Lecture 2: Ctenophores
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Ctenophore Synapomorphies
Combs made of cilia
biradial/rotational symmetry
Colloblasts
Cilia
Protrusion of cell membrane
move using organized metachronal beating
the power and recovery of each cilium follows its neighbors
9 microtubules made of tubulin bundled around 1 in the middle
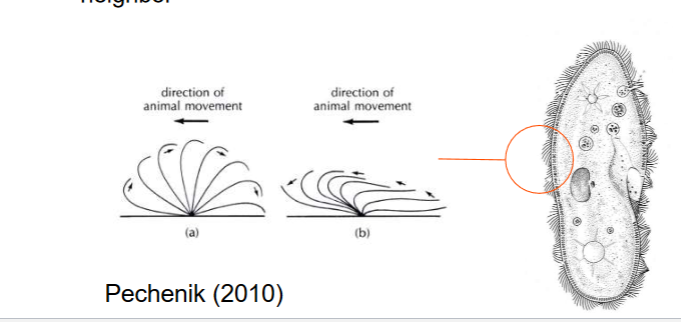
Ctenophore life style
predatory
pelagic
suspension feeder
key role in estuarine and pelagic ecology
Ctenophore cell layers
epiderms
cellular mesoglea
gastrodermis
Ctenophore body plan
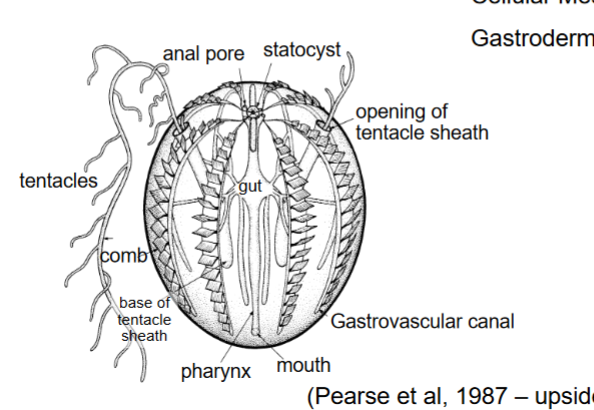
Ctenophore body plan part 2
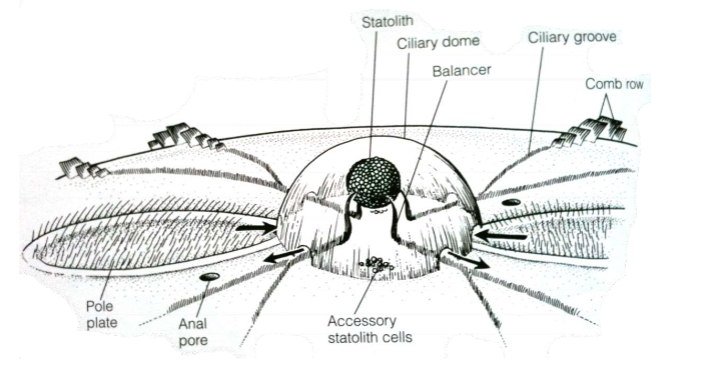
Ctenophore symmetry
Rotational symmetry
2 planes
tentacular plane
pharyngeal plane
Colloblast
Ctenophore synapomorphy
adhesive cell with sticky secretion used to capture prey (contrast nematocyst)
Ctenophore Digestion
gastrovascular system
branched extensions of the gut that circulate nutrients+water
it is not clear whether they excrete through mouth or anal pore
Ctenophore nervous/muscular system
subepithelial nerve net
bidrectional or unidirectional synapses
muscles for locomotion
Cydippid
ctenophore body plan
ball-like body
tentacles
cilliary locomotion
Lobate
no tentacles
wing-like lobes
ciliary locomotion and muscular locomotion
Beroe
no tentacles
no lobes
ciliary locomotion
predatory sock- a tube open at one end
feed on other ctenophores and jellies
teeth made of cilia
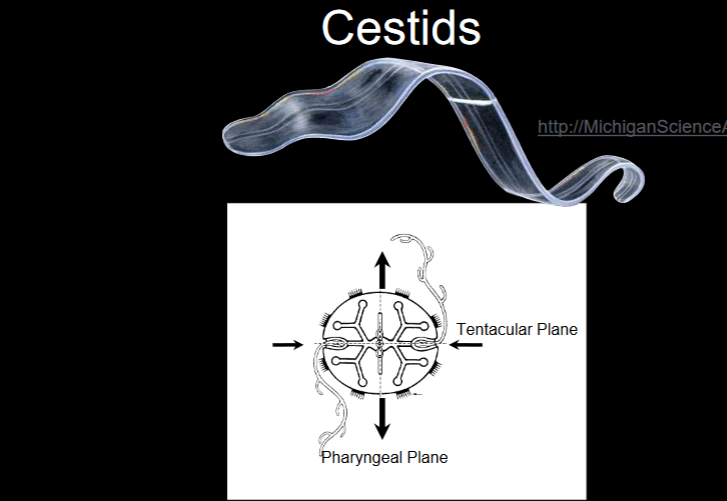
Cestid
no tentacles
no lobes
ciliar locomotion and muscular locomotion by undualtion of the body
flattened along pharyngeal plane
Benthic
tentacles
no lobes
creeping locomotion along substrate
Reproduction
asexual reproduction by fragmentation (benthic species)
sexual reproduction
gametes expelled through mouth
external fertilization
hermaphroditic
Pigment
chemicals that differential absorb some colors
Refraction
bending of light path, angle of bending depending on wavelength (ctenophore rainbows)
Iridescence
structural coloring (color changes with angle of view)

Fluorescence
light absorbed at one wavelength and re-emitted at a different wavelength (often paired with bioluminescence)
Bioluminscence
light generated by chemical reaction (often symbiotic bacteria)
Purposes of biolumenscence
