American Pageant Chapter 6
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Huguenots
French Protestant dissenters, the Huguenots were granted limited toleration under the Edict of Nantes; after King Louis XIV outlawed Protestantism in 1685, many Huguenots fled elsewhere, including to British North America

Battle of Québec
British victory in Montreal 1759-60. The last time the French flag flew in Canada.

Coureurs de bois
Translated as "runners of the woods," they were unregulated French fur-trappers.

Acadians
French residents of eastern Canada many of whom were uprooted by the British in 1755 and scattered as far south as Louisiana, where their descendants became known as "Cajuns"
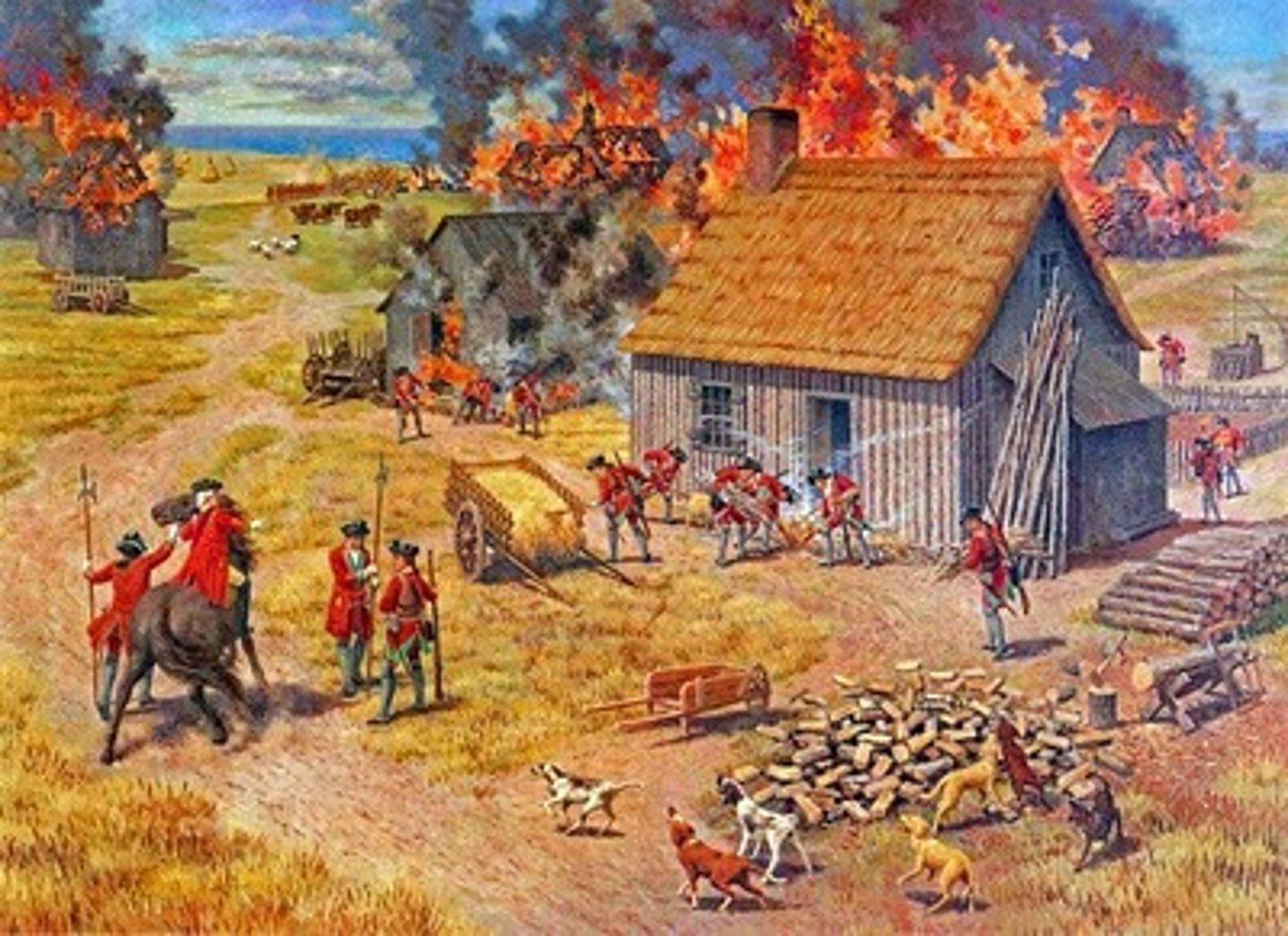

Pontiac's uprising
Ottawa Chief who united Indian tribes and French trappers who had stayed in the frontier against the British - killing up to two-thousand British colonists.
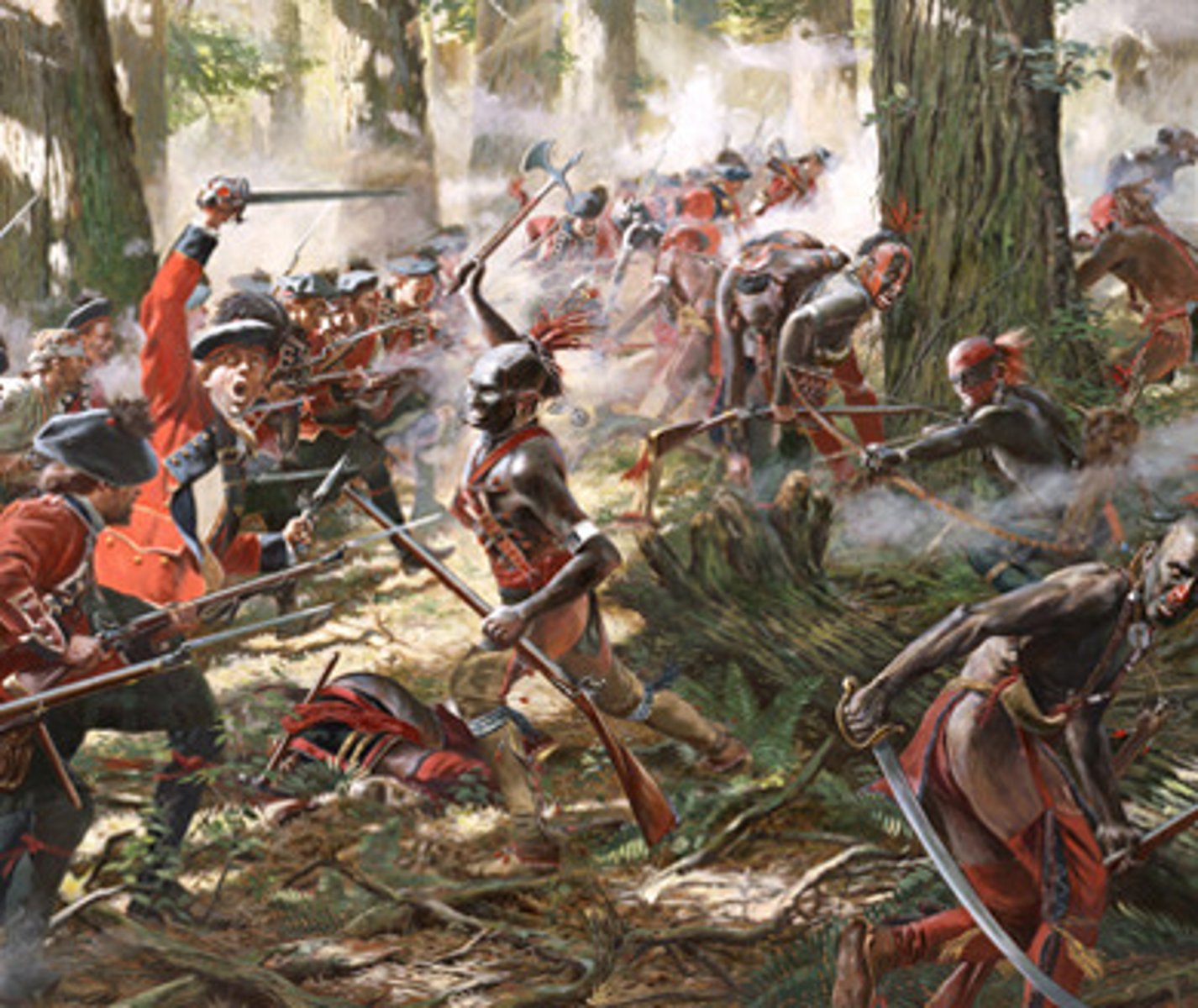

Voyageurs
French fur-trappers, more regulated than the "coureurs de bois."

French and Indian War (Seven Years' War)
(1754-1763) Nine-year war between the British and the French in North America; it resulted in the expulsion of the French from the North American mainland.
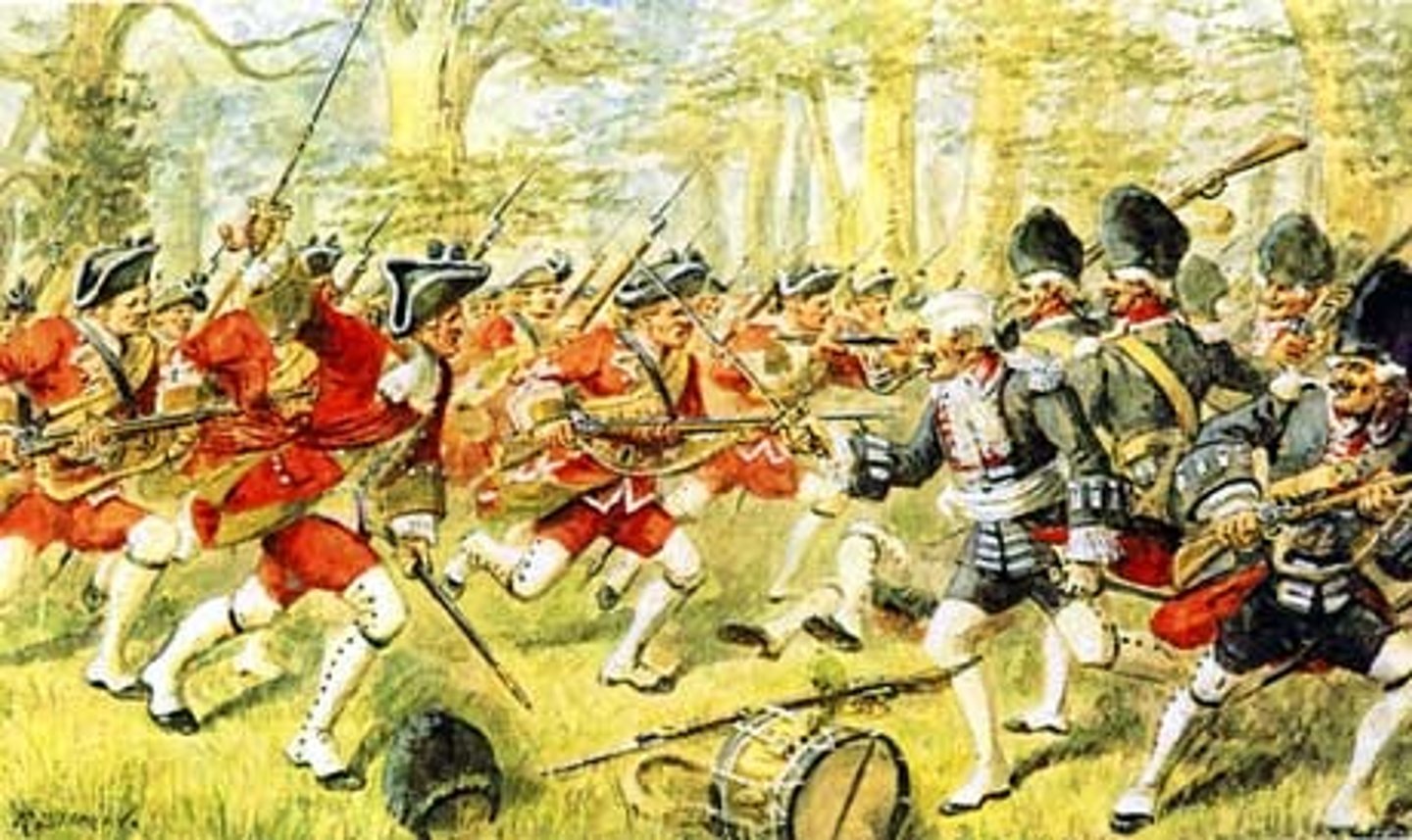

King William's War
(1689-1697) First conflict between French settlers and British (American) colonists.
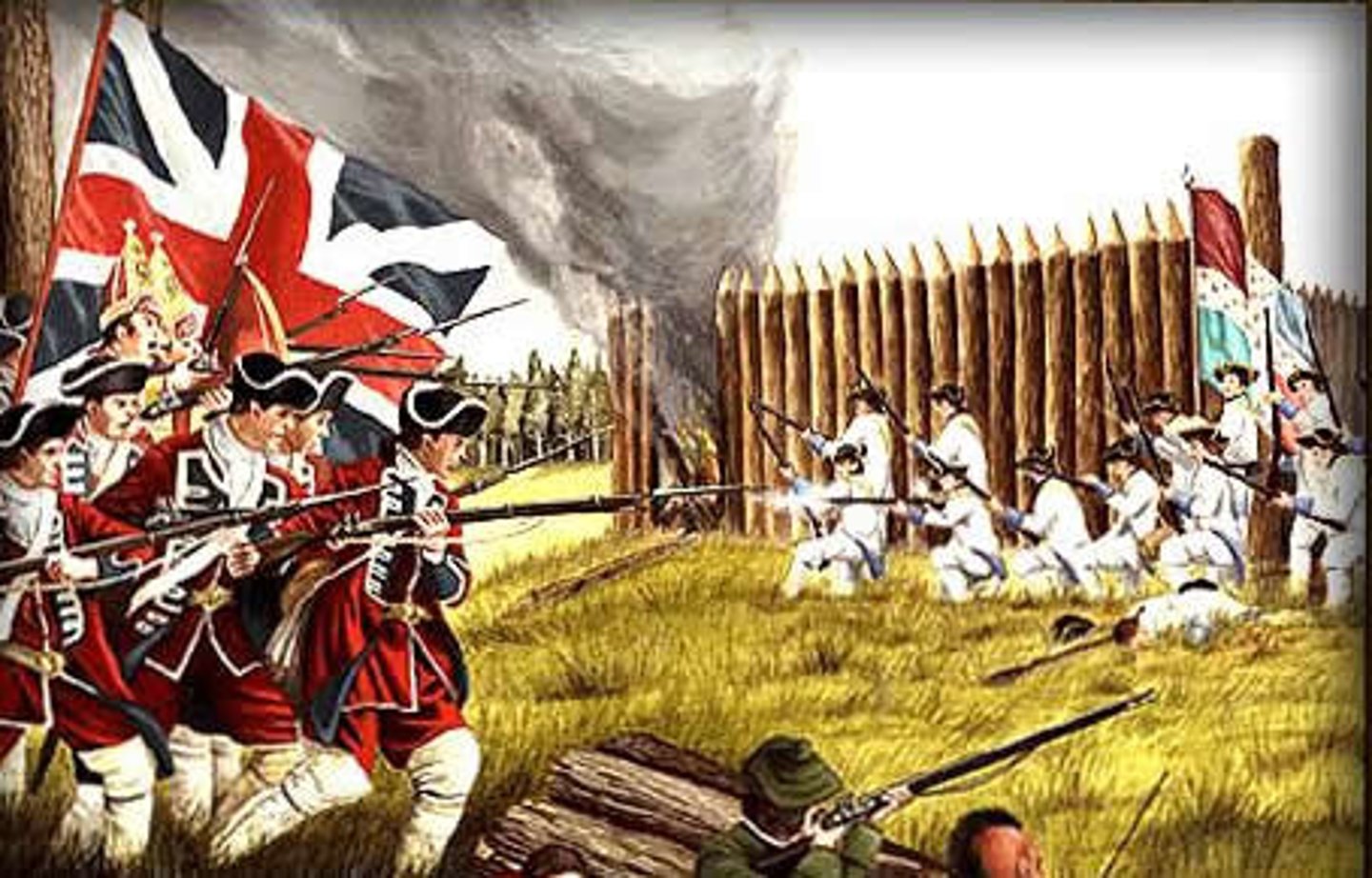

Queen Anne's War
(1702-1713) Second in a series of conflicts between the French settlers and British (American) colonists.
Albany Plan of Union
Intercolonial congress summoned by the British government to foster greater colonial unity and assure Iroquois support in the escalating war against the French.

Louis XIV
long reigning French monarch who took a deep interest in overseas colonization, sending French explorers throughout the New World who established outposts in present-day Canada and Louisiana; he brought France to global superiority and Louisiana was named after him.

Samuel de Champlain
"Father of New France" - Led the Huron Indians in a battle against their enemies (and British allies), the Iroquois.

Edward Braddock
British major-general in America during the French & Indian War who blundered through the forest, being beaten and killed by a small French and Indian force.

William Pitt
British "Organizer of Victory" decided to focus British resources on Canada and the Ohio River Valley rather than the West Indies.

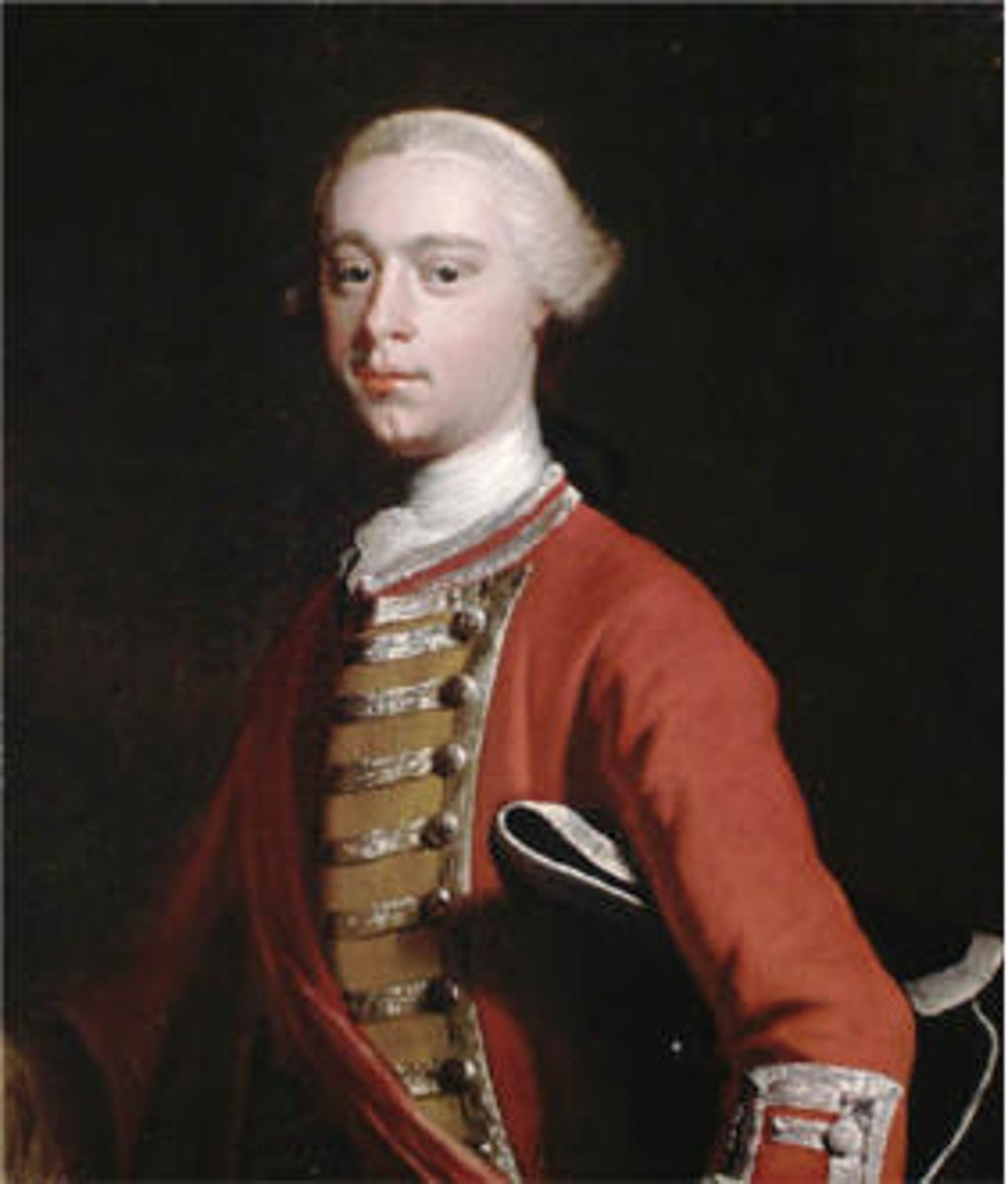
James Wolfe
Young British commander who was appointed by William Pitt to command in the Battle of Québec; although fatally wounded, his skillful strategies resulted in British victory

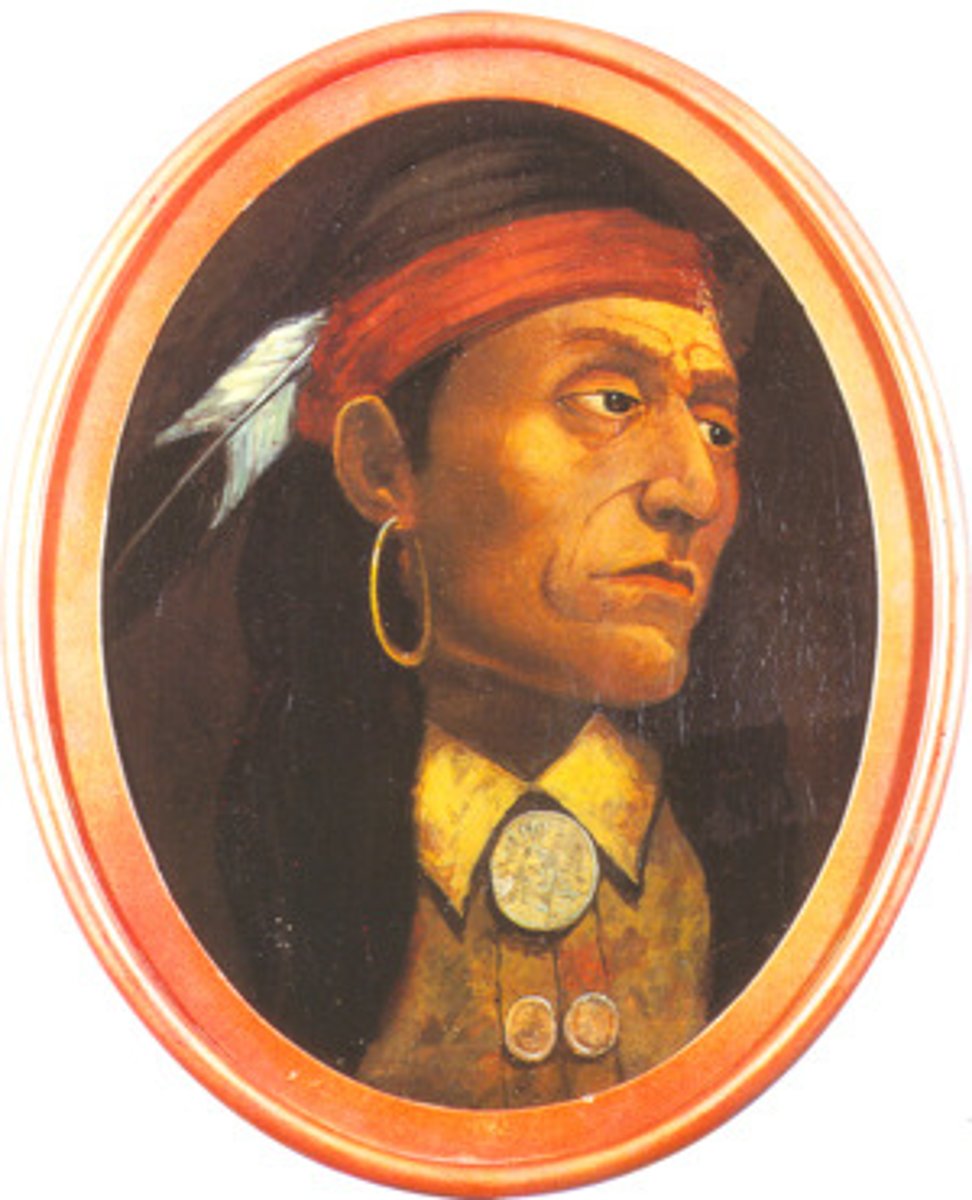
Pontiac
Ottawa chief who led an uprising trying to drive the British out of the Ohio Country.

New France
France's colonies in North America. Occupied present-day Eastern Canada, the American Midwest, and the Mississippi River Valley.

Beaver
Animal whose fur which was in high demand in Europe.

Robert de la Salle
Frenchman who explored the Great Lakes and Mississippi River Valley.

Treaty of Utrecht
1713 treaty which gave Britain French land in the Americas.

James Oglethorpe
British member of Parliament who came up with a plan to create Georgia, partly as a place to send British prisoners.

Louisbourg
French seaport town in on Cape Breton island, taken by the British during the French and Indian War.
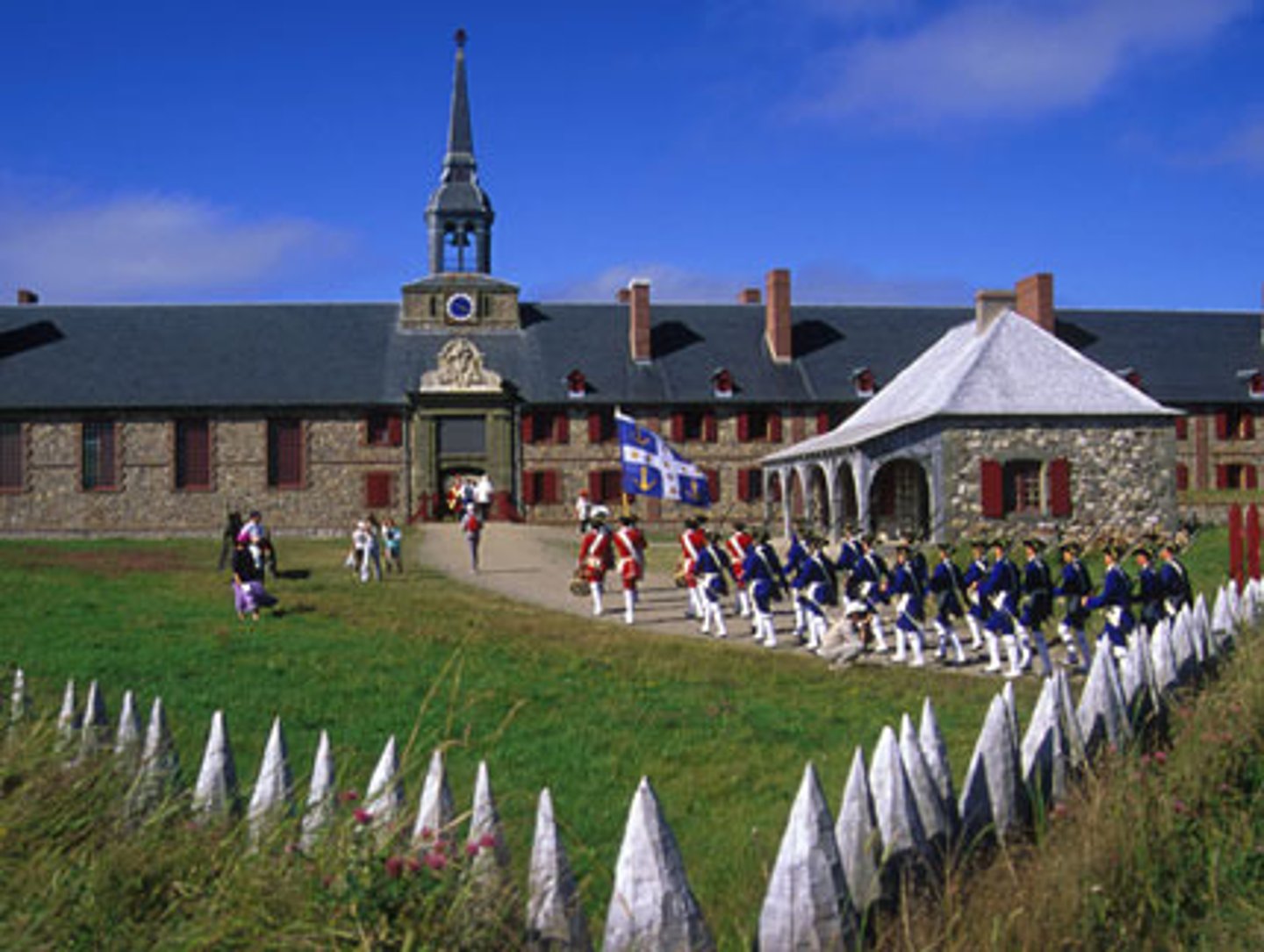

Fort Duquesne
French fort at the forks of the Ohio River in what is now downtown Pittsburgh. The French captured this fort near the end of the war and named it Fort Pitt.

George Washington
British colonial commander tasked with removing the French from the Ohio River Valley.

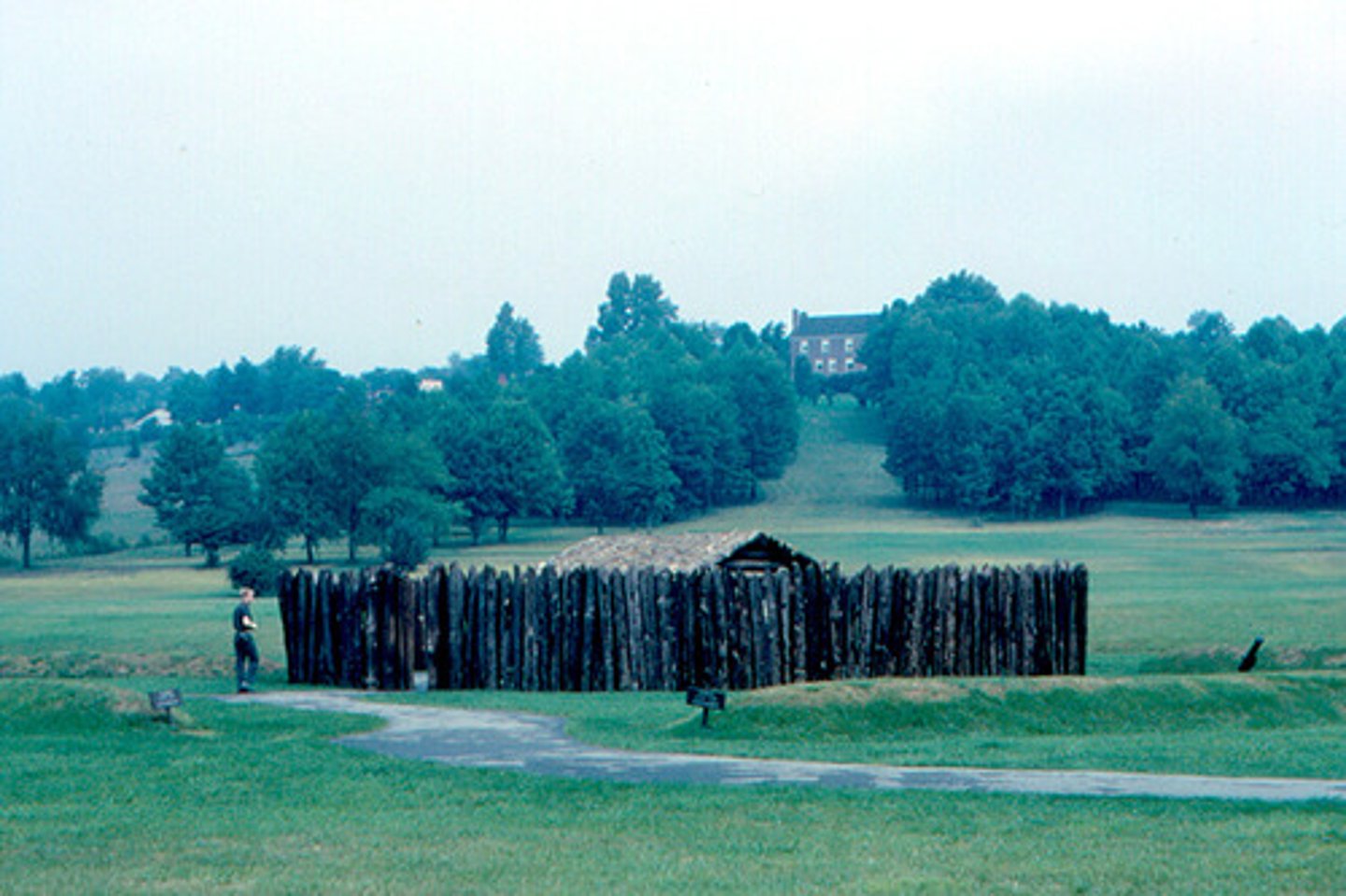
Fort Necessity
Fort in Pennsylvania surrendered by George Washington at the beginning of the French and Indian War.

Benjamin Franklin
Colonial leader who pushed for the colonies to "join or die!" in fighting against the French.

The Great Displacement
The forced eviction of French Acadians by the British during the French and Indian War.

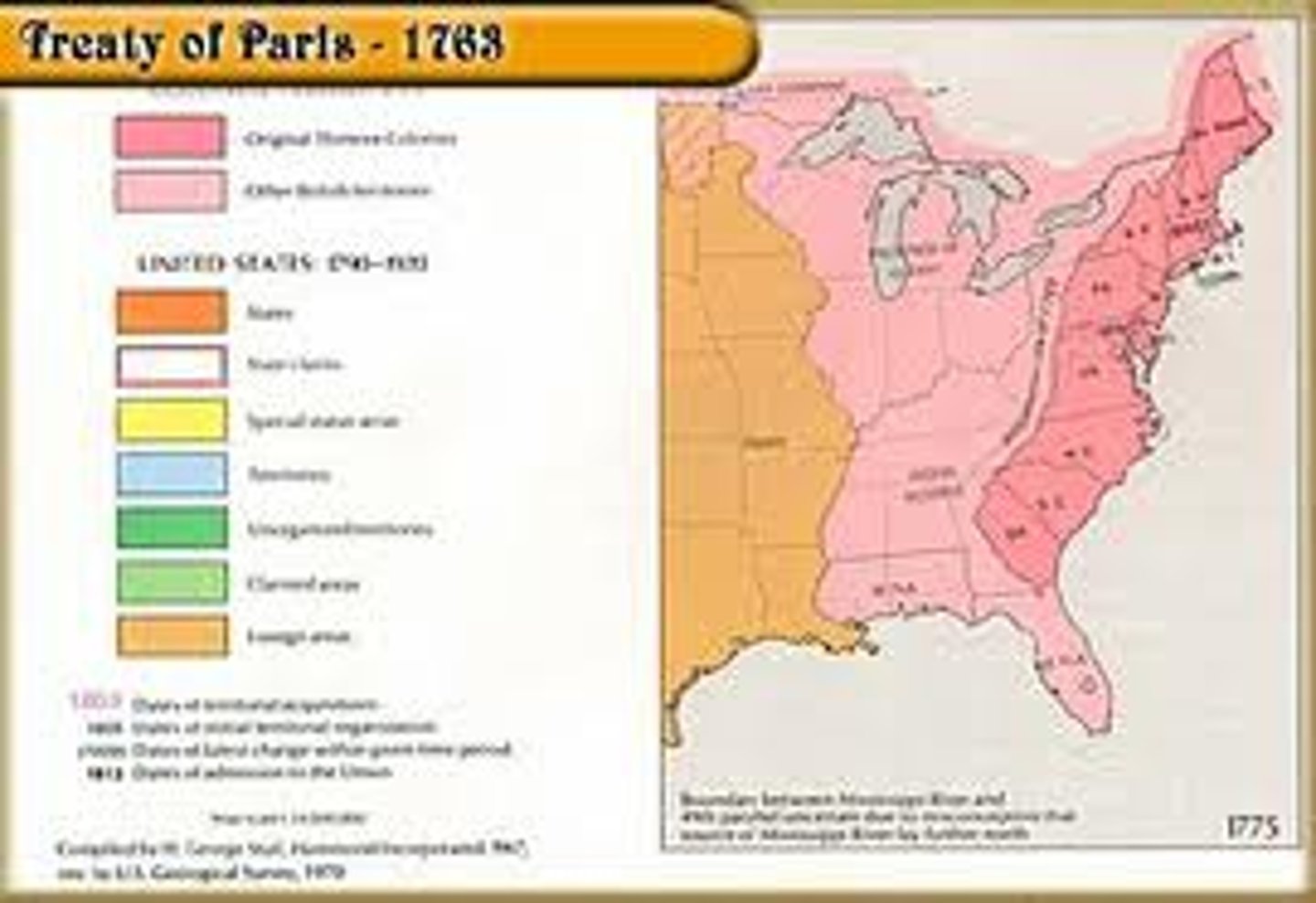
Treaty of Paris 1763
Treaty ending the Seven Years' War. Granted a majority of land in the Americas to the British.
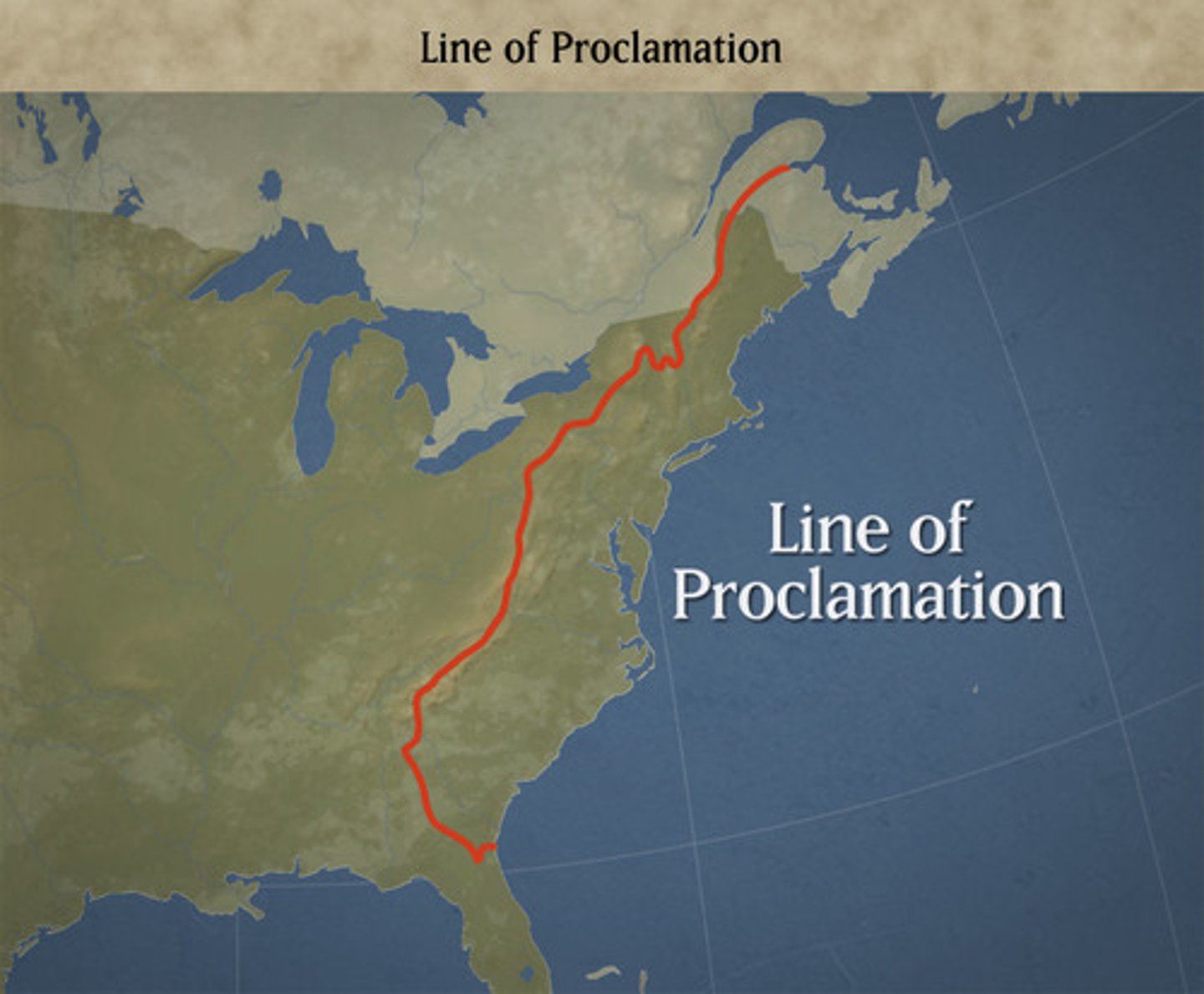
Proclamation of 1763
British proclamation preventing American colonists from moving west into the American frontier. Passed after Pontiac's Uprising. Angered colonists.
Daniel Boone
American frontiersman who first explored west of the Cumberland Gap and the Appalachian Mountains into what is now Kentucky.
