Air Pollution and Ozone Depletion Overview
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Air Pollution
The introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants, animals, and materials such as buildings, or to alter ecosystems.
Sulfur dioxide (S02)
A corrosive gas that comes primarily from combustion of fuels such as coal and oil. A respiratory irritant and can adversely affect plant tissue.
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Motor vehicles and stationary fossil fuel combustion are the primary anthropogenic sources of nitrogen oxides. Respiratory irritant, increases susceptibility to respiratory infection.
Carbon monoxide (CO)
A common emission in vehicle exhaust and most other combustion processes. CO can be a significant component of air pollution in urban areas.
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Released by burning fossil fuels has led to its becoming a major pollutant. CO2 recently exceeded a concentration of 400 parts per million in the atmosphere.
Particulate matter (PM)
Solid or liquid particles suspended in air. Particulate matter can be natural or anthropogenic and can absorb or scatter light, creating haze.
Haze
Reduced visibility.
Photochemical oxidant
A class of air pollutants formed as a result of sunlight acting on compounds such as nitrogen oxides.
Ozone (O3)
A secondary pollutant made up of three oxygen atoms bound together.
Smog
A type of air pollution that is a mixture of oxidants and particulate matter.
Photochemical smog
Smog that is dominated by oxidants such as ozone. Also known as Los Angeles-type Smog; Brown smog.
Sulfurous smog
Smog dominated by sulfur dioxide and sulfate compounds. Also known as London-type smog; Gray smog; Industrial smog.
Lead
A gasoline additive, also found in oil, coal, and old paint. Impairs central nervous system.
Volatile organic compound (VOC)
An organic compound that evaporates at typical atmospheric temperatures. A precursor to ozone formation.
Primary pollutant
A polluting compound that comes directly out of a smokestack, exhaust pipe, or natural emission source.
Secondary pollutant
A primary pollutant that has undergone transformation in the presence of sunlight, water, oxygen, or other compounds.
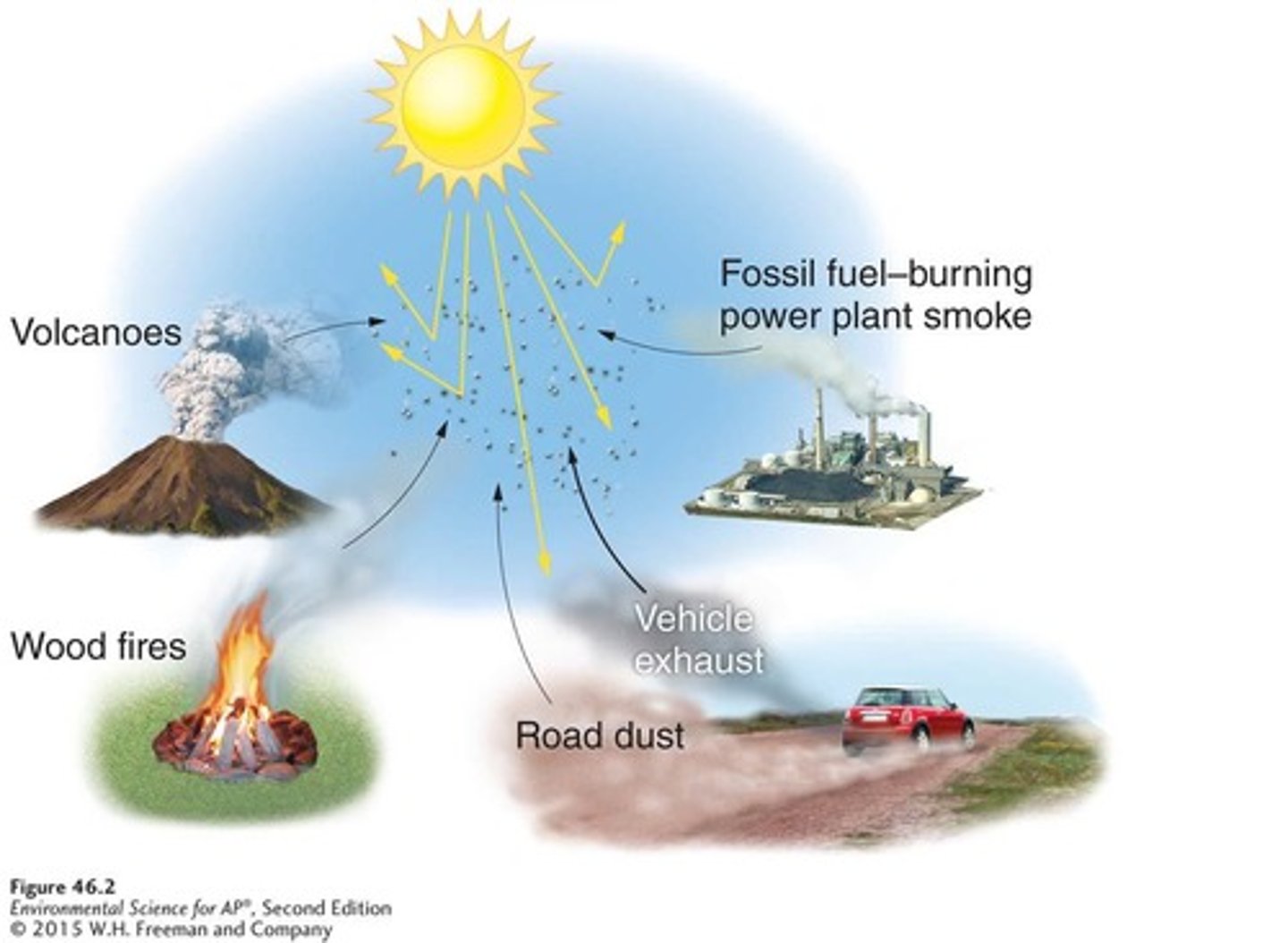
Natural emissions
Pollution sources that include volcanoes, lightning, forest fires, and plants, both living and dead.
Anthropogenic sources
Pollution sources that include on-road vehicles, power plants, industrial processes, and waste disposal (incinerator).
Anthropogenic Emissions
In the United States, emissions from human activity are monitored, regulated, and in many cases controlled.
Anthropogenic sources
On-road vehicles, power plants, industrial processes, and incineration.
Clean Air Act
Requires that EPA establish standards to control pollutants that are harmful to 'human health and welfare'.
National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS)
EPA periodically specifies concentration limits for each air pollutant.
Carbon monoxide
Largest source of carbon monoxide emissions is on-road vehicles.
Nitrogen oxides
Largest source of nitrogen oxides emissions is on-road vehicles.
Anthropogenic sulfur dioxide
Major source is the generation of electricity, primarily from coal.
Particulate matter
Sources include road dust, industrial processes, electricity generation, and natural and human-made fires.
Criteria air pollutants
All criteria air pollutants have decreased in the United States between 1990 and 2010.
Lead
The decrease for lead is the greatest among criteria air pollutants.
Photochemical smog
Formation is complex and involves a number of pollutants undergoing transformations in the atmosphere.
Acid deposition
Occurs when nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides combine with atmospheric oxygen and water to form nitric and sulfuric acid.
Thermal inversion
A situation where a warm layer of air at mid-altitude covers a layer of cold, dense air below.
Inversion layer
The layer of warm air that traps emissions in a thermal inversion.
Effects of acid deposition
Includes lowering the pH of lake water, decreasing species diversity of aquatic organisms, and damaging statues, monuments, and buildings.
Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides
Primary pollutants that are precursors to acid deposition.
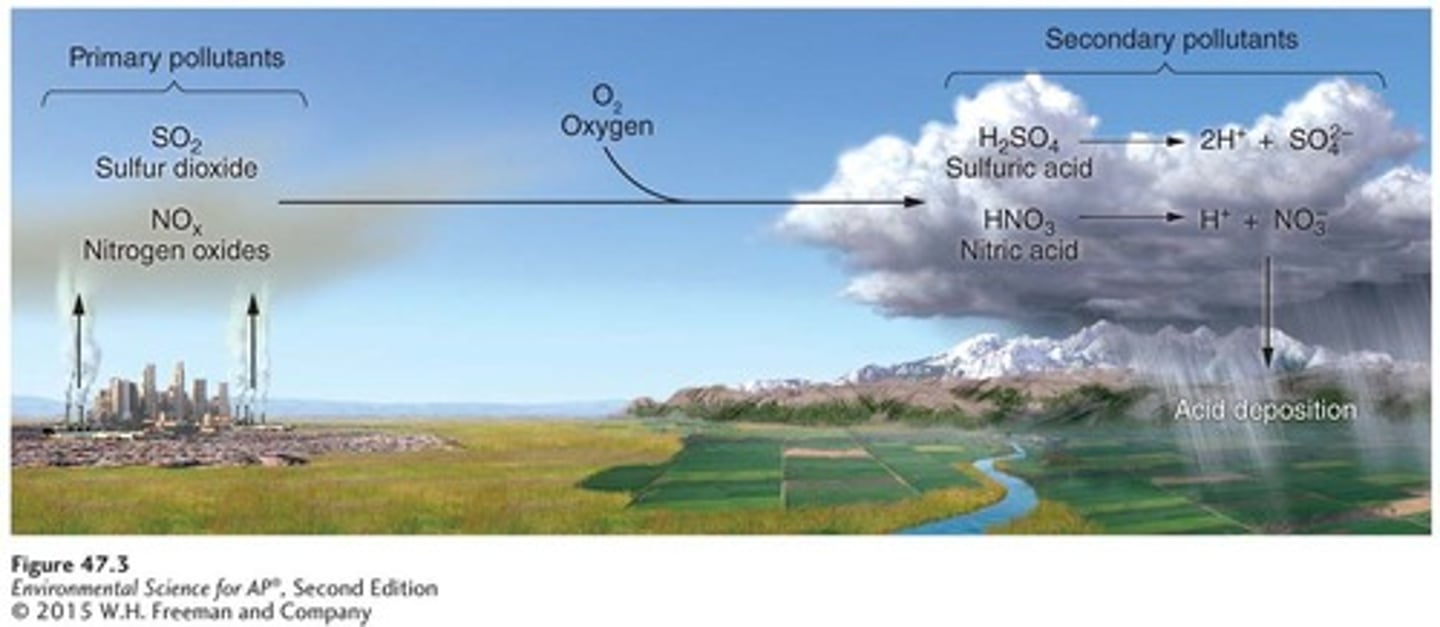
Secondary pollutants
Formed from the transformation of primary pollutants, including nitric acid and sulfuric acid.
Hydrogen ions (H+)
Contribute to the acidity in acid deposition.
Acid deposition reduction
Has improved in the United States due to lower sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions.
Photochemical oxidants
Formed when VOCs combine with nitrogen oxides, reducing the breakdown of ozone.
Ozone formation
Occurs during daylight hours in the absence of VOCs.
Ozone breakdown
Occurs after sunset.
Acid deposition effects on ecosystems
Includes mobilizing metals found in soils and releasing them into surface waters.
Pollution control measures
Strategies and techniques for controlling sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter.
Acid deposition
Has many harmful effects including lowering the pH of lake water, decreasing species diversity of aquatic organisms, mobilizing metals that are found in soils and releasing them into surface waters, and damaging statues, monuments, and buildings.
Pollution control
Includes prevention, technology, and innovation to address air pollution.
Ways to address air pollution
Avoid emissions in the first place, use cleaner fuel, increase efficiency, and control pollutants after combustion.
Ways of controlling emissions
Remove sulfur dioxide from coal by fluidized bed combustion, install catalytic converters on cars, use baghouse filters, use electrostatic precipitators, and install scrubbers on smokestacks.
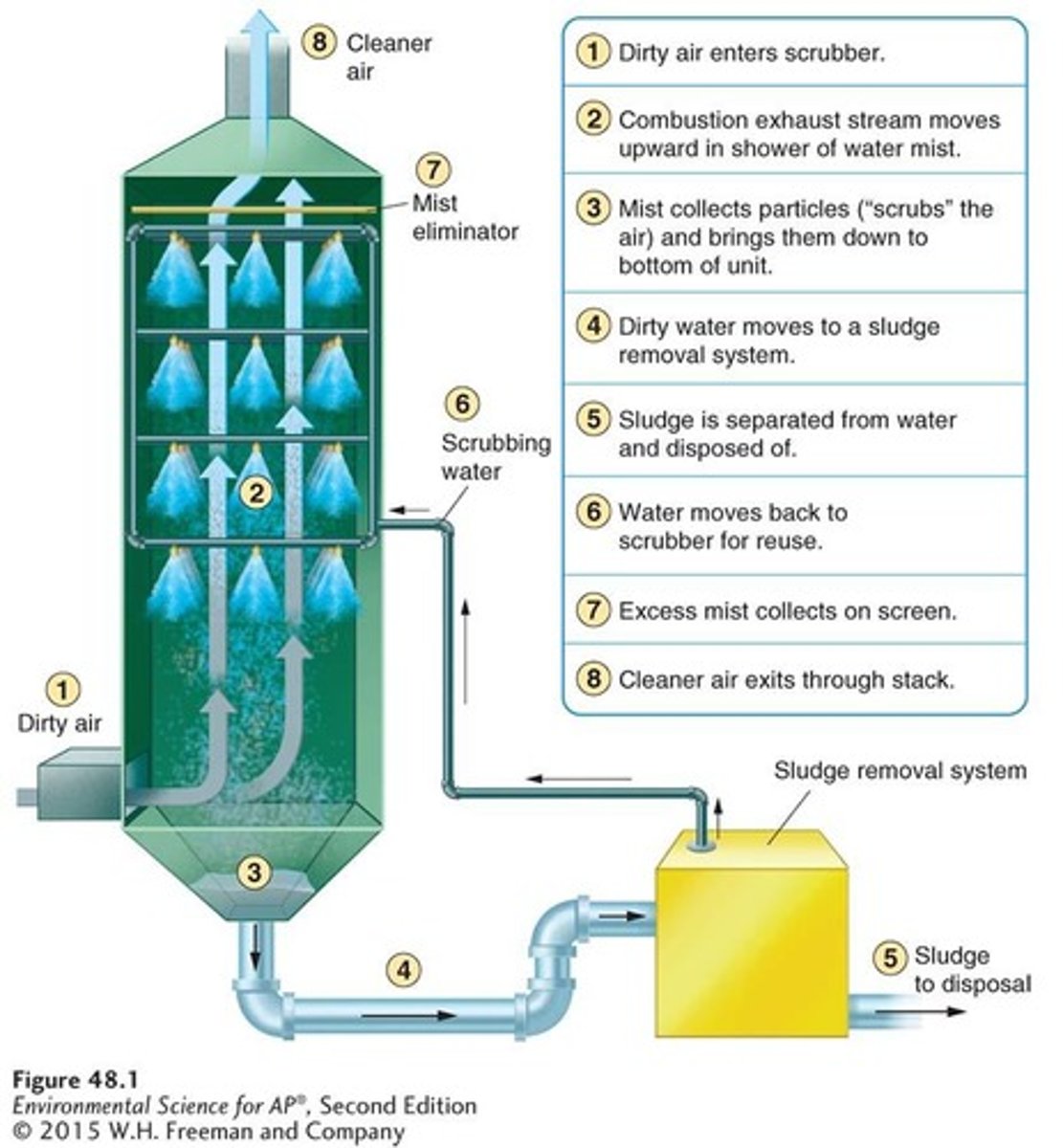
Scrubber
An air pollution control device that scrubs particles from the exhaust stream by water droplets, collecting a water-particle sludge for disposal.
Innovative pollution control measures
Strategies implemented by municipalities to reduce gasoline spills, restrict evaporation of dry-cleaning fluids, and limit the use of wood-burning stoves.
Stratospheric ozone
Beneficial to life on Earth and exists roughly 45-60 kilometers above Earth, absorbing ultraviolet radiation.
Ultraviolet (UV) spectrum
Made up of three increasingly energetic ranges: UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C.
Formation of stratospheric ozone
Occurs when UV-C radiation breaks the molecular bond of O2, producing free oxygen atoms that combine with O2 to form O3.
Breakdown of stratospheric ozone
Chlorine from CFCs can catalyze the breakdown of ozone molecules, producing chlorine monoxide and free oxygen.
Chlorine atom
Can catalyze the breakdown of as many as 100,000 ozone molecules until it finds another chlorine atom.
Depletion of the ozone layer
Stratospheric ozone concentration shows a decreasing trend from 1970 to 2011 in certain areas.
Indoor air pollution
A significant hazard in both developing and developed countries, with approximately 4 million deaths attributed to it each year.
Major indoor air pollutants
Include carbon monoxide, asbestos, radon, and VOCs used in furniture, paint, and building materials.
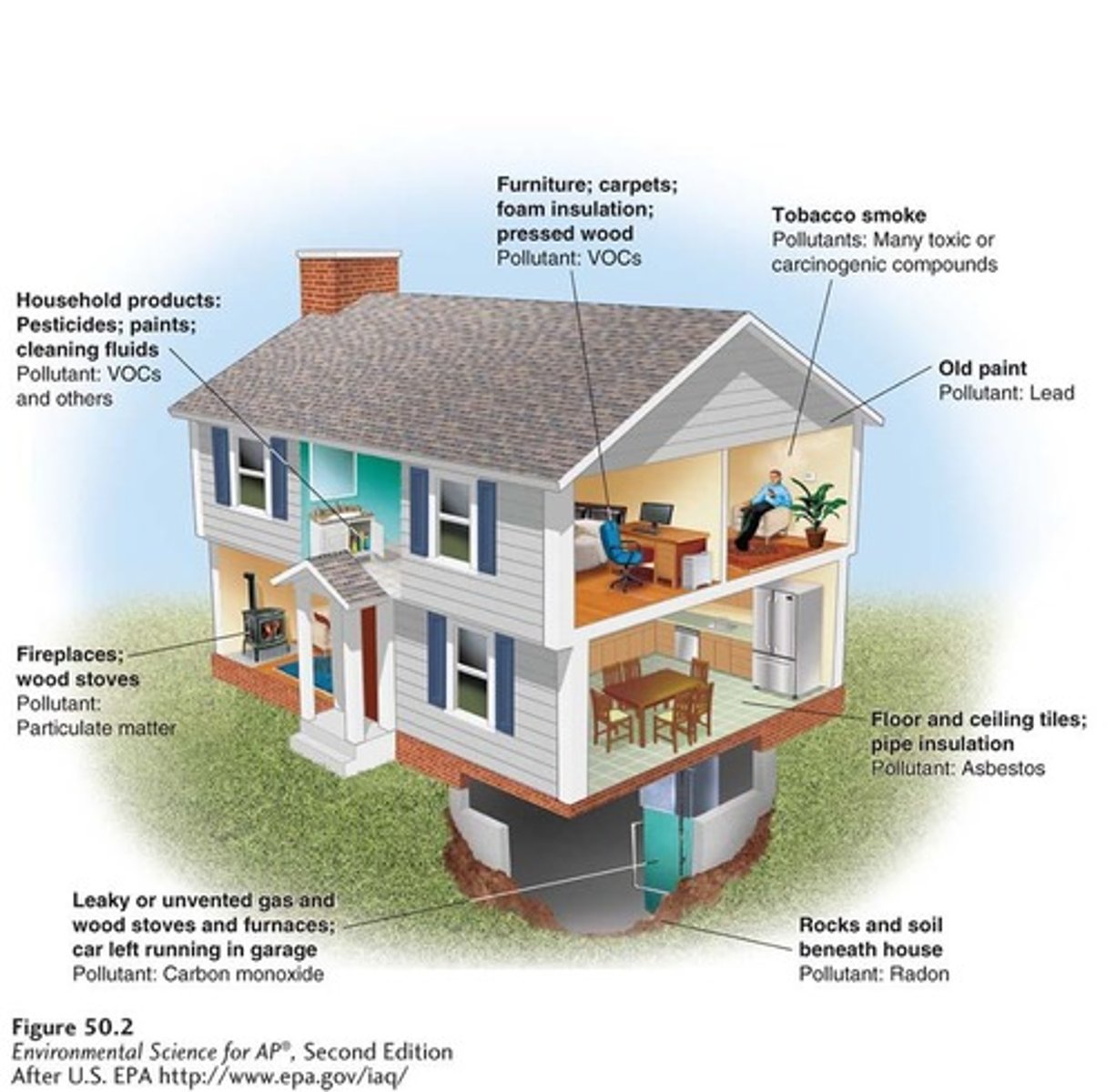
Carbon monoxide
A pollutant that can come from malfunctioning heating equipment.
Asbestos
A long thin fibrous silicate mineral with insulating properties that can cause cancer when inhaled.
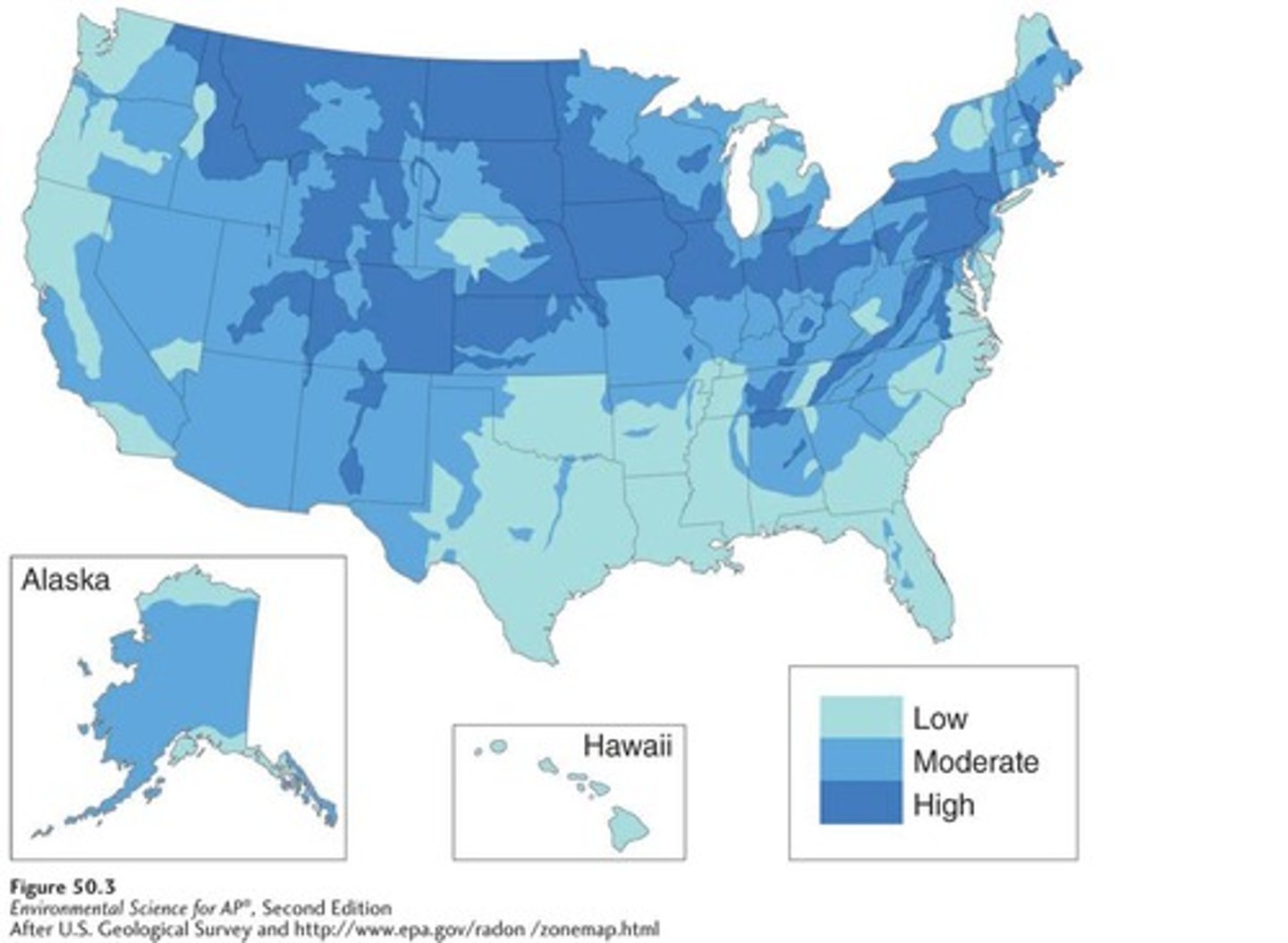
Radon
A gas that seeps into homes through cracks in the foundation, groundwater, or rocks.
VOCs
Volatile organic compounds used in furniture, paint, and building materials that can contribute to indoor air pollution.
Sick building syndrome
Caused by inadequate or faulty ventilation, chemical contamination from indoor or outdoor sources, and biological contamination.