General Chemistry 1 lab final exam
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
molar mass
the mass of one mole of a pure substance
how to use molar mass
mass/molar mass
synthesis reaction
A+B->AB
decomposition reaction
AB->A+B
single replacement reaction
AB+C->B+AC
double replacement reaction
AB+CD->AC+BD
precipitation
(aq)+(aq)->(s)+(aq)
combustion reaction
x+O2->CO2+H2O
acid-base reaction
A+B->H2O+C
molarity equation
M = moles of solute/liters of solution
percent composition
(mass of element/molecular mass) * 100
lab 1 pennies
calculated density of pre and post 1982 pennies
lab 1 glassware used
plastic graduated cylinder
density equation
density=mass/volume
water displacement method
a method that involves putting an object into water and carefully recording how much the water level rises
lab 2 hydrocarbons
observe the physical and chemical properties of different hydrocarbons.
alkane compound
a hydrocarbon containing only single covalent bonds
alkene compound
C=C double bond
aromatic compound
a compound that contains the ring structure of benzene
lab 4 copper
observe a type of reaction involving isolation of copper while exploring the concepts of solubility.
precipitate
A solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.
supernatant
Clear liquid remaining after sediment settles
theoretical yield
the maximum amount of product that can be produced from a given amount of reactant
percent yield
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
lab 3 calcium phosphate
synthesize calcium phosphate and determine percent yield
limiting reagent
any reactant that is used up first in a chemical reaction; it determines the amount of product that can be formed in the reaction
lab 5 hydrogen peroxide
determine the concentration of a commercial sample of hydrogen peroxide solution
lab 5 glassware
250 mL Erlenmeyer flask
50 mL buret
25 mL graduated cylinder
titration
A solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of another solution.
titrant
a solution of known concentration
analyte
Substance being analyzed
equivalence point
the point at which the two solutions used in a titration are present in chemically equivalent amounts
end point
the point in a titration at which an indicator changes color
color change hydrogen peroxide
light pink
lab 6 antacids
determine the mass of hydrochloric acid (HCl) neutralized per gram of one of two antacids
back titration
Method where an excess of a reagent is reacted with a sample. The unreacted reagent is then determined by titration.
color change antacid
iridescent yellow end pt
lab 7 Boyles law
use a gas pressure sensor and a syringe to measure the pressure of an air sample
hess' law def
the overall enthalpy change in a reaction is equal to the sum of enthalpy changes for the individual steps in the process
calorimeter
a measuring instrument that determines quantities of heat
lab 8 hess's law
use a foam cup calorimeter to measure the heat released by 3 reactions
thermal equilibrium
when two objects are at the same temperature and no heat flows
why is calculating the MM of air hard?
because air is not a single compound, but rather a mixture of various gases like nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide, each with its own molar mass
most abundant gases in the atmosphere
nitrogen and oxygen
real gas law equation
(P + an2 /V2 )(V-nb) = nRT.
What is the formula for density?
d=v/m
d=m/v
d=2mv
d=πr^2h
d=m/v
How do you get an accurate reading when measuring the volume of water in a graduated cylinder? (Select all that apply.)
by reading the meniscus at eye level
by reading the highest point of the meniscus
by reading the bottom of the meniscus
by reading the meniscus from above
by reading the meniscus at eye level
by reading the bottom of the meniscus
T/F: The composition of the penny changed in 1928.
True
False
false (it changed in 1982)
What is the first step in Experiment 1?
Calculate the volume from a mass measurement and a given density
Calculate the density of the post-1982 penny
Calculate the volume of a penny using a ruler
Measure the volume of a penny by using water displacement
Calculate the volume of a penny using a ruler
T/F: To determine the final volume of a penny using water displacement, you would subtract the final volume from the initial volume (Vi - Vf).
True
False
False
What are the three types of hydrocarbons investigated during Experiment 2?
Alkanes, Alcohols, and Aldehydes
Esters, Ethers, and Alcohols
Amides, Aldehydes, and Alkenes
Alkanes, Alkenes, and Aromatic compounds
Alkanes, Alkenes, and Aromatic compounds
Why is an alkane considered to be a saturated hydrocarbon?
Because it contains only triple bonds between carbon atoms
Because it contains only double bonds between carbon atoms
Because it contains all types of bonds between carbon atoms
Because it contains only single bonds between carbon atoms
Because it contains only single bonds between carbon atoms
T/F: Aromatic compounds are relatively unreactive.
True
False
true
Which hydrocarbon reacts with potassium permanganate (KMnO4) to form a diol?
Alkenes
Alkanes
None of the above
Aromatic compounds
alkenes
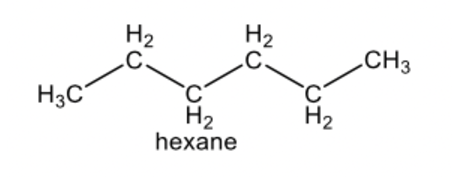
alkane
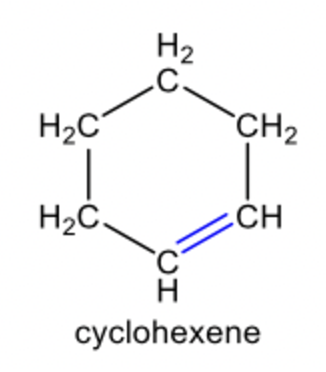
alkene
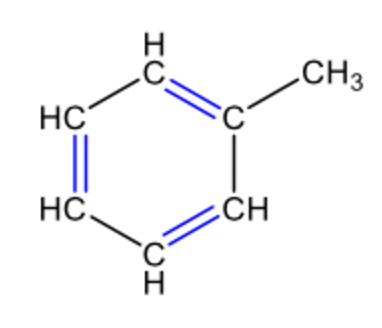
aromatic
What are the correct stoichiometric coefficients for the following chemical reaction?
CaCl2(aq) + Na3PO4(aq) ---> NaCl(aq) + Ca3(PO4)2(s)
3CaCl2(aq) + 2Na3PO4(aq) ---> 1NaCl(aq) + 6Ca3(PO4)2(s)
6CaCl2(aq) + 3Na3PO4(aq) ---> 2NaCl(aq) + 1Ca3(PO4)2(s)
4CaCl2(aq) + 3Na3PO4(aq) ---> 1NaCl(aq) + 2Ca3(PO4)2(s)
3CaCl2(aq) + 2Na3PO4(aq) ---> 6NaCl(aq) + 1Ca3(PO4)2(s)
3CaCl2(aq) + 2Na3PO4(aq) ---> 6NaCl(aq) + 1Ca3(PO4)2(s)
T/F: Calcium phosphate can be synthesized from calcium chloride and sodium phosphate in a single displacement reaction.
True
False
false
What is the purpose of the vacuum filter in Experiment 5?
to activate the chemical reaction
to isolate the precipitate from the solution
to add a specific amount of water to the solution
to cool the solution to a particular temperature
to isolate the precipitate from the solution
T/F: The form of calcium phosphate found in teeth and bones is called apatite.
True
False
true
CaCl2
110.98 g/mol
Na3PO4 . 12H2O
380.12 g/mol
Ca3(PO4)2
310.18 g/mol
What is the overall chemical reaction when copper (II) sulfate reacts with magnesium metal?
CuSO4(aq) + Mg(s) ---> MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
CuSO4(aq) + Mg(s) ---> MgCu(s) + SO4(aq)
MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s) ---> CuSO4(aq) + Mg(s)
MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s) ---> CuSO4(aq) + Mg(s)
CuSO4(aq) + Mg(s) ---> MgSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
What is the formula for percent yield?
Percent yield = (actual yield / theoretical yield) x 100%
Percent yield = (theoretical yield / actual yield) x 100%
Percent yield = (actual yield / theoretical yield)
Percent yield = (theoretical yield / actual yield)
Percent yield = (actual yield / theoretical yield) x 100%
What is the stoichiometric ratio between copper sulfate (CuSO4) and copper metal (Cu)?
2 mol CuSO4 = 1 mol Cu
1 mol CuSO4 = 2 mol Cu
3 mol CuSO4 = 1 mol Cu
1 mol CuSO4 = 1 mol Cu
1 mol CuSO4 = 1 mol Cu
What is added to dissolve the solid magnesium (Mg) that did not react with the copper sulfate (CuSO4)?
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Hydrobromic acid (HBr)
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
T/F: When metals are ionized, they become insoluble in water and precipitate.
True
False
false
Which of the following are true at the equivalence point of a titration? (Select all that apply)
The resulting solution turns colorless
All of the H2O2 has completely reacted
The resulting solution turns pink
All of the KMnO4(aq) has completely reacted
The resulting solution turns colorless
All of the H2O2 has completely reacted
In Experiment 6, how do you know the end point has been reached in the titration?
The solution turns a faint yellow color
The solution turns a faint blue color
The solution turns colorless
The solution turns a faint pink color
The solution turns a faint pink color
What is the stoichiometric ratio between KMnO4(aq) and H2O2(aq)? Refer to the chemical equation if needed.
3:4
2:5
5:3
1:5
2:5
What is the titrant used in this experiment?
KMnO4
H2O2
O2
MnSO4
KMnO4
At the beginning of the experiment, what solution is in the buret? What solution is in the Erlenmeyer flask?
Buret - hydrogen peroxide solution
Erlenmeyer flask - H2O
Buret - aqueous potassium permanganate
Erlenmeyer flask - hydrogen peroxide solution
Buret - H2O
Erlenmeyer flask - hydrogen peroxide solution
Buret - hydrogen peroxide solution
Erlenmeyer flask - aqueous potassium permanganate
Buret - aqueous potassium permanganate
Erlenmeyer flask - hydrogen peroxide solution
T/F: In this experiment, the dissolved antacid will be directly titrated with HCl (aq).
True
False
false
How does an antacid neutralize the excess stomach acid?
The antacid acts as a base to accept protons
The antacid acts as a base to donate protons
The antacid acts as an acid to accept protons
The antacid acts as an acid to donate protons
The antacid acts as a base to accept protons
What is added to the analyte to indicate the end point? (exp. 6)
Methyl orange
Phenolphthalein
Potassium permanganate
Methyl red
Methyl orange
What is the titrant used in this experiment?
NaOH
HCl
KMnO4
Antacid mixture
NaOH
What color will appear in solution when the end point is reached?
Red
Yellow
Pink
Orange
Yellow
Boyle's Law relates which two variables for a confined gas?
enthalpy and entropy
volume and temperature
enthalpy and pressure
pressure and volume
pressure and volume
What is assumed to remain constant throughout the experiment?
temperature
pressure
volume
all of the above
temperature
What gas will be confined in the syringe? (exp 7)
argon
air
oxygen
carbon dioxide
air
What is purpose of the Gas Pressure Sensor?
to monitor the change in volume
to monitor the change in pressure
to monitor the change in termperature
to monitor the change in volume, temperature, and pressure
to monitor the change in pressure
For this experimental setup, how do you get an accurate total volume when reading the syringe?
You subtract 0.8mL from the volume contained in the syringe
You multiply 0.8 mL times the voulme contained in the syringe.
You divide 0.8mL form the volume contained in the syringe.
You add 0.8mL to the value contained in the syringe
You add 0.8mL to the value contained in the syringe
What is used as a calorimeter in Experiment 8, Hess's Law?
A polystyrene foam cup in a beaker
A plastic cup in a beaker
A glass cup in a beaker
A copper metal cup in a beaker
A polystyrene foam cup in a beaker
What do solid sodium hydroxide and aqueous hydrochloric acid react to form? (Select all that apply)
H2(g)
Cl-(aq)
NaOH(s)
H2O(l)
Na+(aq)
Cl-(aq), H2O(l), Na+(aq)
T/F: The heat lost to the calorimeter and the surrounding air has a large effect on the results and should be considered in the calculations.
True
False
False
Why is it important to weigh the solid sodium hydroxide and proceed to the next step without delay?
Because solid sodium hydroxide picks up moisture from the air
All of the above
Because solid sodium hydroxide produces toxic fumes
Because solid sodium hydroxide can quickly turn into a liquid
Because solid sodium hydroxide picks up moisture from the air
In this experiment, on of the reactions performed is the same as the combination of the other two reactions. According to Hess's Law, the heat of reaction of the one reaction should be equal to ...
the sum of the heats of reaction for the other two reactions
the difference of the heats of reaction for the other two reactions
the product of the heats of reaction for the other two reactions
the first heat of reaction divided by the second heat of reaction
the sum of the heats of reaction for the other two reactions
T/F: Air is not a single pure gas, but a homogeneous mixture of several different gases.
True
False
true
What is the ideal gas equation?
Pn=VRT
Vn=PRT
PV=nRT
VT=nPR
PV=nRT
How is the molar mass of the air determined in this experiment?
the ratio of the mass that is lost to the change in the number of moles in the flask
MM = ∆m / ∆n
MM = ∆n / ∆m
the ratio of the change in the number of moles in the flask to the mass that is lost
the ratio of the mass that is lost to the change in the number of moles in the flask
MM = ∆m / ∆n
T/F: In this experiment, you will be directly measuring the mass of the air.
True
False
false
What are the units for temperature in the ideal gas law?
All of the above
Fahrenheit
Celsius
Kelvin
Kelvin