2.1 | Intro to Macroeconomics and GDP
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential concepts in macroeconomics, focusing primarily on GDP, its components, and related measures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the three major economic goals of all countries?
Promote economic growth 2. Limit unemployment 3. Keep prices stable (limit inflation).
How is GDP defined?
The dollar value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s borders in one year.
What types of goods are excluded from GDP?
Intermediate goods, used goods, and non-market activities.
What is the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP?
Nominal GDP is measured in current prices and does not account for inflation, whereas real GDP adjusts for inflation.
What is GDP per capita and why is it important?
GDP divided by the population. It identifies on average how many products each person makes.
GDP per capita is the best measure of a nation’s standard of living.
What does the Income Approach to calculating GDP encompass?
Add up all the income that resulted from selling all final goods and services produced in a given year.
How do you calculate the percent change in GDP?
% Change in GDP = (Year 2 GDP - Year 1 GDP) / Year 1 GDP × 100. (New - Old) / Old
What are four components of GDP?
Consumer Spending 2. Business Investment 3. Government Spending 4. Net Exports.
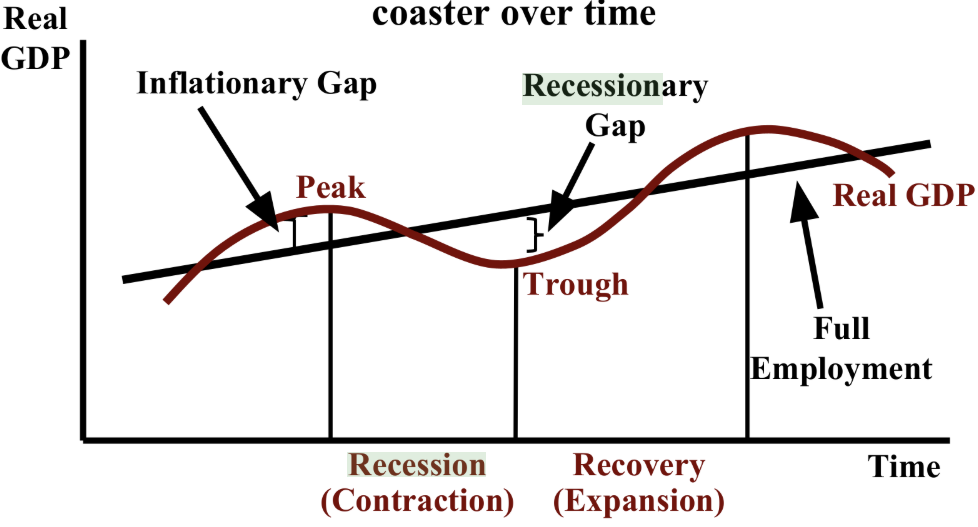
What is a recession?
A 6-month period of decline in Real GDP.
What is real GDP the best measure of?
Economic growth.
What is national income accounting (which helps measure well the economy is doing)?
Economists collecting statistics on production, income, investment, and savings.
What is the expenditures approach to calculating GDP?
Add up all the spending on final goods and services produced in a given year.
How to calculate GDP through the expenditures approach?
GDP (Y) = C (consumer spending) + I (business investment) + G (government spending) + (X (exports) - M (imports))
Consumer spending (C) is made up of three components:
Durable goods
Non-durable goods
Services
What is investment, and what is never investment?
When businesses buy capital like machines/resources/tools. It’s NEVER when individuals buy assets like stocks and bonds.
What is inventory?
Goods produced and held in storage in anticipation of later sales.
What year is inventory counted toward GDP?
Inventory is counted toward GDP in the year it is produced, regardless of whether it is sold.
Government (G) expenditures tracks the spending made in the public sector.
Which one(s) of the three below counts toward government spending?
Money spent on transfer payments (e.g. welfare, social security, subsidies).
Payments made by the government for goods and services (e.g. fighter jets & the pilots’ salaries).
Interest payments on the national debt.
Only payments made by the government for goods and services.
What four components make up the income approach, and what are they collectively called?
Labor income (wages from work), rental income (income earned from property owned by individuals), interest income (interest earned from loaning money to businesses), and profit (money businesses have after paying all their costs).
These are called factor payments.