1) Lake Morphology
1/26
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
what is lake morphology?
physical shape of lakes
what is morphometry?
measurement of the shape of lakes
what is the most common lake morphology?
glacial
characteristics of glacial lakes
glacier scoured the ground, creating a depression that water filled
characteristics of riverine lakes
lakes created by movement of rivers
erosion or flowing water
meandering stream creates oxbow lake
characteristics of tectonic lakes
elongated shape
tectonic movement causes a depression where the water pools
characteristics of coastal lakes
may have a mixture of saline/brackish water
characteristics of volcanic lakes
may be high elevation
may create a dam in a river valley
low productivity because of elevation (cold/less oxygen)
what are the morphometric parameters
surface area, max fetch, length of shoreline, volume, max depth, mean depth
what does surface area of lake influence?
sunlight entering water column
thermal stratification
evaporation from lakes surface
gas exchange
number of species present and length of food-chain
what is maximum fetch? what does it influence?
longest stretch wind can blow
effect of wind on lake
wave height
shoreline disturbance
thermal stratification
what does length of shoreline influence?
shoreline development index
what does volume influence?
how much water and solutes are present
how long water stays in the lake (retention time)
sediment-water interaction
what does maximum depth influence? example?
how much light gets into the lake, in the bottom
shallow may allow some water plants at the bottom, deep may only allow phytoplankton on the surface
What is the shoreline development index?
closer index is to 1 = closer the lake is to perfect circle
DL = L/ (2*sqrt(pi*A))
A = area (may include islands in area of the lake)
L = perimeter (not usually including islands within lake)
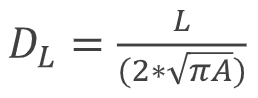
what is the littoral zone?
shallow shoreward region of a lake (less than 6m deep)
light penetration to the bottom and occupied by rooted macrophytes
may not be a uniform area around the lake
steep slope = small littoral area
what is pelagic zone?
light does not reach bottom of the lake here
what is the photic zone?
depth that light reaches in lake
what is the aphotic zone? important?
no light penetrates
no primary producers
what is the thermocline
biggest temp diff vertically, fastest change as you move down
how temp varies from surface to bottom of lake
what is important about fetch?
depends on wind direction to be which shoreline gets most affected
what is a hypsographic curve?
depth area curve
graphs used to provide visual representation of relationship btwn SA of lake basin and depth
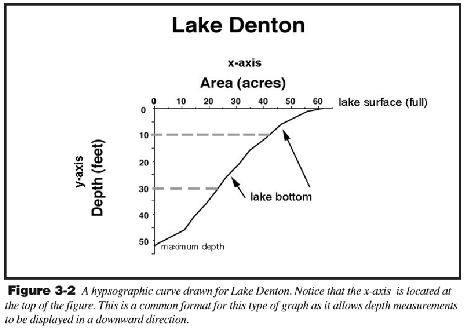
how many acres at A) 30 ft depth, B) 5 ft, C) 40 ft?
A) 25 acres
B) 50 acres
C) 12 acres
why is relative percentage of depth and SA helpful?
to compare different lakes with varying SA and depth
why are some lakes more susceptible to acidification
local emissions
mineral composition: limestones can neutralize acid
volume/area: large flat lake can dilute more than small deep lake
catchment/basin: what drains into the lake
explain fish assemblages
need to have low trophic levels to support the larger fish
larger fish require more oxygen and cooler water deeper down have more oxygen to support the big fish