6. BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What defenses protect the central nervous system (CNS)?
The CNS is protected by the bony skull, the blood–brain barrier, and phagocytic cells like microglia and macrophages. It has low MHC expression and reduced complement activity.
What types of meningitis exist?
Meningitis can be bacterial, viral (aseptic), or fungal.
Why is bacterial meningitis especially dangerous in newborns?
Newborns represent only ~10% of cases but account for ~50% of deaths. Their underdeveloped blood–brain barrier allows easier pathogen entry.
How do bacteria usually enter the CNS to cause meningitis?
Most CNS infections like meningitis arise from bacteremia or distal infections. Coinfections or recent viral upper respiratory infections facilitate entry.
Do all forms of meningitis cause similar symptoms?
Yes, bacterial, viral, and fungal meningitis present with similar clinical symptoms. Severity differx.
Which bacteria most commonly cause meningitis in adults?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common cause of community-acquired meningitis.
Which bacteria most commonly cause meningitis in children?
Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) and Neisseria meningitidis are the primary causes.
Which bacteria most commonly cause meningitis in newborns?
Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Streptococcus) and Escherichia coli are most common.
How does a bacterial capsule increase meningitis risk? How does bacteremia relate to risk?
Capsules increase virulence by inhibiting phagocytosis. Risk of developing this disease is directly related to the magnitude and duration of bacteremia
Describe mortality rates with treatment for bacterial meningitis?
10-15% with treatment. higher if cause is S. pneumoniae, which causes up to 50% of cases.
What is the basic pathogenesis of meningitis?
Bacteria cross the blood–brain barrier and rapidly multiply due to low immune defenses. Neutrophil influx causes inflammation and swelling of the meninges. Low levels of IgG, IgA, MHC, or complement.
What is the classic triad of meningitis symptoms?
Fever, headache, and stiff neck.
What additional symptoms may occur in meningitis?
Patients may have vomiting, seizures, photophobia(sensitivity to light), and petechiae. Petechiae do not occur with Streptococcus pneumoniae.
How does meningitis present in infants?
Infants show weak sucking, lethargy, temperature instability, vomiting, and diarrhea.
How is meningitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis is confirmed by lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
How do bacterial and viral meningitis differ in CSF findings?
Bacterial meningitis shows bacteria with gram stain, increased neutrophils, and elevated C-reactive protein. Viral meningitis shows no bacteria with gram stain and increased lymphocytes.
What are the defining features of Neisseria meningitidis?
It is a Gram-negative, kidney bean–shaped diplococcus. It causes severe acute and epidemic meningitis.
Which serotypes of Neisseria meningitidis are most common in the U.S.?
Serotypes B, C, and Y are most common. A and W-135 are less common.
What virulence factors does Neisseria meningitidis possess?
It has a capsule and produces IgA protease (breaks down igA antibodies).
How is Neisseria meningitidis differentiated from N. gonorrhoeae?
N. meningitidis can ferment maltose. N. gonorrhoeae cannot.
What are the key features of Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib)?
It is a Gram-negative rod and rarely infects individuals over age 5. It causes most invasive H. influenzae disease.
What virulence factors does Hib possess?
Hib has a capsule, IgA protease, and some strains produce β-lactamase. These increase invasiveness and antibiotic resistance.
What are the characteristics of Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS)?
It is a Gram-positive coccus in chains. It commonly causes postpartum infections (meningitis, pneumonia, and sepsis)
How is Group B Streptococcus transmitted to newborns?
Transmission usually occurs during vaginal delivery. It can also occur in utero.
How is bacterial meningitis treated and prevented?
Treatment involves appropriate antibiotics. Prevention includes conjugate vaccines for Hib, S. pneumoniae, and N. meningitidis.
What causes tetanus?
Tetanus is caused by Clostridium tetani. Toxin blocks acetylcholine signal at the inhibitory neuron so muscles don’t receive the signal to relax, only receiving the signal to contract. It is associated with wound infections affecting neuromuscular function.
How does Clostridium tetani cause disease?
The bacteria remain at the wound site while the toxin enters the bloodstream. The toxin causes irreversible synaptic damage.
Who is most at risk for tetanus-related death?
Individuals over 60 account for most deaths. Case fatality rates are 10–15%.
What are the key characteristics of Clostridium tetani?
It is a Gram-positive, anaerobic, spore-forming rod. Its virulence factor is tetanospasmin toxin.
Why are puncture wounds high-risk for tetanus?
They create anaerobic conditions ideal for spore germination. Spores commonly originate from soil.
How does tetanospasmin cause spastic paralysis?
The toxin blocks inhibitory neurotransmitter release. Muscles receive continuous contraction signals.
What are the clinical manifestations of tetanus?
Muscle spasms begin in the jaw, neck, arms, and back. They may progress to the diaphragm, causing death.
Why is cardiac muscle unaffected in tetanus?
Cardiac muscle has different electrical properties. It does not rely on the affected synaptic pathways.
How is tetanus treated and prevented?
Treatment includes tetanus immunoglobulin TIG or antitoxin TAT. Prevention is achieved through toxoid vaccines given every 5–10 years.
What are the defining characteristics of Clostridium botulinum?
It is a Gram-positive, anaerobic, endospore-forming rod. Types A, B, E, and rarely F cause human disease.
What is botulism?
Botulism is a neuroparalytic disease caused by botulinum toxin. It can occur as food intoxication or infant food infection.
How does foodborne botulism occur?
Spores survive food preparation and germinate in anaerobic containers like home-canned foods. Heat kills bacteria but not the toxin.
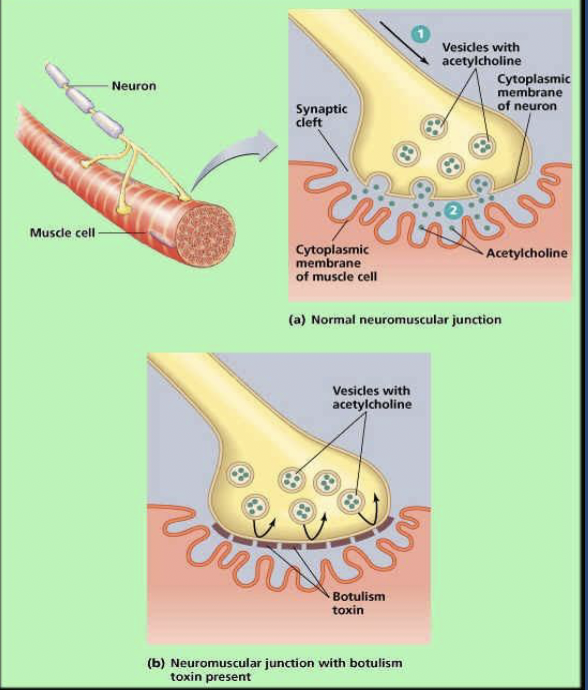
How does botulinum toxin affect neuromuscular transmission?
It prevents acetylcholine release at motor neurons. This causes flaccid paralysis.
Why is botulinum toxin especially dangerous?
It is the most potent bacterial toxin known. Even small amounts can be fatal.
What are common symptoms of botulism?
Symptoms include double vision, drooping eyelids, difficulty swallowing, slurred speech, and muscle weakness. Weakness descends through the body.
How is adult botulism treated?
Treatment includes trivalent ABE antitoxin. Medications like Guanidine hydrochloride or 4-aminopyridine may increase acetylcholine release.
What is infant botulism?
It is a food infection caused by ingested spores that germinate in the gut. It can be fatal if untreated.
What are symptoms of infant botulism?
Constipation, lethargy, weak sucking, and poor muscle tone occur. This condition is known as floppy baby syndrome.
How is infant botulism treated?
Treatment involves removing organisms via enemas or stomach pumping. Antibiotics and antitoxin are not used.