Understanding Parasitism and Symbiotic Relationships
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Symbiosis
A close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms.
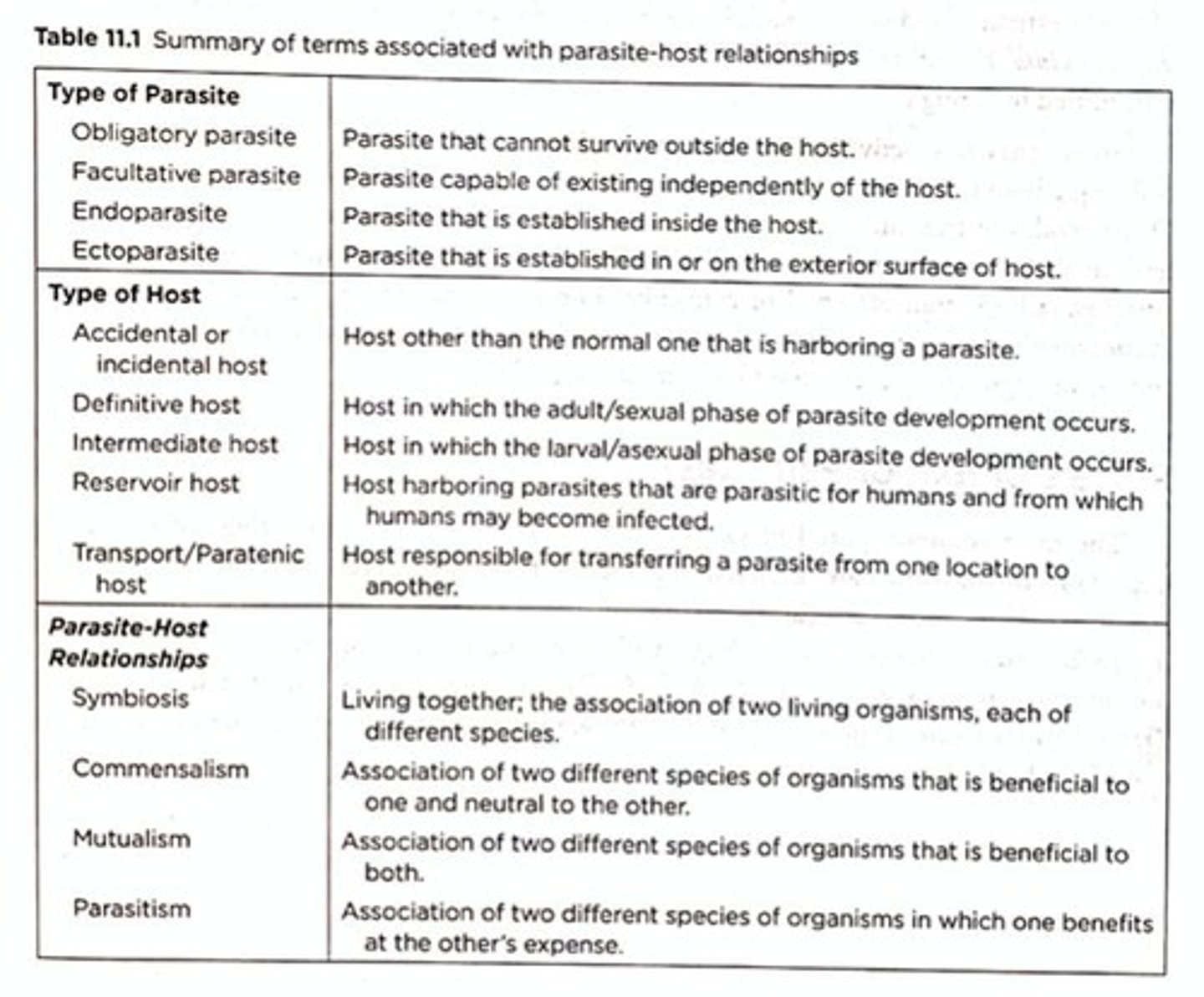
Commensalism
A type of symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits while the other is neither helped nor harmed.
Mutualism
A type of symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit from the interaction.
Parasitism
A type of symbiotic relationship where one organism benefits at the expense of another.
Hosts
Organisms that harbor parasites.
Ectoparasites
Parasites that live on the external surface of a host.
Endoparasites
Parasites that live inside the host's body.
Facultative parasites
Parasites that can live independently of their host.
Obligate parasites
Parasites that cannot live outside of their host.
Permanent parasites
Parasites that remain in or on the host for their entire life cycle.
Intermittent parasites
Parasites that do not remain on the host continuously.
Incidental parasites
Parasites that are not normally found in a particular host.
Transitory parasites
Parasites that are temporary and do not establish a permanent relationship with the host.
Erratic parasites
Parasites that are found in an unusual location in the host.
Definitive hosts
Hosts in which the parasite reaches maturity and reproduces.
Intermediate hosts
Hosts that harbor the parasite during its immature stages.
Reservoir hosts
Hosts that harbor the parasite and serve as a source of infection for other hosts.
Paratenic hosts
Hosts that are not essential for the parasite's development but can help in its transmission.
Modes of Transmission
The various ways parasites are transmitted from one host to another.
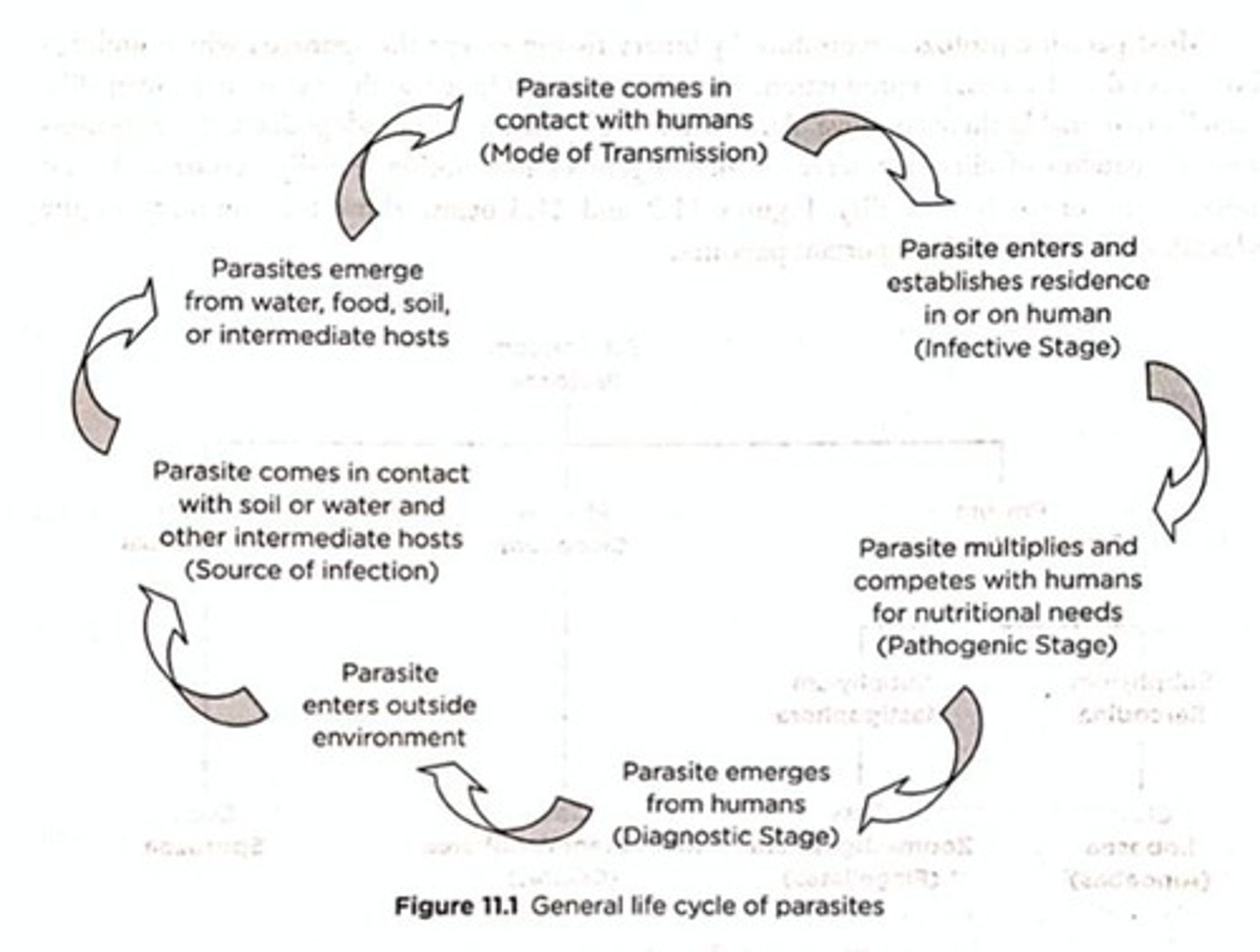
Pathogenesis
The dynamics of any disease process caused by parasites.
Specimen Collection
The proper way of collecting and handling specimens for laboratory analysis.
Microscopic Examination
A laboratory procedure used to identify parasites in specimens.