Environmental Crisis and Disaster
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
Crisis
A disruption that physically affects a system as a whole and threatens its basic assumptions, its subjective sense of self, and its existential core (Pauchant and Mitroff, 1992, 15).
Crisis
An abnormal situation which presents a high risk to business and may trigger rapid policy changes, since it draws public and media attention and threatens public trust (Sawalha, Jraisat, and Al-Qudah, 2013).
Crisis
A situation faced by an individual, group, or organization which they are unable to cope with by the use of normal routine procedures and in which stress is created by sudden change (Booth 1993, cited in Moe and Pathranarakul, 2006, 402)
Crisis
perception or experiencing of an event or situation as an intolerable difficulty that exceeds the person's current resources and coping mechanisms (James & Gilliland, 2013)
Crisis
Stressful event or perceived threat + lack of efficient coping skills, resulting in emotional unbalance
Limited in time: 1-6 weeks
During the ________, the subject asks for help
During the _________, the subject is more compliant to external intervention
The evolution in _________ depends on the timing of the intervention
Stages of Crisis
Stage I: Immediate response
Stage II: Emotional reactions
Stage III: Resolution
Stage I: Immediate response
Stage of Crisis
astonishment, denial
Stage II: Emotional reactions
Stage of Crisis
anxiety, anger, guilt, regression, depression
Stage III: Resolution
Stage of Crisis
acceptance, planning the future
Maturational Crisis
Type of Crisis
• Periods in life which entail changes in social roles, biological and social pressures;
Maturational Crisis
Type of Crisis
• Adolescence, marriage, birth of a child, retirement;
Maturational Crisis
Type of Crisis
• Adolescence: _______________ - originality, hormonal and psychological unbalance
Situational Crisis
Type of Crisis
A specific external event that disrupts the internal psychological balance of the individual:
• Death of spouse
• Divorce
• Illness
• Accidental pregnancy
• Childbirth
• Sexual dysfunction
Situational Crisis
Type of Crisis
• The experience of loss (of a loved one, of self- esteem, of normal functioning, of status, of job...)
Situational Crisis
Type of Crisis
• Issues concerning change (transition, marriage, birth of a child, moving, change of job...)
Situational Crisis
Type of Crisis
• Interpersonal issues (family conflicts)
Situational Crisis
Type of Crisis
• Environmental factors (pollution, work environment...)
Catastrophic Crisis (Social)
Type of Crisis
accidental, unusual, unexpected:
• Fire, earthquake, flood, kidnapping, nuclear accidents...
Catastrophic Crisis (Social)
Type of Crisis
• Causes severe stress
Catastrophic Crisis (Social)
Type of Crisis
• Requiring maximal coping strategies and abilities
Disaster
Occurs as a result of a combination of hazards, vulnerabilities, and a lack of measures, where using special measures for planning, coordinating, and utilizing appropriate resources will minimize the adverse impact of disasters (The United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNISDR, 2009).
Disaster
Are largely defined as sudden unforeseen events in natural, technological or social causes that lead to destruction, loss, and damage (Alexander, 2005b)
Disaster
complex global problem; it is an inevitable truth of our life.
Disaster
Every year individuals and communities are being affected by ________________, which disrupts their mental health and well-being.
Disaster
Economic and social development throughout the world is frequently interrupted by natural _________________
Disaster
a serious disruption of the functioning of a community or a society causing widespread human, material, economic or environmental losses which exceed the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own resources. (United Nation International
Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UN-IDSR))
Disaster
sudden ecologic phenomenon of sufficient magnitude to require external assistance (World Health Organization (WHO))
Natural and Man-made
Types of Disaster
Natural Disaster
Type of Disaster
result of natural causes, for example cyclones, earthquakes, tsunamis and tropical cyclones.
Man-made Disaster
Type of Disaster
brought about by human actions, including military conflicts, terrorism, political unrest and industrial accidents
Disaster
Both natural and social factors cause _______________, e.g. flooding might be the result of the combination of deforestation and climate change.
Disaster
All in all, a _____________ is a natural or human-caused occurrence (e.g., hurricane, tornado, flood, tsunami, earthquake, explosion, hazardous materials accident, mass criminal victimization incident, war, transportation accident, fire, terrorist attack, famine, epidemic) that causes human suffering.
Disaster
A _____________ creates a collective need that overwhelms local resources and requires additional assistance.
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
Distractibility
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
Declining Performance
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
Recurrent intrusive recollections
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
Flashbacks, nightmares
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
memory loss
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
reduced attention span
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
decision making difficulties
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
calculation difficulties
Cognitive
General Effect of Disaster to People
confusing trivial with major issues
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
clinging, isolation
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
thrill seeking behaviors
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
re-enactments of the trauma
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
increased substance abuse
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
hyper-vigilance
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
elevated startle reflex
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
insomnia
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
gallows humor
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
gait change
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
ritualistic behavior
Behavioral
General Effect of Disaster to People
unwillingness to leave the scene
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
shock symptoms
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
insomnia
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
loss of appetite
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
headaches
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
muscle weakness
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
elevated vital signs
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
fatigue
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
profuse sweating
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
fine motor tremors
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
chills teeth grinding
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
muscle aches
Physical
General Effect of Disaster to People
dizziness
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
depression, anxiety
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
numbness
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
constricted affect
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
guilty, shame, fear
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
intolerance of fear response
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
global pessimism
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
feeling overwhelmed
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
anticipation of harm to self or others
Affective
General Effect of Disaster to People
irritability
Psychological Illness which may develop
• Disasters may put the victims in a state of despair and shock.
• This traumatic experience disrupts the fully-functioning life of the victims and brings loss for individuals, families and communities.
• Emotional instability, stress reactions, anxiety, trauma and other psychological symptoms are observed commonly after the disaster and other traumatic experiences.
• These psychological effects have a massive impact on the concerned individual and also on communities
Anxiety
• The presence of excessive anxiety and worry about a variety of topics, events, or activities.
Anxiety
• Worry occurs more often than not for at least six months and is clearly excessive.
Anxiety
• The worry is experienced as very challenging to control.
Anxiety
• The worry in both adults and children may easily shift from one topic to another.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) Symptoms
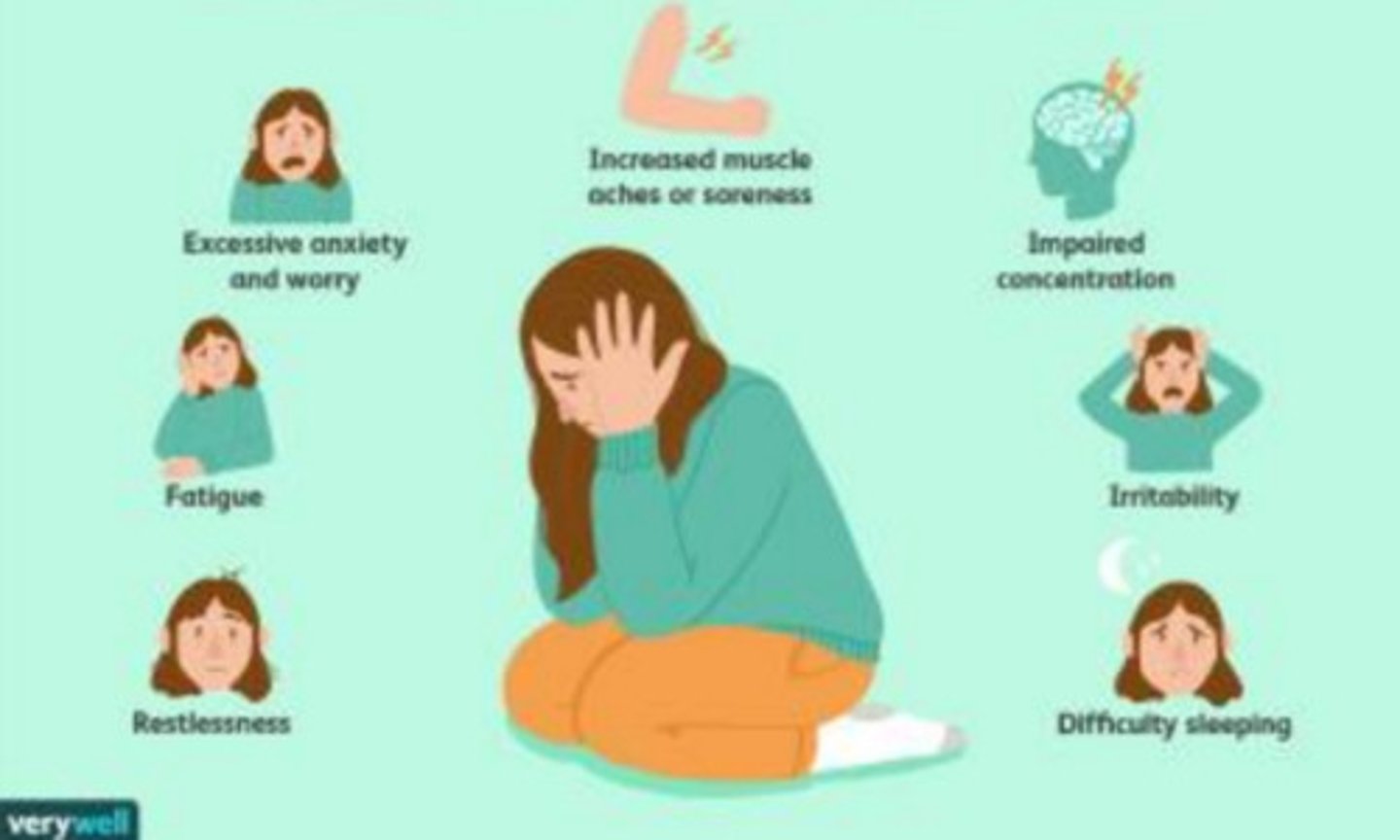
Anxiety
The _______________ and worry are accompanied by at least three of the following physical or cognitive symptoms (In children, only one of these symptoms is necessary for a diagnosis of GAD):
• Edginess or restlessness
• Tiring easily; more fatigued than usual
• Impaired concentration or feeling as though the mind goes blank
• Irritability (which may or may not be observable to others)
• Increased muscle aches or soreness
• Difficulty sleeping (due to trouble falling asleep or staying asleep, restlessness at night, or unsatisfying sleep)
Depression
• Feelings of sadness, low mood, and loss of interest in their usual activities must mark a change from a person's previous level of functioning and have persisted for at least two weeks.
Depression
• These symptoms must cause the individual clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
Signs and Symptoms of Depression

Depression
These feelings must also be accompanied by at least five other common symptoms of depression, including:
• Change in appetite, losing or gaining weight
• Sleeping too much or not sleeping well (insomnia)
• Fatigue and low energy most days
• Feeling worthless, guilty, and hopeless
• An inability to focus and concentrate that may interfere with daily tasks at home, work, or school
• Movements that are unusually slow or agitated (a change which is often noticeable to others)
• Thinking about death and dying; suicidal ideation or suicide attempts
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
psychiatric disorder involving extreme distress and disruption of daily living that happens in relation to exposure of a traumatic event
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
• The DSM-5 outlines PTSD
symptoms into four categories:
• Intrusion symptoms
• Avoidance of thoughts and behaviors
• Negative changes in thoughts and mood
• Changes in arousal and reactivity
• These symptoms are associated with a traumatic event.
PTSD Diagnostic Criteria

Intrusion
Post-traumatic stress disorder
• Reoccurring, involuntary, and intrusive upsetting memories of the event
• Repeated upsetting dreams related to the event
• You experience some type of dissociation (for example, flashbacks) where you feel as though the event is happening again.
• Strong and persistent distress to cues that are either inside or outside of your body that are connected to the event
• Strong bodily reactions (for example, increased heart rate) when reminded of the event
Avoidance
Post-traumatic stress disorder
• You avoid people, places,
conversations, activities, objects, or situations that bring up memories of the event
• You avoid thoughts, feelings, or physical sensations that bring up memories of the event
Negative Changes in Thoughts and Mood
Post-traumatic stress disorder
• You can't remember an important aspect of the event
• Persistent and elevated negative evaluations about yourself, others, or the world (for example, "I am unlovable," or, "The world is an evil place")
• Elevated self-blame or blame of others about the cause or consequence of the event
• A pervasive negative emotional state (for example, shame, anger, or fear)
• Loss of interest in activities that you used to enjoy
• Feeling detached from others
• You can't experience positive emotions (for example, happiness, love, joy)
Changes in Arousal and Reactivity
Post-traumatic stress disorder
• Difficulty concentrating
• Feeling constantly "on guard" or like danger is lurking around every corner (or hypervigilance)
• Heightened startle response
• Impulsive or self-destructive behavior
• Irritability or aggressive behavior
• Problems sleeping
The important role of psychological science in behavior changes and addressing the impacts of climate change
Psychology can help individuals, communities, and nations mitigate and adapt to climate change in many ways:
• Educating and communicating with the public about climate change;
• Preventing and treating mental health problems stemming from climate change;
• Enhancing individual and community resilience in the face of natural disasters;
• Planning for, and adjusting to, migrations and population displacements;
• Facilitating rapid transitions to new forms of energy, transportation, and agriculture
The important role of psychological science in behavior changes and addressing the impacts of climate change
1. Psychology tells us how to educate and communicate with the public about climate change
2. Psychology tells us how to prevent and treat mental health problems stemming from climate change at individual and community levels
3. Psychology tells us how to plan for and adjust to climate-caused migration and instability
Psychology tells us how to educate and communicate with the public about climate change
The important role of psychological science in behavior changes and addressing the impacts of climate change
• Psychological science identifies many of the drivers of climate skepticism and inaction: Climate change impacts are perceived as distant, uncertain, and complex, which can lead to inaction and a desire to uphold established ways of life. Additionally, confronting climate change requires prioritizing long-term wellbeing over short term costs. Psychological science also offers tools to address these challenges.
Psychology tells us how to educate and communicate with the public about climate change
The important role of psychological science in behavior changes and addressing the impacts of climate change
• Information about climate change must be clear and straightforward, repeatedly delivered by trusted messengers, and discussed within communities in order to speak to personal needs and realities.
• We must stress actionable, relevant solutions that foster efficacy and empowerment.
• We must draw on people's need to belong in order to create a shared vision for action and a set of social norms that guide behavior.
Psychology tells us how to prevent and treat mental health problems stemming from climate change at individual and community levels
The important role of psychological science in behavior changes and addressing the impacts of climate change
Individual Level
- Trauma, depression, anxiety, and other mental health issues
Community Level
- Long term economic stress
- Social instability
Psychology tells us how to plan for and adjust to climate-caused migration and instability
The important role of psychological science in behavior changes and addressing the impacts of climate change

Climate Change
_______________________ is the primary challenge of our era.
Urgent action is required, and psychological science can provide answers on how to mitigate and adapt to its consequences
Climate Change
________________ has important implications for mental health. These implications may arise from the physical, social and economic impacts of extreme and acute climatic changes or the psychological distress and anxiety evoked by awareness of the short- and long-term impacts of _____________________