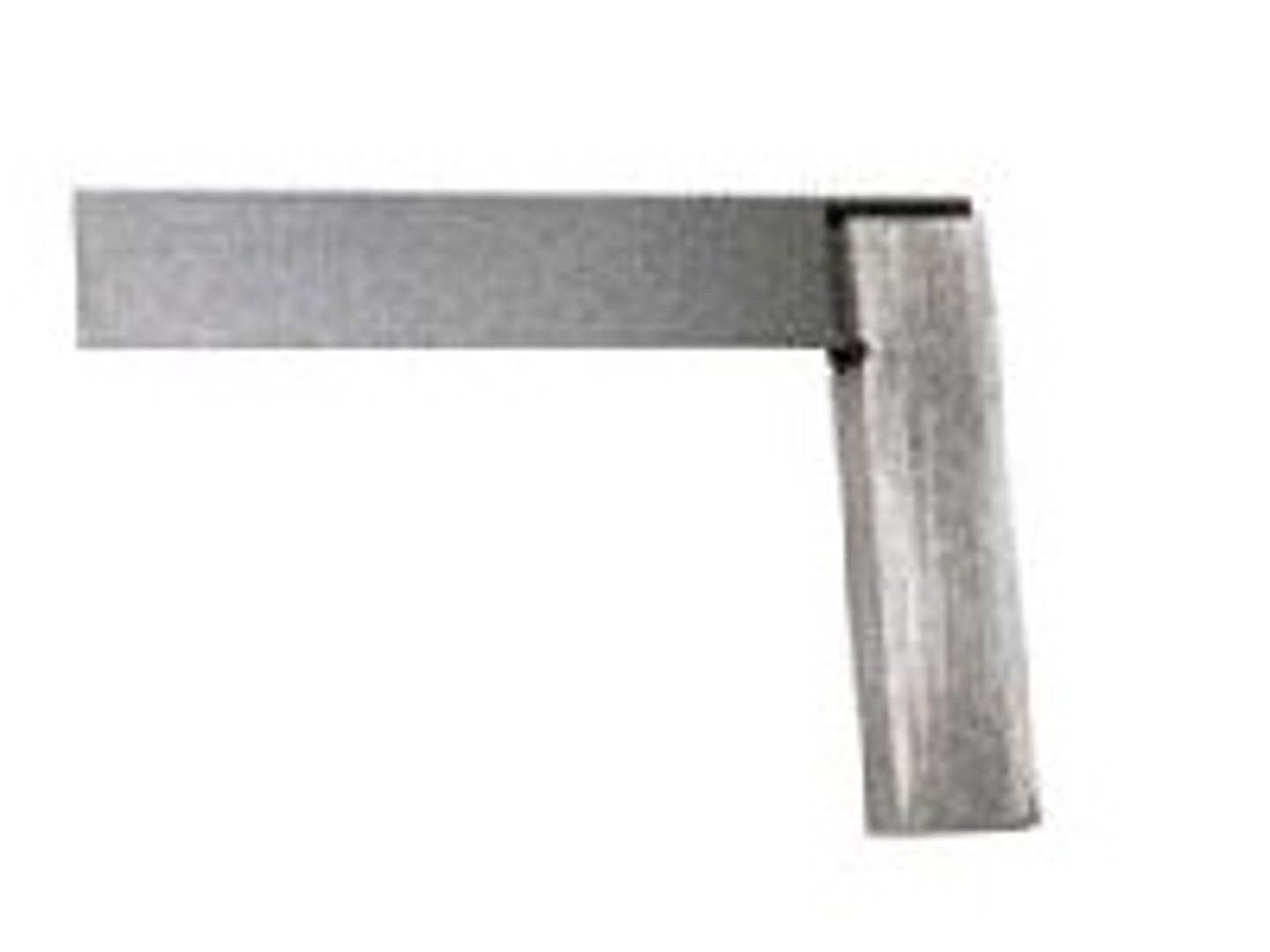
Engineer's Square
Tool. Marking out or checking right angles on metal or plastic

Mitre Square
Tool. Marking out o checking angles of 45 or 135

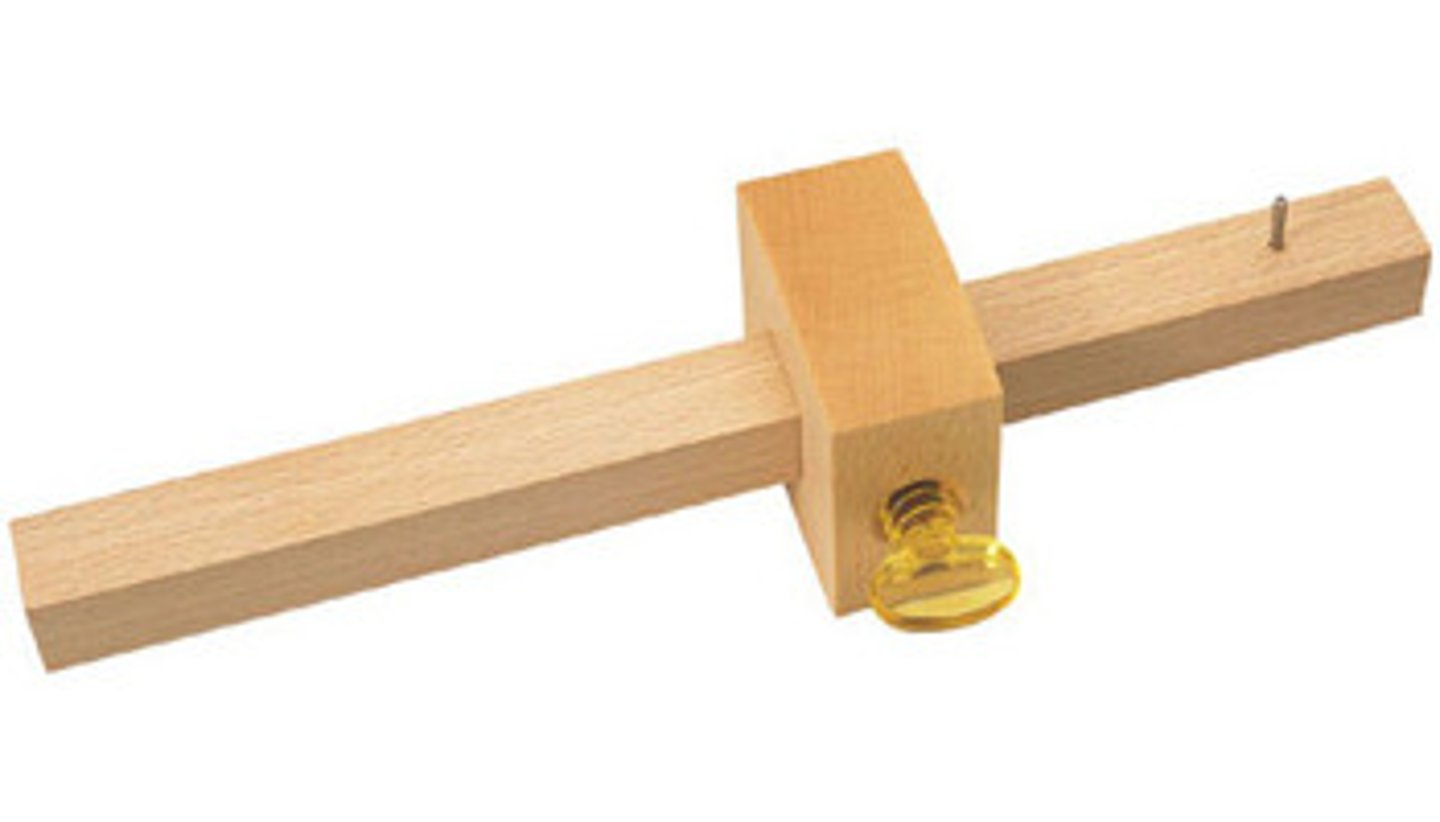
Marking Gauge
Tool. Used for marking lines parallel to the face edge and side of the wood

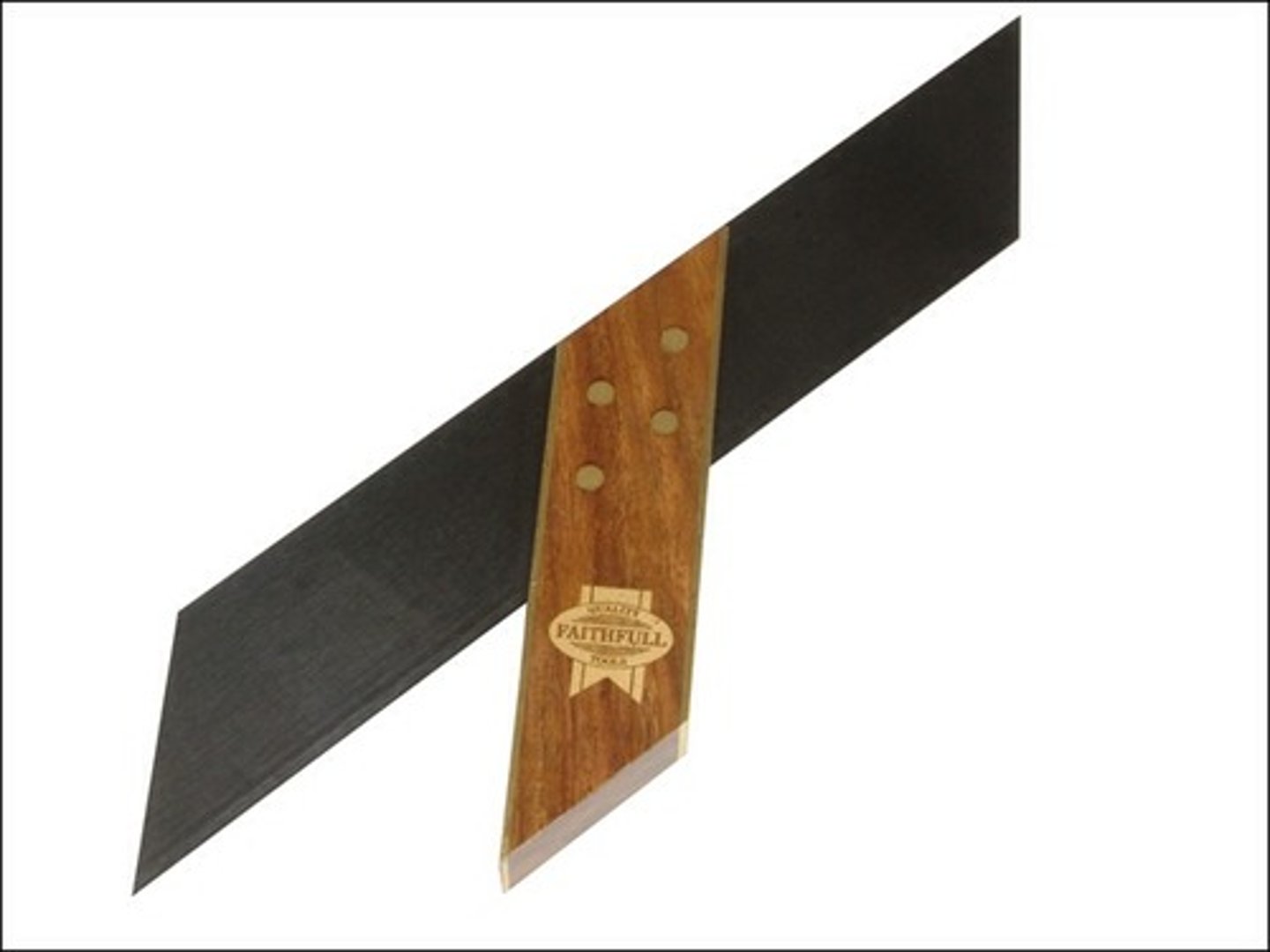
Cutting Gauge
Tool. Used for cutting across the grain of wood.

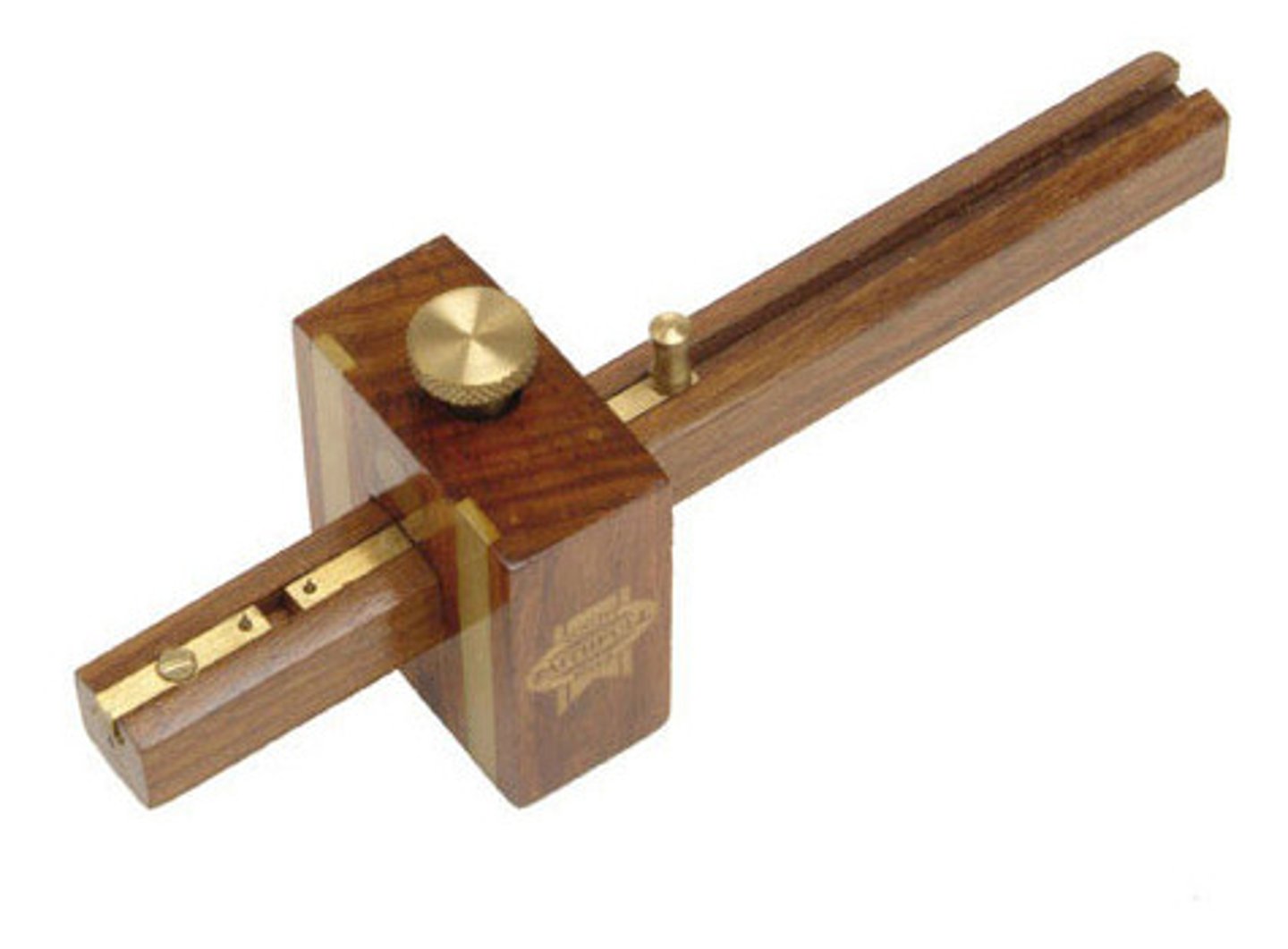
Mortise Gauge
Tool. Used for marking two parallel lines where a mortise and tenon joint is to be cut

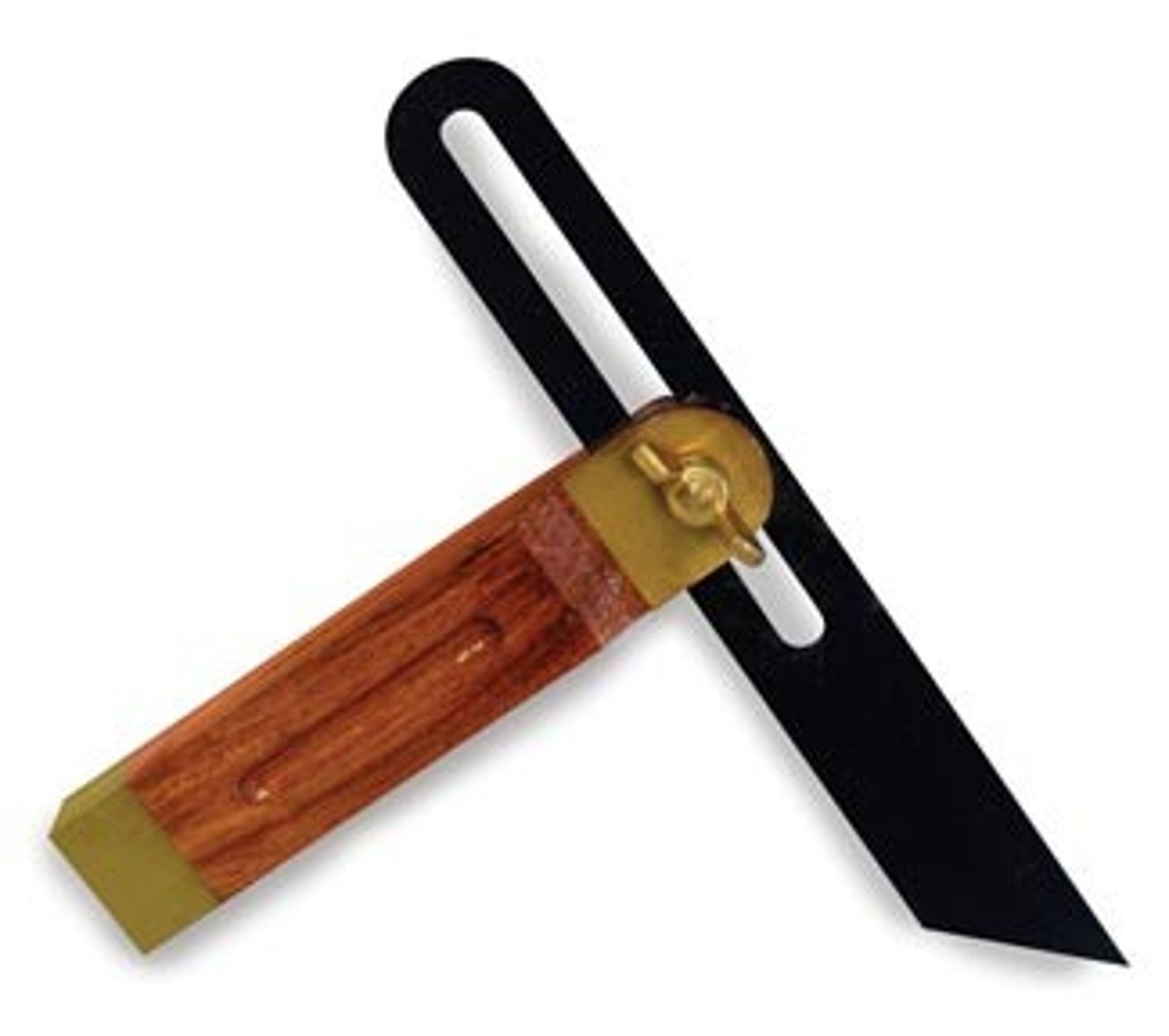
Scriber
Tool. Used to scratch the surface of metal and plastic lightly
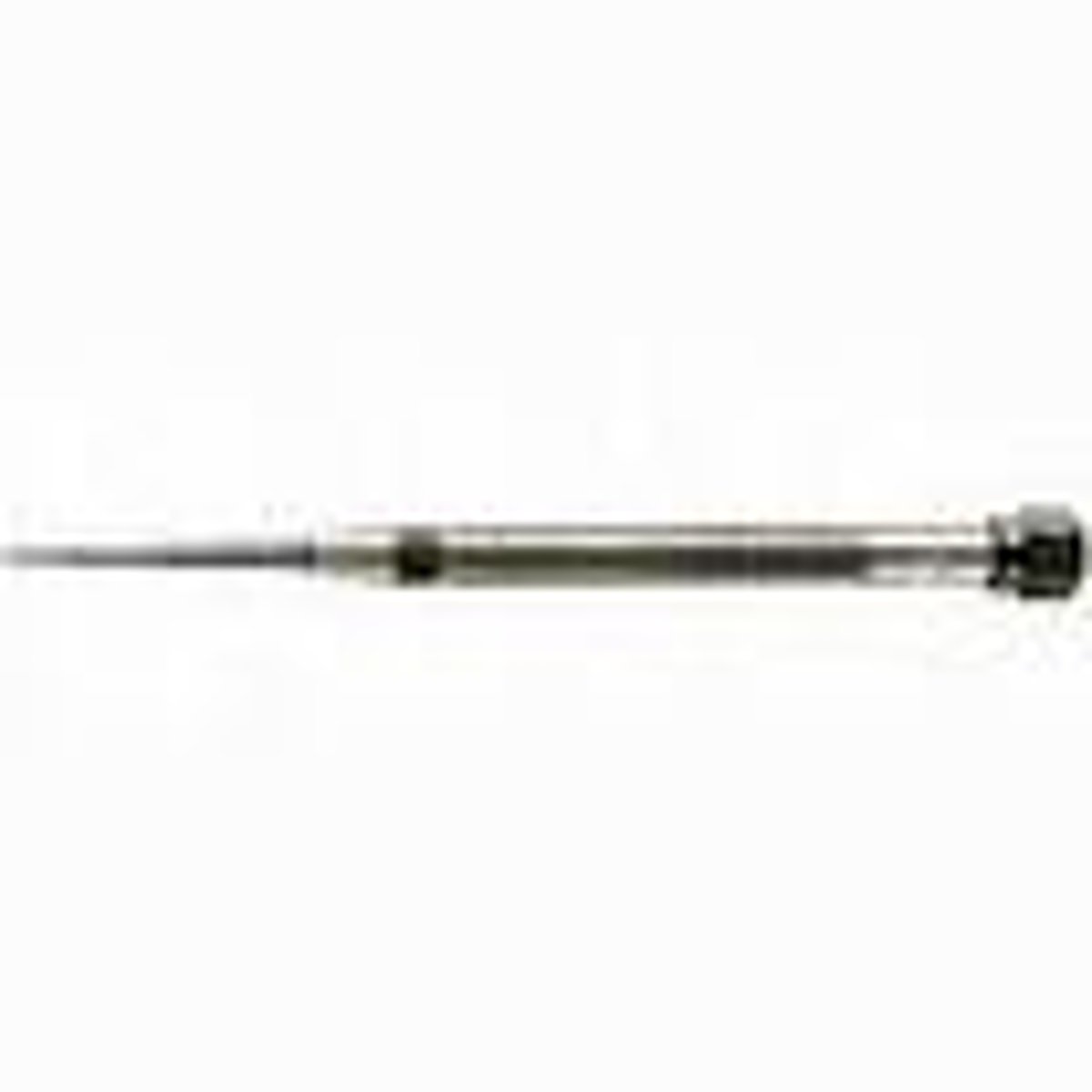

Centre Punch
Tool. Used to make an indent on the surface where holes are to be drilled in the metal
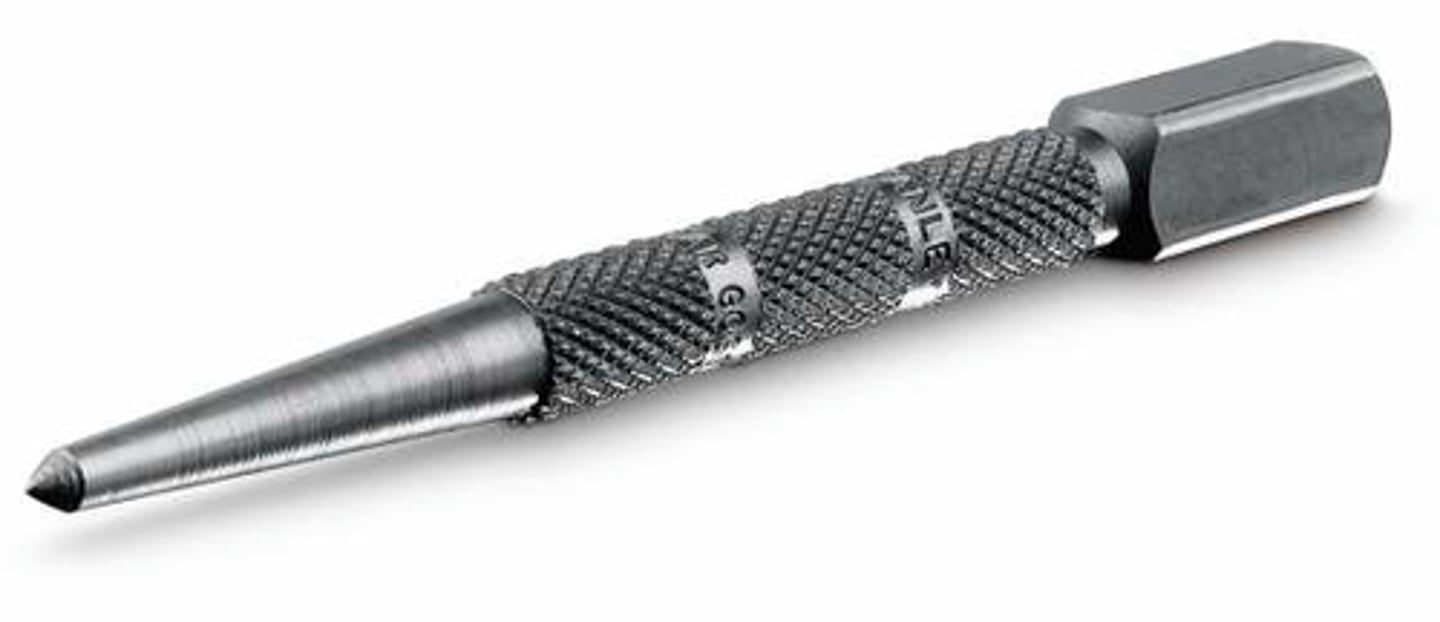

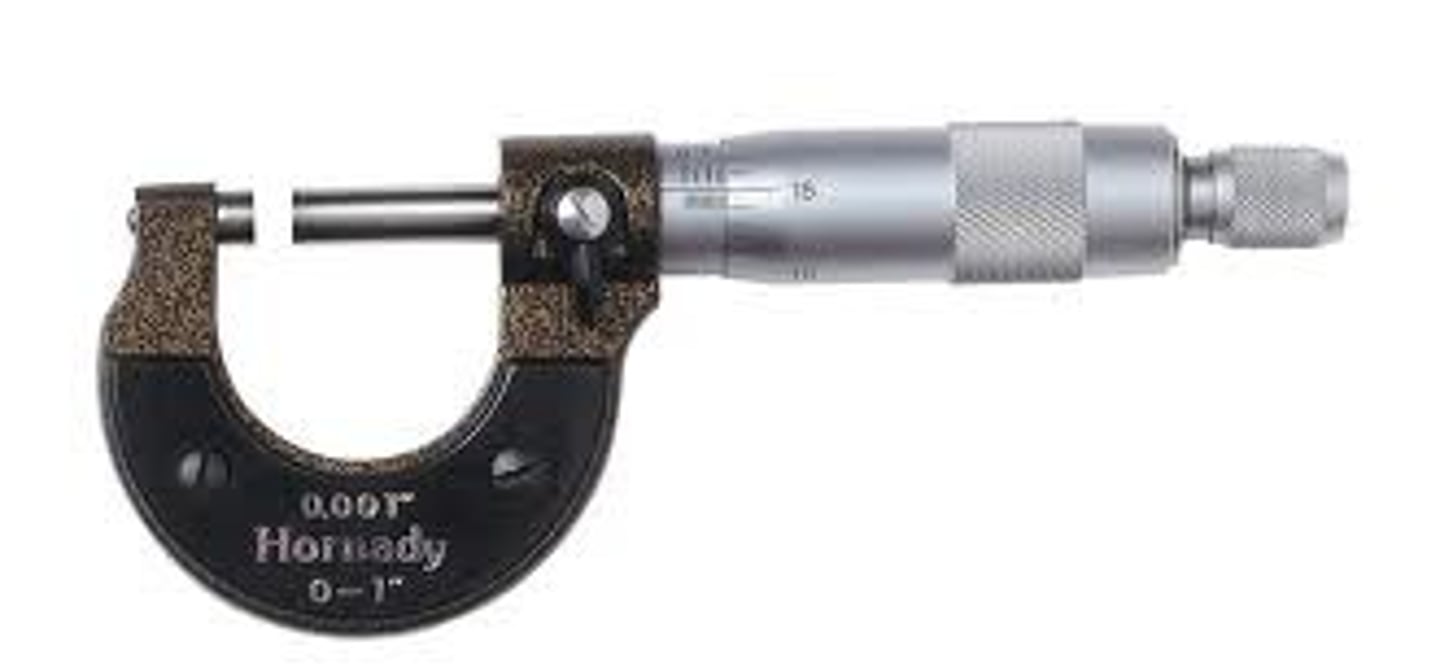
Micrometer
Tool. Used to make accurate measurements

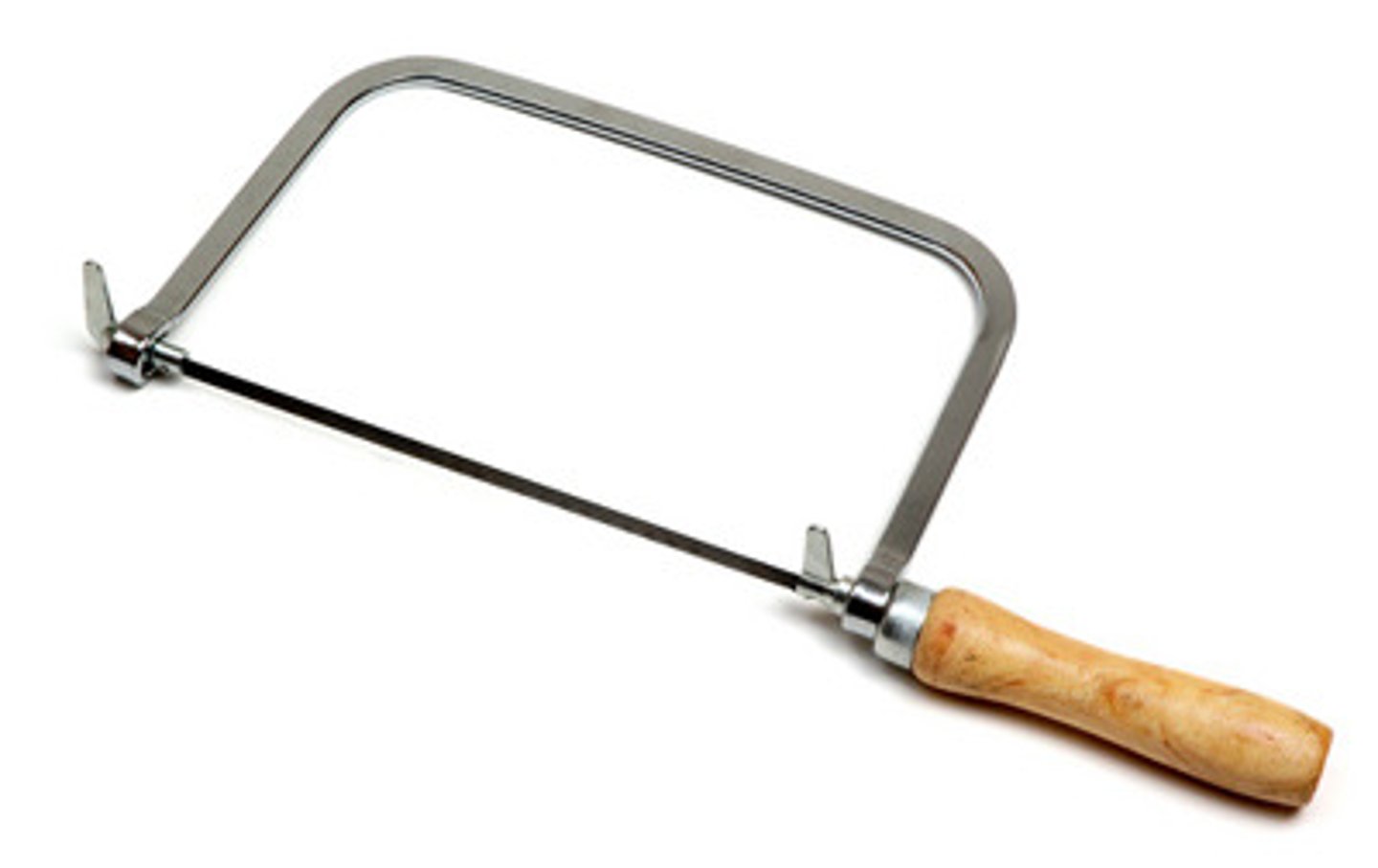
Coping Saw
Tool. Cuts curves in woods and plastics

Tenon Saw
Tool. Cuts wood
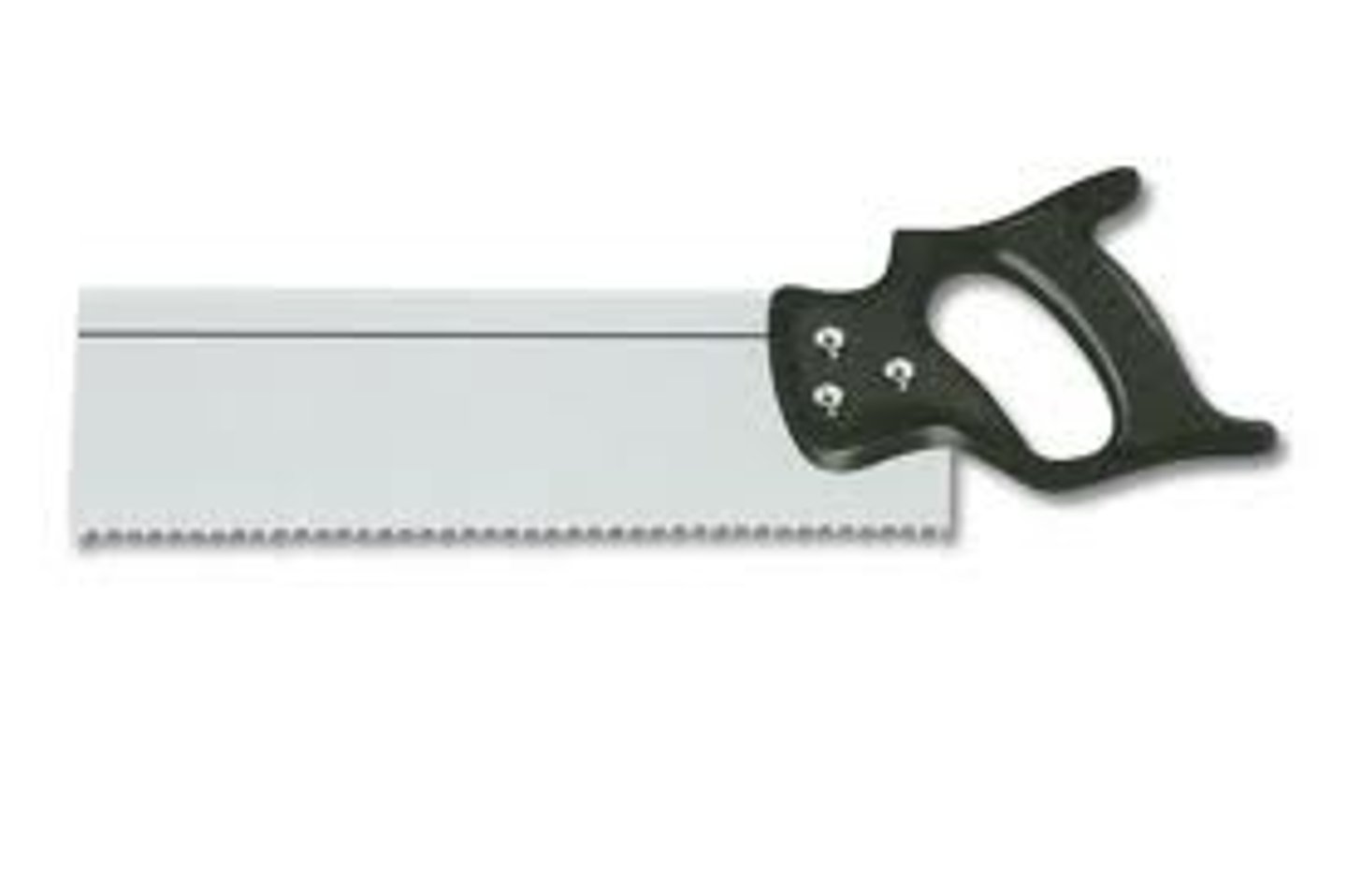

Dovetail Saw
Tool. Used for small, accurate joints such as dovetail joints.

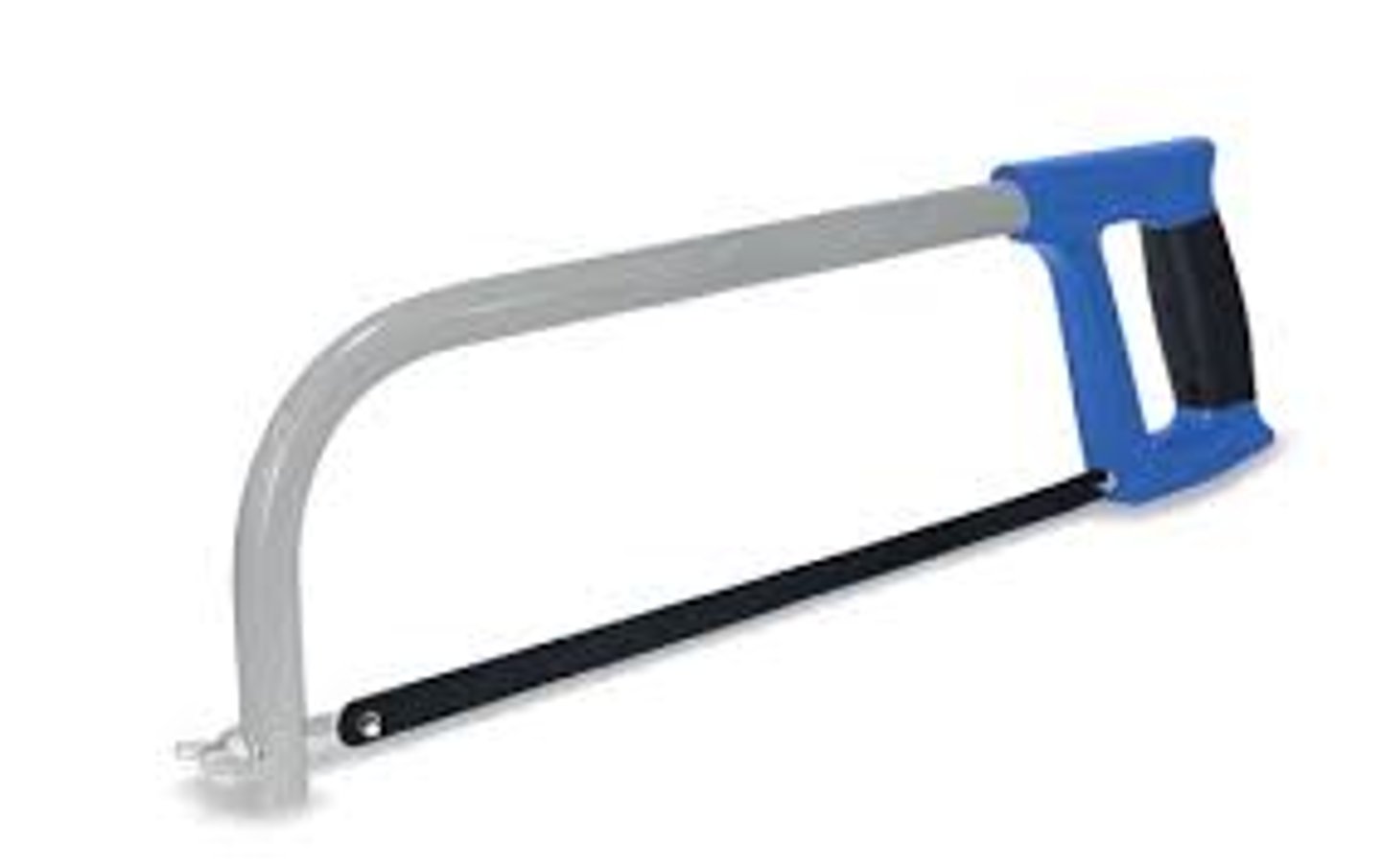
Adjustable Hacksaw
Tool. Cuts straight or angled cuts in plastic and metal.

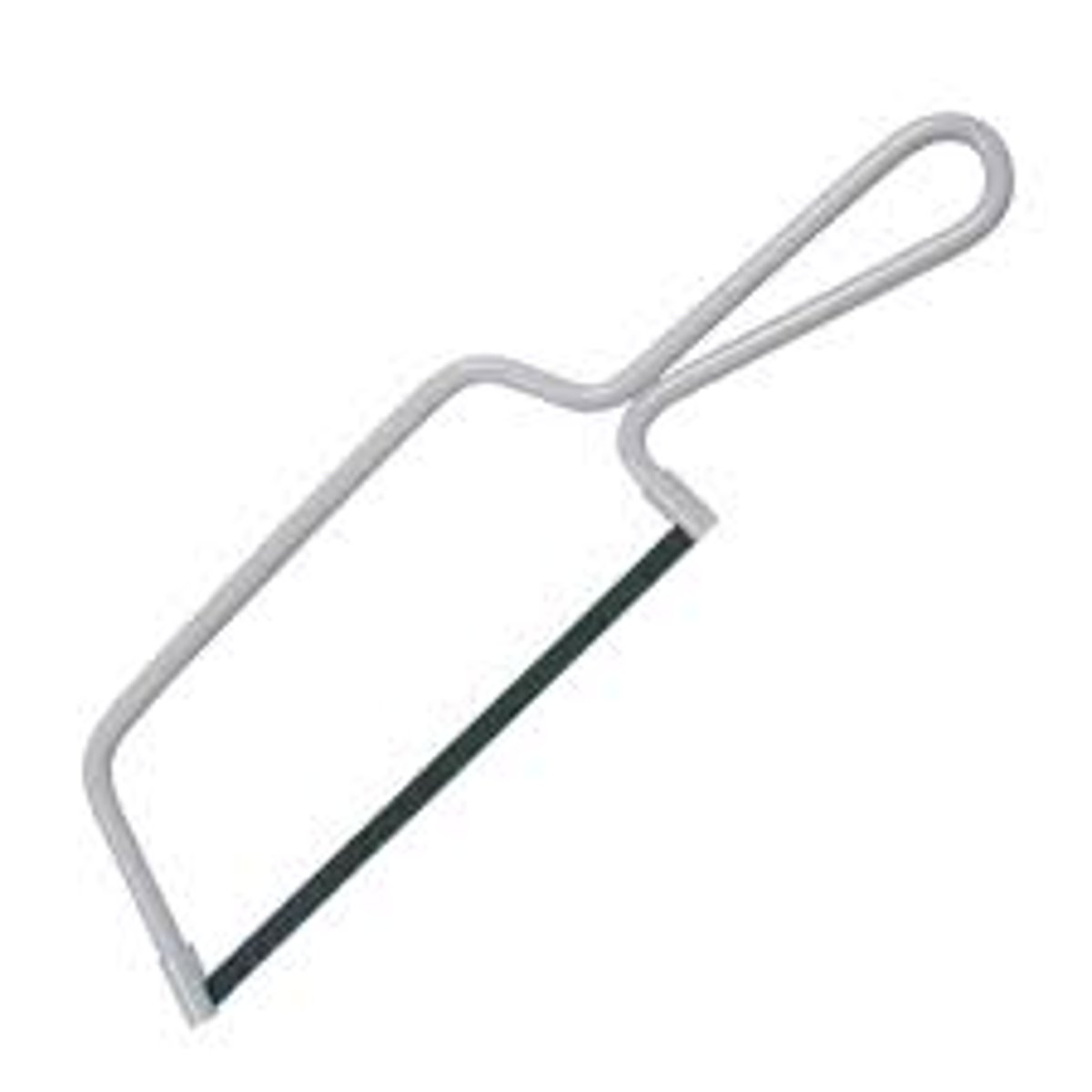
Junior Hacksaw
Tool. Cuts straight or angled cuts in plastic and metal.

Jack Plane
Tool. Smooths and flattens wood to size.
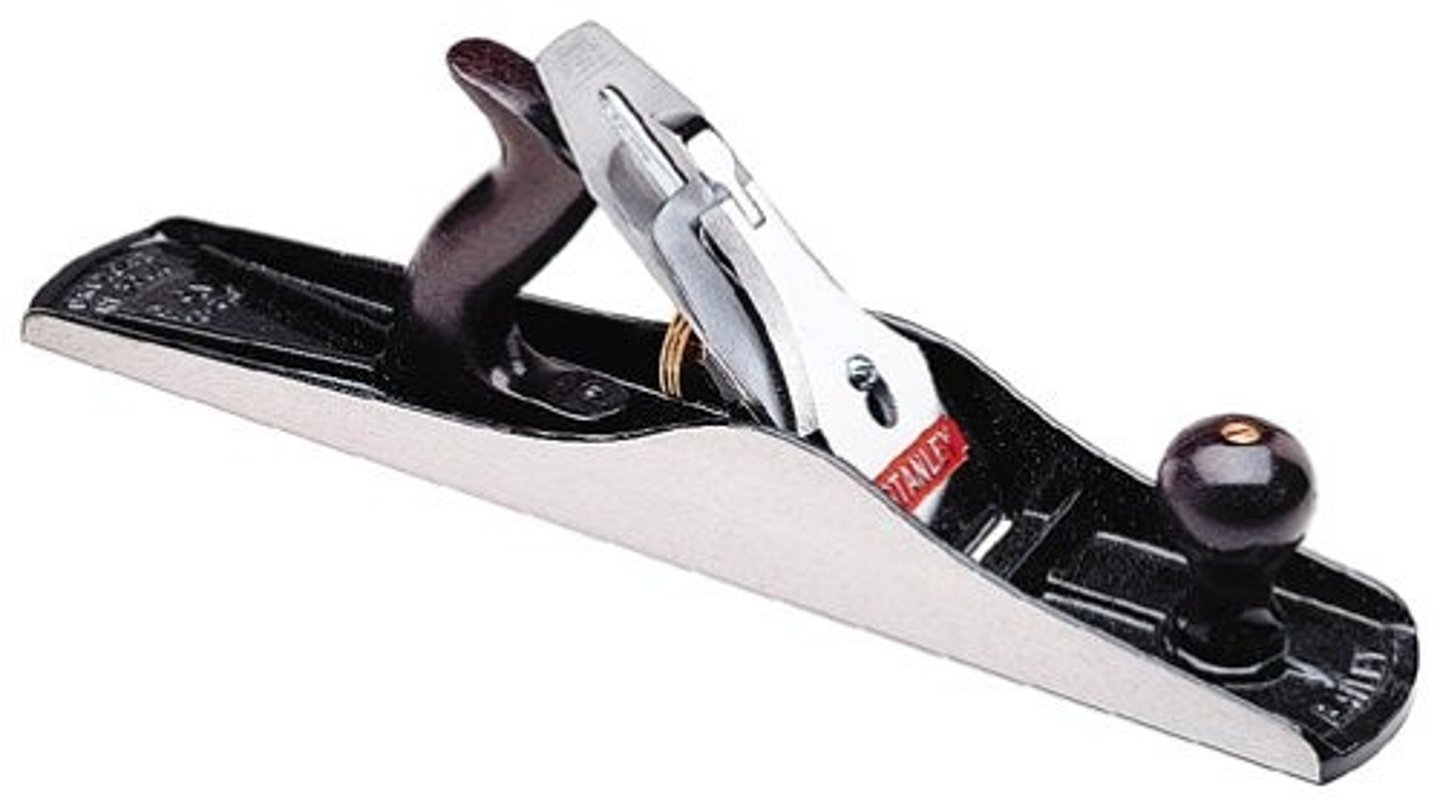

Smoothing Plane
Tool. Used for finishing a surface and for use on the end grain
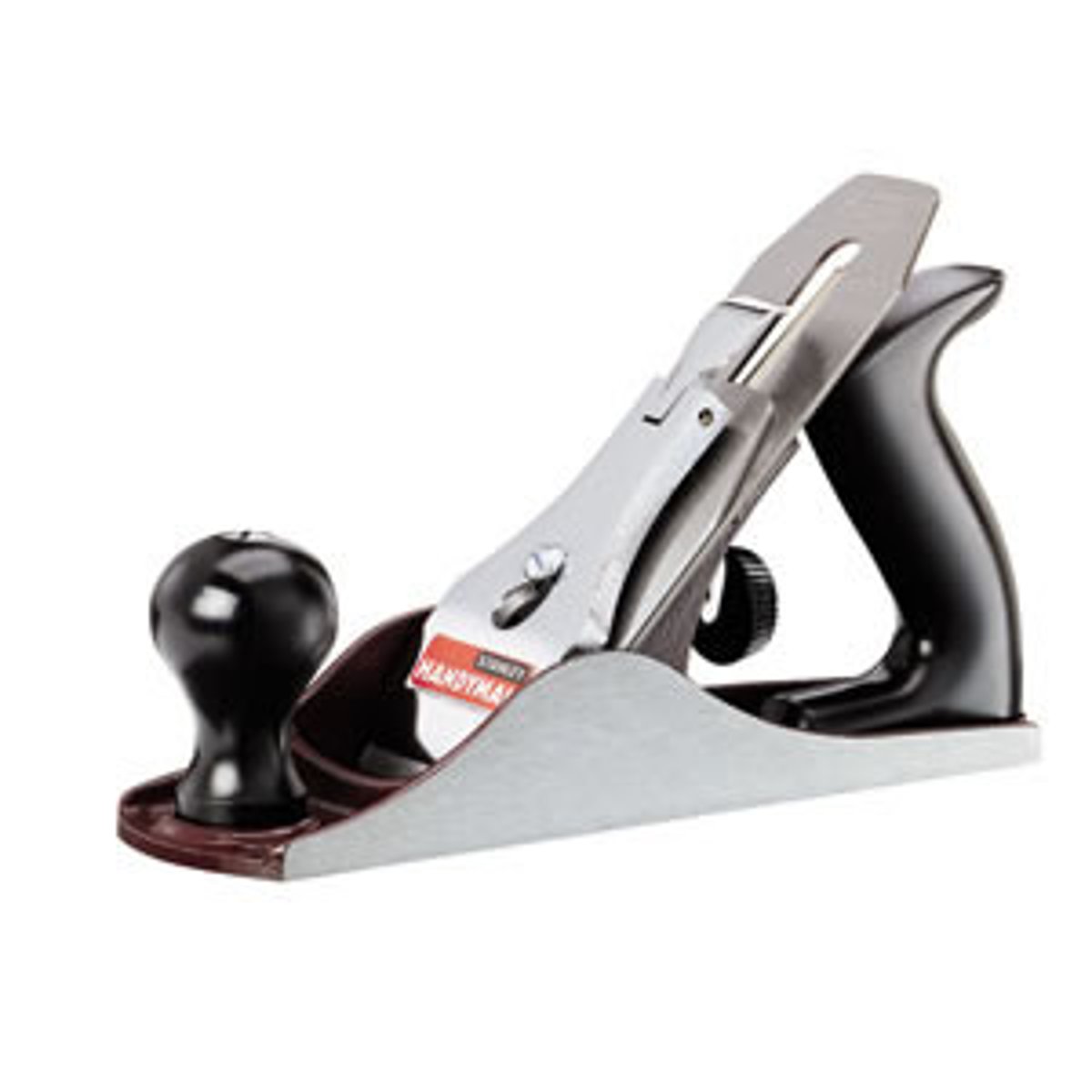

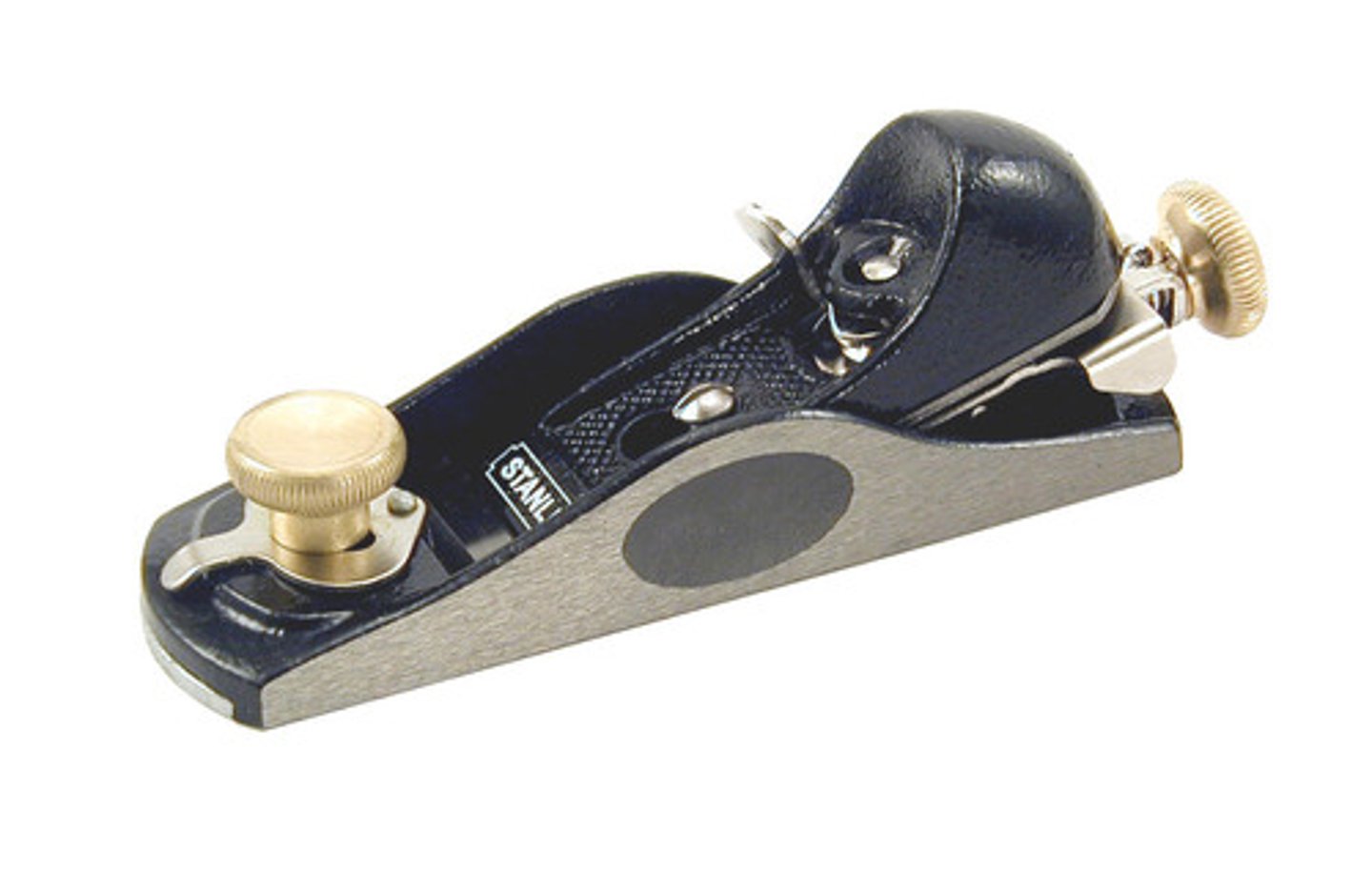
Block Plane
Tool. Removes sharp edges and makes a bevelled edge.

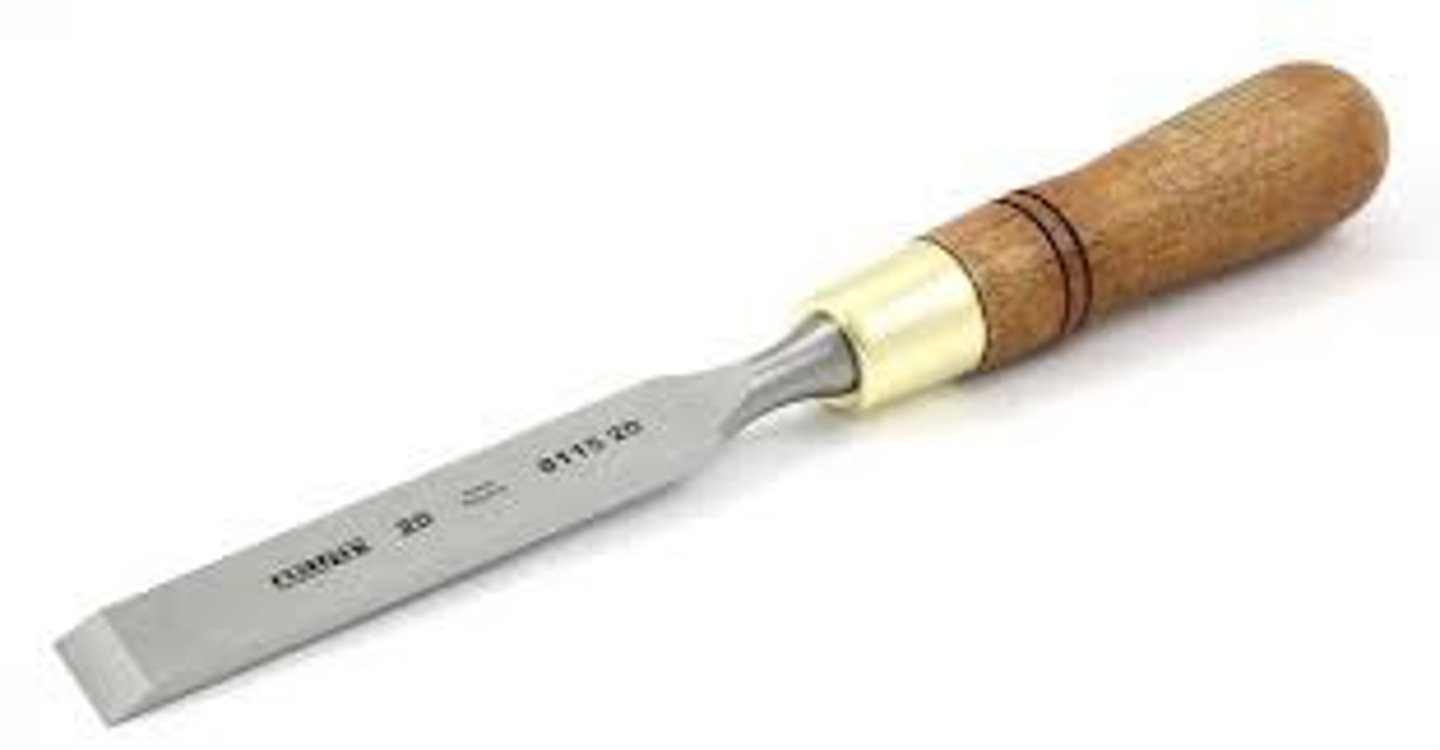
Firmer Chisel
Tool. General purpose chisel, with a square edge

Bevel-Edge Chisel
Tool. Has a bevelled edge that allows it to get into corners, and for cutting dovetails
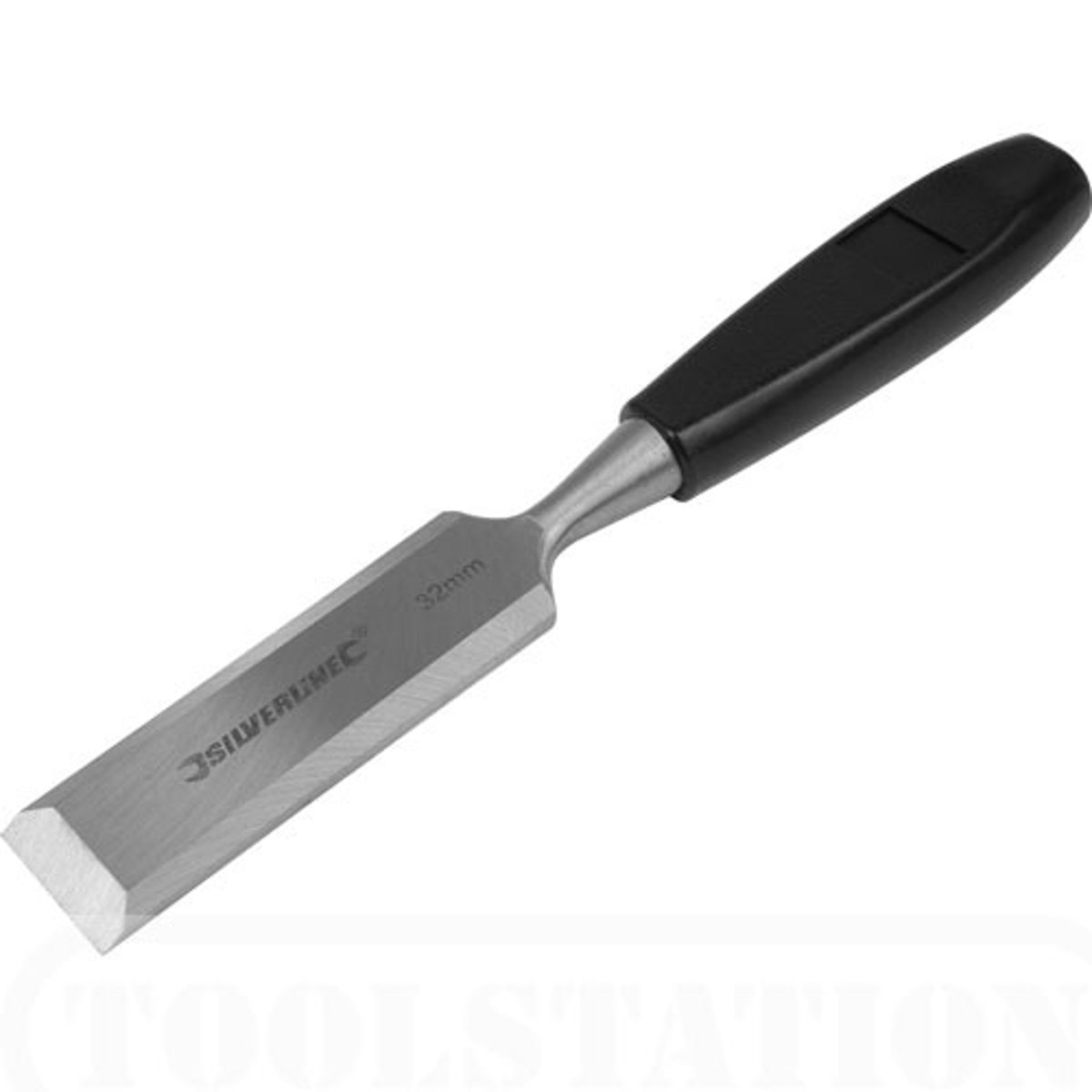

Mortise Chisel
Tool. Has a deeper blade, and used to cut mortise joints
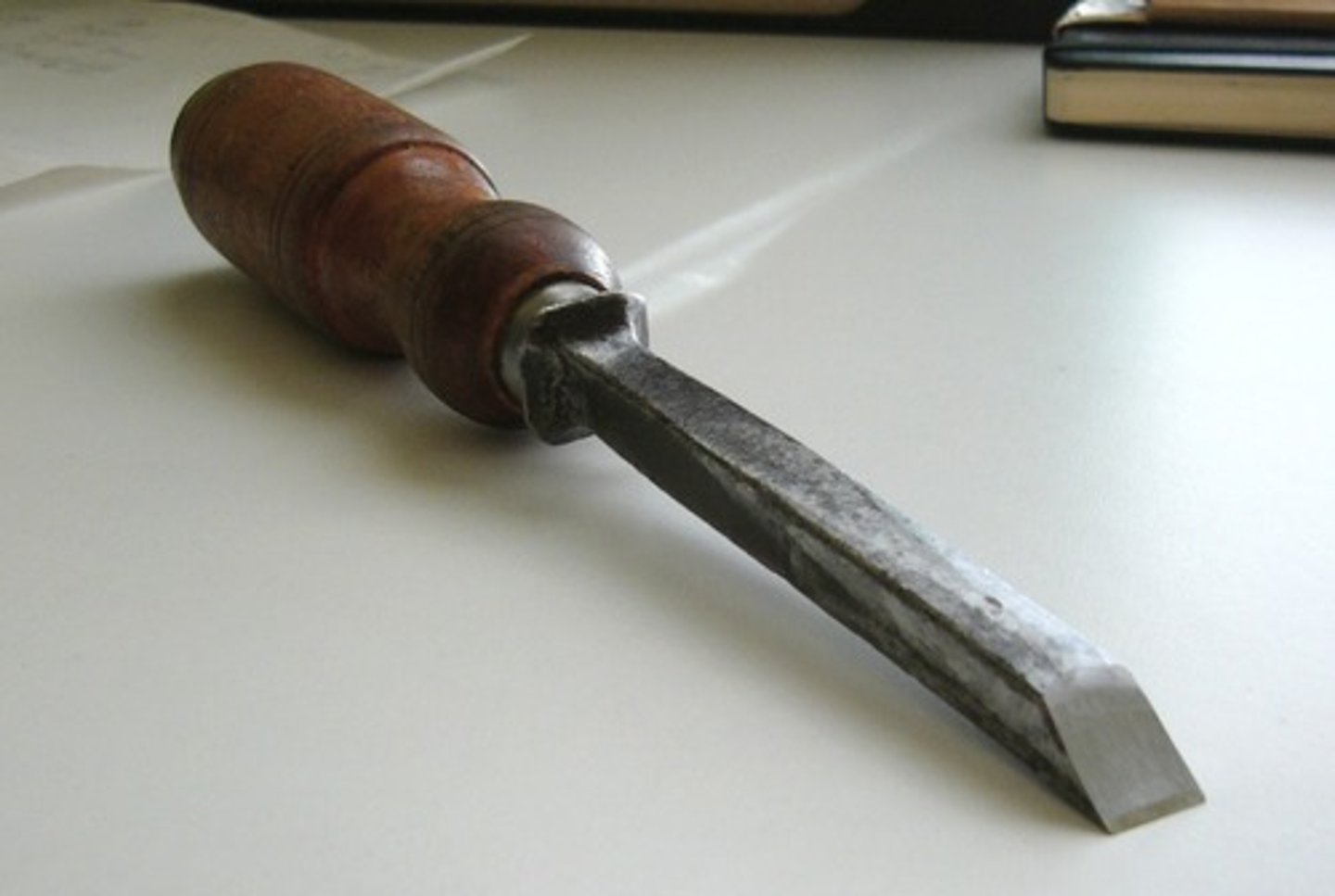

Gouge
Tool. Has a curve blade and used for carving
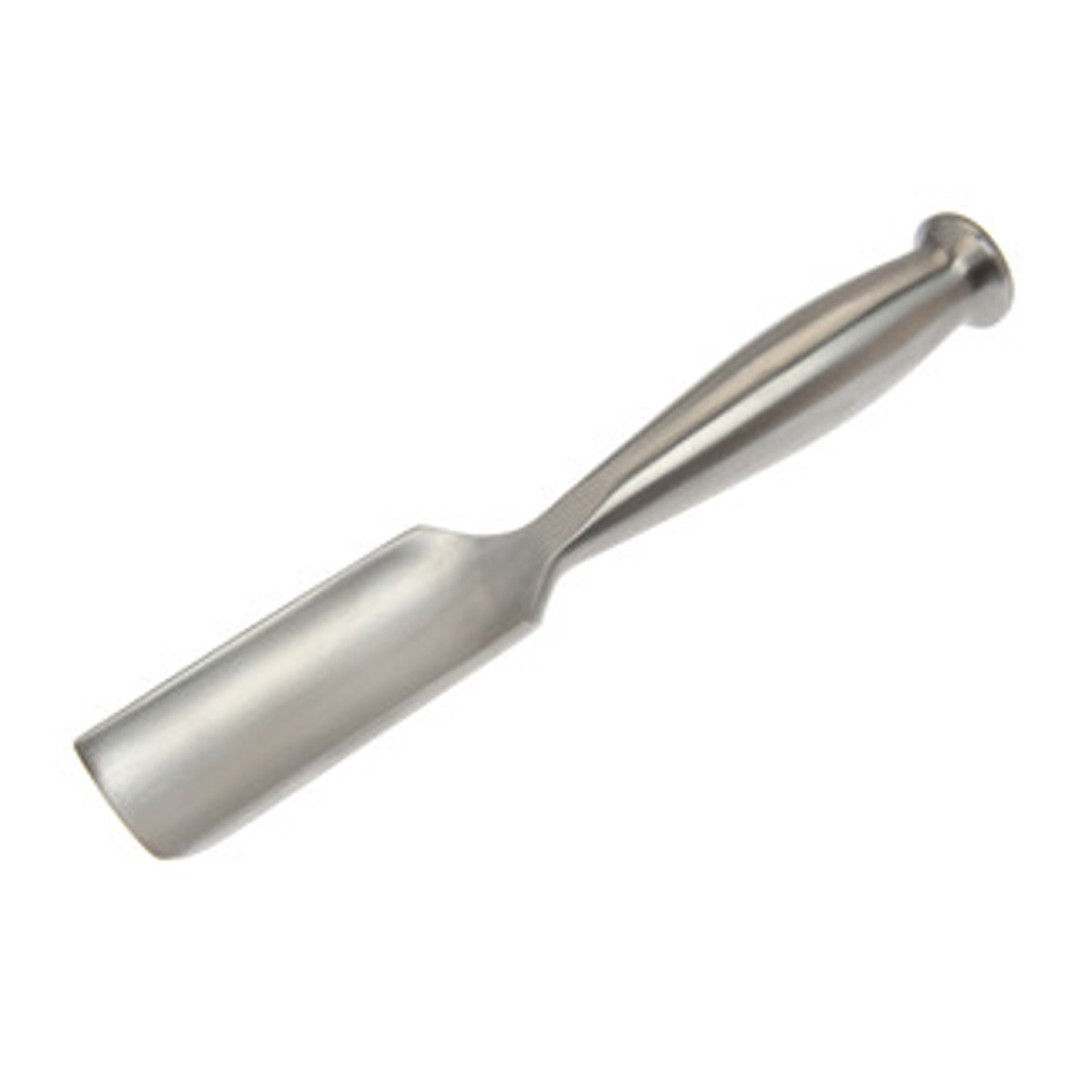

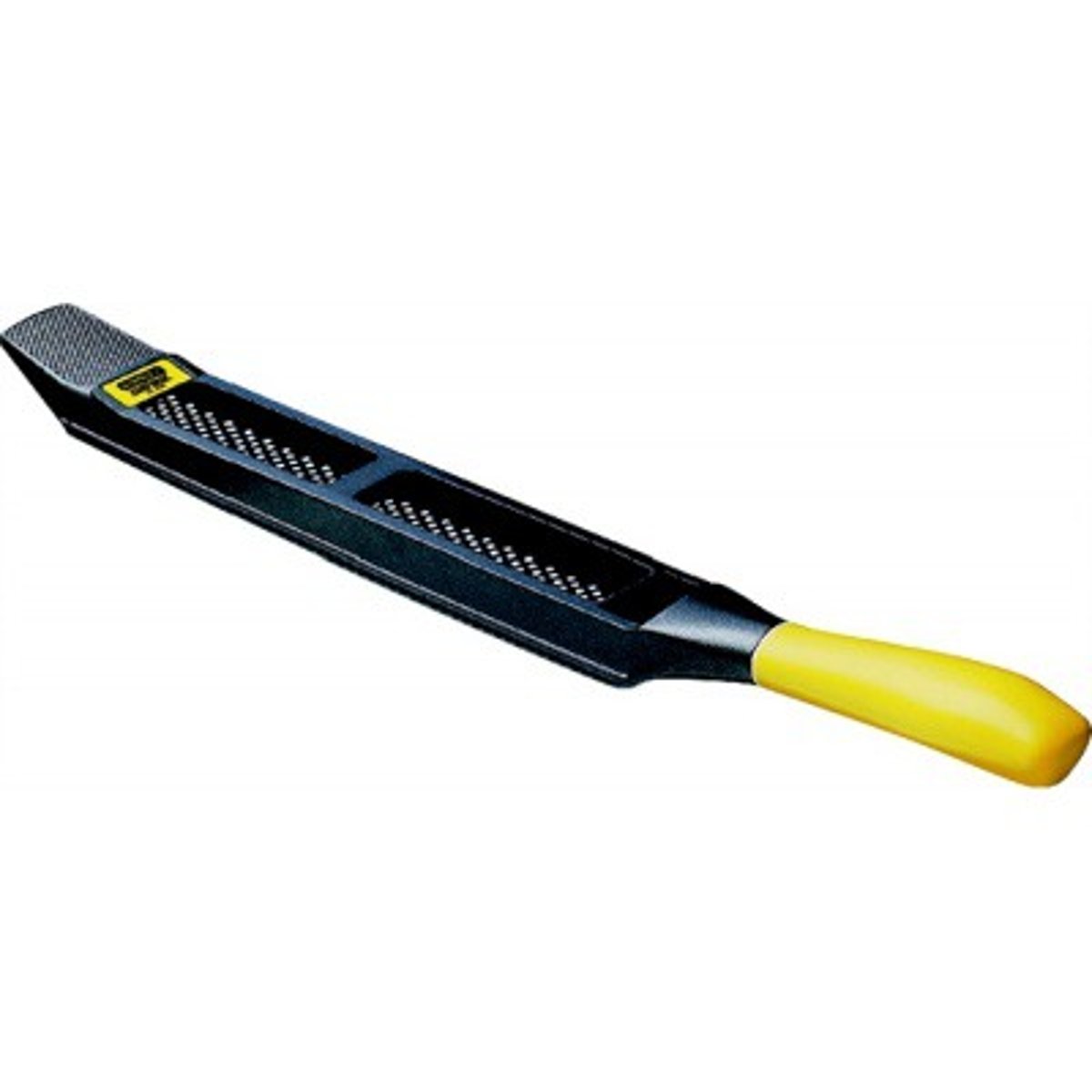
Rasp
Tool. Used for the quick removal of waste wood
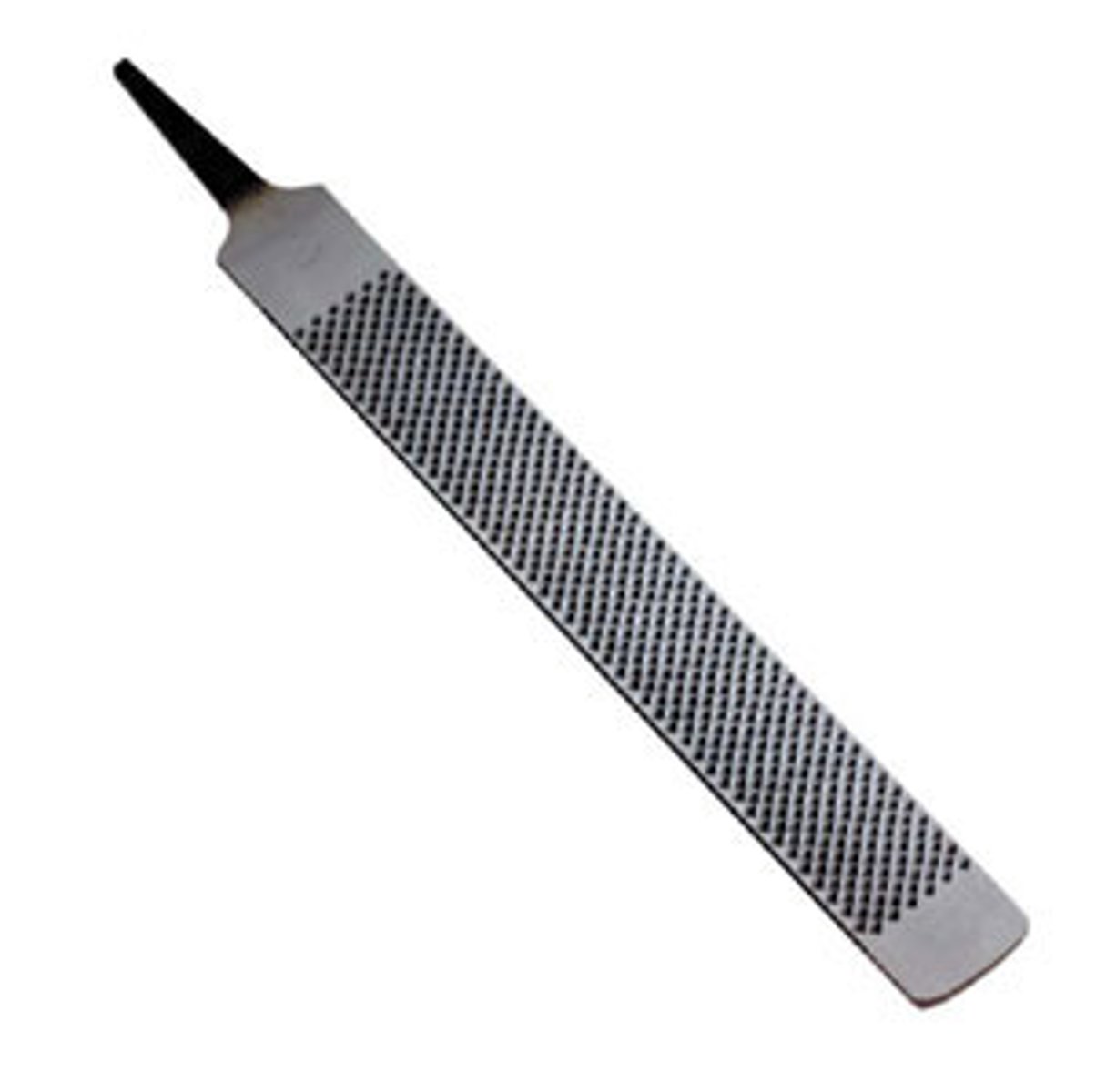

Surform
Tool. Used for the fast removal of soft material

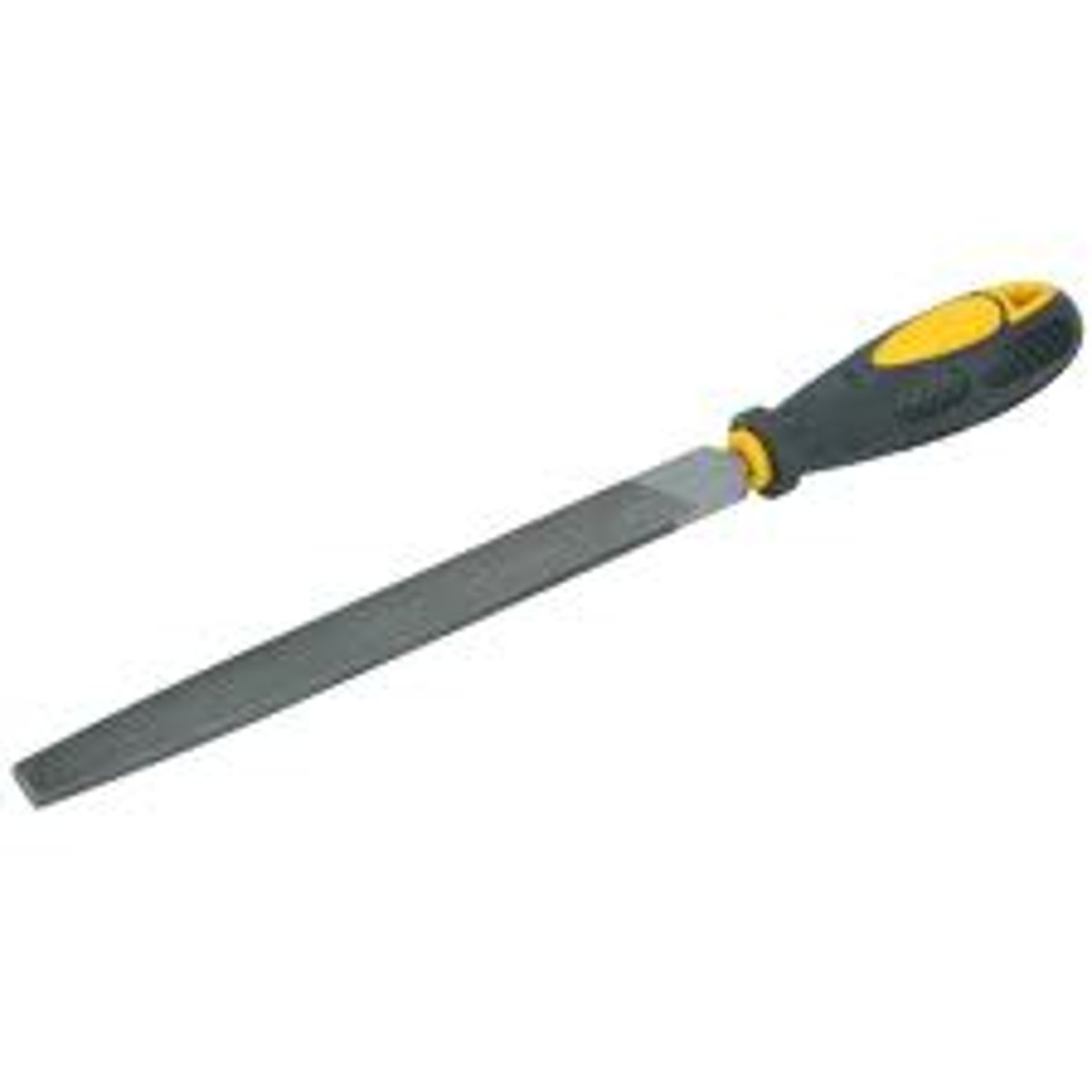
Flat File
Tool. Removes waste on large, flat surfaces quickly

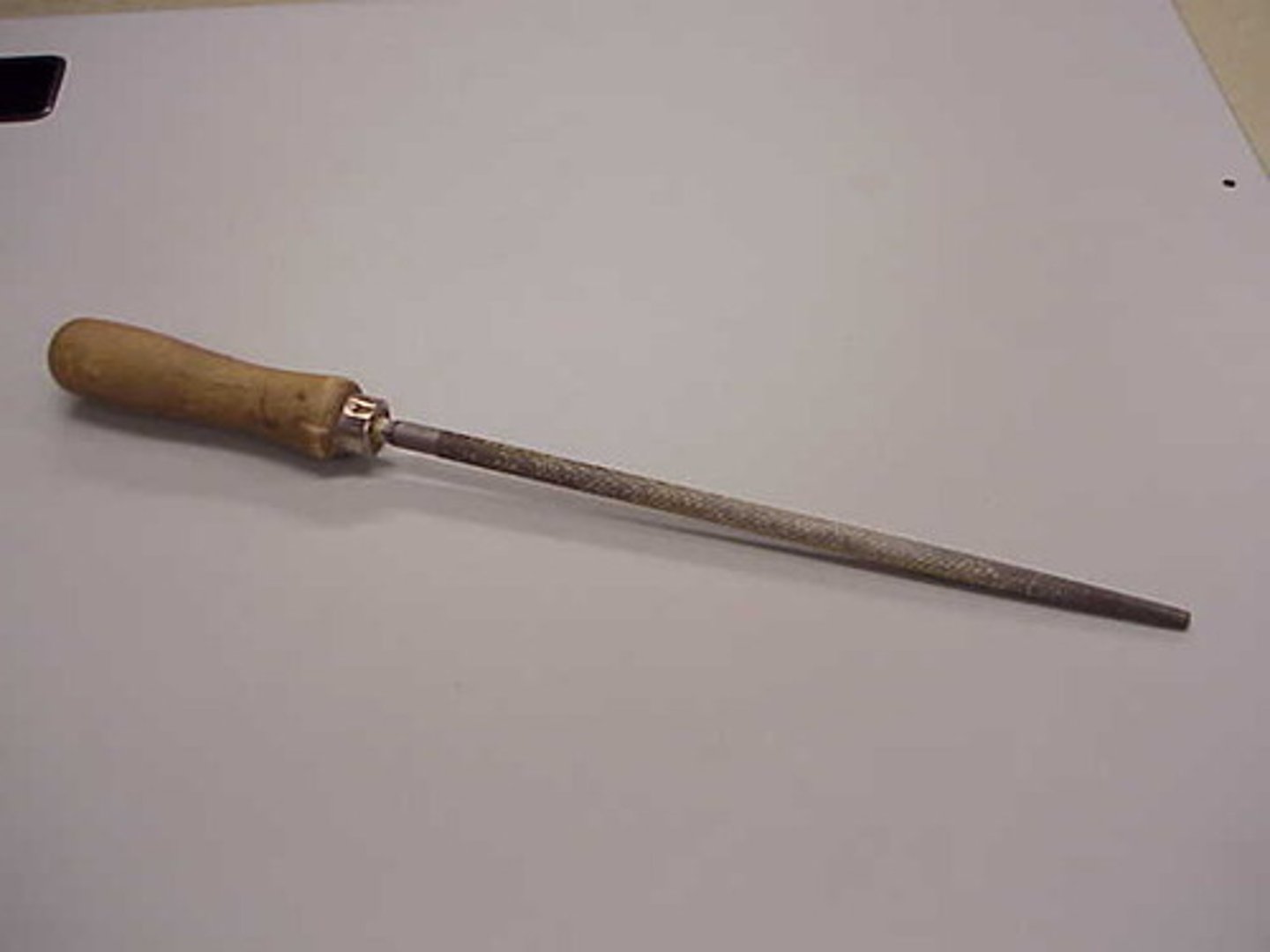
Round File
Tool. Creates curves and fillets

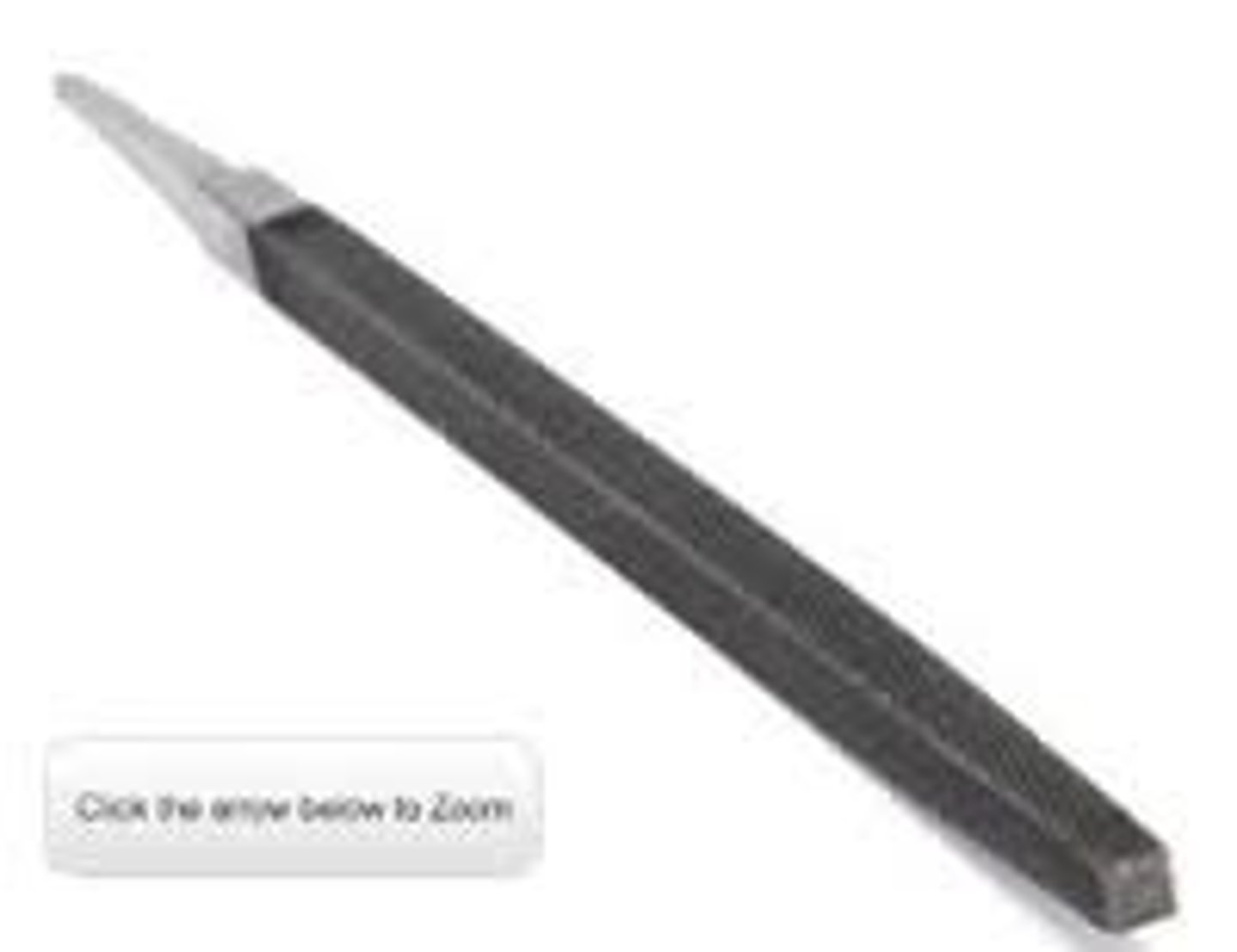
Three Square File
Tool. Cuts into corners less than 90 degrees

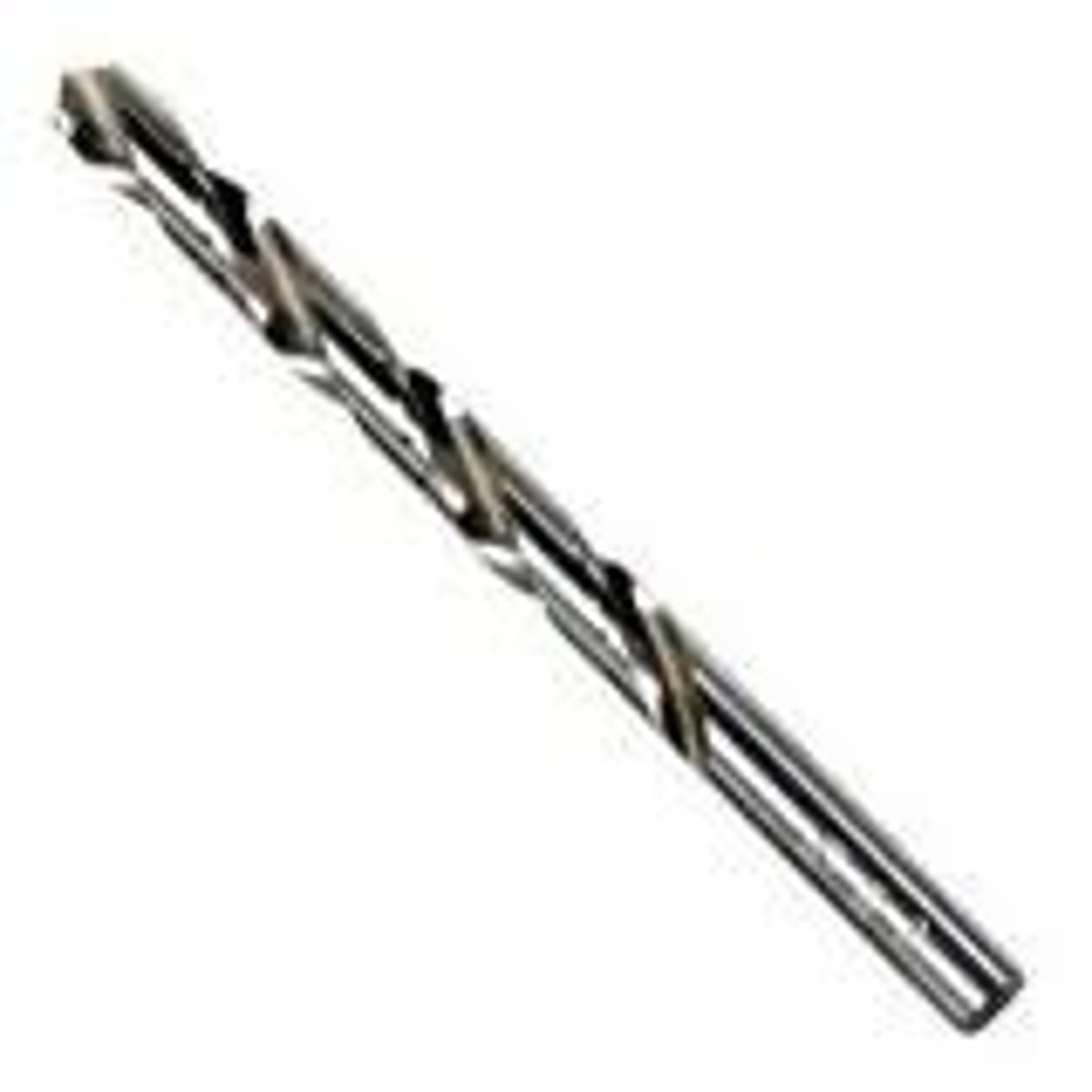
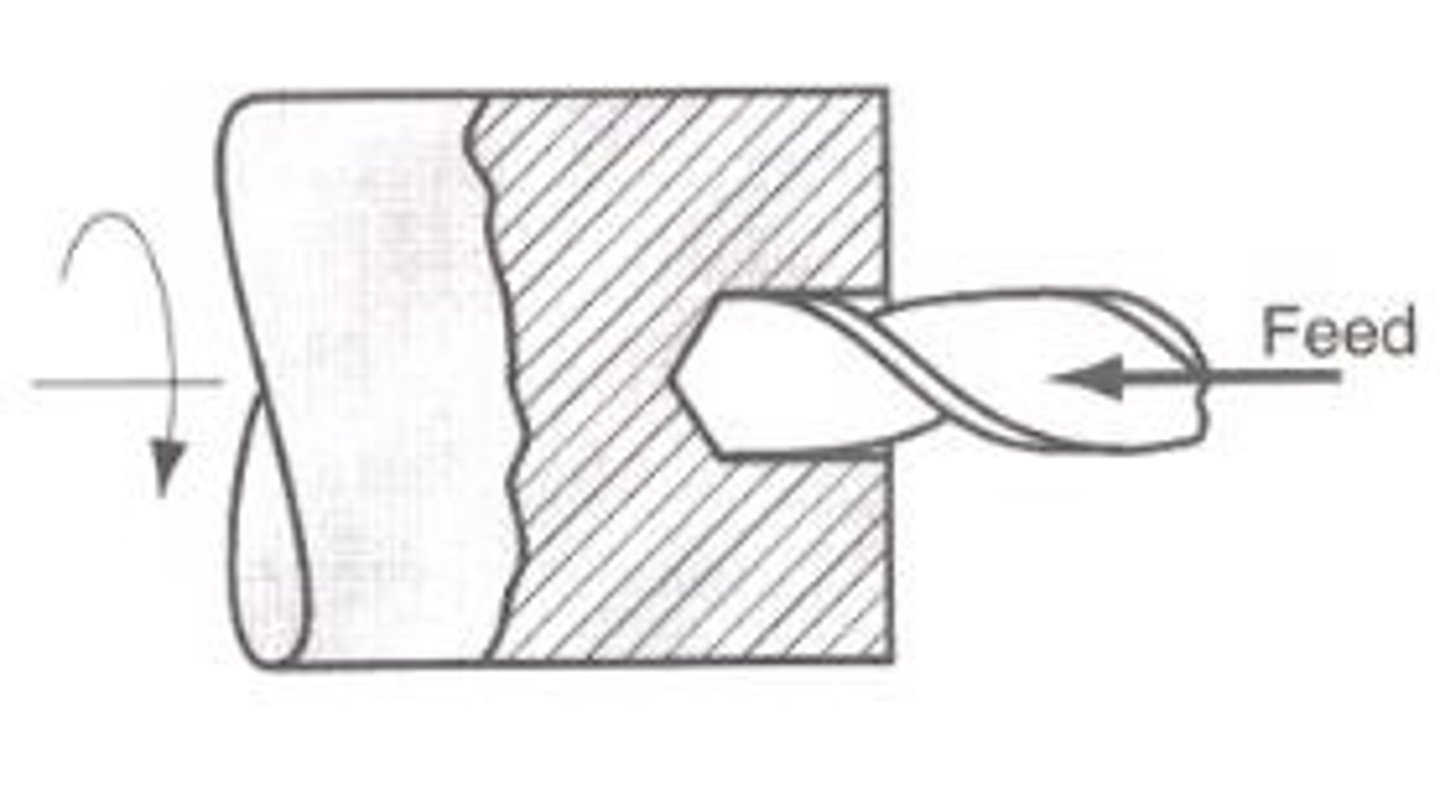
Twist Drill
Tool. Twists or flutes away swarf

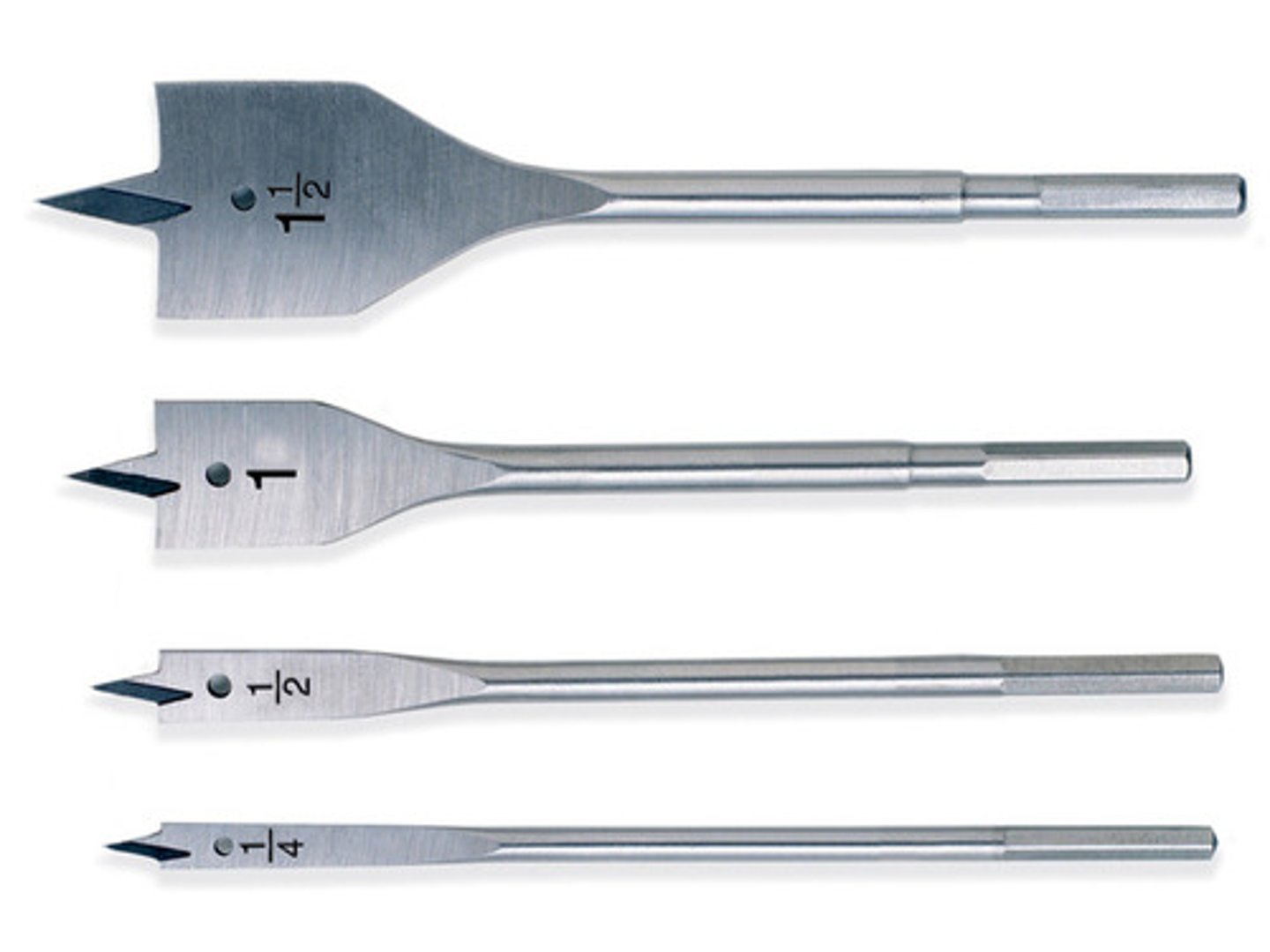
Flat Bit
Tool. Used to dril a hole through wood
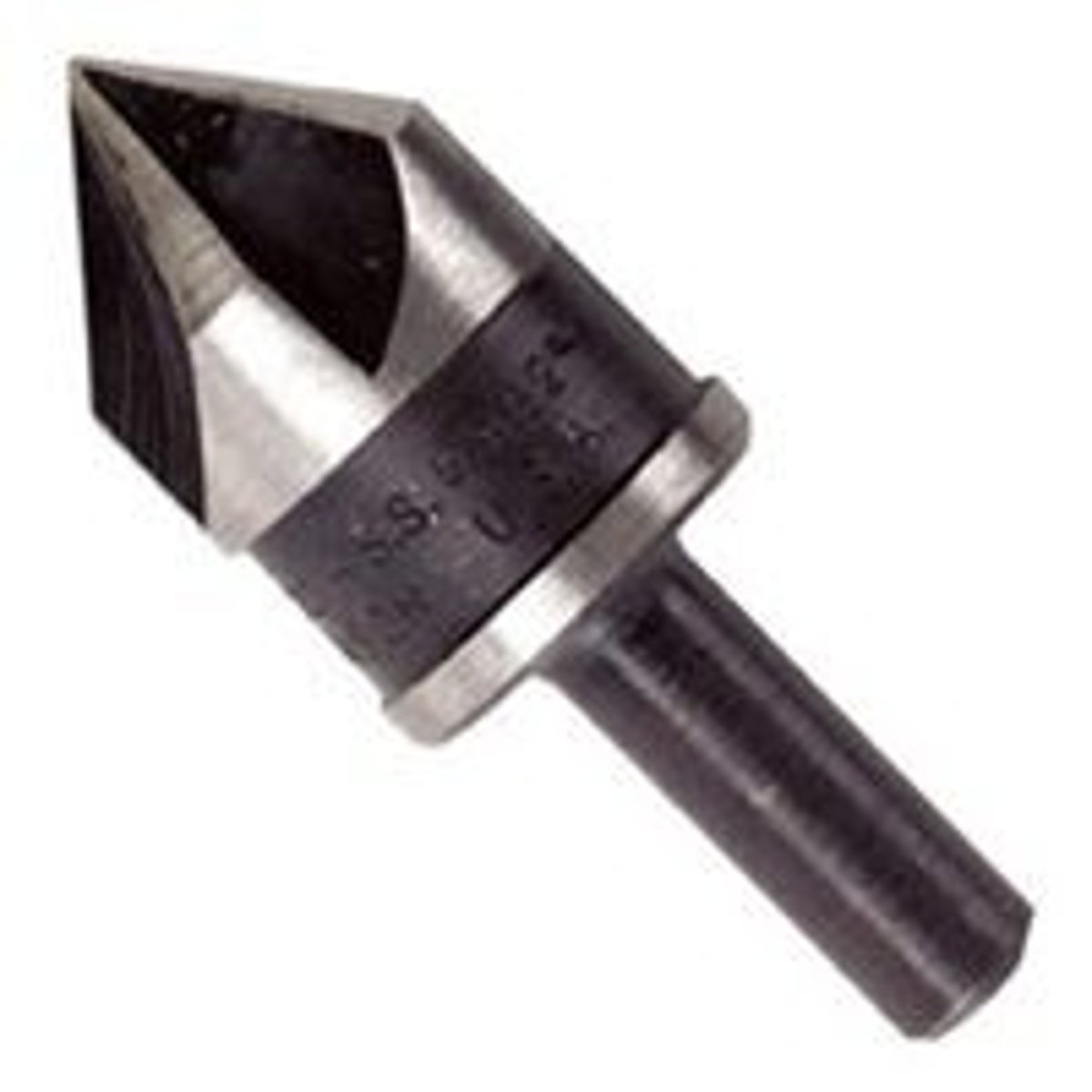
Countersink Bit
Tool. Creates a depression for the head of a countersunk screw.

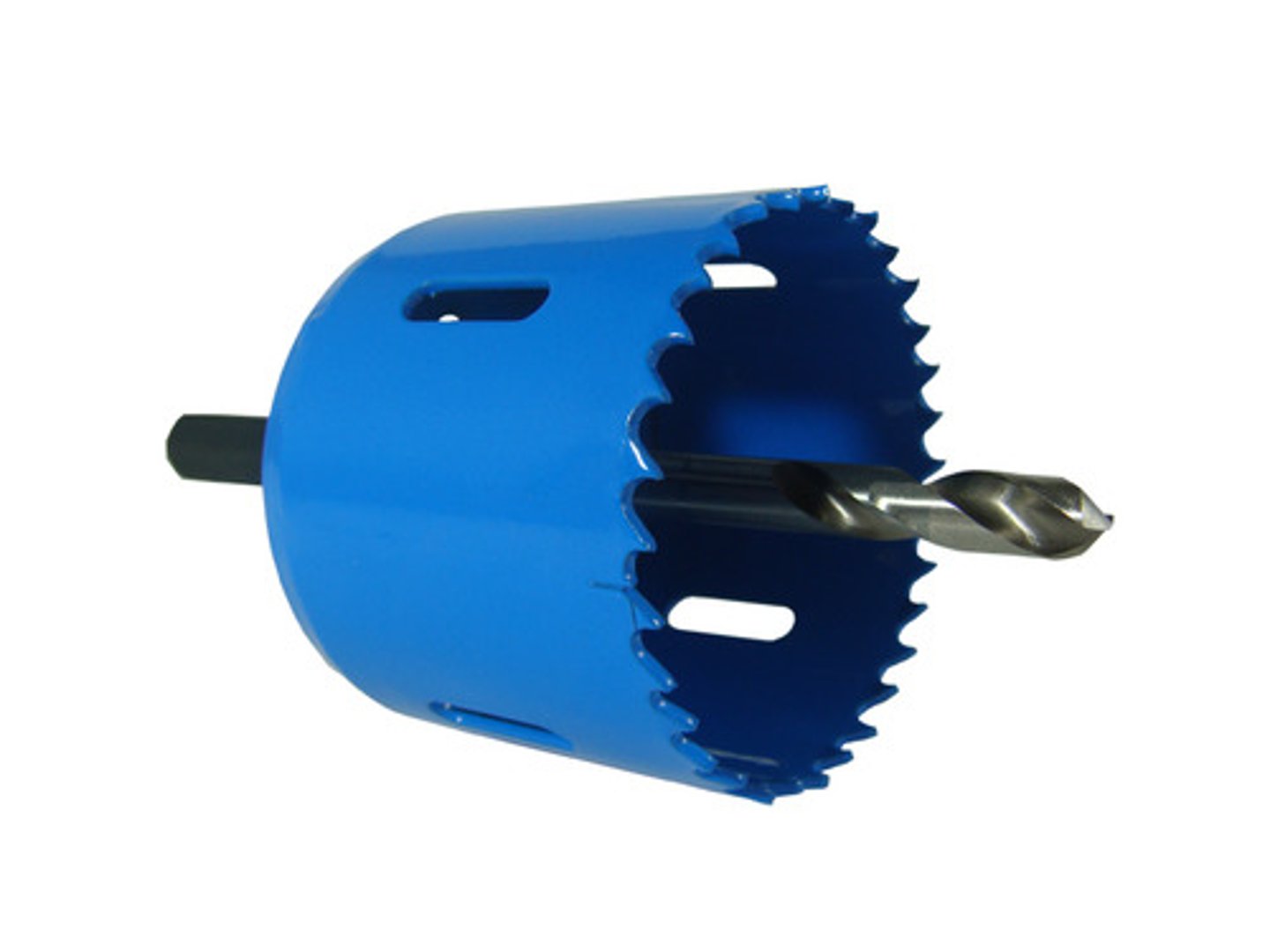
Hole Saw
Tool. Used on thin materials to make a large hole

Facing
Lathe Process. Tool moved at a right angle to axis, facing the end surface
Parallel Turning
Lathe Process. Tool moved parallel to axis to form a cylinder, reducing the diameter
Taper Turning
Lathe Process. Tool moved at angle to axis to produce a taper
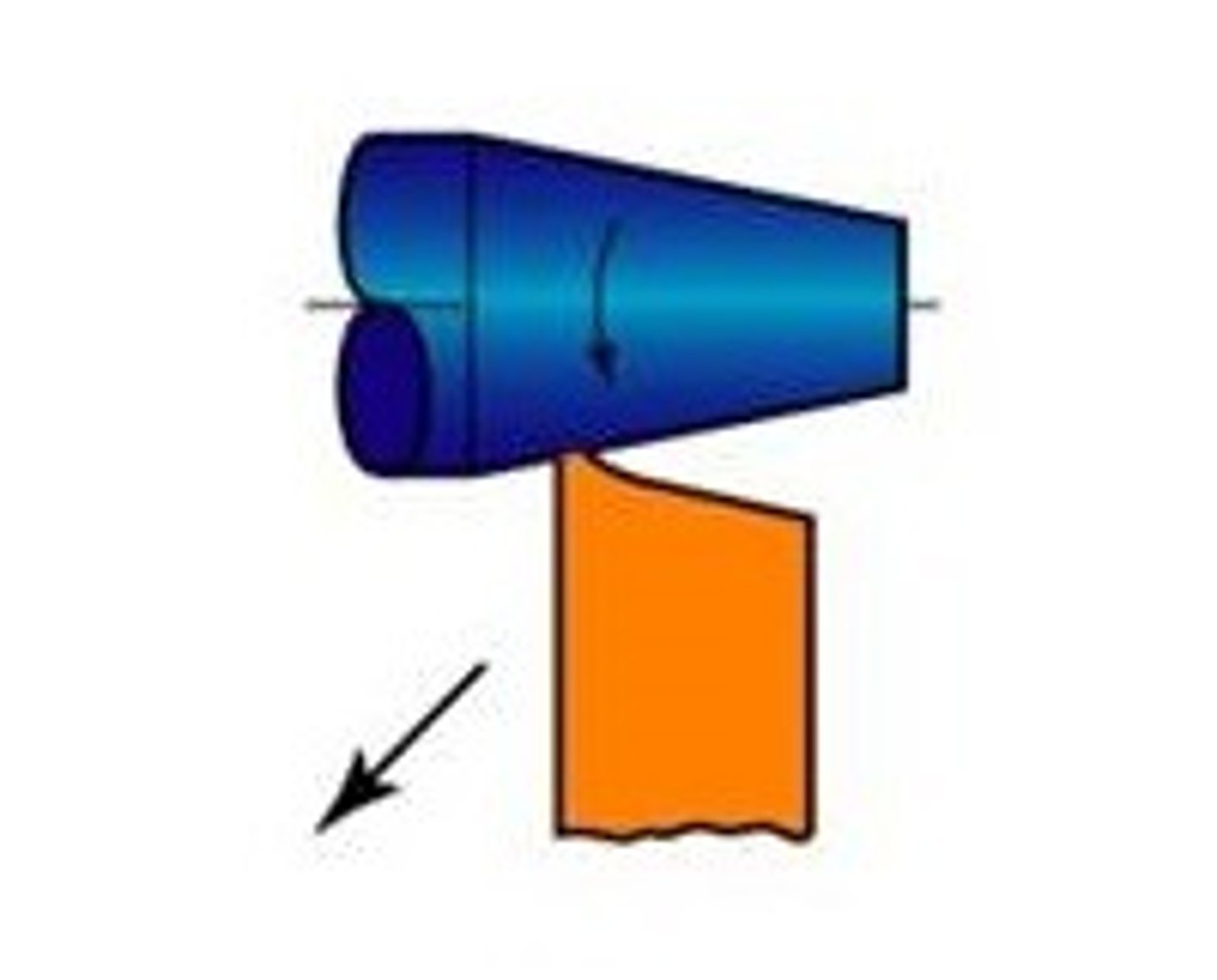
Parting
Lathe Process. Narrow tool fed into work to trim the length or part from stock bar
Drilling
Lathe Process. Tail stock used to hold chuck into which a drill can be placed; as work rotates, the drill is fed into the work
Knurling
Lathe Process. Hardened steel wheel is pressed into the rotating work to produce a straight or diamond pattern
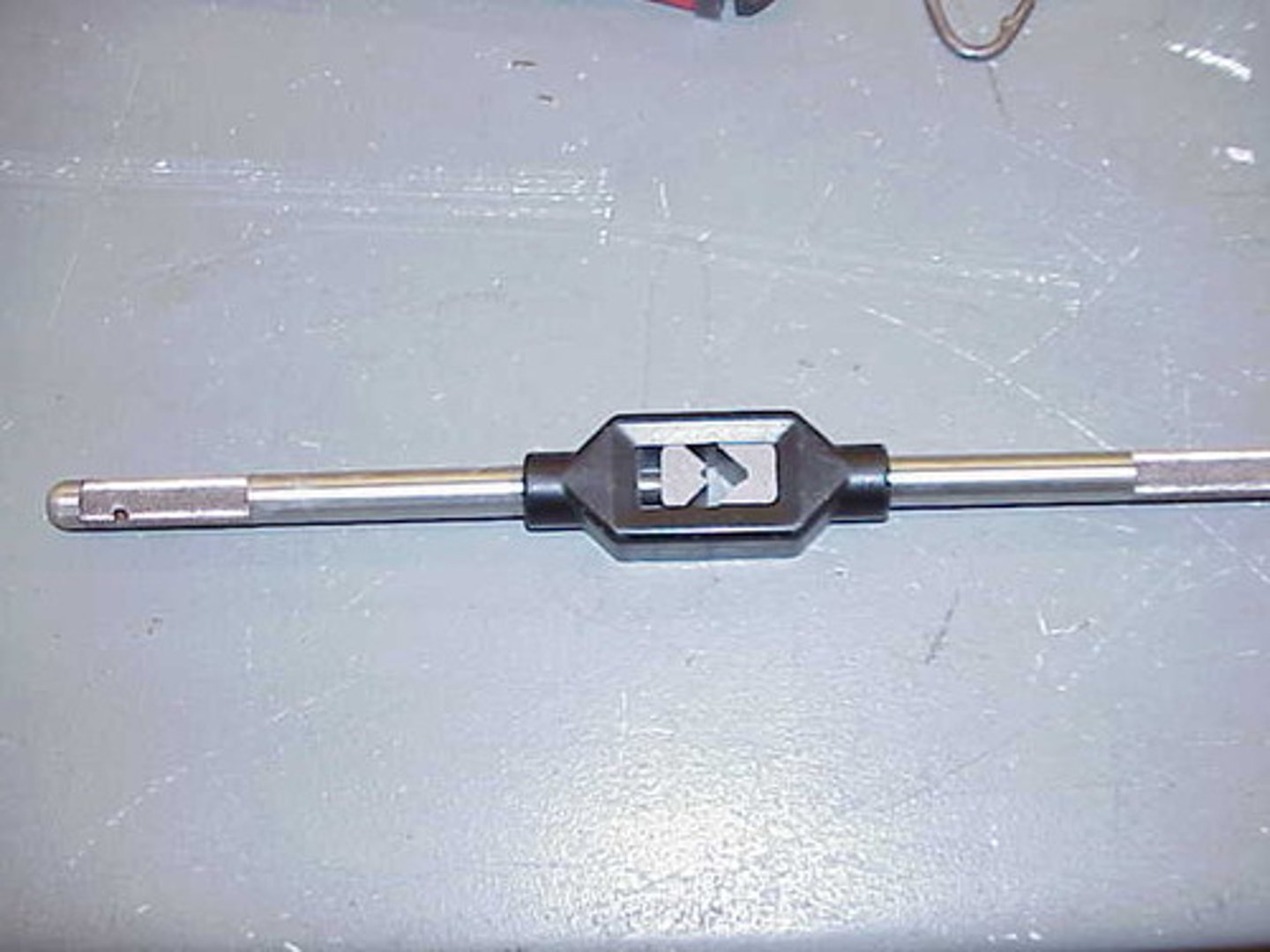
Tap Wrench
Tool. Used to hold and turn the tap

Taper Tap
Tool. Used to create an internal thread in a hollow tube

Split Die
Tool. used to create an external thread on a cylinder
Nut
Component. A threaded collar in which a bolt screws into

Washer
Component. A metal disc which helps spread the load generated by the tightening bolt

Bolt
Component. Made from high tensile steel. Has a hexagonal head, and screws into a bolt.

Countersunk Screw
Component. Screws into wood, with a countersunk head.

Roundhead Screw
Component. Screws into wood, with a rounded head

Knock Down Fitting
Component. Used in the construction of many flatpack furniture.
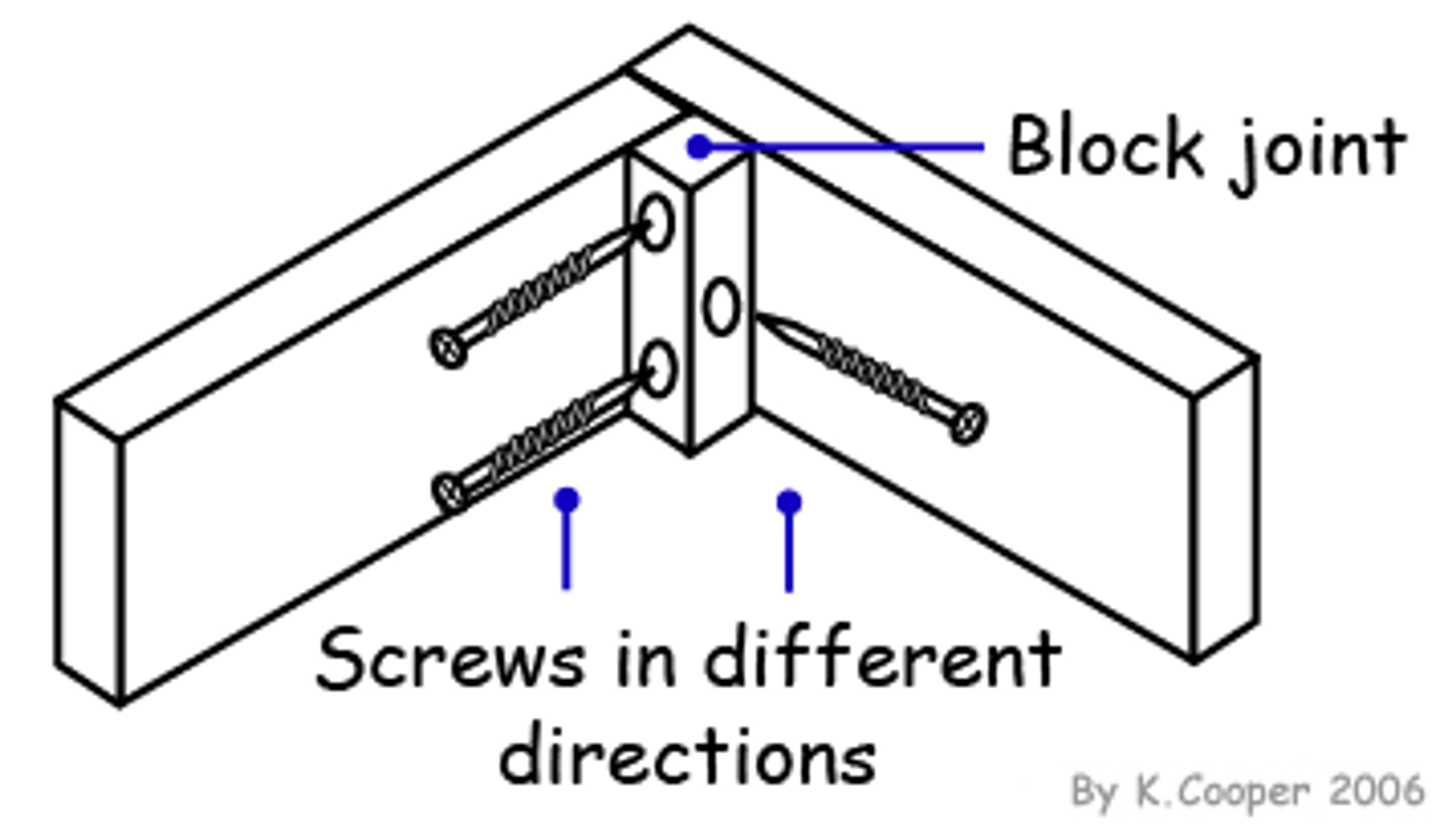
Round Wire Nail
Component. Nail with a large flat head, made from steel wire

Oval Wire Nail
Component. Nail with a head that can be punched below the surface, and have the hole filled.

Panel Pin
Component. Thinner nail with a head that can be punched below the surface, and have the hole filled

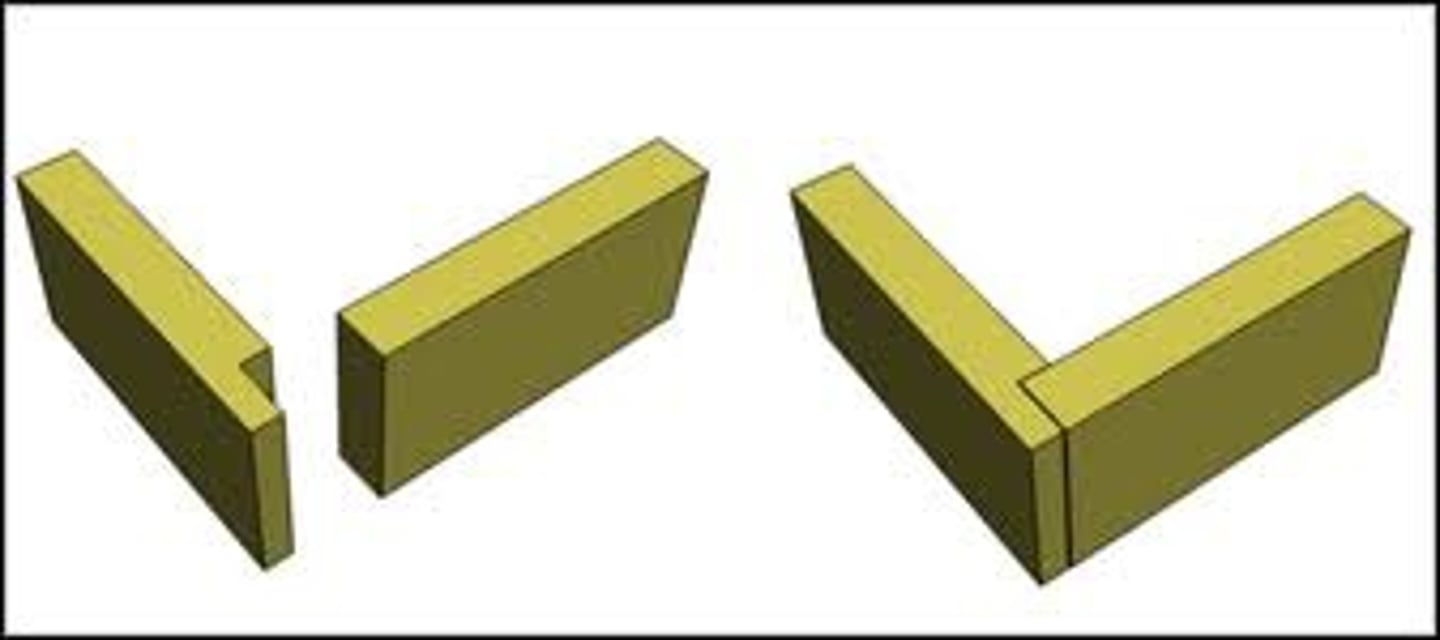
Halving Joint
Joint. Made by cutting away half the thickness of the material on each half of the joint. Can be used on corners, tees or cross halving. Can be strengthened by adding dowels
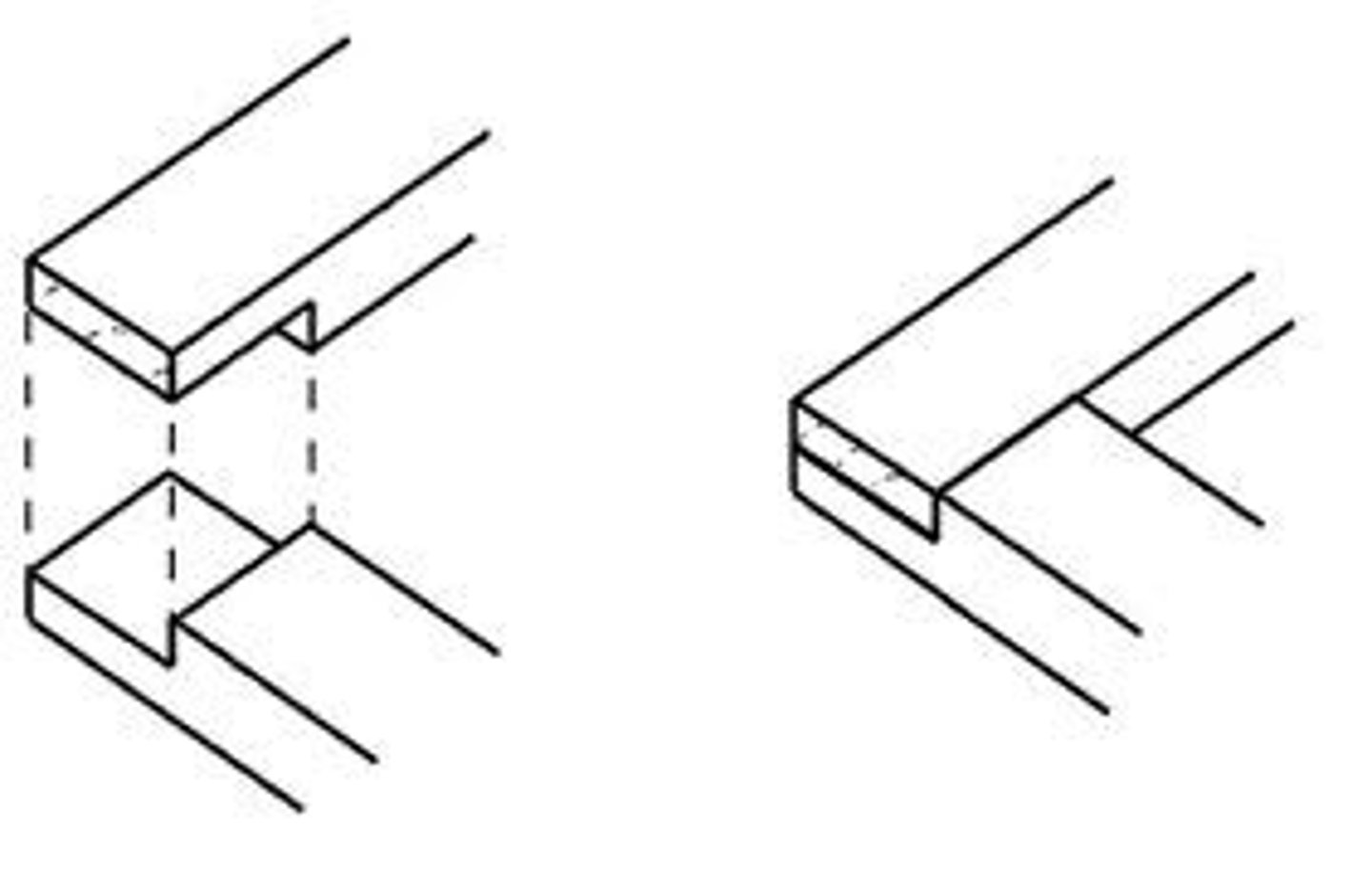
Butt Joint
Joint. The simplest form of joint, and the weakest. Formed by gluing the end of one side to the other.
Rebate/Lap Joint
Joint. One part of the piece being joined is left plain, and the other has a rebate cut into it, which means that the thickness of the material is removed to form a lip.