EKG Interpretation
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
normal sinus
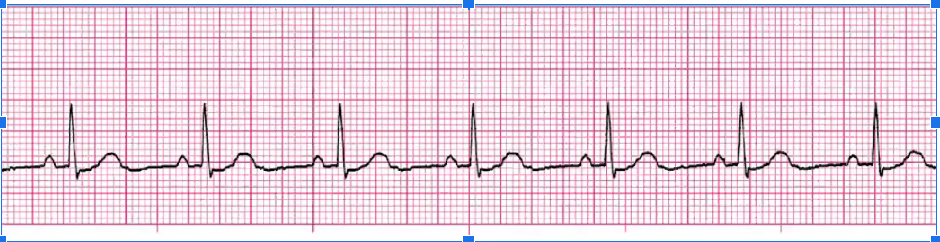
sinus brady
Treat ONLY if symptomatic:
d/c meds that cause it, Atropine if symptomatic
Pacer if chronic tx needed
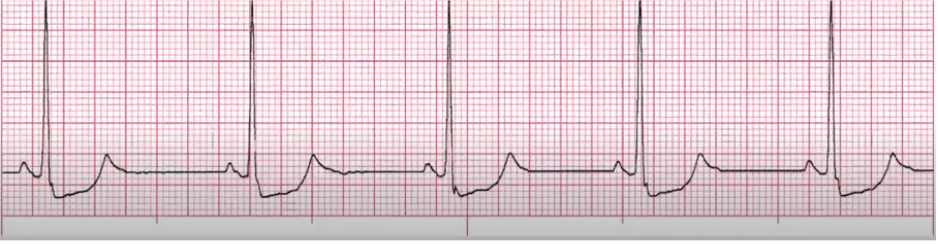
sinus tachy
If sx: TAKE BP!
treat underlying cause (usually compensation)
meds to slow HR: BB, Ca Channel Blocker
Dehydrated? IVF
pain meds
cut back on smoking/caffeine
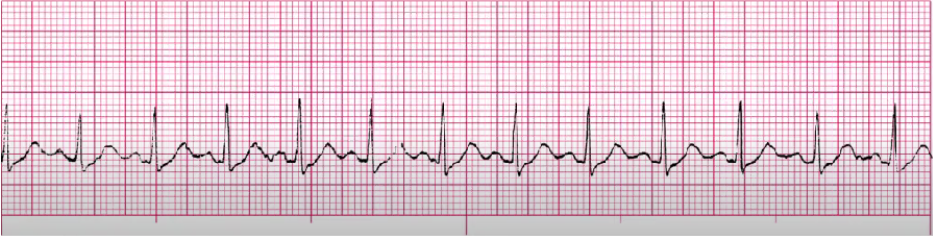
sinus arrythmia
NSR but regular, SA node fires irregularly
no clinical significance, no tx
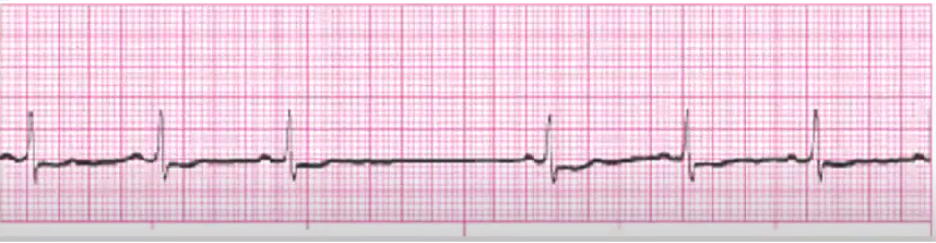
sinus block
Tx if symptomatic:
stop meds that cause, IV atropine if too slow, pacer if chronic
sinus arrest
tx if symptomatic
stop meds that cause it
IV atropine if too slow
pacer if chronic
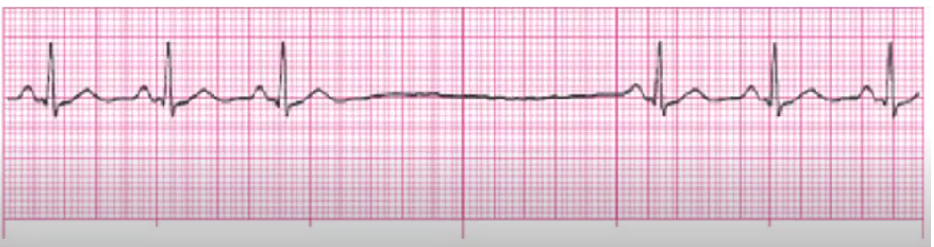
NSR with PACs
treat underlying cause if sx
BBs, Ca Channel Blockers, anti-anxiety meds
monitor someone with LOTS of PACs, could turn into atrial dysrhythmia
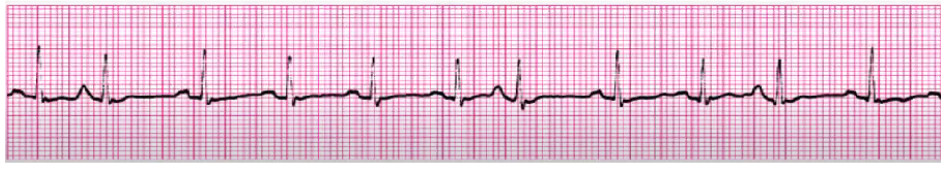
SVT (paroxysmal/multifocal)
O2, IV access
Vagal maneuvers (things to slow HR down - ice around face, bear down, breathe thru a straw)
Anti-arrhythmic (adenosine) (given QUICKLY over SECONDS, stop caulk and flush immediately - stuns heart asystole into sinus), can give twice 6 mg to 12 mg
Ca Channel Blockers, Amiodarone, BBs
Cardioversion (synchronized shock to sync heartbeat) - avoid R on T phenomenon (Torsades), Sometimes use conscious sedation; TEE done before to look for clots prior to shock, heparin drip as well
Ablation for chronic (surgery to burn off abnormal pathways)
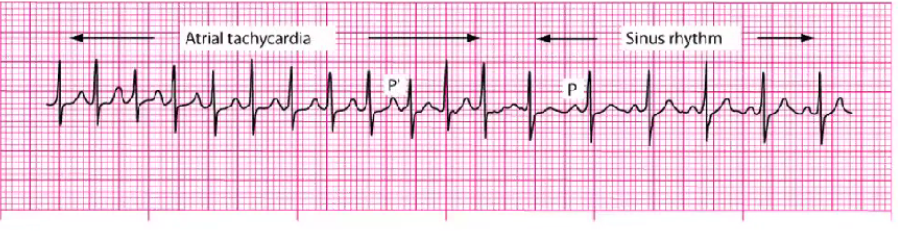
Atrial flutter
cardioversion for sx and unstable pts
Digoxin, Ca Channel blockers, amiodarone, BBs
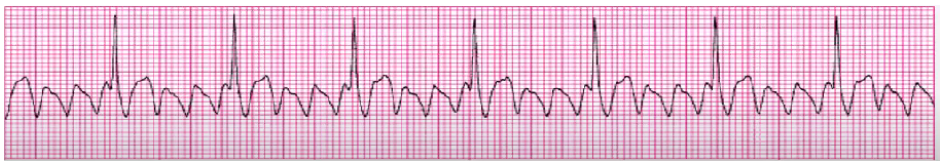
A fib
if sustained with rapid ventricular response: control ventilation rate and return to sinus, pacer
Ca Channel Blocker (Cardizem), Digoxin, amiodarone, BBs
cardioversion (if meds not working/pt is unstable)
Coumadin (anti coag)
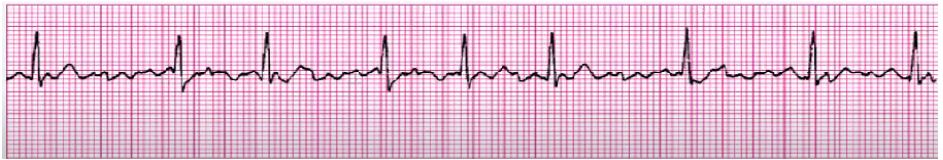
NSR with PJCs
treat the underlying cause (stimulants, heart disease, electrolyte imbalance, fatigue)
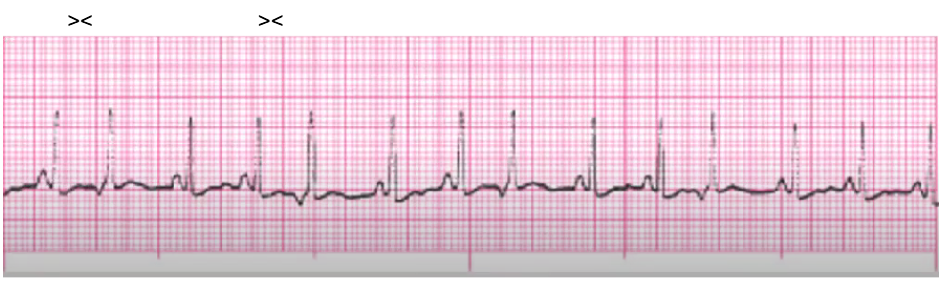
junctional escape
rate 40-59
slow rates lead to decreased CO (change in LOC, SOB, chest pain, decreased BP)
atropine, temporary pacer
treat underlying cause (RHD, valve disease, post-CABG, hypoxia, Ca Channel Blockers, BBs, increased vagal tone)
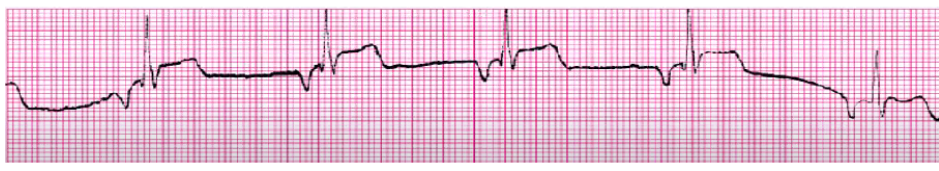
accelerated junctional
rate 61-100
no tx (NSR rate)
can be caused by MI, post-cardiac surgery, RHD, COPD, hypokalemia, dig toxicity
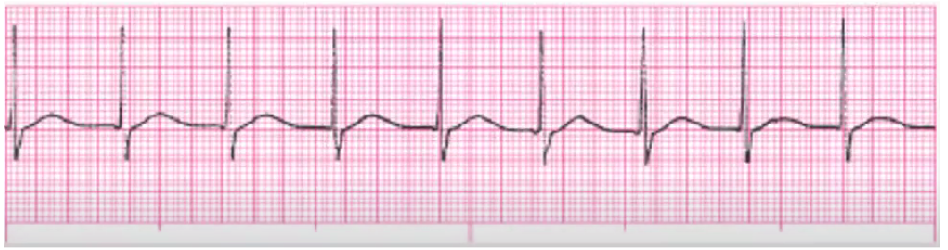
junctional tachycardia
rate 101-180
stop meds if they’re the cause
treat as SVT - slow HR w adenosine
amiodarone, Ca Channel blockers, BBs
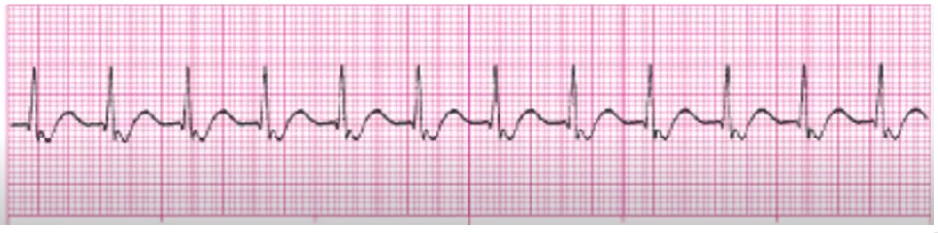
unifocal PVCs (w NSR)
assess BP, change in LOC, breathing, chest pain
Asx - monitor, treat underlying cause (hypoxia, electrolytes, HF, MI, post CABG, reperfusions, catheters in RV, anxiety, caffeine/stimulants)
DO NOT COUNT PVCs IN HR COUNT
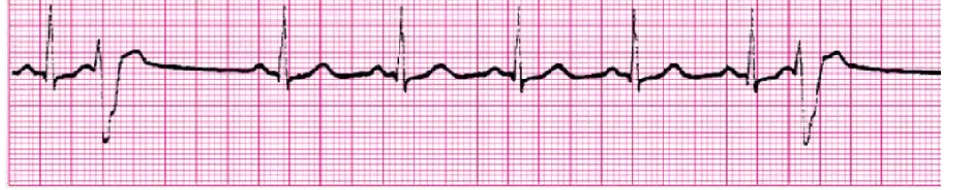
multifocal PVCs (sinus tach)
assess BP, change in LOC, breathing, chest pain
Asx - monitor, treat underlying cause (hypoxia, electrolytes, HF, MI, post CABG, reperfusions, catheters in RV, anxiety, caffeine/stimulants)
DO NOT COUNT PVCs IN HR COUNT
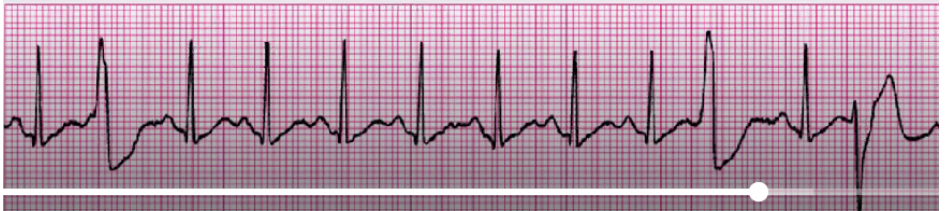
V tach
follow algorithm:
pulse and stable: 02, IV access, anti-arrhythmics
pulse and unstable: O2, cardiovert (sedate prn), antiarrhythmics
no pulse: treat as vfib
chronic: PO meds, ICD, ablation
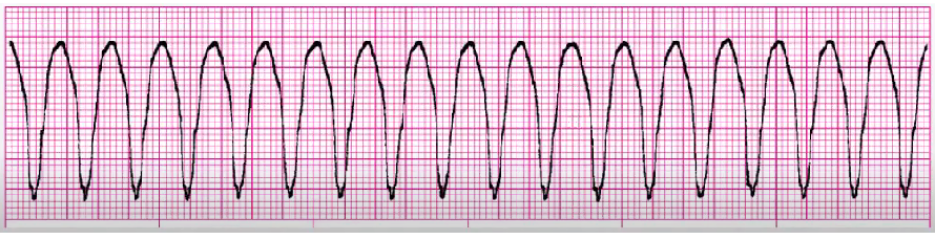
torsades de pointes
treat cause (low Mg++/K+), amiodarone can cause
Mg++ bolus to slow HR
cardioversion
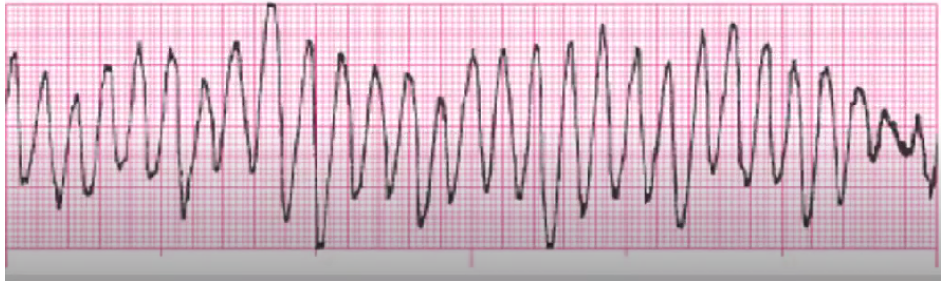
coarse V fib
above 3 mm - more recent
Follow algorithm sequence:
CPR (no pulse)
Defibrillate* (120 to 150-200 joules) + CPR after
Epinephrine, amiodarone, O2/ventilation
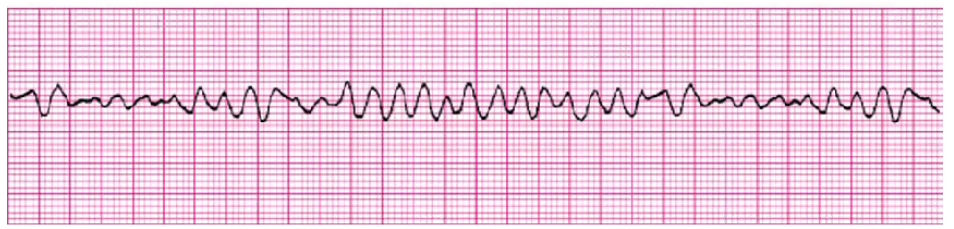
fine v vib
under 3 mm, present for longer, harder to get person back
Follow algorithm sequence:
CPR (no pulse)
Defibrillate* (120 to 150-200 joules) + CPR after
Epinephrine, amiodarone, O2/ventilation
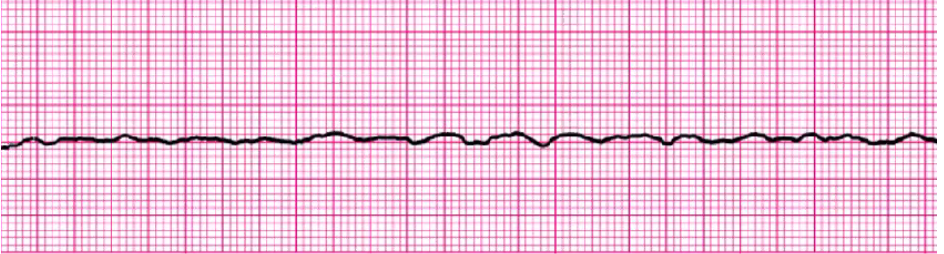
asystole
CPR, epi
Hs and Ts: hypovolemia, hypoxia, hydrogen ions, hypothermia, hyper/hypokalemia, hypoglycemia, toxins (drug overdose), tachycardia, tamponade, tension pneumo, thrombosis (MI/PE), trauma
no CO, no perfusion
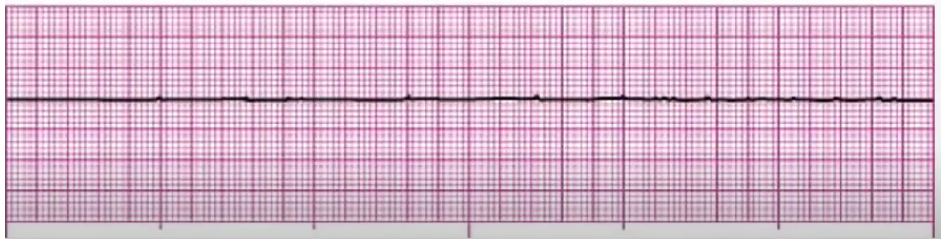
PEA
regular electrical rhythm with no pulse, no actual perfusion is getting through
Hemorrhage, Tamponade
CPR, epi
Hs and Ts: hypovolemia, hypoxia, hydrogen ions (acidosis), hypothermia, hyper/hypokalemia, hypoglycemia, toxins (drug overdose), tachycardia, tamponade, tension pneumo, thrombosis (MI/PE), trauma
shockable cardiac arrest rhythms
pulseless v tach, v fib
unshockable cardiac rhythms
asystole, PEA
1st degree AV heart block
delay within underlying rhythm, slowing down (not an actual block)
regular rhythm, just > 0.20 PR interval
occurs within underlying rhythm
hold meds if over 0.26 seconds
check with pcp with digoxin or antiarrhythmics
post MI: monitor for more serious block
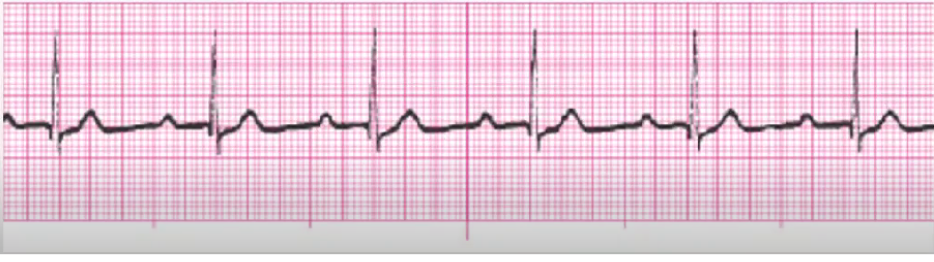
2nd degree type 1 AV heart block (Wenkebach)
happens with inferior MI (RCA is what is blocked)
monitor for worse block
hold meds if the cause
atropine/pacing for slow rate
(atropine increase SA node firing (increases P waves, increasing impulses)
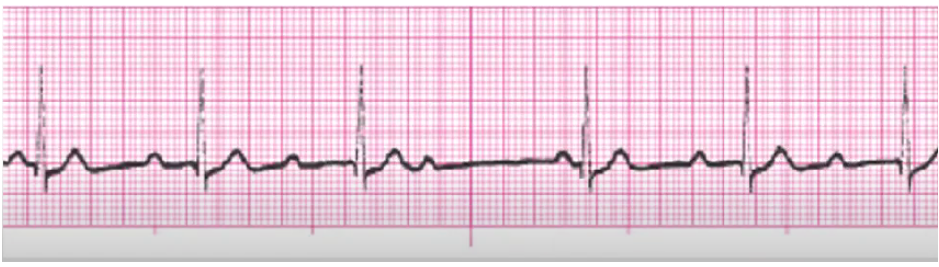
2nd degree type 2 AV block
anterior MI
monitor for worse block, especially MI (3rd degree or asystole)
temporary/perm pacer
hold anti-arrhythmic
NO ATROPINE - atropine increases SA node firing = P waves… we don’t need those
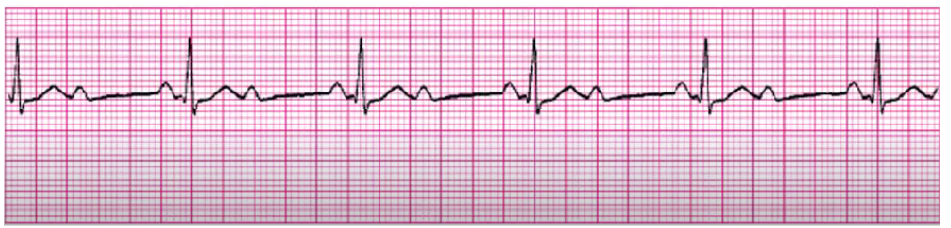
3rd degree complete heart block
pace maker
monitor EKG post-MI
limit activity, 02
(inferior/anterior MI)
AV dissociation, Ps and QRS have no association
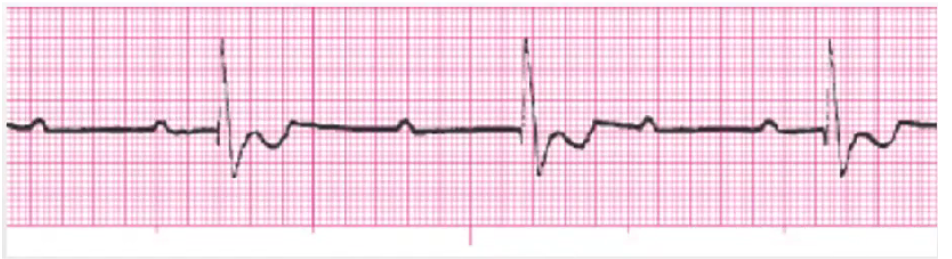
atrial pacer
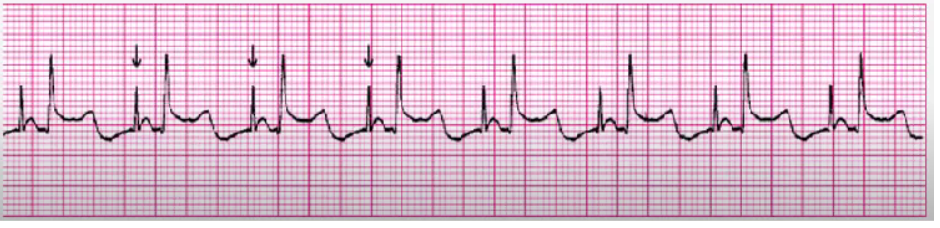
ventricular pacer
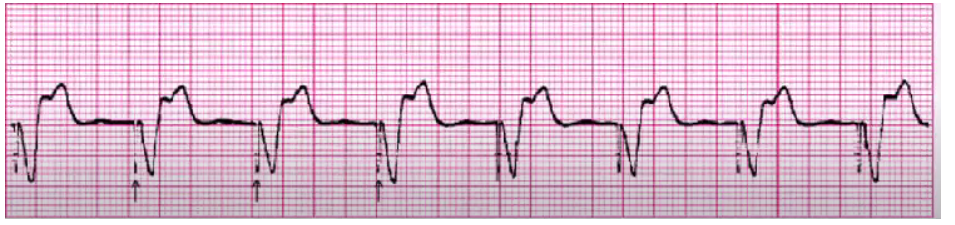
atrial/ventricular pacer
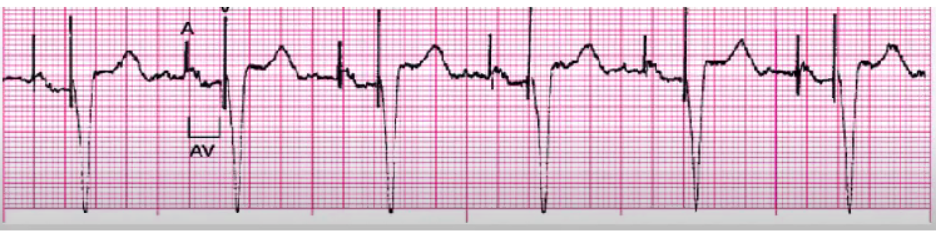
AV blocks
delay/block that occurs within AV node
PR interval key to determine type of block
junctional dysrhythmias
retrograde depolarization of atria: SA to AV almost ‘going backwards”
Inverted P Wave (before, after, or hidden in QRS)
HR distinguishes junctional type (<60, 60-100, >100
atrial dysrhythmias characteristics
hallmark feature= shape of atrial P wave (different from sinus)
can be pointed, inverted, sawtooth, or wavy