CHMA 2002 - Module 2D: Protein folding
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
The folded structure of a protein is 3d and called it's
native conformation
two kinds of folding at the secondary level are called
alpha helix and beta sheet
The primary structure has influence on later folding because of the the
non-covalent interactions in the primary structure
-H bonding
- hydrophobic interaction
-ionic interactions )salt bridge, ion pairing)
-Disulphide bonding (this is covalent)
hydrophobic interactions are
lipophilic
Alpha helix coils are formed by
intramolecular hydrogen bonds formed by the Hydrogen from the amino to the oxygen from the carboxyl
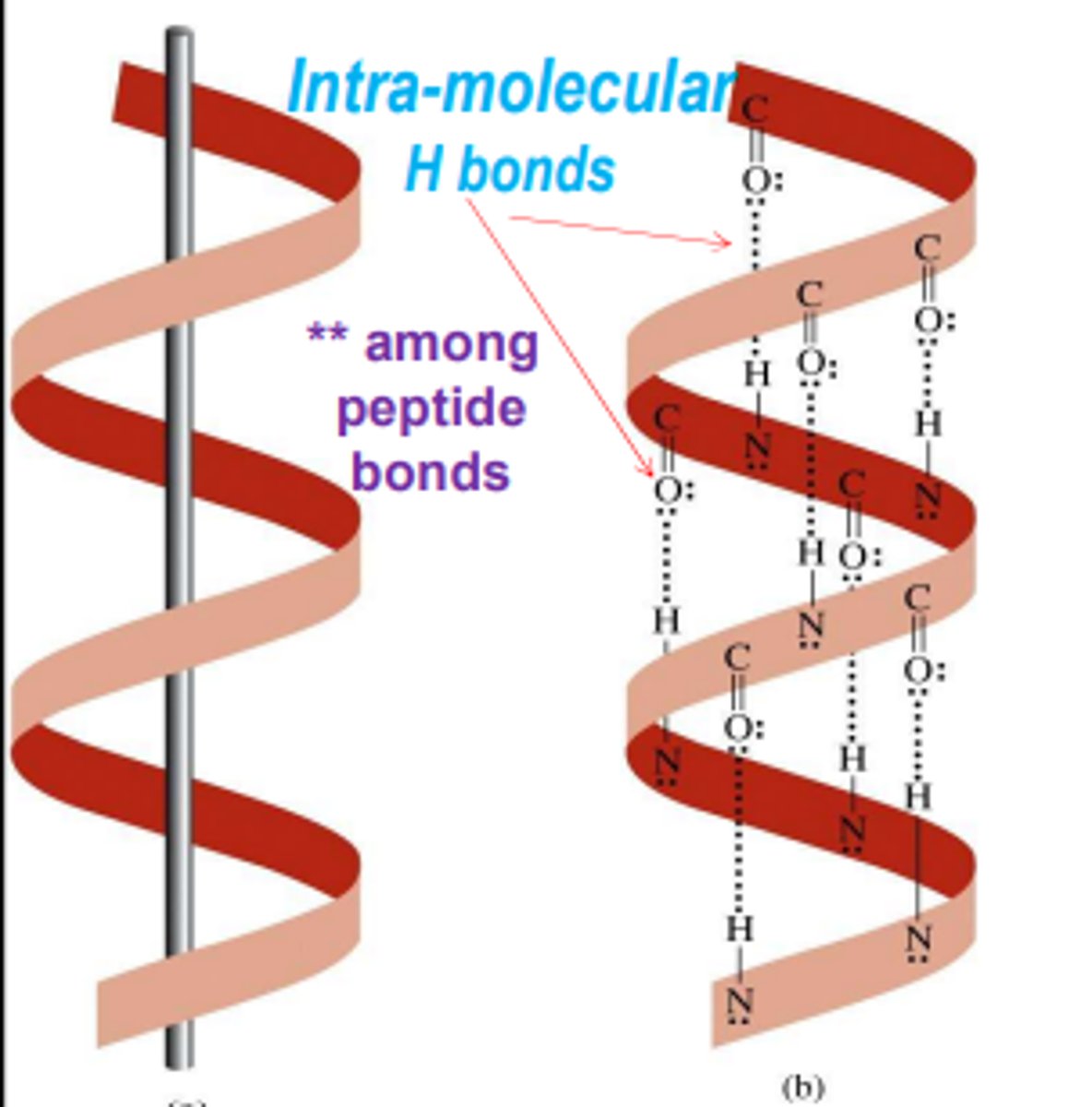
examples of alpha helix proteins
collagen and alpha keratin
collagen is a super helical protein, meaning it has a
triple helix
the three helixes of collagen are joined by
inter molecular hydrogen bonds
alpha keratin is a
coiled coil
how is alpha keratin fromed
two alpha helices make a dimer, which combine to make protofilaments, two of which combine to make protofibrils, four of which combine to make microfibrils which constitute a hair.
super secondary structures are also called
structural motifs
structural motifs are in what level of protein folding
secondary
a tertiary structure is a combination of several
structural motifs to from a compact unit for a specific biological function (a domain)
the shape of GFP is a
beta barrel
quaternary structures contain more than one
subunit (multiple tertiary structures)
Homotypic proteins are
quaternary proteins containing identical subunits
Heterotypic proteins are
quaternary proteins containing different subunits
The hydropathy index measures the
hydrophobicity of a protein (higher numbers are more hydrophobic, lower numbers are least hydrophobic and more polar)
The hydropathy can also be used to find
membrane-bound domains of proteins
the highest energy level of proteins during folding is
primary, decreasing in energy successively through to the tertiary and quaternary structure
Some folding processes require assistance from
molecular chaperones
molecular chaperones help with
-folding
-protects proteins from unfolding or misfolding
-protects from heat (HSP)
Protein unfolding is the loss of
biological activity
Protein denaturation occurs when
-there is a change in pH or heat
-dehydration
-other stressors and detergents
Proteopathy diseases are those which are caused due to
protein misfolding
an example of a proteopathic disease
Alzheimer's