Chemistry - C4 (Predicting and Identifying Reactions and Products) *GCSE OCR, Higher*
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Group 1 Elements
- They are alkali metals
- They react with water to form alkaline solutions and they are held in oil to stop reactions with air
- They are shiny when cut and are good conductors of electricity
- They only have 1 electron in their outer shell which means they are extremely reactive
- Trends = Softness increases going down the group
= Density increases going down the group
= Reactivity increases going down the group
= Melting point decreases going down the group
Anions
- A negatively charged ion
- Formed when an atom gains at least one electron
Catalyst
- Increases the rate of reaction by providing a different reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
- They are not used up during the reaction
Cations
- A positively charged ion
- Formed when an atom loses at least one electron
Displacement
A chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound
Flame Test
- Qualitative test used to identify metal ions (cations)
- Carried out by inserting a nichrome wire loop with the unknown compound on into a flame and observing the colour
- Metal ions are heated and energy is transferred to electrons
- The electrons move into higher electron shells and when they move back to their normal shells, energy is transferred to the surroundings as radiation (light)

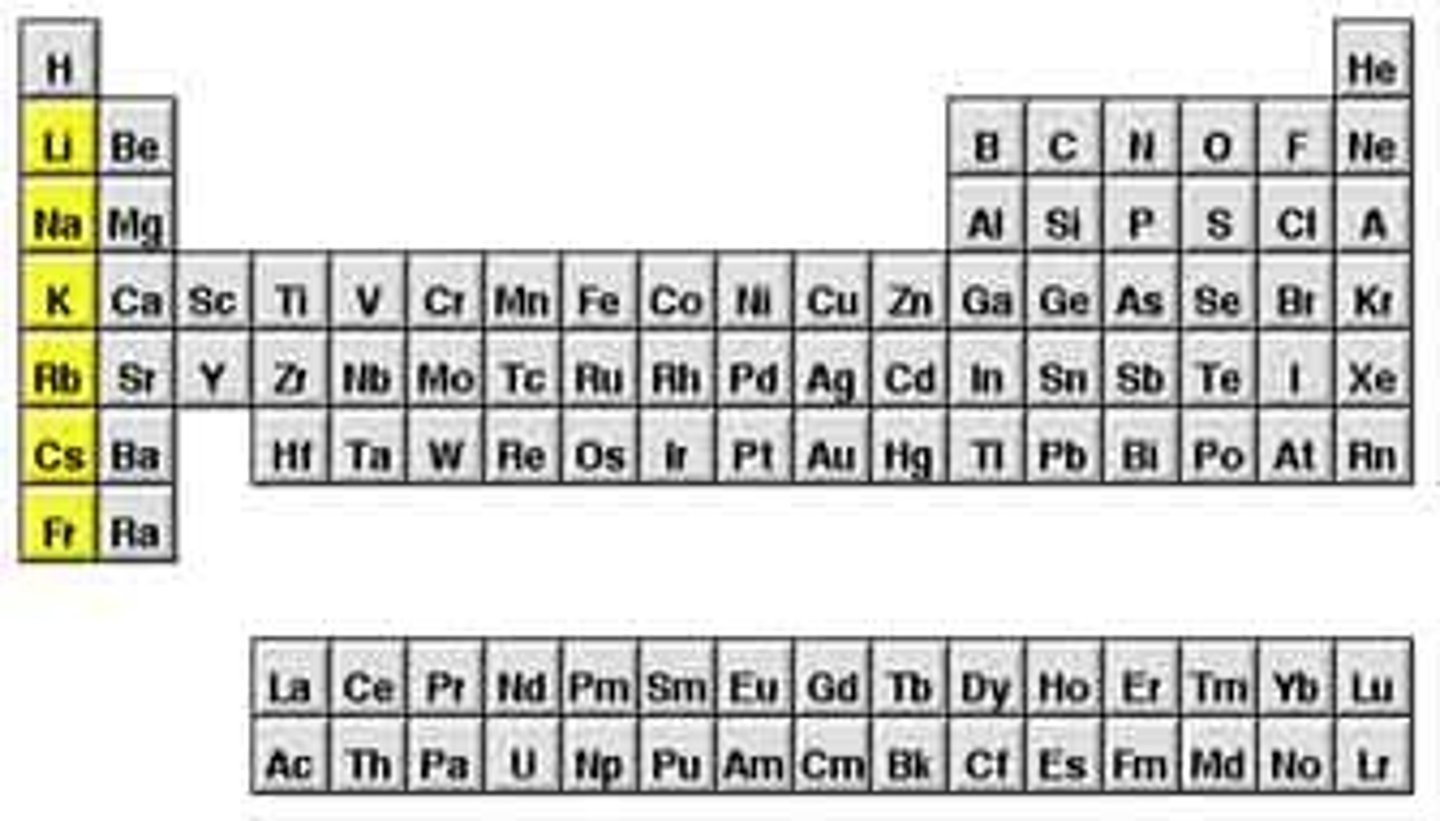
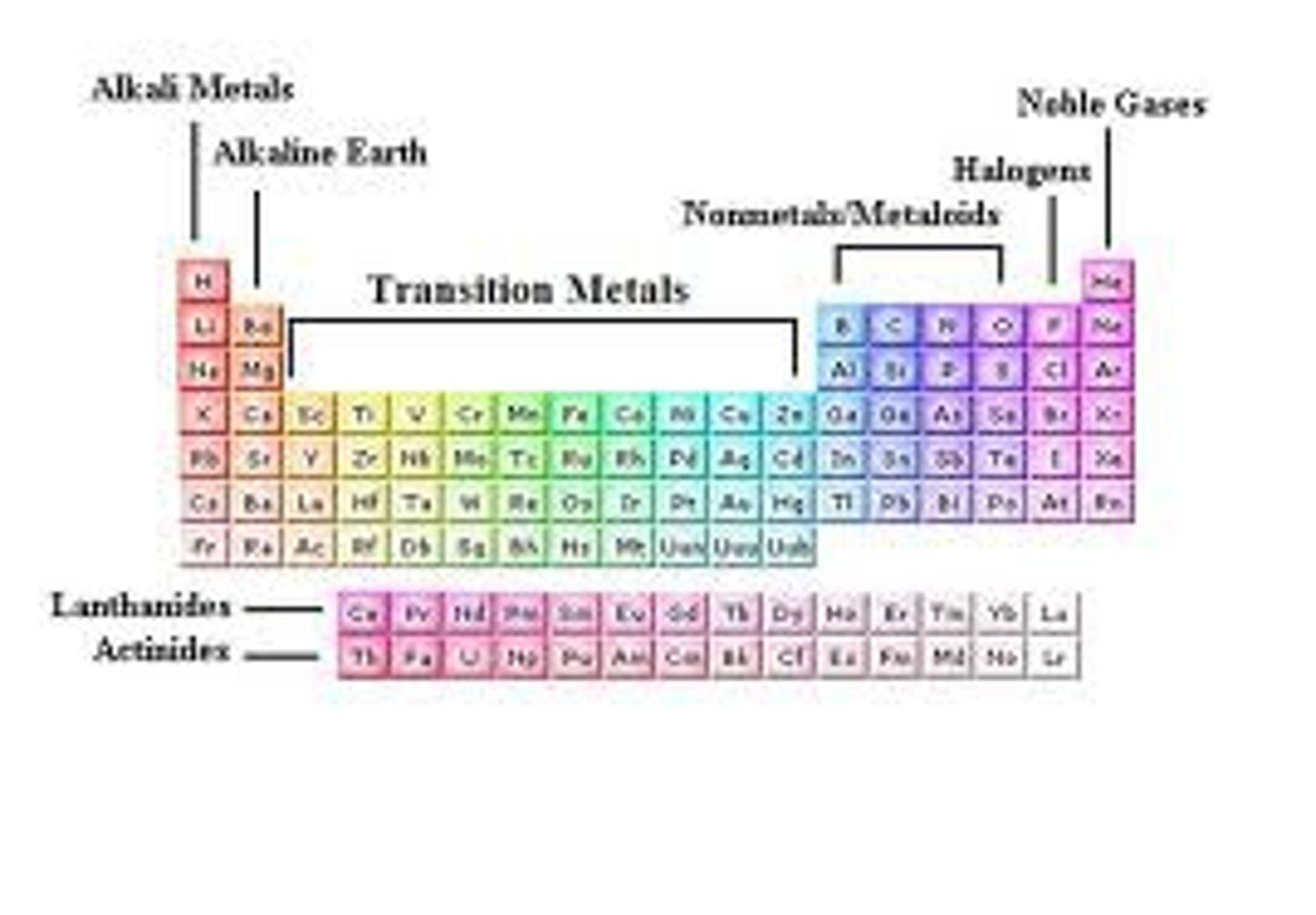
Group (periodic table)
- A column of the periodic table
- Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties.
Halides
- The ions formed by halogen atoms when they gain an electron
- It is a compound of a halogen and hydrogen / metal
- They have a 1- charge. E.g. Cl-, Br- and I-
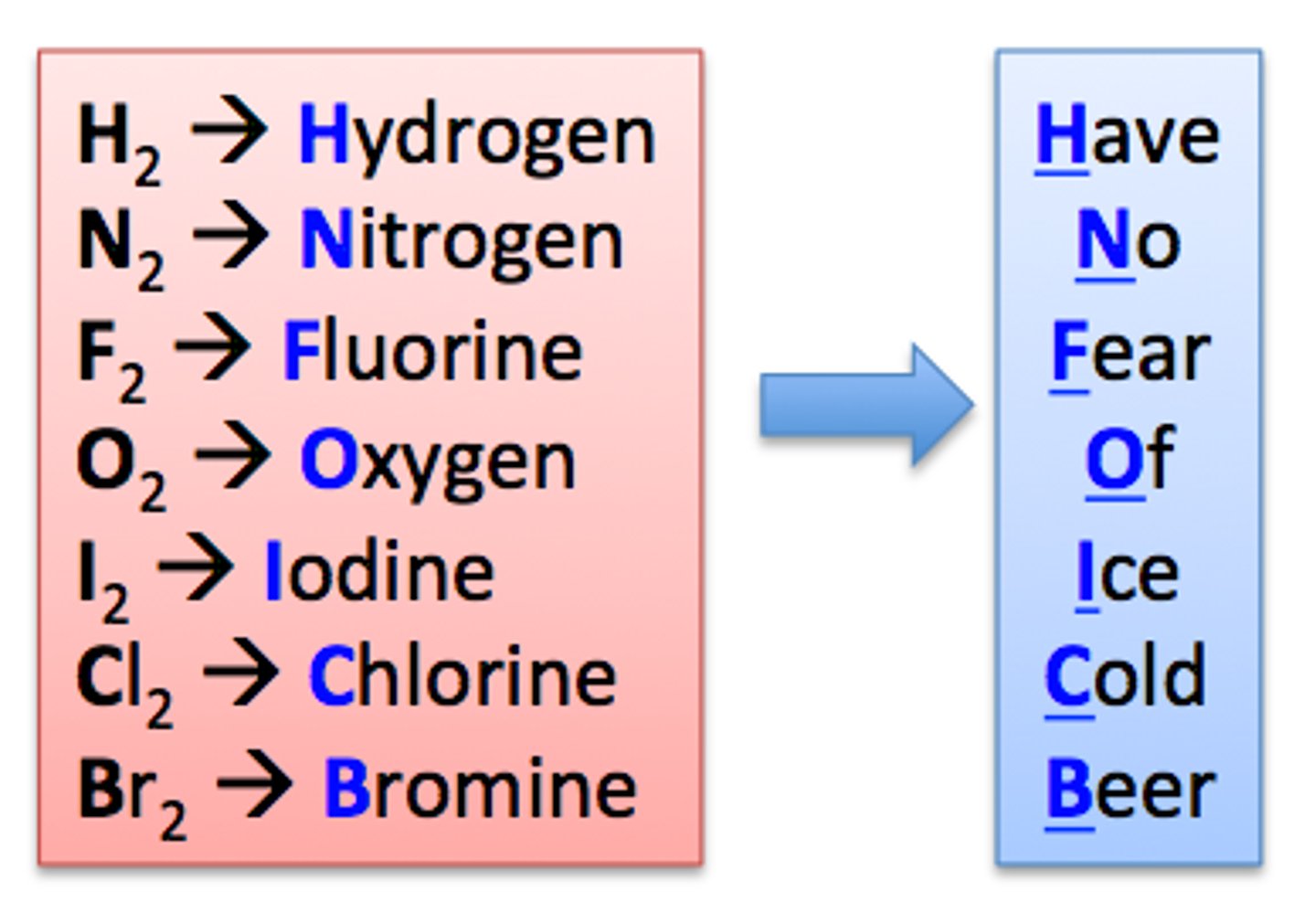
Group 7 Elements
- They are halogens
- The halogens gain an electron to form halide ions with a 1- charge
- They are brittle and poor conductors of electricity
- They are diatomic molecules with weak intermolecular forces
- They form coloured vapours and react with metals to form salts
- They react vigorously with Group 1 metals due to only having 7 electrons in the outer shell
- Trends = Reactivity decreases going down the group
= Density increases going down the group
= Melting point increases going down the group
= Boiling point increases going down the group
Instrumental Analyses Methods
- Used to detect and identify elements and compounds
- A machine is used
- They are accurate, sensitive and rapid
Group 0 / 8 Elements
- They are called noble gases
- They have a stable full outer shell of electrons which makes them very unreactive
- They are monatomic and have weak forces of attraction
- Trends = Boiling point increases going down the group
= Attractive forces increase going down the group
= Density increases going down the group
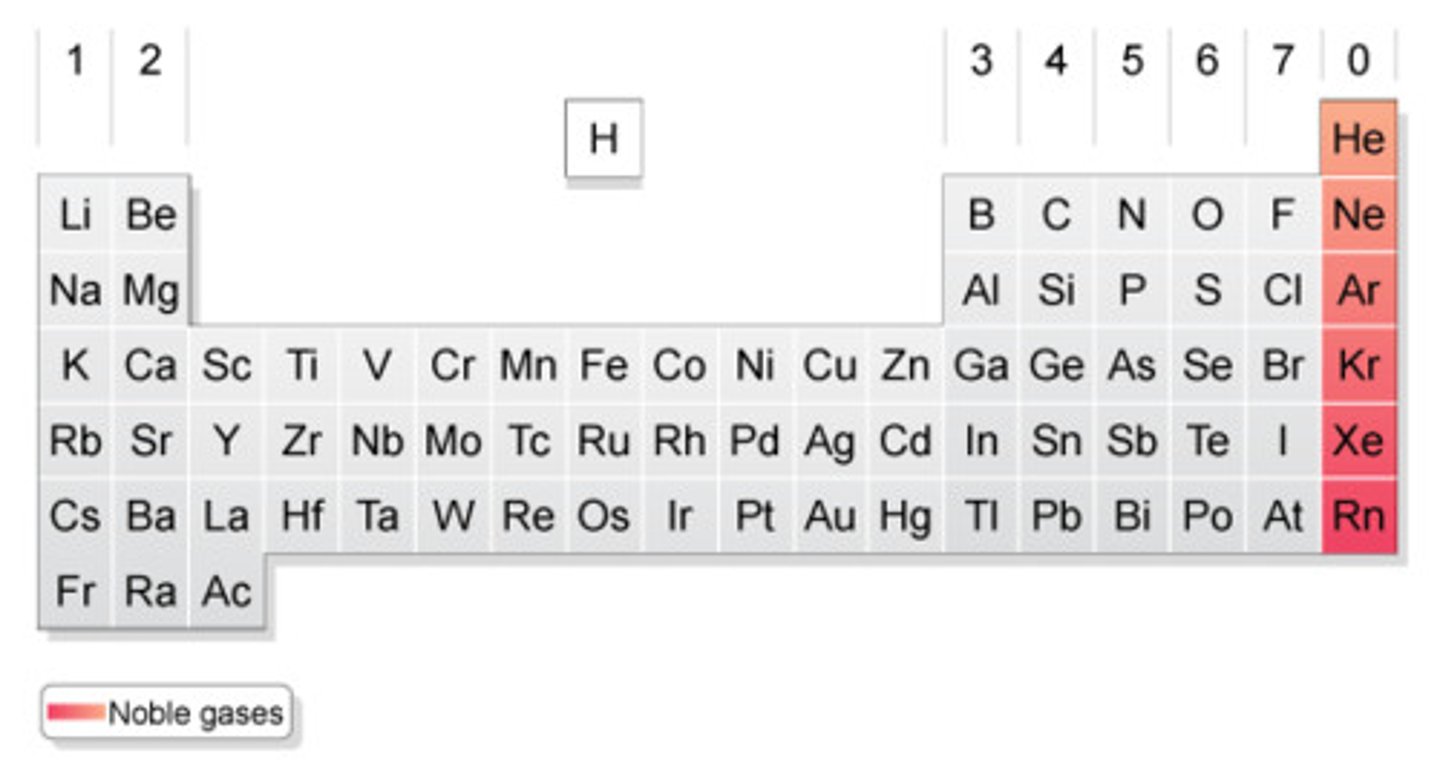
Periodic Table
Table of elements arranged in order of increasing atomic number and such that elements with similar properties are in the same column (group)
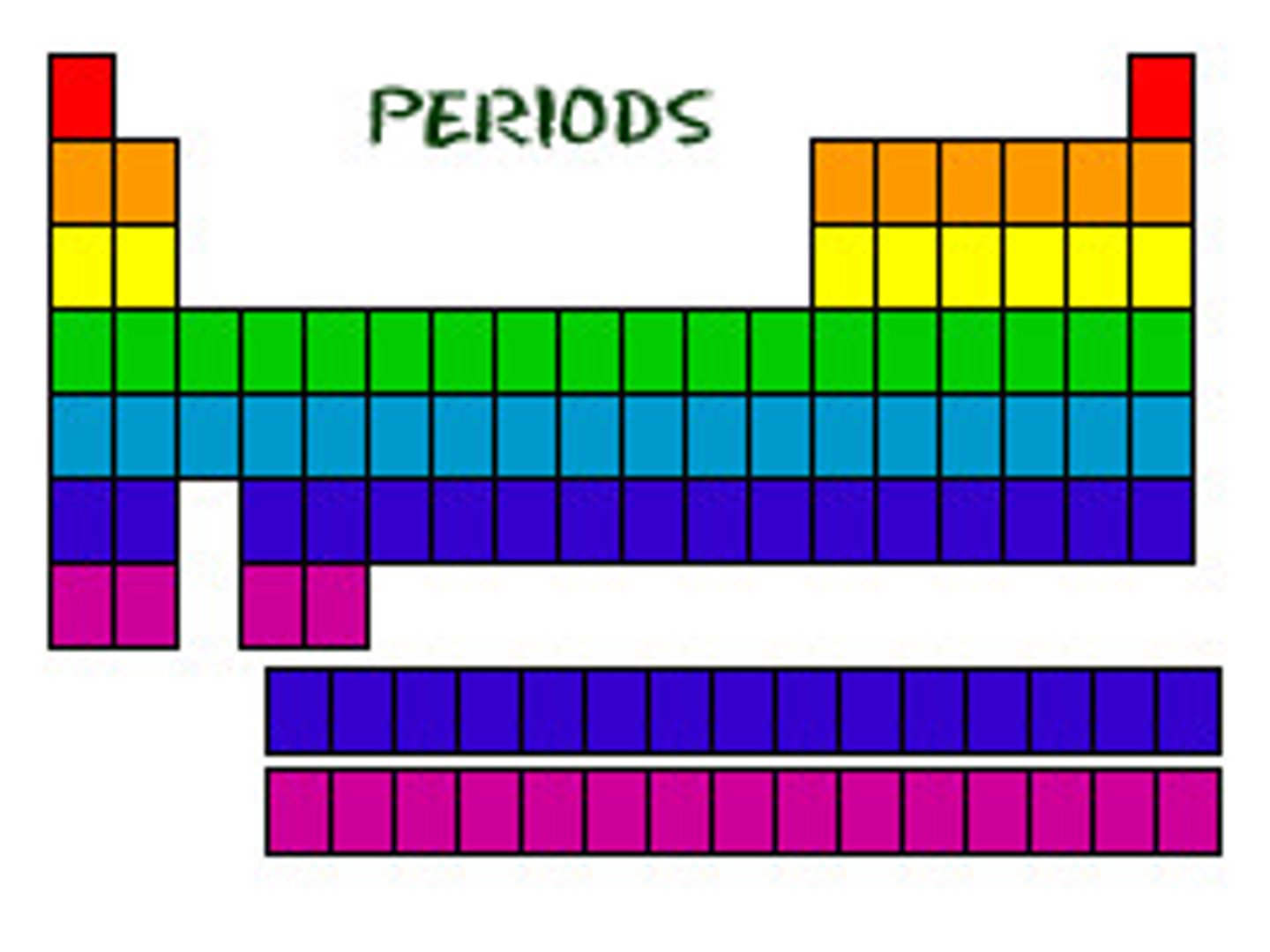
Period (periodic table)
- A row of the periodic table
- Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells
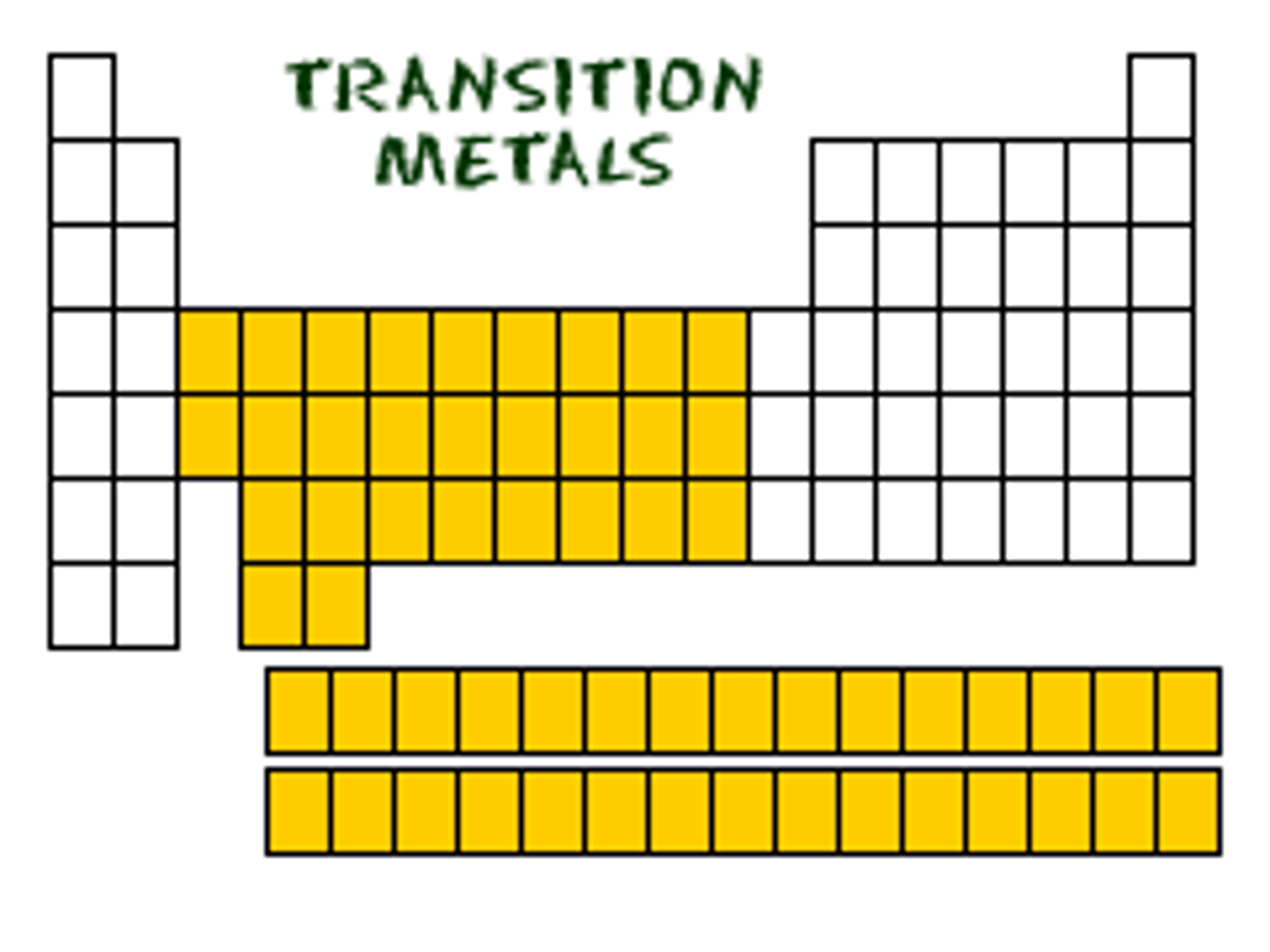
Transition metal
- A metal found between Group 2 and 3 of the periodic table.
- They are shiny when cut freshly cut, they are good conductors of electricity, they are strong and malleable
- They have high melting points, high densities and are good catalysts
- They produced coloured ionic compound which names reflect their colour
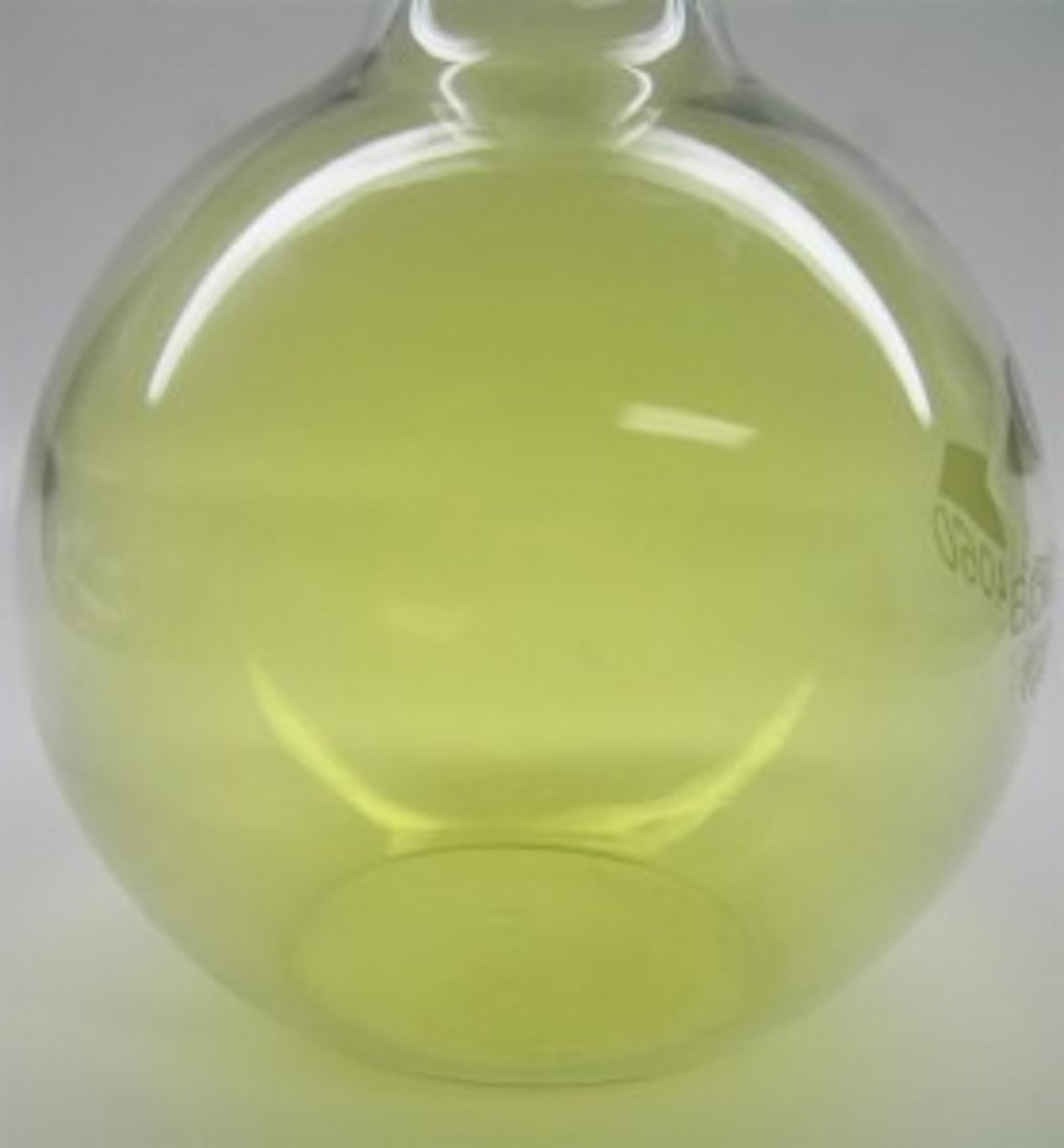
Group 7 Element - Fluorine
A bright yellow liquid that turns to a pale yellow gas at room temperature
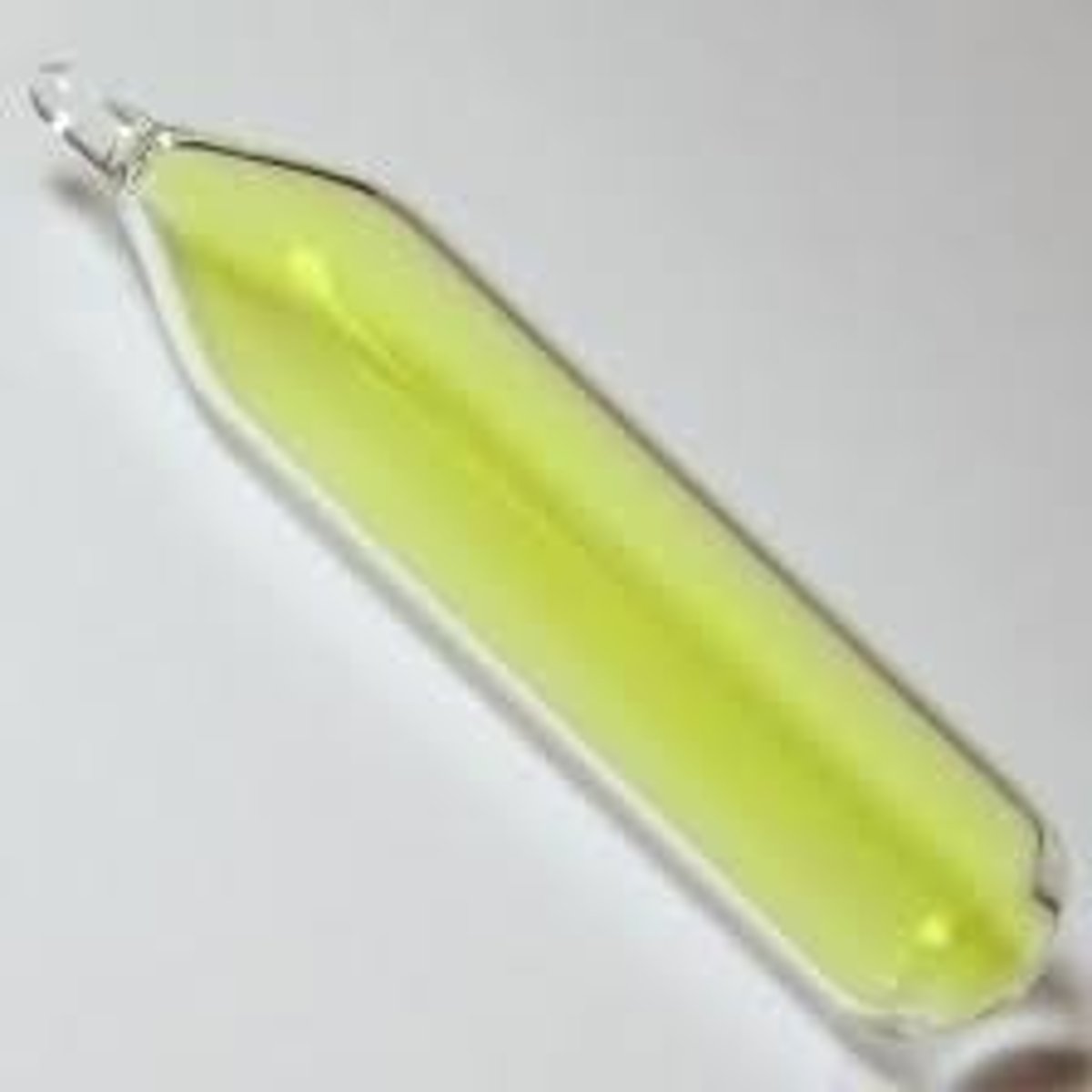

Group 7 Element - Chlorine
An amber liquid that turns to a green gas at room temperature

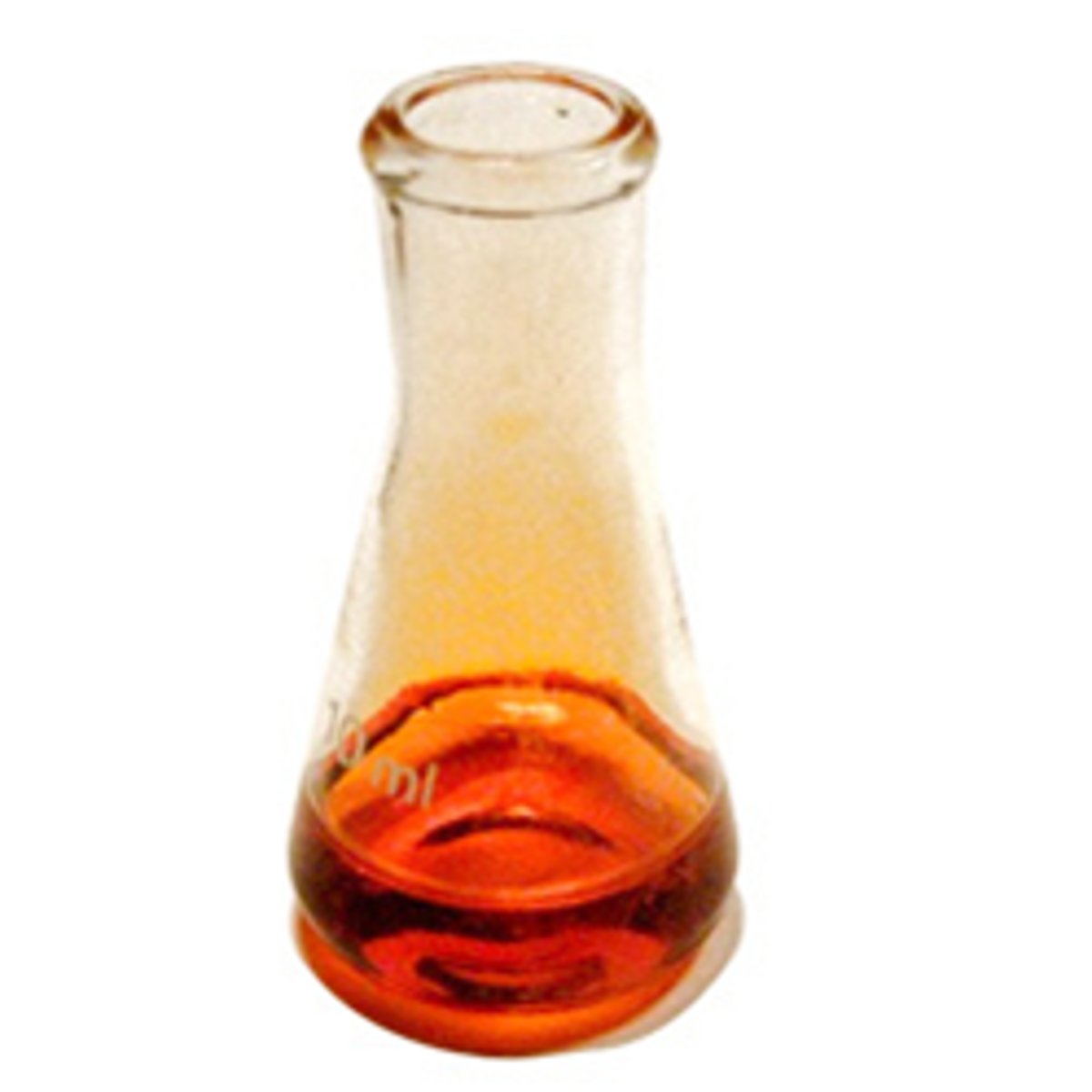
Group 7 Element - Bromine
Orange-brown liquid the vaporises to amber vapour easily

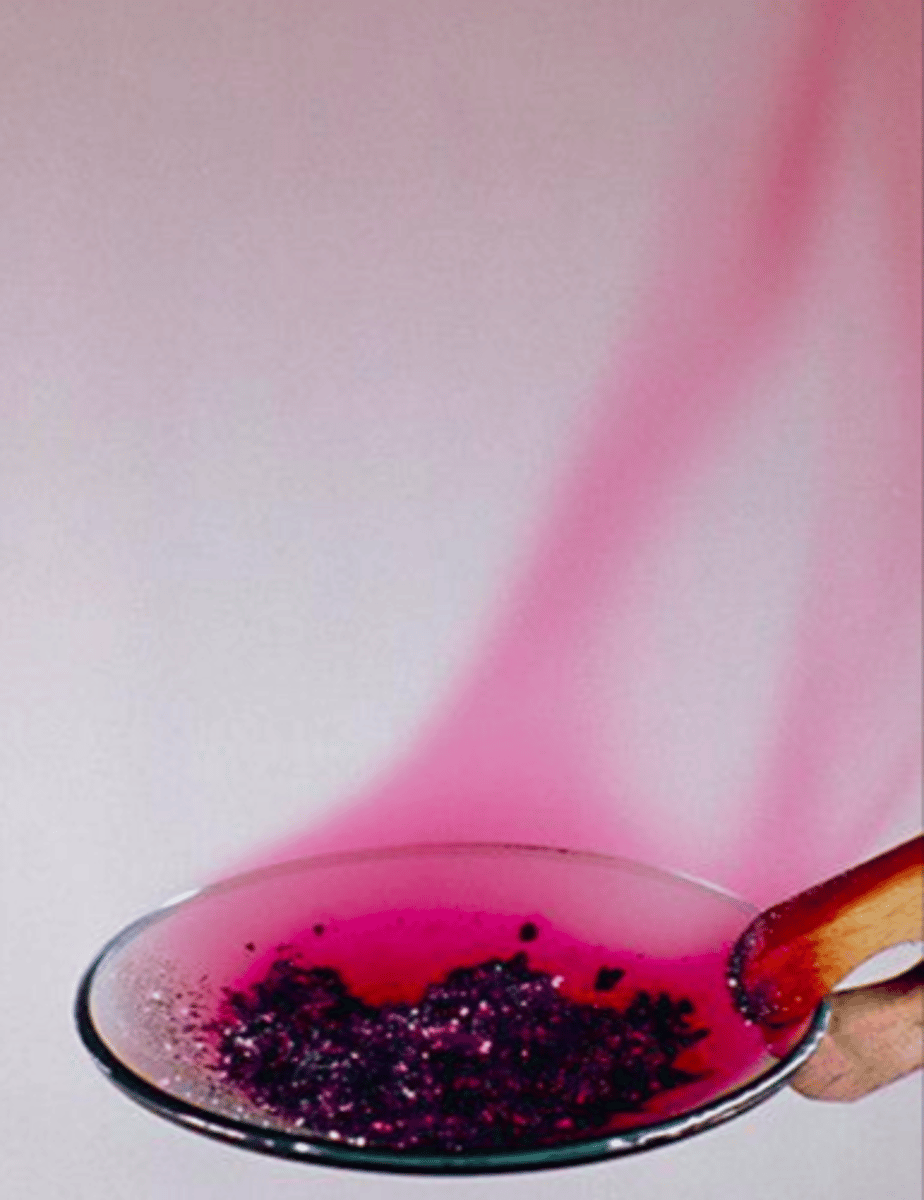
Group 7 Element - Iodine
Grey-black crystalline solid that sublimes to purple vapour

Group 1 Element Reactions - Lithium
It fizzes steadily and slowly disappears
Group 1 Element Reactions - Sodium
It melts to form a silvery ball, fizzes vigorously and disappears quickly
Group 1 Element Reactions - Potassium
It immediately ignites, burns with a lilac flame and disappears quickly due to it being able to lose its electron easier that lithium as its outer shell is further from the nucleus
Halogen Displacement Reactions
- Halogens react with halides in a solution
- A more reactive halogen can displace a less reactive halogen from a salt solution
- E.g. Cl2 + 2NaBr → 2NaCl + Br2
Chlorine can DISPLACE (push out) Bromine from the sodium bromide in a Displacement Reaction
Ionic Equations
- You can write a half equation to model what happens to each reactant
- E.g. Cl2 + 2e- → 2Cl- (reduction)
2Br- → Br2 + 2e- (oxidation)
You can combine the half equations to make the ionic equations = Cl2 + 2Br- → 2Cl- + Br2
Carbon Dioxide Test
- Pass LIMEWATER through the solution
- If Carbon Dioxide is present the limewater turns cloudy
Chlorine Test
Blue litmus paper BLEACHES RED then white
Hydrogen Test
- Place a light splint into the test tube
- If there is a SQUEAKY POP (small explosion), Hydrogen is present
Oxygen Test
- Place a GLOWING SPLINT into the test tube
- If it relights, Oxygen is present
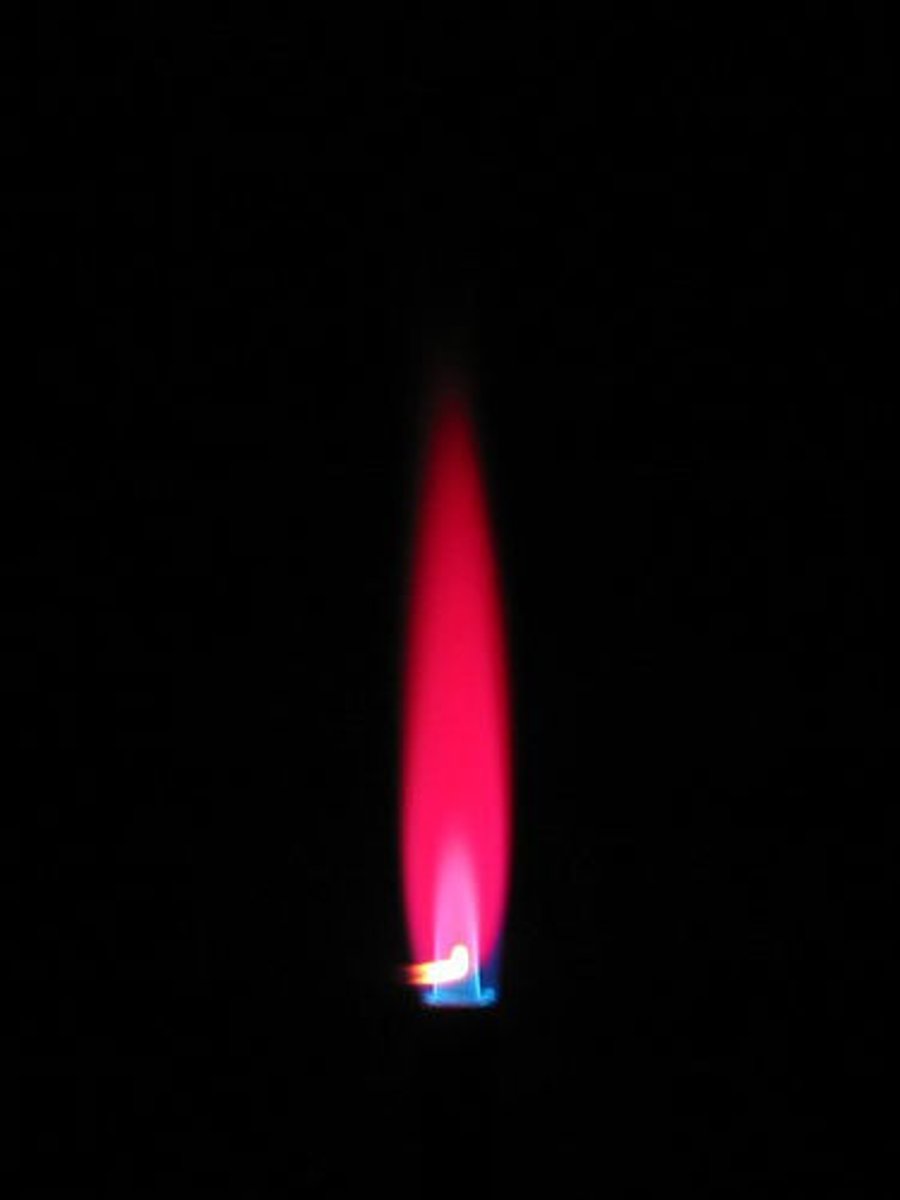
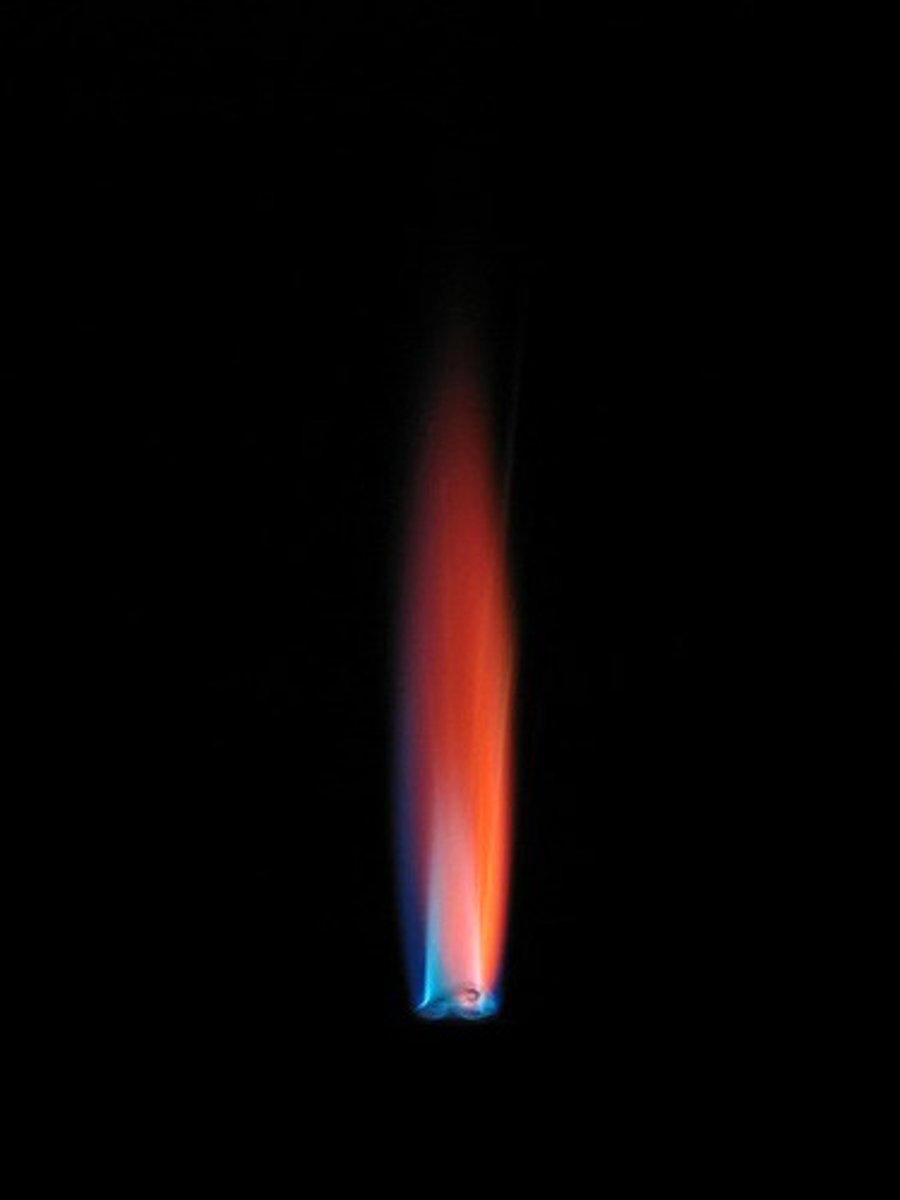
Flame Test - Lithium (L+)
Red flame produced

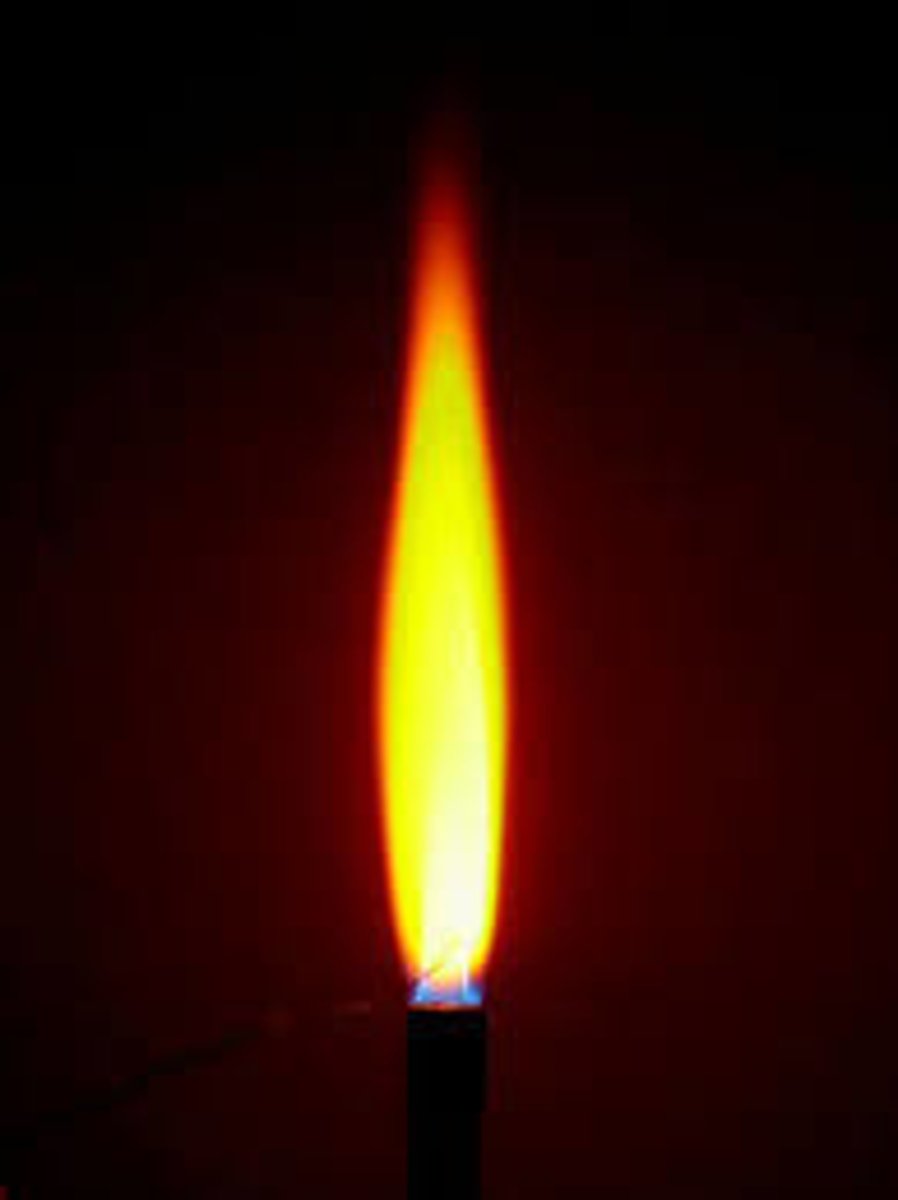
Flame Test - Sodium (Na+)
Yellow flame produced

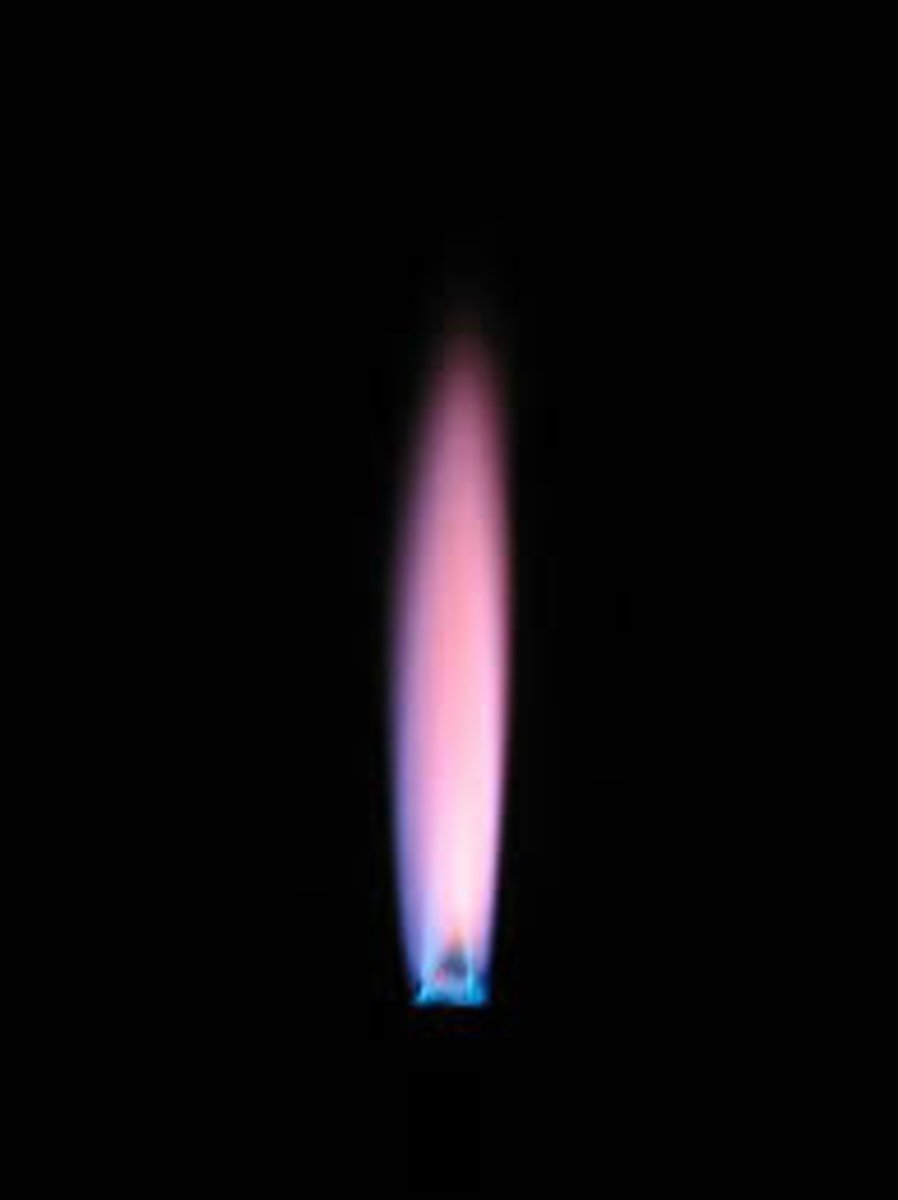
Flame Test - Potassium (K+)
Lilac flame produced

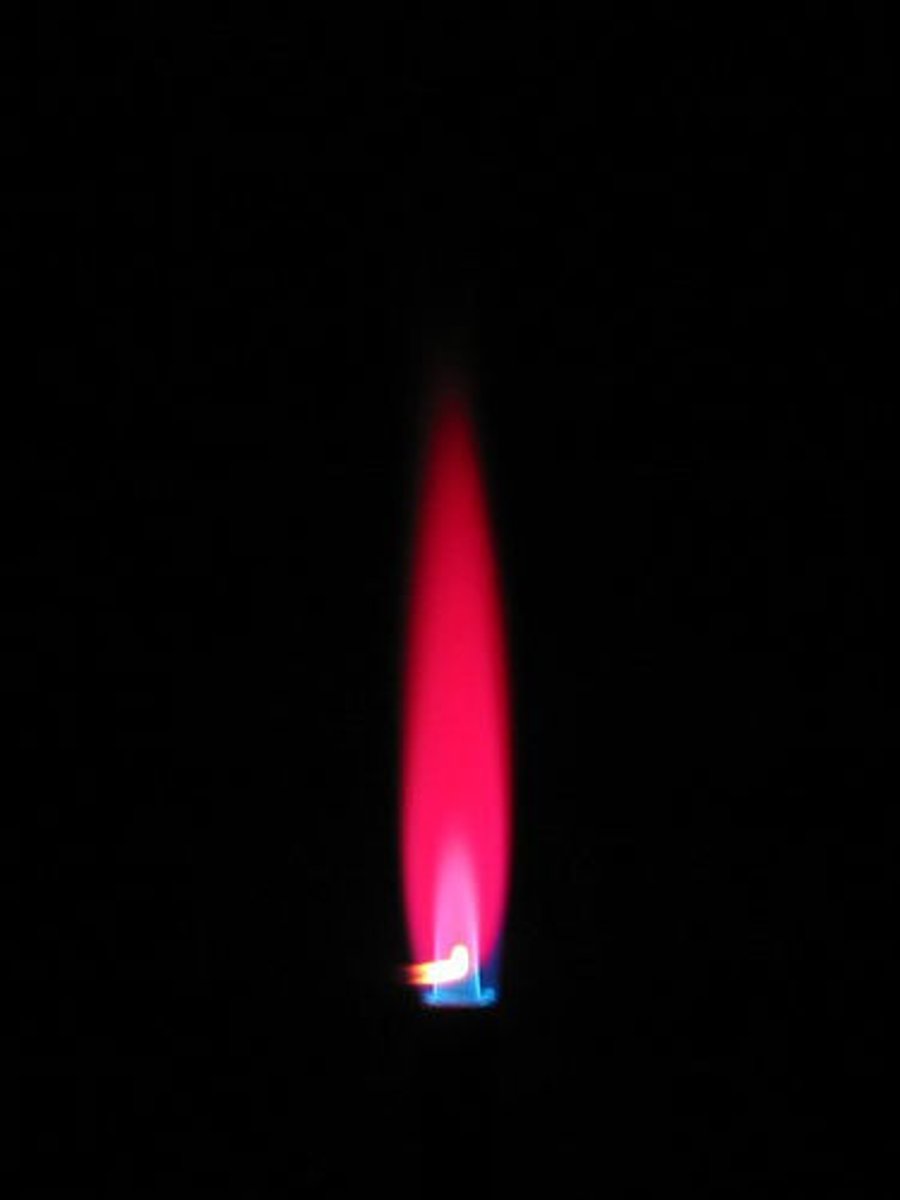
Flame Test - Calcium (Ca 2+)
Orange-red flame produced

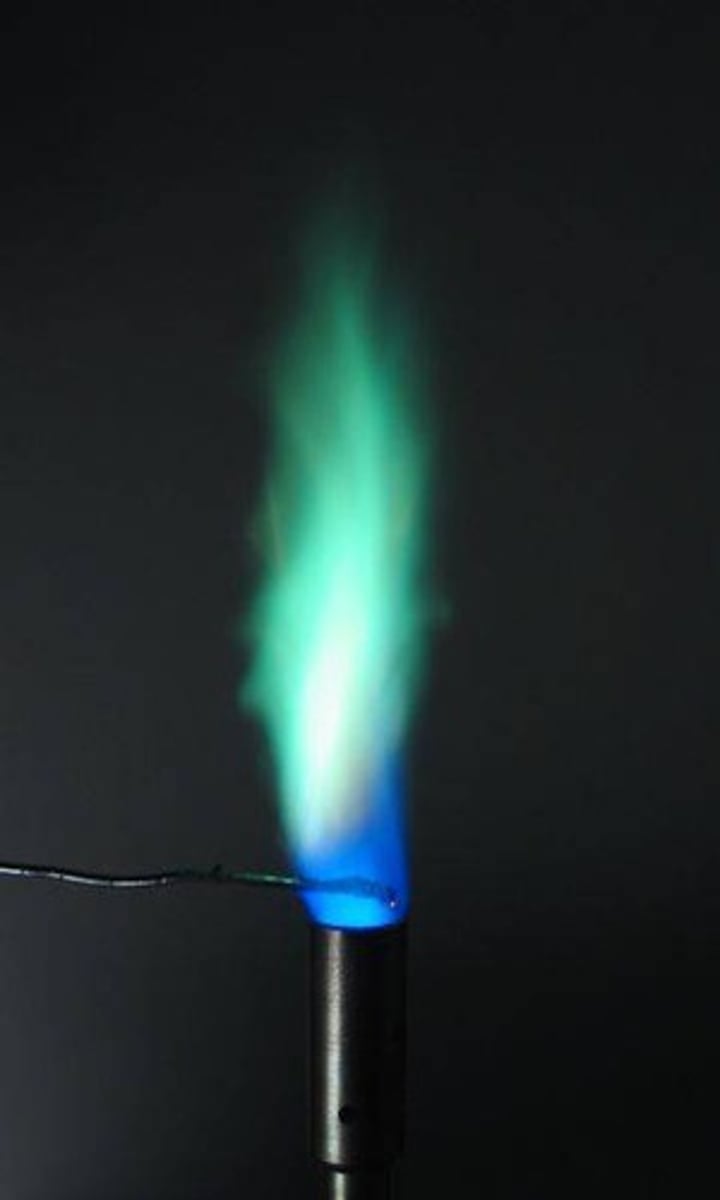
Flame Test - Copper (Cu 2+)
Green-blue flame

Hydroxide Precipitate Test
- Some group 1 metal hydroxides are soluble but others are insoluble
- Different metals produce different coloured precipitates
- To do the test, add sodium hydroxide solution containing metal ions
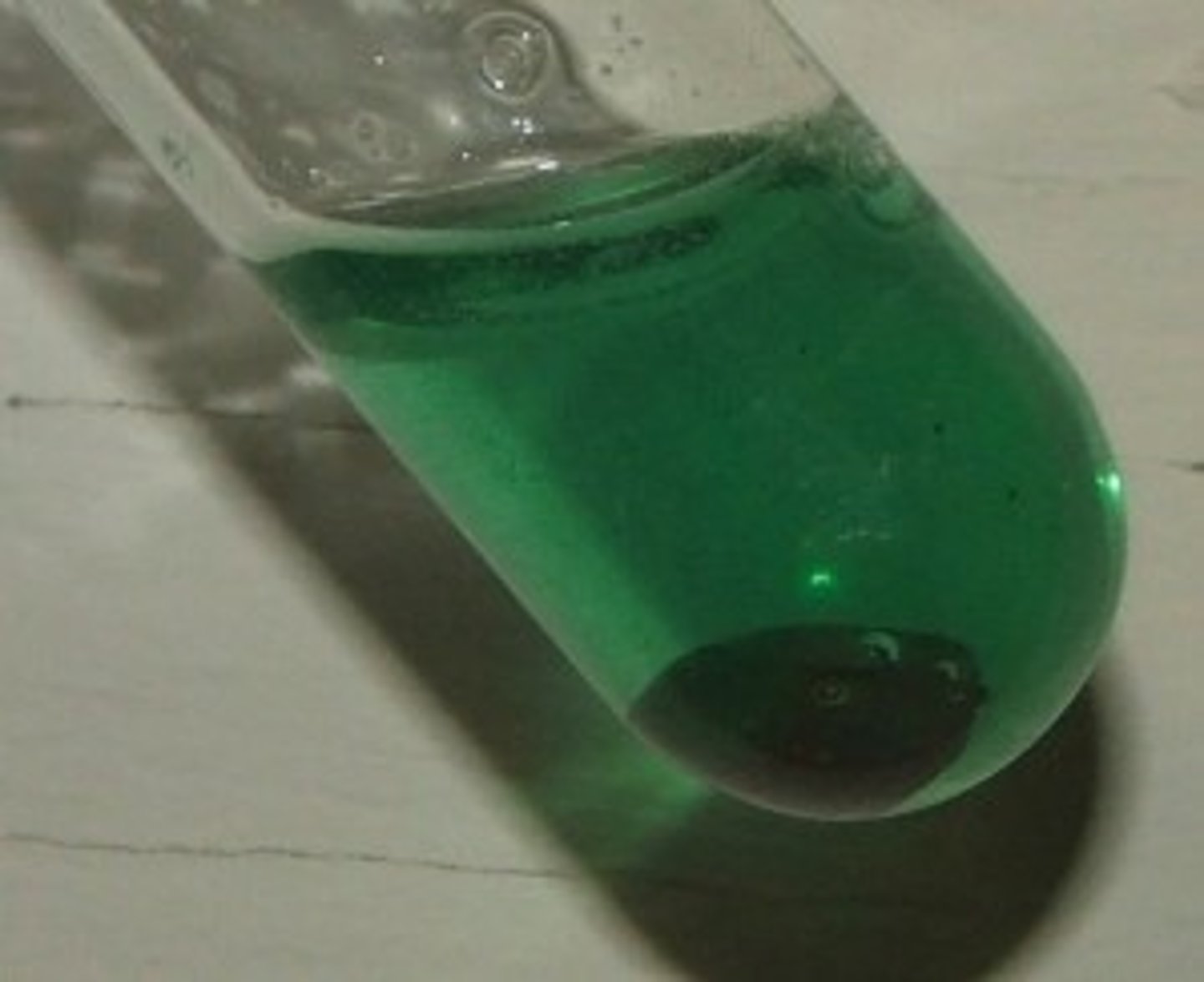
Hydroxide Precipitate Test - Iron (II) (Fe 2+)
Green precipitate produced

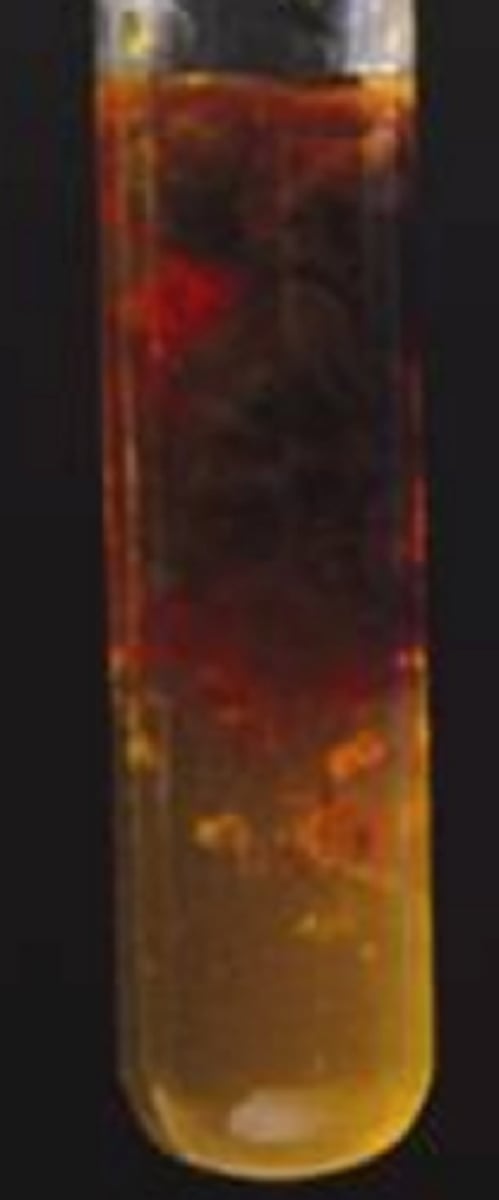
Hydroxide Precipitate Test - Iron (III) (Fe 3+)
Orange-brown precipitate produced

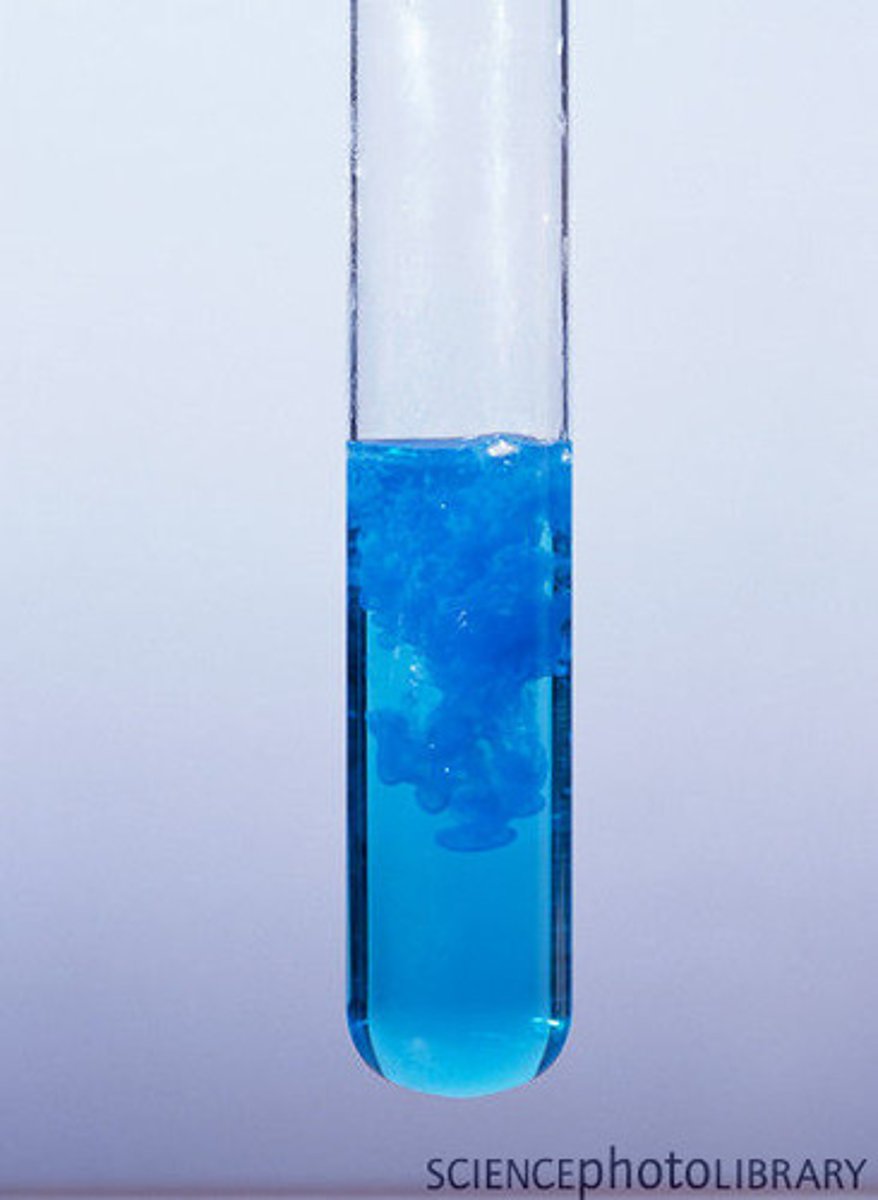
Hydroxide Precipitate Test - Copper (II) (Cu 2+)
Blue precipitate produced

Hydroxide Precipitate Test - Calcium (Ca 2+)
White precipitate produced
Hydroxide Precipitate Test - Zinc (Zn 2+)
White precipitate produce ( if more sodium hydroxide is added it becomes colourless)
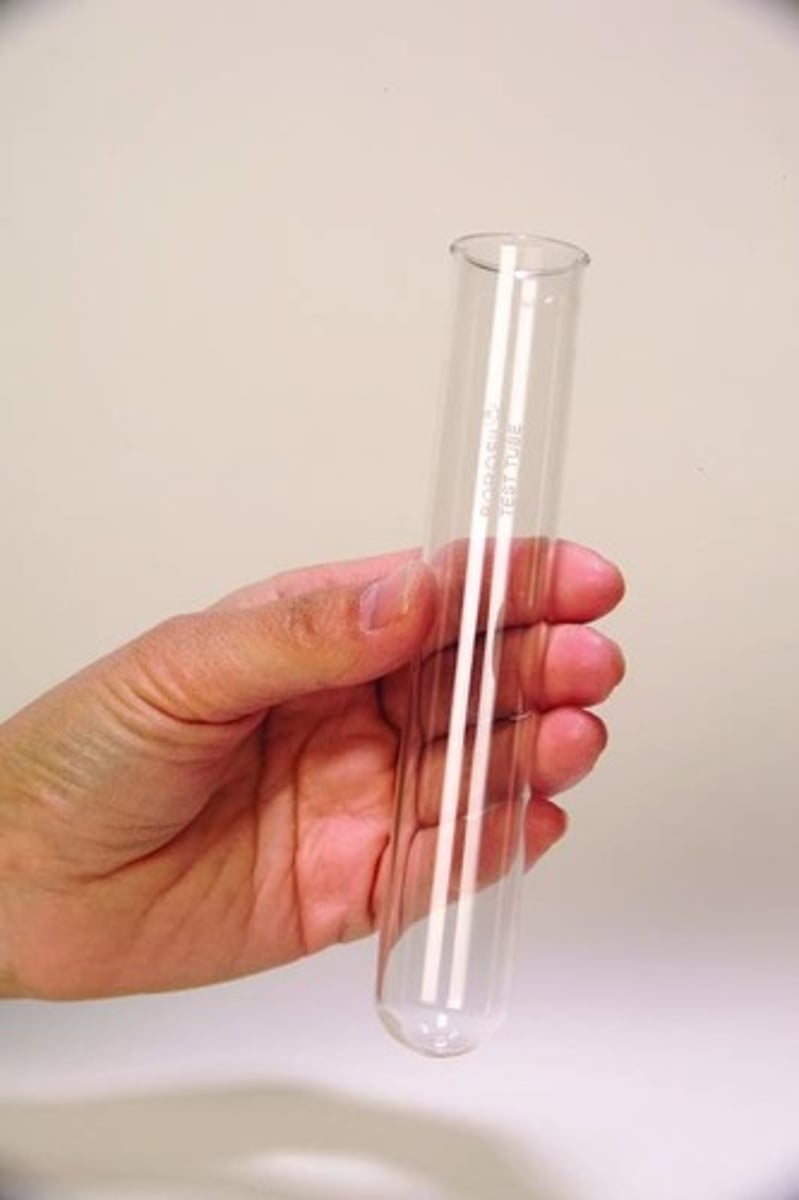

Testing for Sulphate Ions
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid and barium chloride
- If there is a white precipitate sulphate ions are present
Testing for Carbonate Ions
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid
- If bubble of gas (carbon dioxide) are seen, carbonate ions are present
- Do the carbon dioxide test to check
Rate of Reaction Test
- Reactions of metal and water help us put metals in order of reactivity
- The more reactive a metal, the more hydrogen it creates (more vicious bubbling)
Halide Ions Test
- Add a dilute nitric acid and then add silver nitrate
- Silver fluorine is soluble in water but other silver halides are insoluble
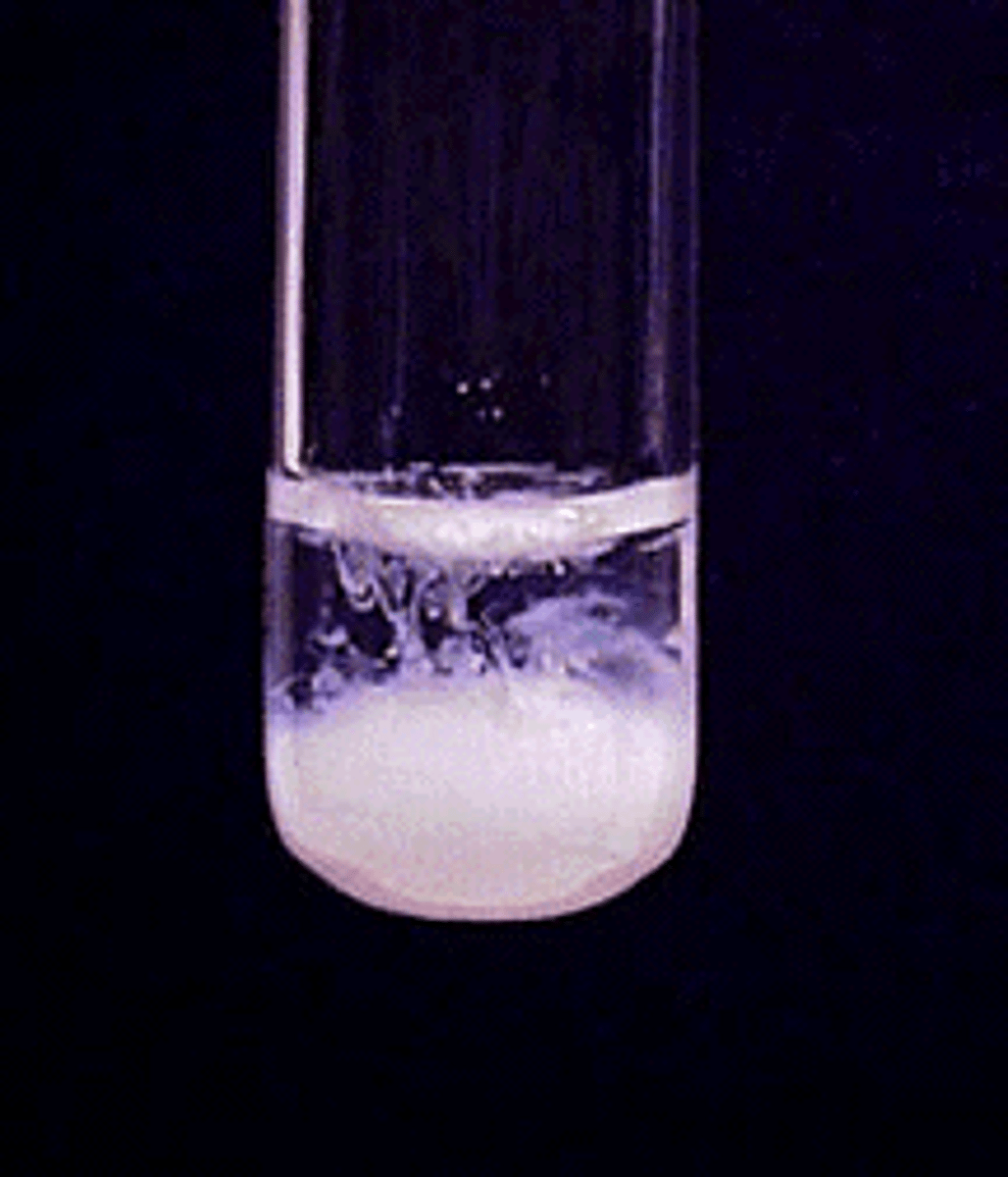
Halide Ions Test - Chlorine (Cl-)
White precipitate produced

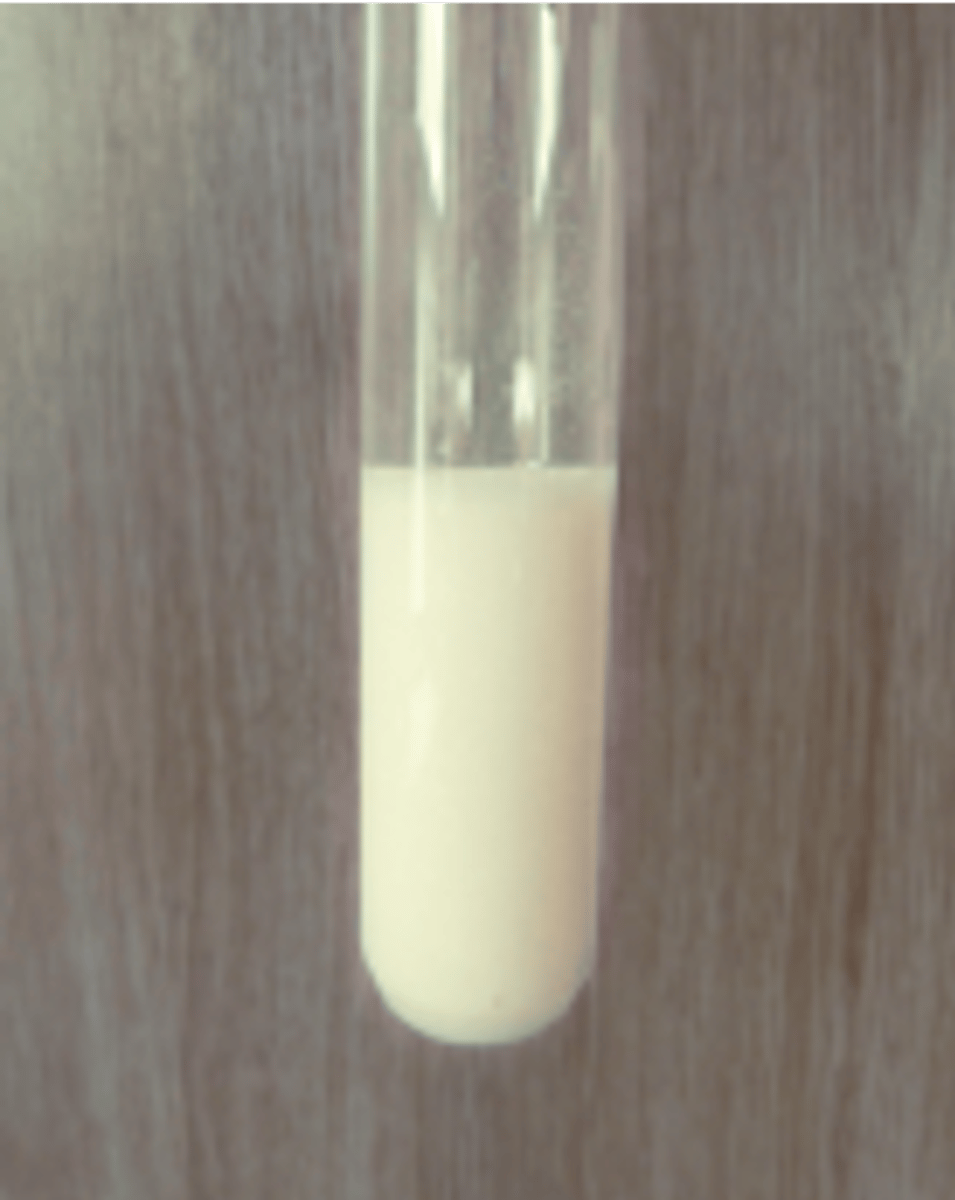
Halide Ions Test - Bromide (Br-)
Cream precipitate produced

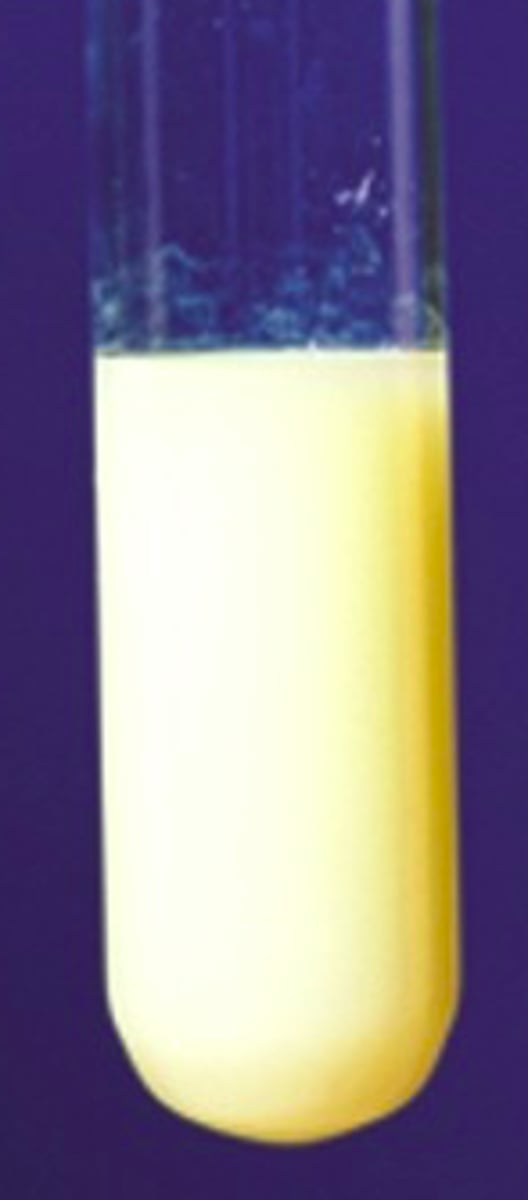
Halide Ions Test - Iodine (I-)
Yellow precipitate produced

Instrumental Analyses Methods - Sensitive
Instruments can analyse small amounts of solution so if the substance is difficult to obtain or expensive, it is easier
Instrumental Analyses Methods - Accurate
Can be calibrated using internationally accepted standards in such a way that all who use it will get the exact same result
Instrumental Analyses Methods - Speed
Instruments can carry out analysis quickly and can run all the time
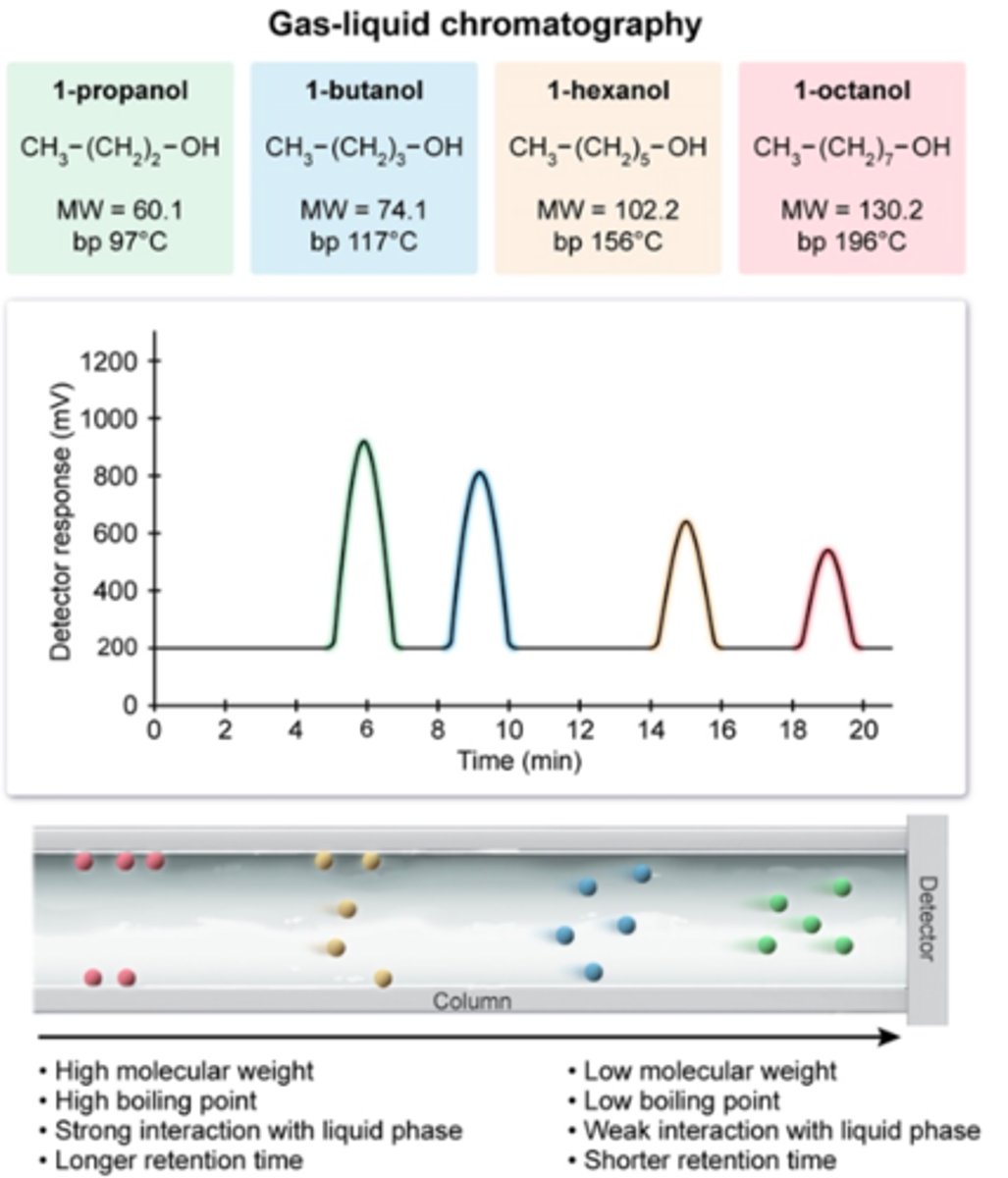
Interpreting Gas Chromatography
- Each peak represents a substance present in the mixture
- Area under the peak shows the relative amount of each substance in the mixture (how much there is)
- the DTETCTION TIME is the time taken for the substance to travel through the chromatography column (different for each substance)
Metals Reacting with Water and Dilute Acids
- Metals form positive ions in reactions
- The easier this happens the more reactive the metal
- A metal can react with water or dilute acids if it is more reactive than hydrogen
- Metal + Water = Metal Hydroxide + Hydrogen
- Metal + Acid = Salt + Hydrogen
Metal Displacement Reactions
- A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from a compound
- They are REDOX reactions
- E.g. Copper is more reactive than silver so it can displace silver
Cu + 2AgNO3 = Cu(NO3)2 + 2Ag
Predicting Reactions
- Elements in Group 8 do not react
- Reactive non-metals may form covalent bonds with each other
- Metals in Group 1 / 2 become more reactive going down the group
- Metals in Group 1 / 2 are more reactive than transition metals
- Non-Metals in Group 7 become less reactive going down the group
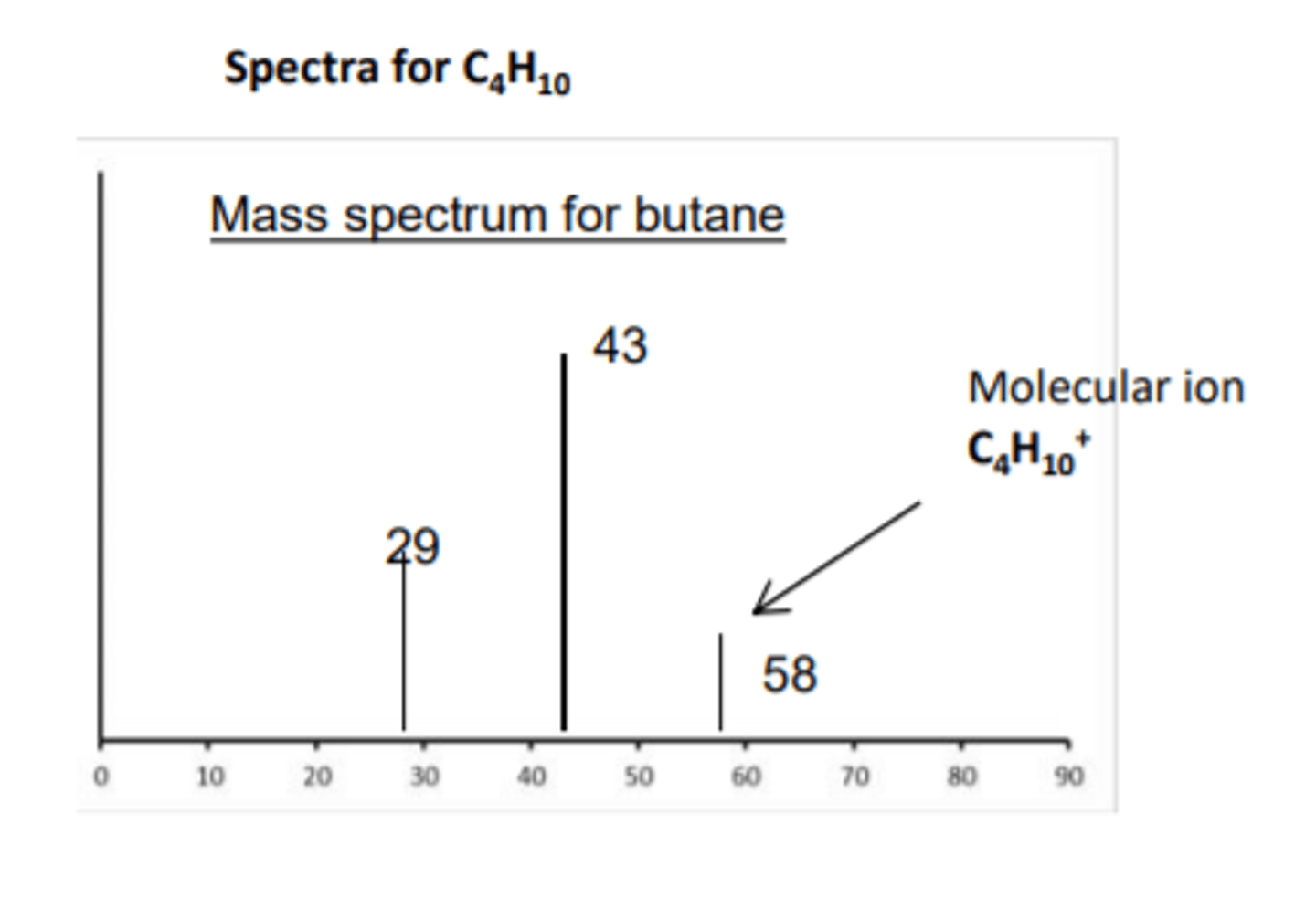
Interpreting Mass Spectra
- A mass spectrometer measures the mass of atoms and molecules
- It analyses the relative amounts of different isotopes of an element and the structure of molecules
- The sample molecules are ionised by the machine to form molecular ions
- They break up to form fragments which the machines separates and detects
- Each peak represents a fragment and the peak on the far right represents the molecular ion
- The mass to charge ratio of the molecular ion peak is equal to the relative formula mass of the molecule