2 Atoms, ions and compounds
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
def relative isotopic mass
the mass of an isotope relative to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
Relative isotopic mass has no units because it’s a ratio of 2 masses.
def relative atomic mass (Ar)
(most elements contain a mixture of isotopes, each with a different isotopic mass) relative atomic mass (Ar) is the weighted mean mass of an atom of an element relative to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
def relative molecular mass (Mr)
the mass of a single molecule on a scale on which the mass of an atom of carbon-12 has a mass of 12 atomic mass units
how is Mr calculated
by adding together the relative atomic mass (Ar) of the atoms in the chemical formula
def isotopes
atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons and different masses
what is the mass of an electron
negligible mass, about 1/1850
def atom
the smallest, electrically neutral particle of an element that can take part in a chemical change
def molecule
the smallest, electrically neutral, particle of an element or compound that can exist on its own
def ion
an atom, or group of atoms, which carries an electric charge
name the diatomic elements
Iodine
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Bromine
Oxygen
Chlorine
Fluorine
what do groups show on the periodic table
the number of electrons in the outer shell
what do periods show on the periodic table
the number of shells
(Ar) how are the percentage abundances of isotopes in a sample of an element typically found
using a mass spectrometer
describe how a mass spectrometer works
a sample is placed in the mass spectrometer
the sample is vaporised and then ionised to form positive ions
the ions are accelerated. Heavier ions move more slowly and are more difficult to deflect than lighter ions, so the ions of each isotope are separated.
the ions are detected on a mass spectrum as a mass-to-charge ratio (m/z). Each ion reaching the detector adds to the signal, so the greater the abundance, the larger the signal.
what are mass spectra produced by
mass spectrometers
what does mass spectra show us
the relative isotopic masses of different elements
and
the abundances of different elements
what can mass spectra be used to work out
the relative atomic masses of different elements
Ar = the weighted mean mass of an atom of an element relative to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
how can you calculate the relative atomic mass (Ar) of a sample using a m/z graph
multiply each relative isotopic mass by its relative isotopic abundance, and add up the results
divide by the sum of the isotopic abundances
what is the avogadro constant
6.022 x10^23 of something
how can you calculate the number of molecules of something when given the mass and compound formula?
calculate the moles
x the moles by the avogadro constant (6.022 x10^23)
how do you get mmol to mol
/1000
how do you get cm^3 to dm^3
/1000
how do you find out the limiting reagent of an equation?
calculate the moles of all reactants then compare how much each reactant needs of the other reactant (ratio)
how do you write an ionic equation
write down the full formula (including state symbols)
identify which compound/element stays in the same state from start to finish - that is the spectator ion. ignore the spectator ion
write down the NON- spectator ions with their charges and state symbols
balance element to element
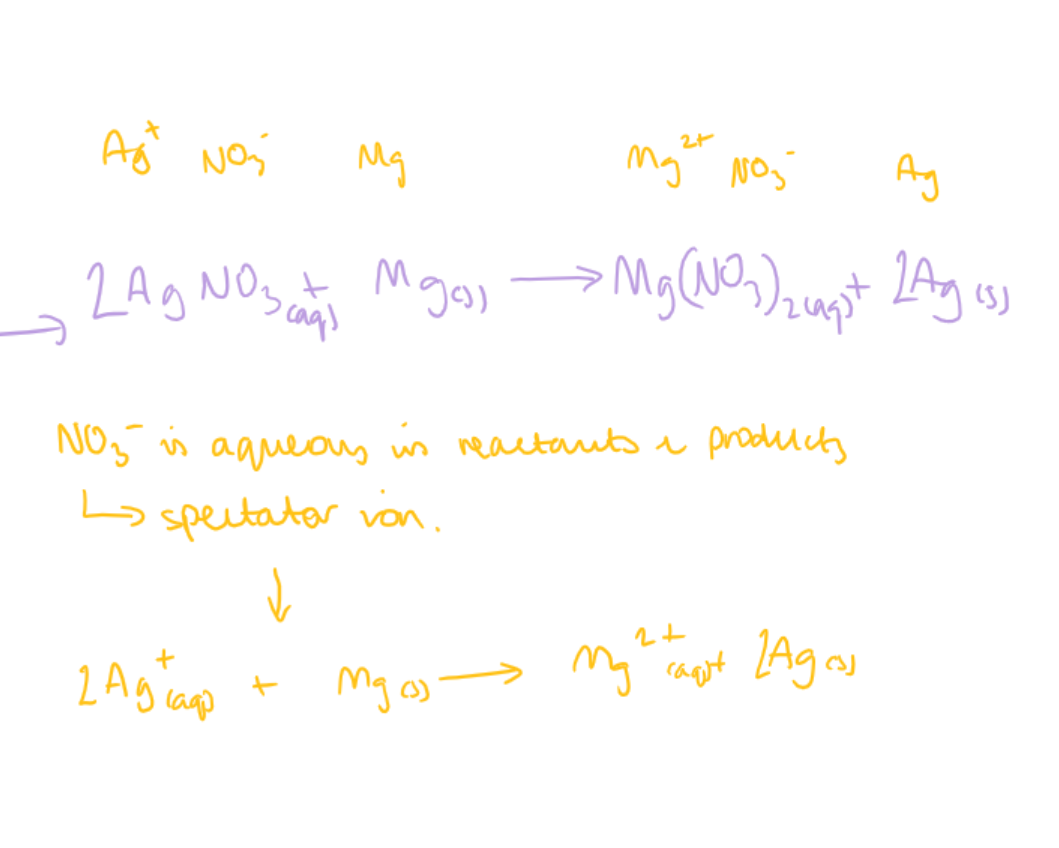
atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
electron
a negatively charged subatomic particle
orbits the nucleus at various energy levels
relative mass is 1/1836
ion
a charged atom or molecule
isotopes
atoms of the same element w the same no. of protons and e- but diff numbers of neutrons
isotopes of an element have diff masses
mass no.
total no. of protons and neutrons in nucleus of atom
mass spectrometry
an instrument which gives accurate info about relative isotopic mass and relative abundance of isotopes
neutron
neutral subatomic particle found in nucleus of atom
relative mass is 1
proton
positively charged subatomic particle found in nucleus of atom
relative mass is 1
relative abundance
amount of one substance compared w another
relative atomic mass
the mass of an atom of an isotope compared w 1/12th mass of an atom of carbon-12
relative formula mass
mass of the formula unit of a compound w a giant structure
e.g. NaCl has a relative formula mass of 58.44gmol-1
relative molecular mass (Mr)
mass of a simple molecule
relative atomic mass =
Σ (%abundance x mass)/100
what r the stages of mass spectroscopy
ionisation (e- gun knocks 1e- off)
acceleration of ions (all ions same speed)
drift zone (speed measured)
detection
how does mass spectroscopy work
atom/molecules are ionised to form 1+ ions
ions are accelerated in an electric field so they all have the same kinetic energy
ion drift: ions enter flight tube
ions with diff masses have a diff time of flight
lighter ions travel faster so take less time to reach detector
detector is a negatively charged plate, current produced when ions hit plate, more ions hitting detector the bigger the current
what is Avogadro constant
6.022 ×10²³ of something
number of particles in each mole of carbon-12
how do u calculate the no. of molecules of something
moles x 6.022 ×10²³