APES AP TEST REVIEW 1, 2, 3....6
1/247
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
248 Terms
Null Hypothesis
Predicts no relationship between two phenomena, no difference among groups.
Independent Variable
What will be changed?
Dependant Variable
What will be measured?
Controlled Variables/ Constants
What remains the same.
Scientific Theory
A widely accepted explanation for something
Tragedy of the Commons
The idea or belief that when individuals act in their own interest, they deplete a shared resource.
System
A set of components that function and act in some regular way.
Feedback loops
any process that increases or decreases a change to a system.
Positive Feedback loop
Where an initial change leads to additional change in the same direction EX: CO2 increases —> warmer atmosphere -→ warmer ocean—→less CO2 uptake. (amplifying loop)
Negative Feedback Loop
Leads to a decrease or stabilization of a factor in a system. Ex: Body temperature, regulation: Body temp falls—> blood vessels constrict so that heat is conserved, and shivering generates heat to warm the body—> Normal body temperature
Ecology
The study of connections in nature between biotic and abiotic components.
Organism
one living being
Population
Many individuals of the same species
Community
Many different individuals of species
Ecosystem
Both the biotic and abiotic components in a habitat
Biosphere
All portions of Earth where life exists.
Niche
A species role in its environment
-Preferred habitat
-Position in the food web
-Mating and eating behaviors
Commensalism
One organism benefits from the relationship, but the other is not affected.
Mutualism
Both organisms benefit from the relationship
Resource Partitioning
Species avoid competition by dividing use of resources
Competitive Exclusion Principle
Two Species competing for the same limiting resource cannot exist
Fundamental Niche
Everywhere that population could live
Realized niche
The actual niche where that population lived due to competition.
Biome
The plants and animals that are found in a particular region
Habitat
more specific; an area that an organism requires within a biome.
Productivity of a Biome
Determined by the amount of biomass or living plant material produced throughphotosynthesis.
Temperate
Temperate
Occurs between poles and tropics; characterized by lack of extremes and seasonal changes (winter/summer or wet/dry seasons) means mild or moderate.
Aquatic Biomes
Characterized by salinity, depth, and water flow. two types: freshwater and marine.
Freshwater
-streams, rivers, ponds, lakes, wetlands
-vital source of drinking water
-low salinity
Marine
Include oceans, coral reefs, marshland, estuaries
-algae supplies large portions of earths oxygen
Littoral Zone
the top, near-shore layer of a lake. This zone is shallow with plentiful sunlight and nutrient inputs from the surrounding land. As a result, this zone supports a wide variety of plants and animals.
Limnetic Zone
Zone of open water, where most photosynthesis takes place.
Profundal Zone
a lake’s deep, open-water layer, which is too dark for photosynthesis. The water in this zone is cooler and contains less dissolved oxygen than the shallower zones. This zone supports fish adapted to these cooler waters.
Benthic Zone
the soil and soil organisms that live at the bottom of a lake. This zone is inhabited mostly by decomposers and other organisms that feed on dead and decaying material, and can withstand a low-oxygen environment.
Intertidal Zone
Open ocean-narrow band of coastline between high tide and low tide.
Photic Zone
Open Ocean-Upper layer of ocean that light penetrates and photosynthesis occurs
Aphotic Zone
Open Ocean-Deep layer lacks enough sunlight for photosynthesis.
Tropical Rainforest
-Found closer to the equator
-Warmer temps and abundant rainfall
-Highly productive because it can support many types of food chains
-hurt by deforestation
Temperate Rainforest
Along western coasts of North America and South America as well as Southwestern Asia
-High precipitation in winter and less in summer, temperature gets warmer in july +August
-Productive, but not as much as tropical rainforests because of logging
Temperate Seasonal Forest
-Northern Hemisphere
-High rainfall in spring and summer and warm temps overall
-Productive because of rainfall + moderate climate
-Human impacts: deforestation, invasive species, and wildfires
Taiga/Boreal Forest
-Alaska, Canada, Scandanavia + Siberia
-Very cold in winter and slightly warmer in Summer
-Not very productive because of extreme cold
-Human Impact: Deforestation and logging
Desert
-Sahara, Southwest America, and Australia
-Very little rain fall and high temperature.
-Not very productive because of extreme heat
-Human impact: plants get damaged by off road vehicles
-fracking for oil
Savanna
-Africa, South America, Australia, Asia and Madagascar
-Wet and dry, 10-13 inches of rain per year. warmer weather
-Productive because it has up to 80% of worlds agricultural land.
-Human Impact: Overgrazing from livestock, logging, and introduction of non native plant species.
Shrubland/Chaparral
Mediterranean climate, California, Southwest Australia, and South Africa
-long hot dry summers, and mild rainy winters
-mildly productive + highly seasonal
-Human impact: urbanization
Tundra
-Antartica, Siberia, Canada
-Very cold temps and low precipitation all year
-Not very productive due to cold
Human impact: oil exploration
Streams/River
Freshwater
-0.001% of Earths water
-Very low salinity
-Depth Zones: Littoral, Limnetic, Profundal, Benthic
-High productivity
-Human impact: pollution
Ponds/FW Lakes
-minimal to no flow
Depth Zones: Littoral, Limnetic +Profundal
-Human impact: Over extraction of Water +Eutrophication
low salinity
Eutrophication
the gradual increase in the concentration of phosphorus, nitrogen, and other plant nutrients in an aging aquatic ecosystem, such as a lake. This process leads to increased growth of microorganisms, which can deplete the oxygen in the water
Wetland (Swamp, marsh, bog)
-low salinity
-found in tropical and subtropical regions
-Human impact: construction and removal of vegetation.
These biomes typically have shallow waters with a profusion of plant life
Due to the low depth and high concentration of nutrients, this is a very productive biome class
Have trees and larger flora
Open Ocean
70% of Earth’s surface
-Low productivity due to the low density of organisms in this region
=-Human impacts: overfishing, introduction of invasive species and pollution
Salt Marsh/Estuary
Marine
-Where fresh and saltwater meet
-high productivity because of species diversity
human impacts: pollution, overfishing and climate change
Coral reefs
Warm, shallow water
Has extremely high biodiversity and productivity
Alongside estuaries, the most productive
Intertidal Zone
Between tides
As the tides come and go, this area transitions from being submerged to above the surface
Extreme conditions for the organisms living here
-Shelled(harder organisms live closer to the surface and soft bodies organisms live closer to the bottom
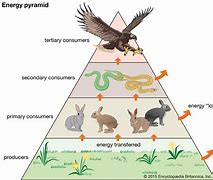
10% rule
only about 10% of the energy available at one trophic level is transferred to the next trophic level
Ecosystem Components
Organism—> Species—> Population—>Community—>Ecosystem—>Biosphere
Photosynthesis
CO2+H20=C6HO(glucose)+O2(oxygen)
Aerobic Respiration
WITH OXYGEN
—complete oxidation of glucose
-end products are CO2 and Water
-occurs in plant and animal cells
-Lot of energy liberated (produced) (36 ATP)
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (ATP)
Anaerobic respiration
NO OXYGEN
-Incomplete oxidation of glucose
-end products are ethyl alcohol and lactic acid
-small amount of energy created (2 ATP)
-occurs in anaerobic bacteria and human muscle cells
C6 H12 06—>2C2 H5 OH + 2 CO2 +56Kcal
Chemosynthesis
no light, so microbes use chemicals in vent water to produce energy,
are the base for an entire food chain of animals
Biogeochemical Cycles
natural processes that involve the flow of nutrients through ecosystems.
Big 6: carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Sulfur, and Phosphorus
Carbon Cycle
forms-organic molecules, cellular structures, proteins and energy storage
most important element in living things, making up 20% of total body weight
Carbon in abiotic environments
-carbon dioxide in the atmosphere-CO2
-HCO3 dissolved in water
-calcium carbonate in rocks like limestone and coral CaCO3
Deposits of coal, petroleum, and natural gas from fossilized organisms
Humus
dead organic matter
Carbon enters the biotic world through
photosynthesis and chemosynthesis
Carbon returns to the atmosphere by..
cellular respiration(opposite of photosynthesis)
-burning, decay
-if carbon present=CO2
-if not=methane(CH4)
Which places store carbon?
Biomass, atmosphere, soil, fossil fuels, + deep ocean settlements
Rapid Cycling of Carbon
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are processes that drive the carbon cycle fast
( ) Water releases carbon back into the atmosphere
Warm
Slow cycling of Carbon
Sedimentation and Burial
Biome that sequesters the largest amount of carbon?
Tropical forest
Anthropogenic disruptions to the Carbon cycle
Ocean acidification, large scale deforestation, burning fossil fuels, burning biomass, and making cement.
Ocean acidification affecting the Carbon cycle
more carbon in the atmosphere due to humans, means more CO2 dissolving into the ocean decreasing the ph. of water
Raising cows/animals affecting the carbon cycle
bacteria in rumen(cows stomach) converts food into a product that can be digested by the animal. This process enteric fermentation produces methane that is exhaled by the animal.
Making cement +affect on carbon cycle
to produce cement limestone and other clay like materials are heated in a kils at 1400 degrees Celsius using a lot of coal. This goes back to burning fossil fuels which releases sequestered carbon during combustion.
Nitrogen Cycle
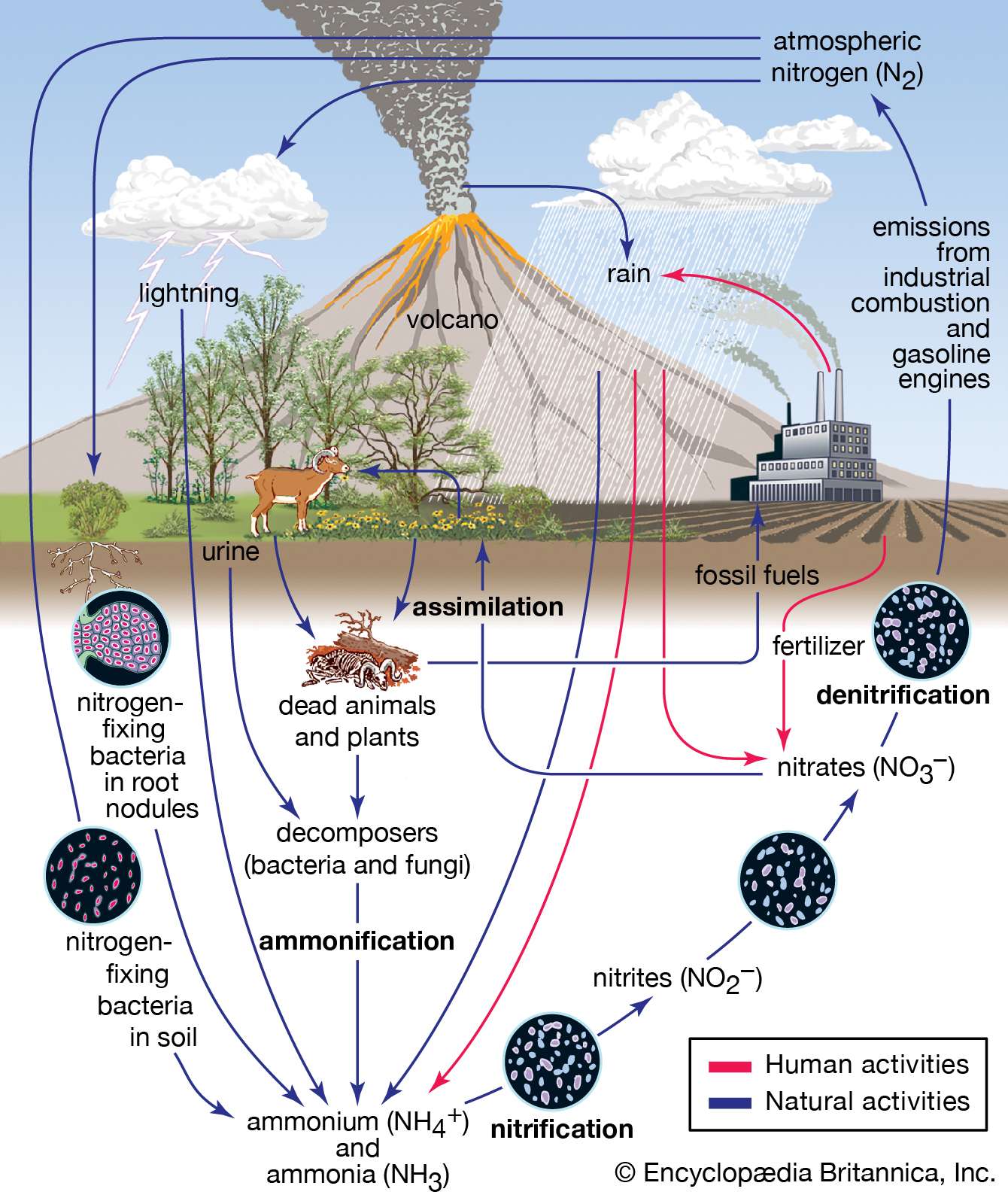
Steps in Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen Fixation—>Nitrification—>Assimilation—>Ammonification—>Denitrification
Nitrogen Fixation
nitrogen fixing bacteria transforms atmospheric nitrogen into “fixed” nitrogen/ammonia/nitrate that can enter soil with rainfall.
Nitrification
-converts ammonia/ammonium to nitrates/nitrites. This allows the nitrogen to be absorbed by plants.
done by bacteria
Assimilation
Plant roots assimilate nitrates into tissues, while animals assimilate nitrogen by eating the plants
Ammonification
Plant or animal dies, and through waste or decomposition, the nitrogen in tissues is decomposed by fungi and bacteria. Then, the nitrogen is released into the ecosystem/soil as ammonia.
Denitrification
Converts nitrates + ammonia into nitrogen gas, removing nitrogen from soil and returning it to the atmosphere.
Anthropogenic affects on the Nitrogen Cycle
Burn fuels at high temperatures=releases NO2=acid rain. Commercial fertilizers + livestock waste, release N stored in plants and soils as gaseous compounds through deforestation. More Nitrogen in aquatic systems from runoff= eutrophication.
Functions of Phosphorus
-essential nutrient for plants and animals- building blocks of DNA, nucleic acids, builds strong bones, maintains energy and blood ph.
Phosphorus cycle
-no gas phase
-VERY slow
-cycles through geological processes.
Processes of the Phosphorus cycle
P is slowly released from rock or soil through weathering
quiclky taken up by plants
movement through food web
break down of organic materials by decomposers, p is returned to the soil
burial in ocean sediments
Phosphorus is an
limiting resource
Human impacts on phosphorus cycle
fertilizers runoff into aquatic systems leading to algal blooms + dead zones
Sulfur cycle
-stored in underground rocks minerals and soil
-plants take up sulfur as sulfate cycles through food web
-enters atmosphere from volcanoes
-H2S organic material in swamps and bogs
Sulfur cycle human impact
released form burning fossil fuels=acid rain
Watershed/Drainage Basin
The land area that delivers runoff, sediment and any dissolved substances to a stream
Aquifer
Underground caverns and porous layers of sand, gravel, or bedrock through which groundwater flows
Unconfined Aquifer
permeable water table
Confined Aquifer
bounded above and below by less permeable beds of rock where the water is confined under pressure.
Artesian Well
Pressure from the confined aquifer pushes water up at a location without a pump
water table
the level below with which the ground is saturated with water
Drought-Flood Cycle
When it rains the water is not absorbed into the compacted earth (earth compacts when trees/roots are removed) and runs off creating a flood. When it stops, the water that was not absorbed into the compacted earth, evaporates and there is none left causing a drought.
First Law of Thermodynamics
also known as the law of conservation of energy, states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to another
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The entropy of any natural and spontaneous process will either increase or remain constant. EX: heat moves from a hot body to a cold body.
Pyramid of Energy Shows
-flow of energy through trophic levels
-90/ of energy is lost at each trophic level—>only 10% goes through