honors biology chapter 3
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/91
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
1
New cards
organic compounds
substance that contains covalently-bonded carbon and hydrogen and often with other elements
2
New cards
isomers
molecules with the same components but different structures (same cunt different slay)
3
New cards
hydrocarbons
organic compound consisting of (you guessed it) hydrogen and carbon
4
New cards
double bond
when two pairs of electrons are shared covalently (two little lines)
5
New cards
triple bond
when three pairs of electrons are shared covalently (three little lines)
6
New cards
functional groups
an atom or group of atoms within a molecule that has similar chemical properties whenever it appears in various compounds
7
New cards
hydrophilic
loves water!
8
New cards
hydrophobic
does not like water.

9
New cards
hydroxyl group
-OH
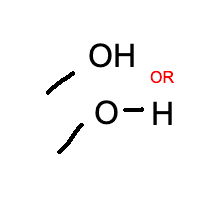
10
New cards
carbonyl group
-C=O
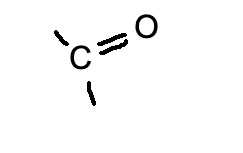
11
New cards
amino group
NH2
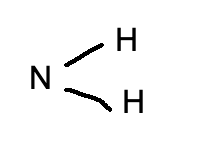
12
New cards
phosphate group
-O-P=O-OH2
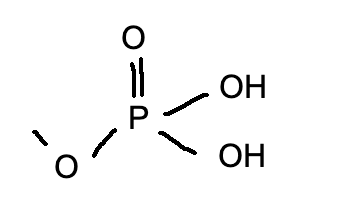
13
New cards
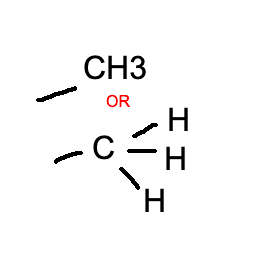
methyl group
-CH3
14
New cards
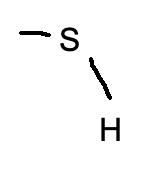
sulfhydryl (thiol) group
-SH
15
New cards
testosterone
lipid that is male sex hormone (MAN JUICE)
16
New cards
macromolecules
four main ones are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acid
17
New cards
polymers
many monomers; large substance built of macromolecules
18
New cards
monomers
molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer
19
New cards
dehydration synthesis
add H2O to put things together!
20
New cards
hydrolysis
takes H2O out to break things apart
21
New cards
enzymes
substance produced by a living organism which acts as a catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction
22
New cards
Carbohydrates
organic compound; built of small, repeating units that form bonds with each other to make a larger molecule; only contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; 3 groups: starches, sugars, and fibers
23
New cards
monosaccharide
one sugar
24
New cards
disaccharide
two sugar
25
New cards
polysaccharide
many sugar
26
New cards
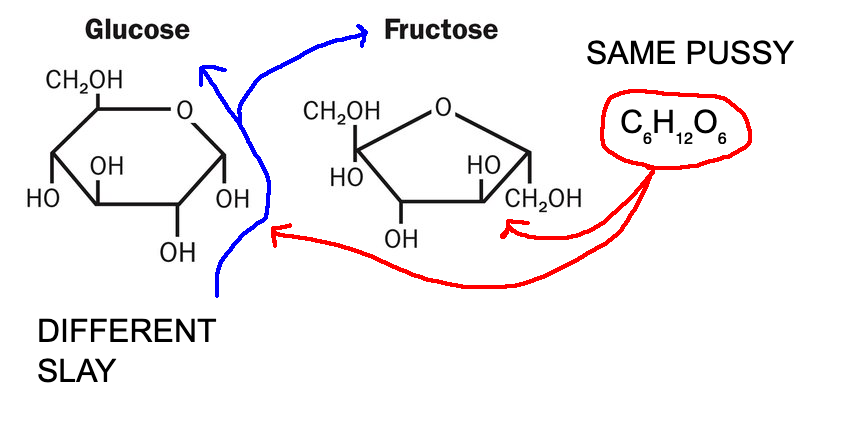
glucose
monosaccharide made via hydrolysis of starch; C6H12O6
27
New cards
fructose
monosaccharide with formula of C6H12O6 with different structure than glucose
28
New cards
galactose
glucose + lactose = __
29
New cards
maltose
glucose + glucose + dehydration reaction = __
30
New cards
sucrose
monosaccharides glucose + fructose = disaccharide __
31
New cards
lactose
monosaccharides galactose + glucose = disaccharide __
32
New cards
high-fructose corn syrup
corn syrup but starch is broken down into glucose via enzymes + that glucose is turned into fructose so there is SO MUCH FRUCTOSE
33
New cards
starch
polysaccharide that stores plant energy
34
New cards
cellulose
polysaccharide that makes up plant cell walls
35
New cards
glycogen
polysaccharide that stores animal energy
36
New cards
chitin
polysaccharide - bug's exoskeleton are made of these
37
New cards
lipids
organic compounds that have a collective characteristic of being hydrophobic
38
New cards
fat
subgroup of lipids that can also be called triglyceride
39
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
kinky fatty acid with at least one or more double bond - good for you (with the exception of trans fats) - liquid at room temperature
40
New cards
saturated fatty acid
not kinky fatty acid with no double bonds or functional groups - bad for you - solid at room temperature
41
New cards
trans fats
unsaturated fats with trans bonds instead of cis bonds - while
42
New cards
glycerol
sugar - head of lipids - when you attach fatty acid tails to it, it becomes a triglyceride
43
New cards
fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain + carboxyl group - attaches to glycerol to form triglyceride (fat)
44
New cards
triglyceride
glycerol + three fatty acid tails - also known as fat
45
New cards
atherosclerosis
hardening of the arteries caused by fatty acids and cholesterol plaques
46
New cards
heart disease
too much cholesterol and fatty acids in your system so you crust up like ice and die i hate this class
47
New cards
phospholipids
lipid + phosphate - hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tails - makes up cell membrane
48
New cards
hydrophilic heads
phospholipid heads that like water
49
New cards
hydrophobic tails
phospholipid tails that hate water
50
New cards
steroids
lipids with certain chemical structures that act as messengers of genetic information in the body
51
New cards
cholesterol
steroid that maintains fluidity in the cell and helps regulate cell function
52
New cards
anabolic steroids
basically manmade testosterone - made through anabolism
53
New cards
anabolism
synthesis of simple molecules to complex ones - constructive metabolism
54
New cards
catabolism
breaking down of complex molecules to simple ones - destructive metabolism
55
New cards
metabolism
chemical reactions that take place within cells in order to break down food into energy
56
New cards
four main classes of organic compounds
carbohydrates, lipids (slay), proteins, and nucleic acid
57
New cards
protein
organic compound who's monomers are amino acids
58
New cards
globular
rounder protein structure, consisting of alpha helices and beta pleated sheets
59
New cards
fibrous
fiber proteins - more structural role
60
New cards
hemoglobin
protein inside red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues and organs in the body and carries carbon dioxide back to the lungs
61
New cards
collagen
fibrous, structural protein that is 30% of body mass
62
New cards
denature
to modify and destroy secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of a molecule by breaking weak hydrogen bonds
63
New cards
parkinson's disease
a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells, causing tremors and loss of body control
64
New cards
amino acids
building block molecule for proteins!
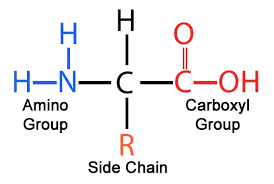
65
New cards
r group
also called side chain - 20 of them - many different properties (p-np, charged/uncharged, hydrophilic/phobic, etc.)
66
New cards
peptide bond
a covalent bond formed between two amino acids
67
New cards
polypeptide
continuous, unbranched chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
68
New cards
primary structure
structure and pattern of amino acids in polypeptide chain
69
New cards
secondary structure
how the polypeptide chain coils and folds - alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets
70
New cards
tertiary structure
3D shape of protein - globular or fibrous
71
New cards
quaternary structure
how protein subunits link to each other - multiple polypeptide chains
72
New cards
polypeptide backbone interactions
atoms common to every amino acid without r group - hydrophilic - hydrogen bonds with polar amino acids
73
New cards
hydrogen bonds
electrostatic bond between hydrogen (postive charge) with another substance with negative affinity
74
New cards
beta pleated sheet
secondary protein structure that folds sharply in a zig-zag pattern
75
New cards
alpha helix
secondary protein structure that coils
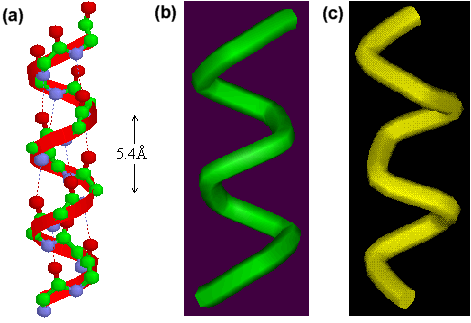
76
New cards
disulfide bridge
bonds created between two sulfhydryl groups and cysteine
77
New cards
hydrophobic r groups
long side chain consisting of hydrogen and carbon
78
New cards
ionic bonds
bonds where atoms give and/or take electrons to reach electrostatic equilibrium
79
New cards
hydrophilic r groups
polar side chains that can form hydrogen bonds with water
80
New cards
subunits
polypeptide chain or single protein molecule that assembles with others to form a protein complex
81
New cards
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid - stores and transfers genetic information
82
New cards
gene
segments of DNA containing genetic characteristics
83
New cards
nucleic acid
organic compound essential to all forms of life; defines what they are
84
New cards
RNA
ribonucleic acid - single stranded - messenger of genetic data
85
New cards
transcription
the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA
86
New cards
translation
the process by which a cell makes proteins using the genetic information carried in messenger RNA
87
New cards
nucleotide
building block of nucleic acids - consists of phosphate group, pentose, and nitrogenous base
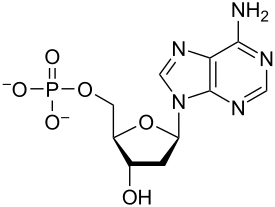
88
New cards
nitrogenous base
also called nucleobase, integral part of nucleotide - there are five of them, adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
89
New cards
double helix
dna shape dawg idk
90
New cards
base pairing rules
adenine goes with thymine, cytosine goes with guanine (in rna swap thymine for uracil)
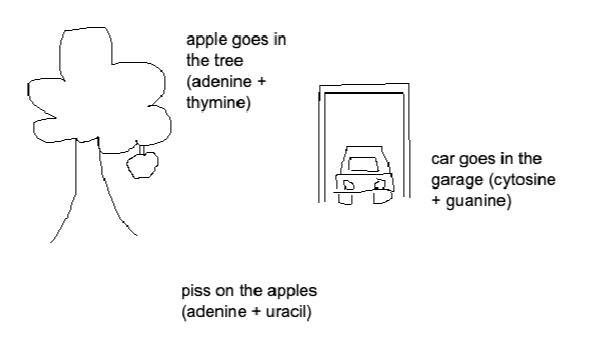
91
New cards
complementary
the relationship between inverse nucleotides (a + t, c + g, etc.)
92
New cards
lactose intolerant
does not have enzyme lactase to break down lactose (weakest of our society)