Surface Final
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Name two of the largest natural gas plays in Western Canada.
Duverney
Montney
What are the top five countries in the world in terms of natural gas production?
Russia
United States
Canada
Qatar
Iran
What types of wells can natural gas be produced from?
Gas wells
Oil wells
Associated or solution gas
Non associated gas or gas cap
Coal bed methane wells
Shale gas wells
Tight gas wells
Give 4 reasons why natural gas is compressed
To boost pressure at the wellhead
To boost pressure within a facility
To meet sales pipeline specs
To boost pressure along transmission lines
Define the term ‘dew point’ in regard to natural gas
The temperature at which the first drop of water is formed when cooling the gas.
It is a measure of the relative humidity (ie. the water content) of the gas at STP.
Processed natural gas will typically contain what percentage of methane?
At wellhead: 75% to 95%
After processing: 95% to 99%
What contaminants are found in natural gas that must be removed by processing?
Carbon Dioxide
Nitrogen
Hydrogen Sulphide
Water
Mercury
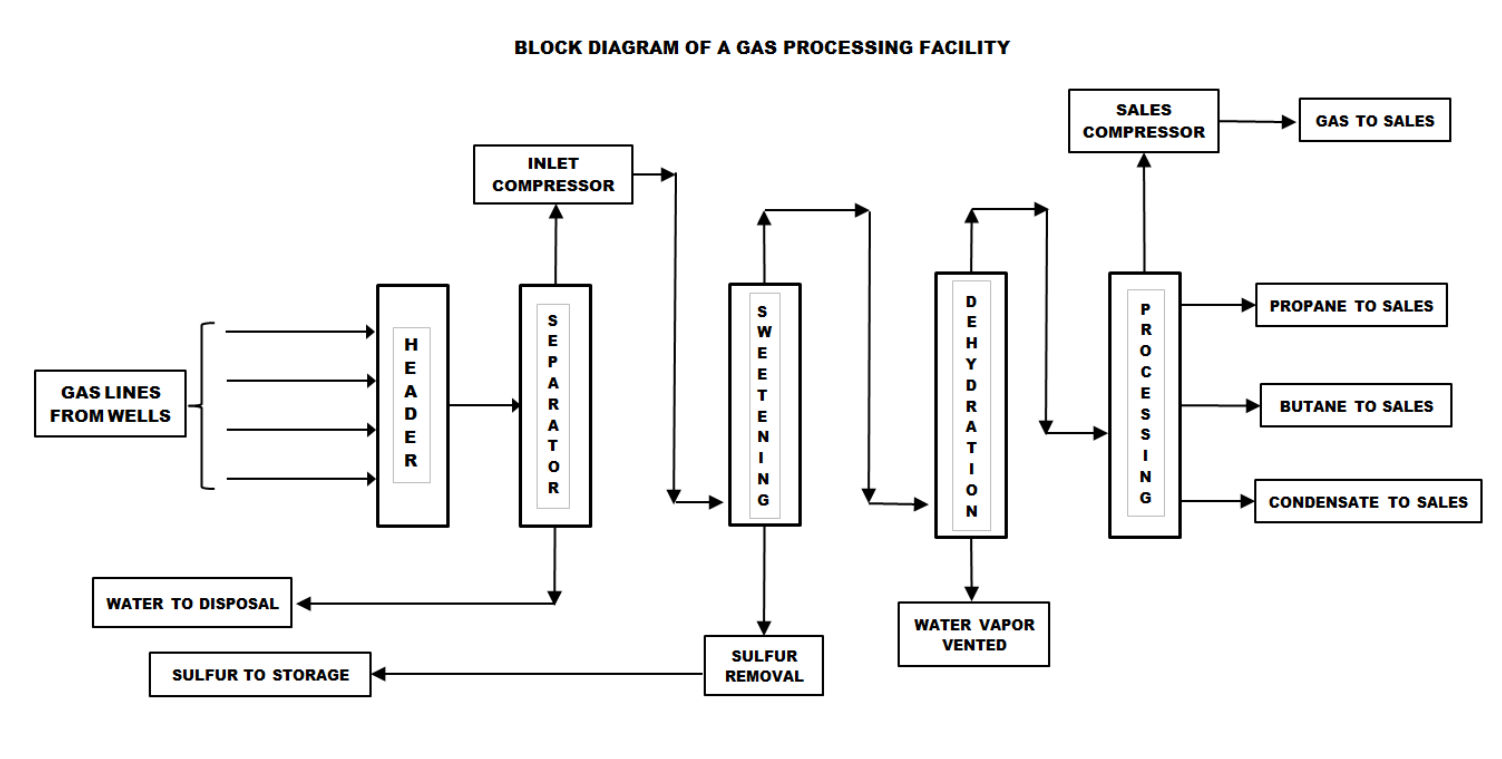
Label the block diagram of a gas processing facility
Define the ‘hydrocarbon dew point’ of natural gas.
The temperature at which the first drop of liquid hydrocarbon appears in a gas mixture.
It is a measure of the amount of liquid hydrocarbon in the gas
What is condensate?
C5+
pentane
hexane
etc.
Liquid at surface
What are the heating value line specs for sales natural gas?
A specific heating value greater than 36 MJ/m3 (966 BTU/ft3) at 20 °C.
When gas contains propane (C3) and butane (C4), the heating value, _________.
a) increases
b) decreases
a) increases
What is the temperature range for a typical refrigeration plant?
- 30 ̊C to - 40 ̊C
Give the recovery ranges for C3 and C4 in a typical refrigeration process (-30°C to -40°C)
C3 → 30% - 60%
C4 → 60% - 80%
Beyond refrigeration, name 2 alternative processes that are used to remove C3 and C4 from a gas stream
Absorption Process
Involves using lean oil in a contact tower with the gas. C3 and C4 molecules are attracted to the lean oil. The oil is then stripped of the C3 and C4 and cycled back through the tower.
Cryogenic Process
This is the same process as the refrigeration plant, however the gas temperature is dropped to below -100 ̊C. This results in higher C3 and C4 recovery as well as some recovery of C2 (ethane)
What are the sales line specs for H2S and CO2 content?
16 ppm H2S
20,000 ppm CO2
What is the most common method used to extract acid gas?
Amine contact tower
Where does the sour gas exit an amine contact tower? What about the sweet gas?
Sour → bottom
Sweet → top
What are the 4 factors that dictate what type of amine solution is used in the contact tower?
Gas composition
Gas flow rate
Processing pressure
Waste product disposal method
Which amine type is best suited for CO2 removal?
Monoethanolamine (MEA)
Which amine type is best suited for H2S removal?
Methyldiethanolamine (MDEA)
Beyond amine sweetening, what is an alternative method used to sweeten natural gas?
Claus Sulfur recovery method
What is the AER tolerance for acid gas flaring?
Zero
What is the most common method used to dispose of acid gases?
Disposal into very large water bearing horizons.
What is the maximum pressure allowed in an acid gas disposal well?
60% of the formation fracture pressure
What are NGLs?
Natural Gas Liquids
C2 - ethane
C3 - propane
C4 - butane
Recovered at surface through refrigeration
What is LNG?
Liquified Natural Gas
C1 to C4 (but mostly C1) at below -160 °C & Standard Pressure
LNG occupies 1/600 of the volume compared to atmospheric conditions
Allows for container shipping
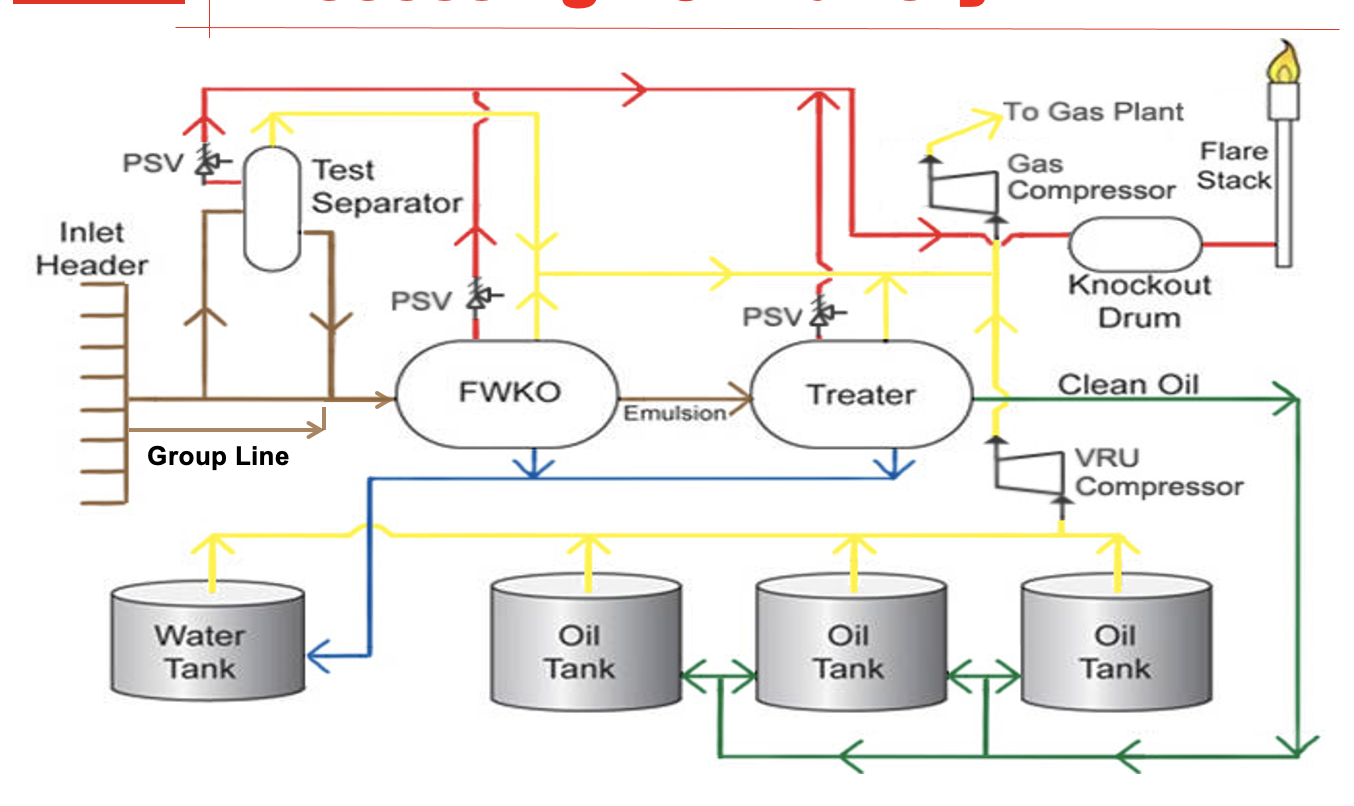
What equipment is used in a typical oil battery?
Oil Battery Equipment
Inlet header or manifold
Separator
Inlet side
Effluent (gas, oil and water)
Outlet side
Gas and emulsion (2 phase)
Gas, emulsion and water (3 phase)
Treater
Inlet side
Effluent (gas, oil and water)
Outlet side
Gas, sales quality oil and water
Flow meters – for oil and water volumes
Orifice meters – for gas volumes
Compressor
What does LACT stand for?
Lease Automated Custody Transfer
What type of devices are used to measure the volume of oil and water? For gas?
Flow meter → oil & water
Orifice meter → gas
What type of equipment is used in natural gas processing?
Natural Gas Processing Equipment
Inlet header or manifold
Separator
Gas and water (2 phase)
Condensate, gas and water (3 phase)
Amine Tower – H2S and CO2 removal (ie. sweetening)
Dehydrator – water removal
Orifice Meter – volume measurement
Compressor
What is the general formula for single chain hydrocarbons (alkanes)?
CnH2n+2
What is condensate?
Light liquid hydrocarbon: C5 to C8 (pentane to octane)
liquid at surface
What are API standard conditions for oil measurement?
Temperature: 15°C (60°F)
Pressure: 101.325 kPa (14.7 psi)
Draw an oil battery with FWKO
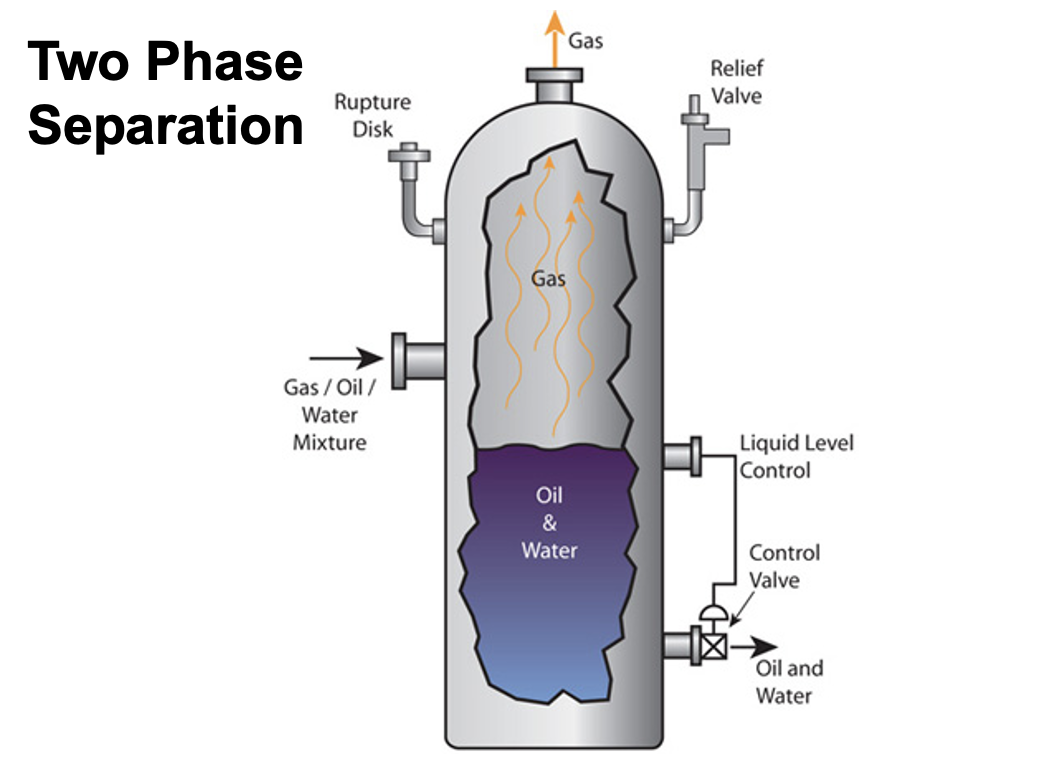
Draw a typical 2 phase separator
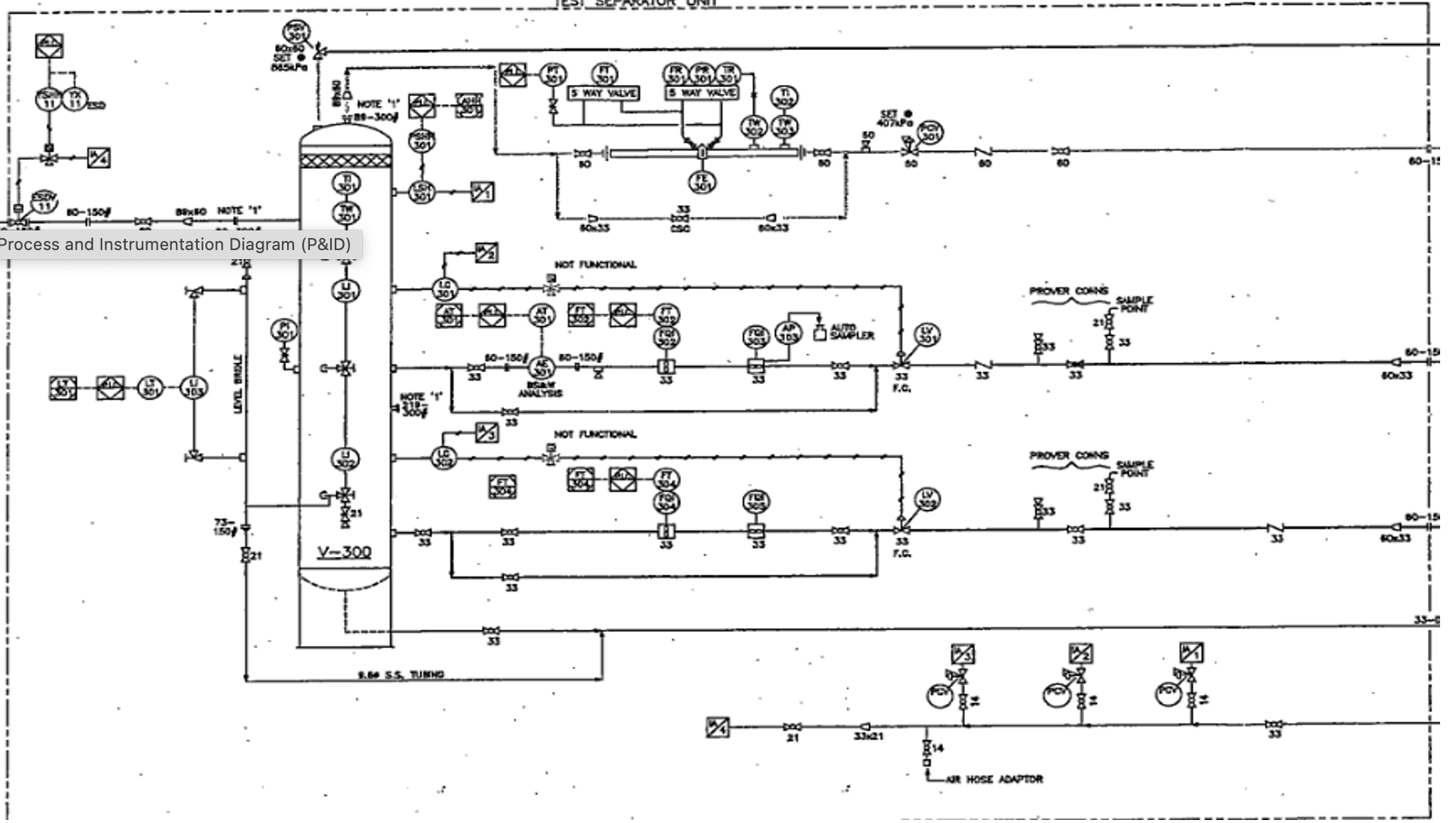
What does P&ID stand for?
Process and Instrumentation Diagram
A diagram that lays out the facility’s equipment and shows how each piece is connected to the next piece without any detail on size, dimensions, instrumentation or controls
Block Diagram
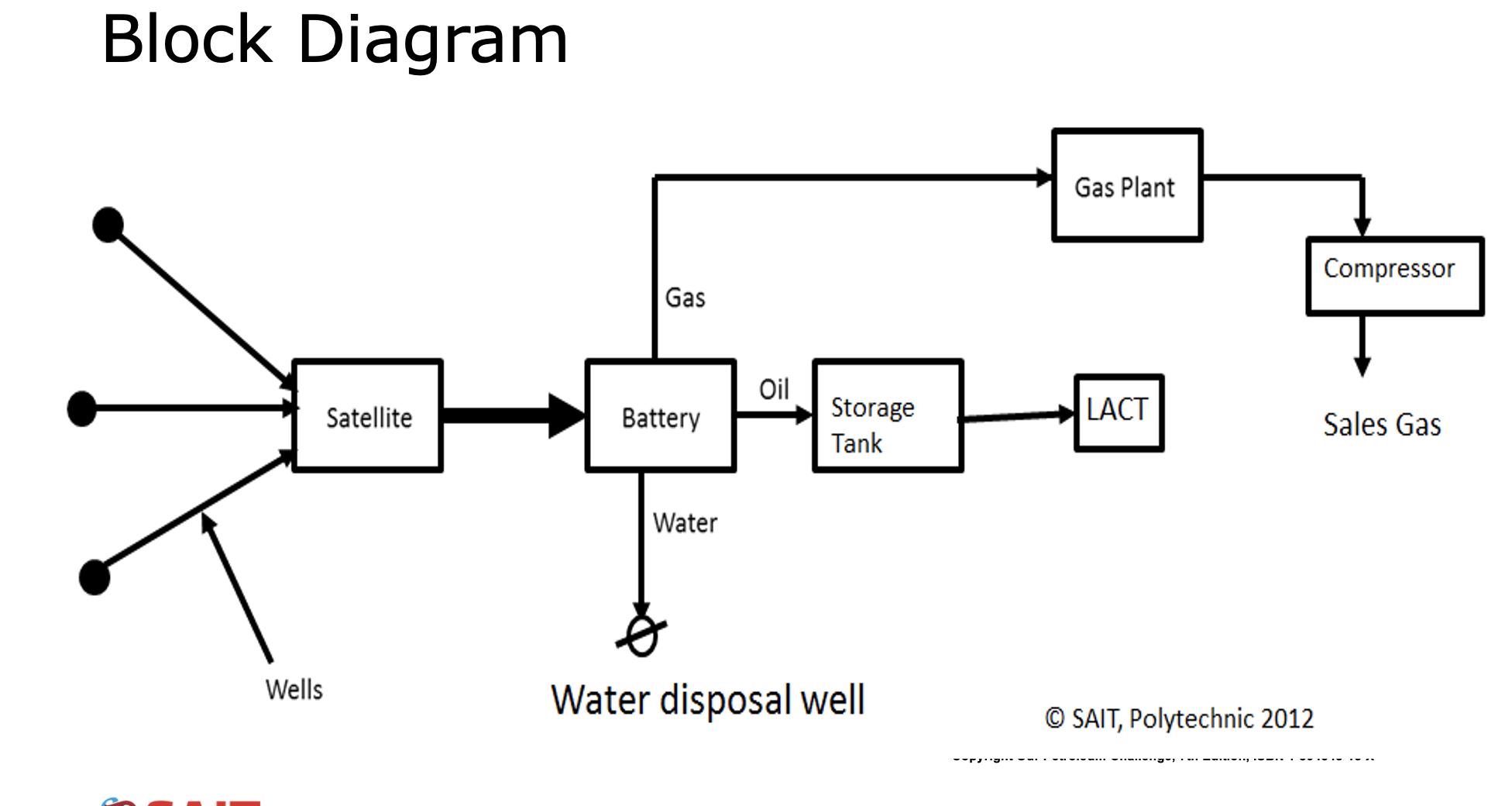
A diagram that includes basic piping, valves, controls, pumps, and meters for an individual process or an entire facility
Process Flow Diagram (PFD)
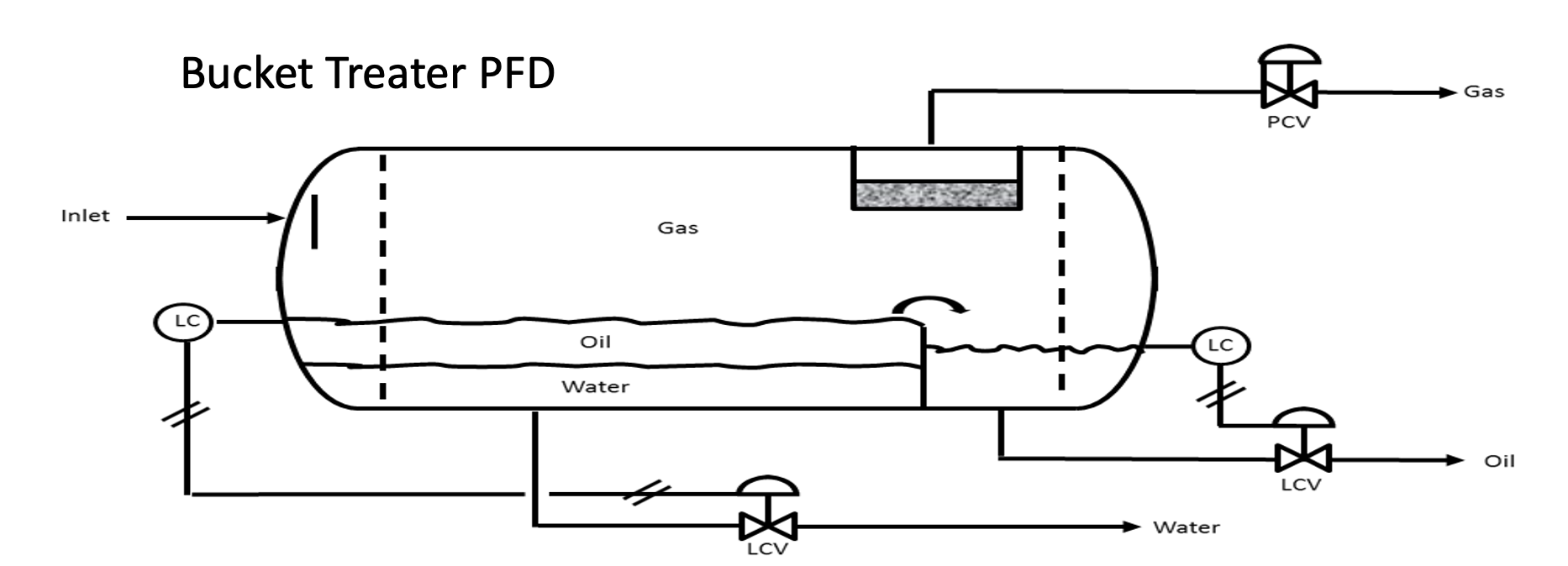
A highly detailed diagram that includes all instrumentation and control, specifications, piping, sizes and dimensions.
Process and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID)
Where would you typically find flow meters?
Installed on lines leaving:
separators
treaters
dehydrators
leases
What does ISA stand for?
International Society of Automation
What are ISA symbols?
A standard set of symbols used in PFD’s and P&ID’s.
used for valves, controllers, meters, pumps, compressors, vessels, tanks
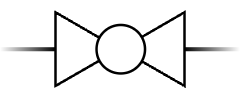
Ball valve
Needle valve
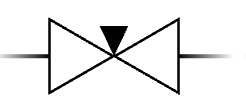
Gate valve
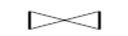
Check valve
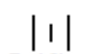
Orifice meter
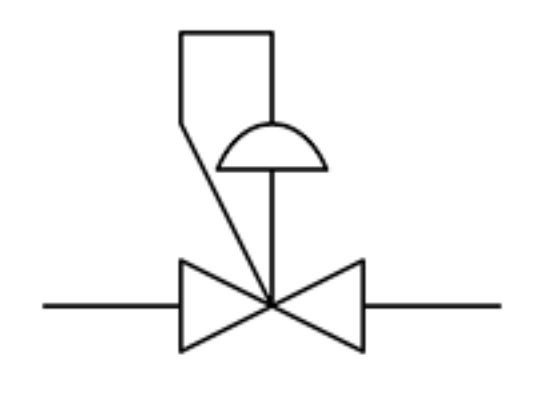
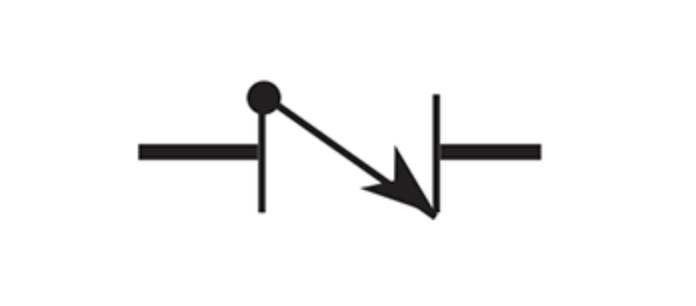
Back pressure control regulator
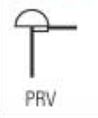
Relief PRV
Name these ISA primary acronyms:
P
T
S
L
F

Name these ISA secondary acronyms:
R
I
C
S
H
L
B

What is a control loop? Give examples.
A control loop is designed to maintain a process variable (e.g., temperature, pressure, flow rate, or level) within a specified range, typically using continuous feedback.
Ex: High Level Shut Down; Temperature Control
These two pieces of processing equipment are used to split production streams so that liquid(s) and gas volumes can be independently determined.
Separators and Treaters
Most commonly a vertical cylindrical vessel that uses agitation and gravity to separate the components of a production stream
Separator
efficiency of a separator is not high enough to create sales quality oil
Most commonly a horizontal cylindrical vessel that uses agitation, gravity and heat to separate the components of a production stream to create sales quality oil.
Treater
What is the BS&W criteria for sales quality oil?
< 0.5% BS&W
A single well or multi-well facility that tests wells individually as per AER requirements
Satellite battery
Gas production rates can be determined directly utilizing this type of meter
Orifice plate meter
How is the total oil production determined from a given well?
Take a reading of the flow meter for the total emulsion (oil + water) coming out of the test separator.
Determine BS&W: Use a centrifuge to find the percentage of water and sediment in the oil.
Calculate Net Oil: Subtract the BS&W from the measured emulsion flow to determine the net oil production
Output of a 2 phase gas well separator
Gas and Water
Output of a 2 phase oil well separator
Gas and Emulsion
Output of a 3 phase gas well separator
Gas, Condensate, Water
Output of a 3 phase oil well separator
Gas, Emulsion, Water
This type of separator is most commonly used for portable testing of new wells
Spherical separator
Name 1 pro and 1 con of a vertical separator
pro → small footprint
con → difficult to transport
What are the 4 zones of the interior of a separator?

What are 3 methods of demulsification used in a treater?
Heat
Electro-static grids
Demulsifying chemicals
These all allow for a decrease in retention time.
What function does heat play in a treater?
Heat aids in demulsification and so reduces the retention time required to break the oil/water emulsion
Oil heats faster than water and rises → cooler denser water coalesces and sinks.
Heat increases the motion of the water droplets, increasing the chance of collision → water droplets coalesce and sink
Multi-phase mixture of two or more substances that appears to be a single phase.
Emulsion
What is a normal emulsion?
Water in oil
What is a reverse emulsion?
Oil in water
Will a tight emulsion (small droplet size) require more or less heat to separate?
More
Compare the retention times between separators and treaters
The retention time in a treater is typically 10-30 times that of a separator - or 10-30 mins.
(Darcy math)
Name some problems caused by using too much heat in a treater
More fuel gas used than necessary
Oil will vaporize
Fire tube can prematurely corrode
Precipitation of solids from water or oil onto firetube leading to hot spots and corrosion
What does the Souders Brown Equation calculate?
Maximum allowable vapour velocity
This velocity is then used to calculate the cross sectional area requirement for a separator → then this area is used to calculate the minimum diameter
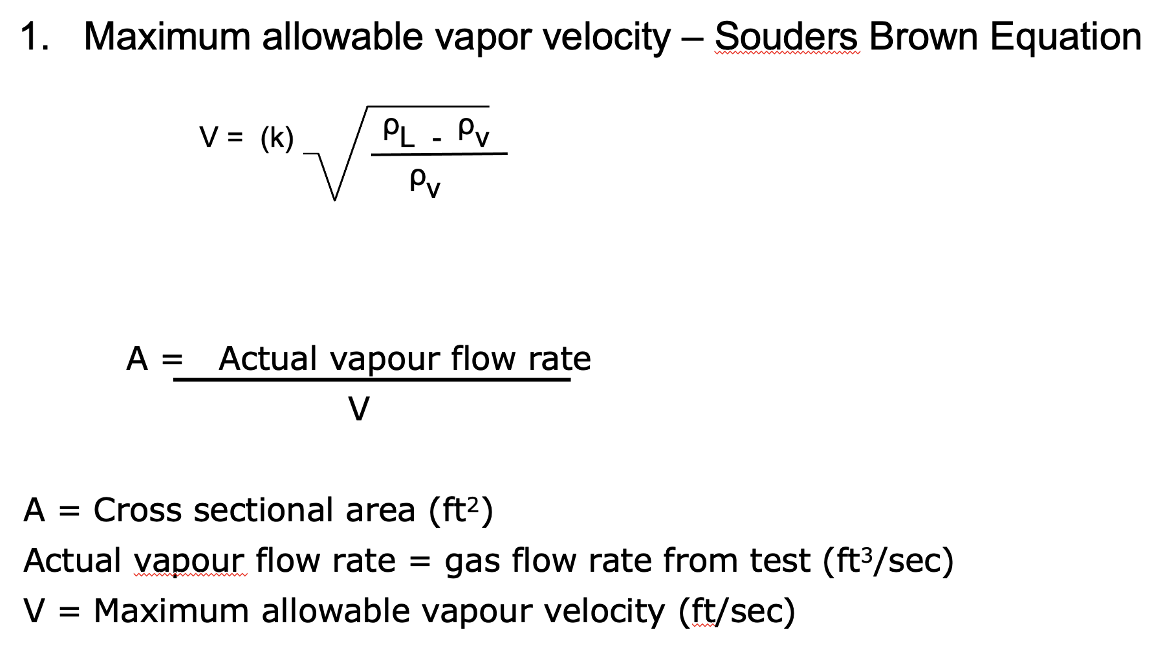
When sizing a separator, what is the initial estimate used for retention time?
What is the estimate used when sizing a treater?
Separator → 3 minutes
Treater → 20 minutes
What does Lss stand for?
seam-to-seam length
In separator sizing, the Lss is the height of the vertical separator.
ie. the total internal length of the vessel from one head (end cap) weld seam to the other
What retention time range for treaters has been observed to be sufficient in order to achieve sales quality oil?
10-30 minutes
The ratio of the height to the length of the treater
Slenderness ratio
Treater manufacturers generally build treaters to a slenderness ratio of 1:3 or 1:4 to minimize chances of buckling. (ie. 3 or 4 times as long as wide/high)
Give the suggested treater heating ranges for the various emulsion types (ie. loose, moderate, tight)
Loose Emulsions → 100oF to 120oF
Moderate Emulsions → 120oF to 140oF
Tight Emulsions → 140oF to 180oF
What are the 4 basic types of compressors?
Reciprocating → back and forth motion (piston/cylinder)
Centrifugal → spinning
Screw → rotary motion
Axial → rotating air foil (ex: turbine)
What is the most common type of compressor used in the oil and gas industry?
Reciprocating
What are the 5 main components of a reciprocating compressor?
Cylinder
Piston
Crankshaft (converts rotational to linear motion)
Suction valve
Discharge valve
A type of compressor in which compression only takes place on one side of the cylinder
Single-acting
A type of compressor in which compression takes place on both sides of the cylinder concurrently
Double-acting
more efficient and smooth running than single-acting
reduced volume on one side of the cylinder due to the rod
What process can improve efficiency in multi-stage compression?
Inter-cooling
What is the “swept volume” ?
The displacement capacity of a compressor
the total volume that a piston moves through (sweeps) as it compresses gas in each cycle.
The ratio of the clearance volume to the swept volume (or displaced volume)
Cylinder clearance (C%)
where:
Clearance Volume → the small space left between the piston and the cylinder head when the piston is at the top of its stroke
Swept Volume (displaced volume) → the volume displaced by the piston moving through its entire stroke

Actual pumping capacity of the cylinder compared to the piston displacement.
Volumetric Efficiency (Ve)
Calculated using the mass of gas delivered compared to the mass of gas that could have been moved with full piston displacement.
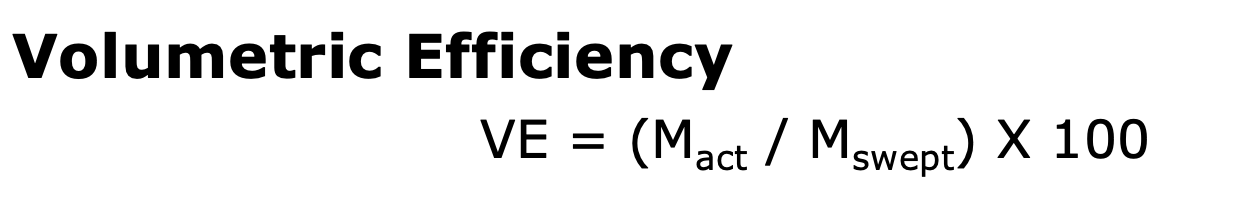
What factor has the largest impact on volumetric efficiency?
The re-expansion of the gas trapped in the clearance volume
How are rod loads generated?
Gas forces → gas loads
Inertial forces → inertial loads
Gas loads cause most of the load on the rods and all of the other components connected to the rod
How:
As the piston moves forward to compress the gas, the differential pressure acting on the piston results in a gas force pushing against the piston, causing a compressional force on the piston rod
This type of load occurs when the piston is at the furthest point during the stroke moving away from the crankshaft.
Head End Load
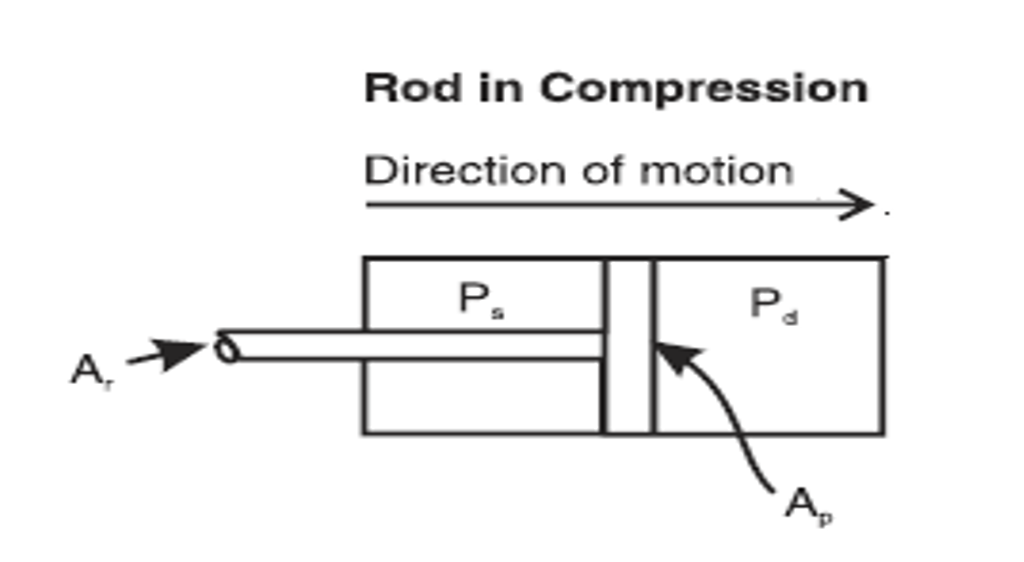
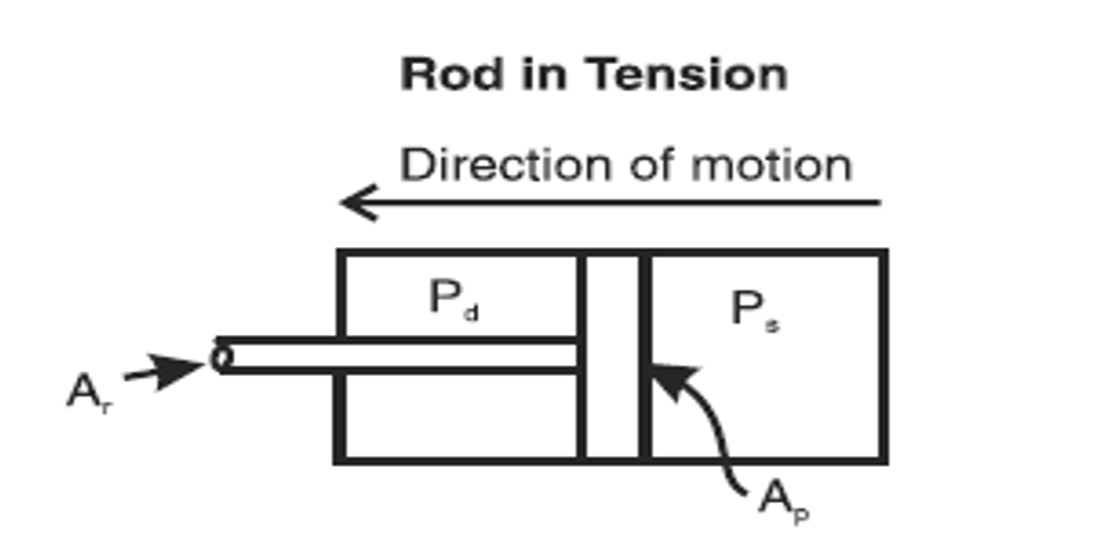
This occurs when the piston is at the closest point during the stroke moving towards the crankshaft
Crank End Load
The Ideal Gas Law states that a reduction in volume of a given mass of gas must ___________ the temperature of the gas.
increase
Name 3 reasons why cooling is important when compressing gas
High temperatures can:
Decrease the efficiency of the compression process
Reduce the life span of the materials in the machinery
Present a significant safety hazard to the operators
What type of valves would you expect to find on the outlet lines of a treater or separator?
Oil/water lines → LCV
Gas lines → PCV
Flare line → PSV
A type of valve designed to protect equipment and personnel from dangerous overpressure by opening rapidly and fully when the pressure exceeds a set limit. Its primary role is safety.
Pressure Safety Valve (PSV)
A valve primarily designed to relieve pressure in a controlled manner to prevent overpressure in a system. It typically opens gradually as the pressure increases, allowing a controlled release of fluid (gas or liquid) to maintain system pressure within safe limits.
Pressure Relief Valve (PRV)
What is calculated using an orifice plate coefficient?
a. Oil flow rate
b. Gas flow rate
c. BS&W
d. None of the above
b. Gas flow rate