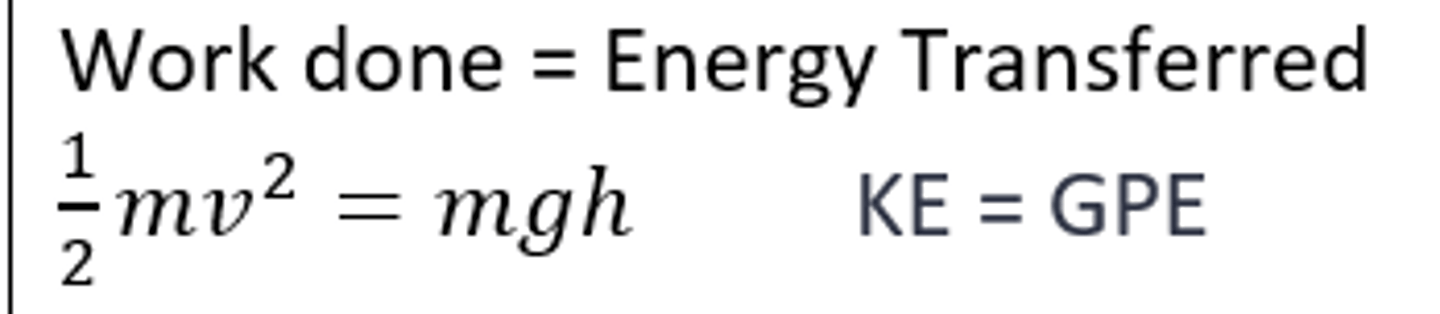Ch.5 Work, Energy, and Power
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Work done
Force x distance moved in direction of force.
(In Joules)
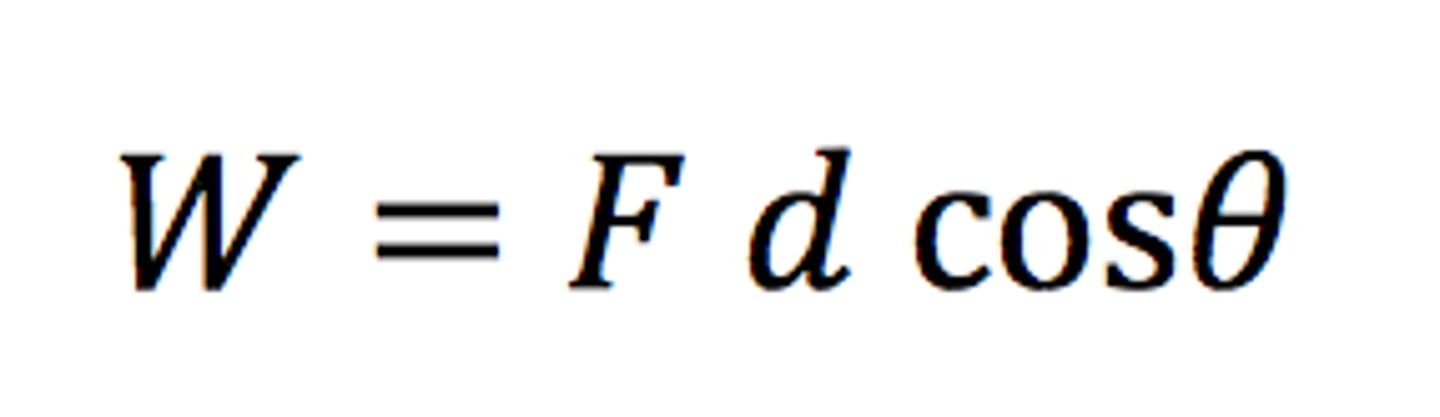
Power
The rate at which work is done. (In Watts)
P=Energy/time
P=Force x Velocity
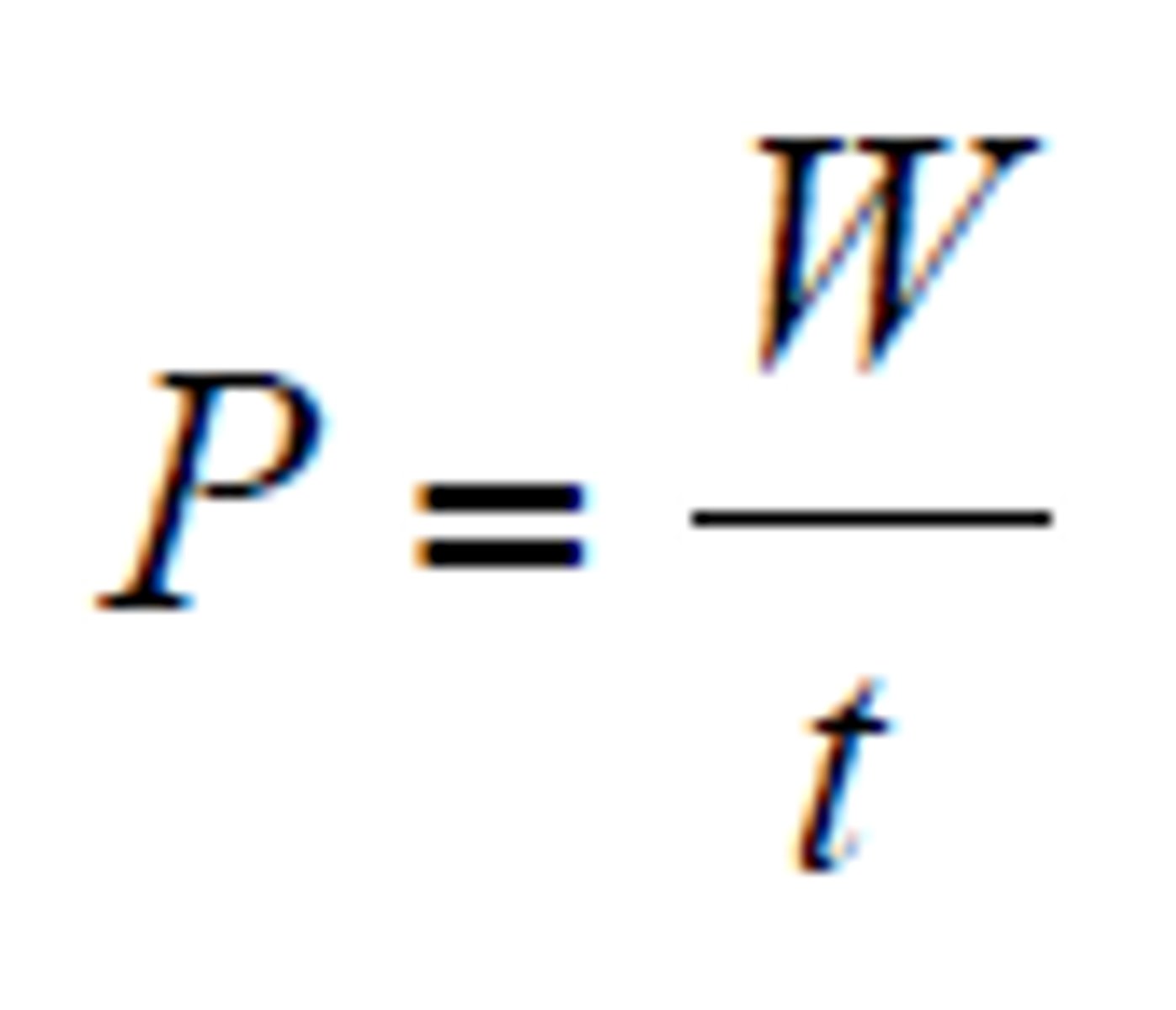
Kinetic energy formula
(In Joules)

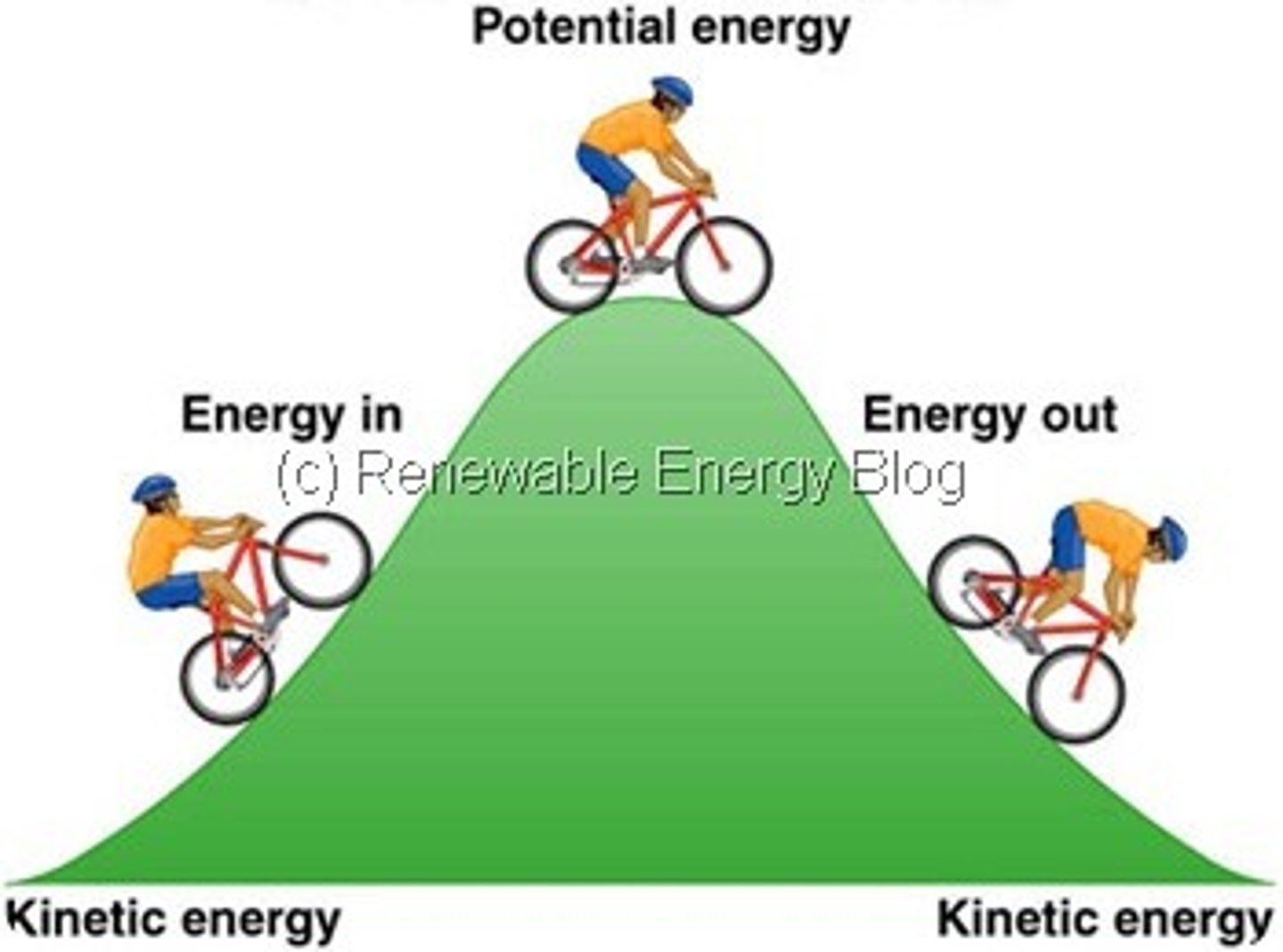
Potential energy
Stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object (In Joules)
PE= mgh
Energy
The ability to do work (in Joules)
Efficiency
The percentage of the input work that is converted to output work.
Useful energy or power/Total energy or Power times 100

Derive KE Formula

Derive GPE Formula
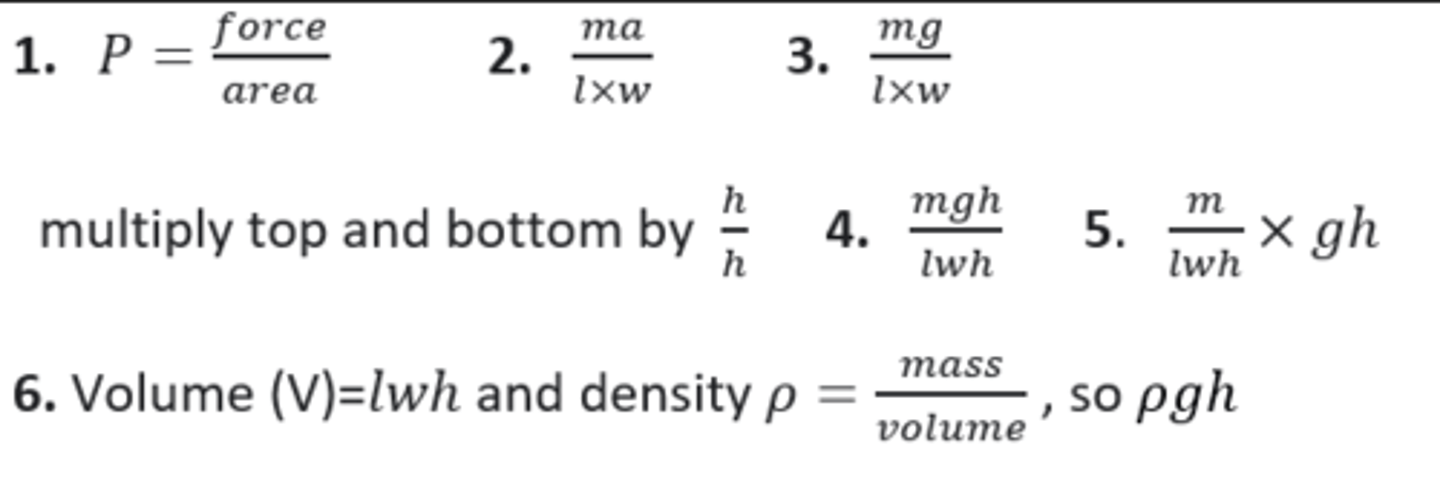
Derive P=Fv
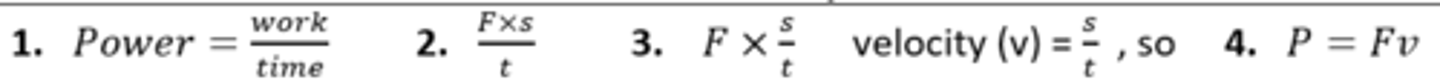
Joule
The force that would give a mass of one kilogram an acceleration of one meter per second squared in the direction of the force.
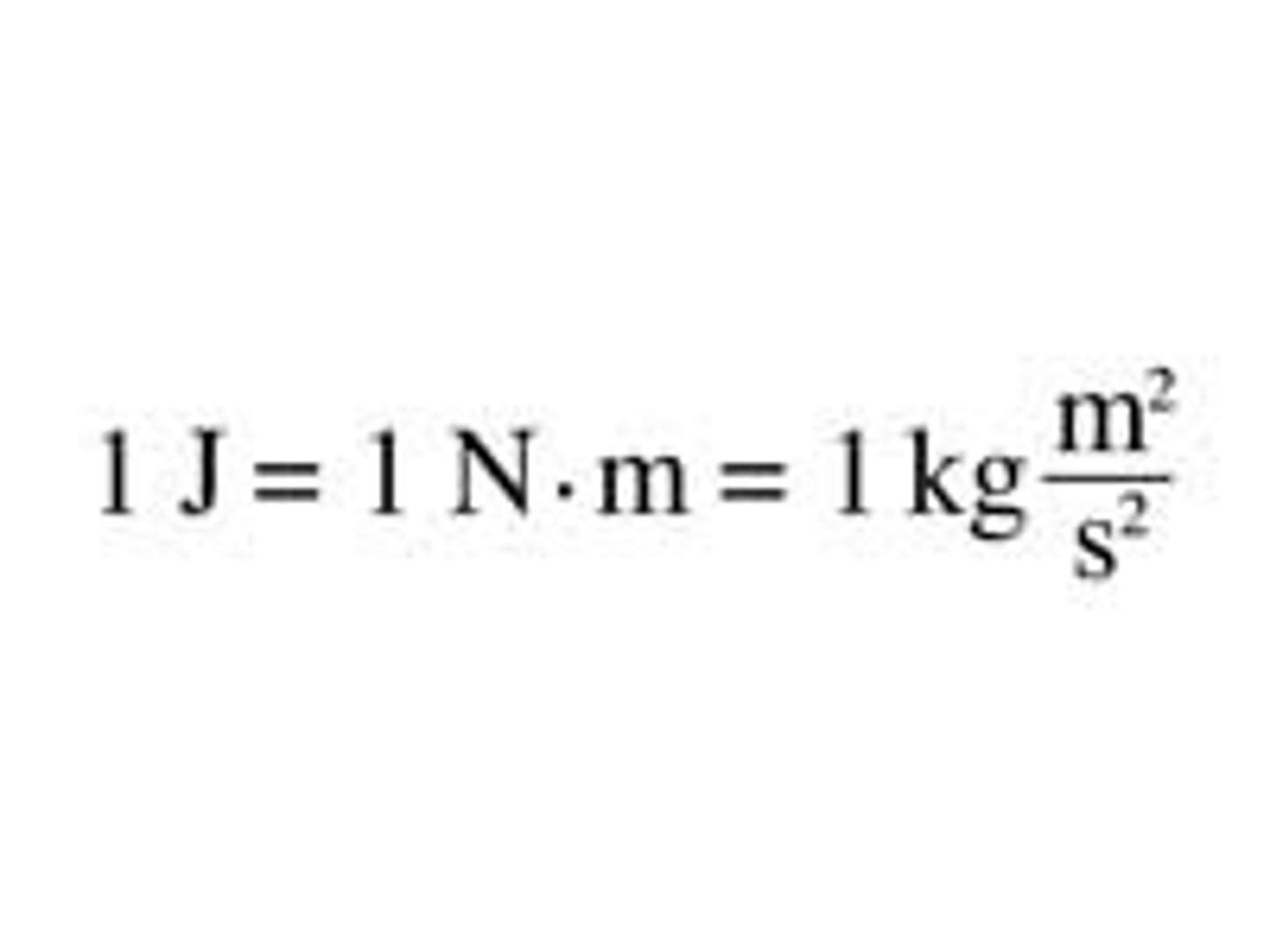
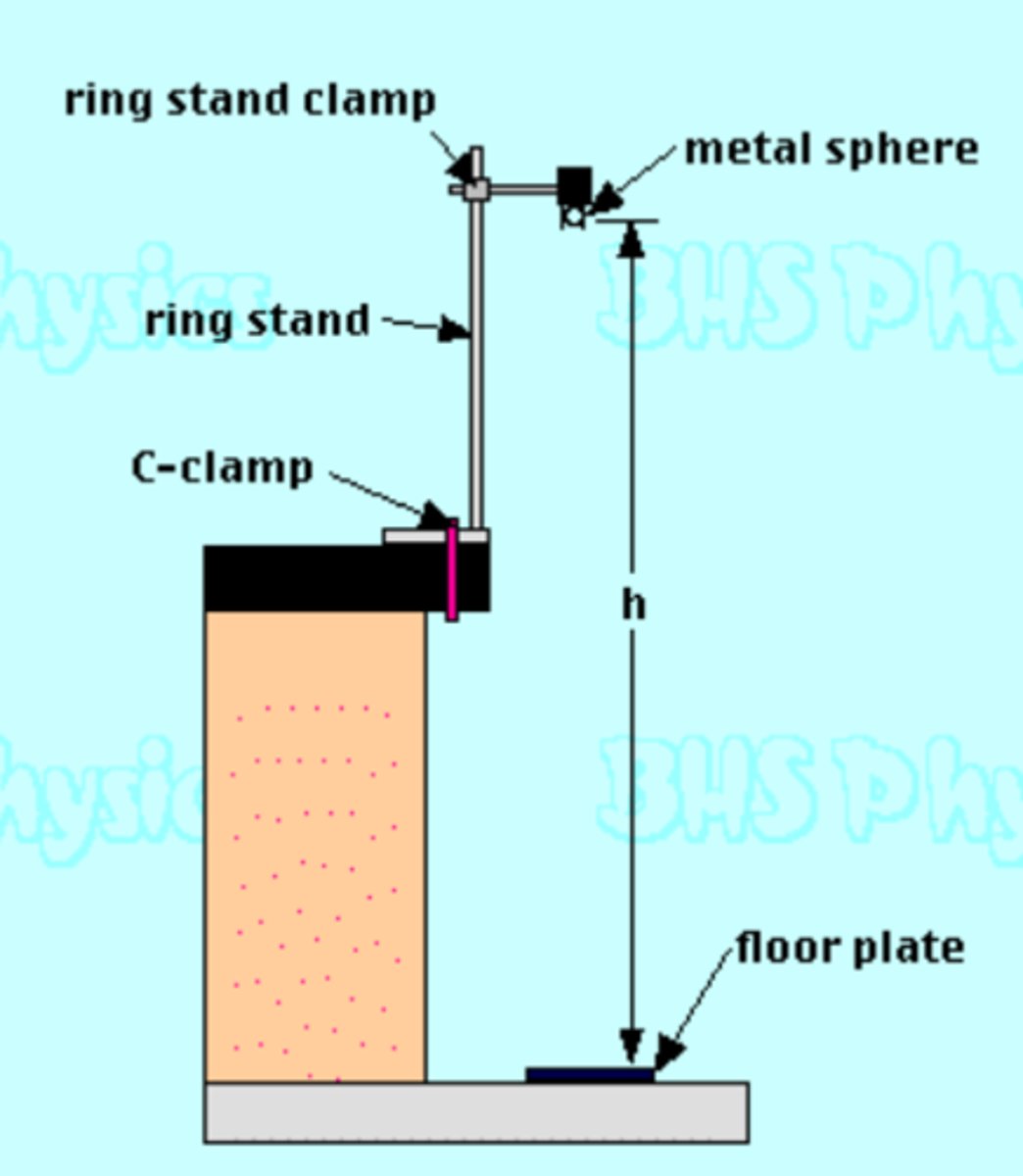
Finding "g=9.81" in an experiment.
1. Use a meter stick to measure the height an object is to be dropped
2. Drop an object with initial “u” velocity of zero.
3. Use a stopwatch. Measure the time it takes the object to hit the
Ground.
4. Plug in height “s”, time “t”, and “u = 0” into the equation s=ut +1/2at^2
.
5. Solve for “a”. This should give you “g” after many trials and
averaging
Gravitational potential energy definition.
Energy stored due to an object due to its position in a gravitational field.
Conservation of Mechanical energy