Advantages and disadvantages in business
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
brand image
adv:
Consumers recognize the firm’s product more easily
Their product can be charged higher than less well-known brands
Easier to launch new products into the market if the brand image is already established
Organizational structure
Advantages:
All employees are aware of which communication channel is used to reach them with messages
Everyone knows their position in the business. They know who they are accountable to and who they are accountable for
It shows the links and relationship between the different departments
Gives everyone a sense of belonging as they appear on the organizational chart
niche market
Advantages:
Small firms can thrive in niche markets where large firms have not yet been established
If there are no or very few competitors, firms can sell products at a high price and gain high profit margins because customers will be willing to pay more for exclusive products
Firms can focus on the needs of just one customer group, thereby giving them an advantage over large firms who only sell to the mass market
Limitations:
Lack of economies of scale (can’t benefit from the lower costs that arise from a larger operations/market)
Risk of over-dependence on a single product or market: if the demand for the product falls, the firm won’t have a mass product they can fall back on
Likely to attract competition if successful
Difficult for business to grow as it only targets a specific group
Multinational companies in home countries (where they started)
Advantages:
MNCs create opportunities for marketing products produced in the home country throughout the world.- which can increase market share and customer awareness
They create employment opportunities to the people of home country, both at home and abroad.
It aids and encourages the economic growth and development of the home country because of repatriation (remittance)
MNCs help to maintain favourable balance of payments as they export their products abroad so the exports will be higher than the imports.
Disadvantages:
MNCs transfer capital from the home country to various host countries causing unfavourable balance of payments.
MNCs may not create employment opportunities to the people of home country if it employs labour from other countries, perhaps due to lower costs or better skills.
As investments in foreign countries is more profitable, MNCs may neglect the home country’s industrial and economic development.
new product development
Advantages:
Can create a Unique Selling Point (USP) by developing a new innovative product for the first time in the market. This USP can be used for the product as well as in advertising.
Charge higher prices for new products (
Increase potential sales, revenue and profit
Helps spreads risks because having more products mean that even if one fails, the other will keep generating a profit for the company
Disadvantages:
Market research is expensive and time consuming
Investment can be very expensive
mass market
Advantages:
Larger amount of sales when compared to a niche market
Can benefit from economies of scale: a large volume of products are produced and so the average costs will be low when compared to a niche market
Risks are spread. If the product isn’t successful in one market, it’s fine as there are several other markets
More chances for the business to grow since there is a large market.
Limitations:
They will have to face more competition
Can’t charge a higher price than competition because they’re all selling similar products
Sole Trader
Advantages:
Profit not shared
maker own decisions
Own boss ➔ can do whatever you want
Independence ➔ can work at own pace etc.
Easy to set up ➔ few formalities ➔ therefore cheaper to set up
Disadvantages:
Unlimited liability ➔ responsible for debts of the business
no continuity
opportunity cost
Limited sources of resources
Partnerships
Advantages:
more capital invested than sole traders
Extra skills / expertise in business ➔ may be able to specialise in aspects of business to provide a better service
More people to make decisions ➔ more considered approach to running the business ➔ more ideas which may lead to success
shared risks
Disadvantages:
partners may disagree ➔ time used up in discussion ➔ decisions take longer
Profits will be shared ➔ compared to a sole trade where the owner can keep all profits to themselves
Some partners may not work as hard as others ➔ may demoralise/ lead to arguments
No continuity
unlimited liability ➔ the partners will be held responsible for the debts of the business
Public Limited Companies (Plc)
Advantages:
Limited liability
Continuity
can sell shares to the public
large capital sums
Disadvantages:
Cost of setting up ➔ with documents
Need to share profits ➔ with shareholders
affairs not kept private ➔ need to publish accounts
May lose ownership if too many shares are bought
Private Limited Companies (LTD)
Advantages:
Limited liability ➔ if business fails ➔ the owner will not lose personal possessions
have Continuity
More capital ➔ by selling shares ➔ may be easier to get bank loans
Specialised management ➔ shareholder /owners / managers can do the work they are skilled at
Invited shareholders ➔ able to maintain control
Disadvantages:
Legal procedure in setting up takes time and
costs money
Having to disclose the accounts ➔ financial
information can be looked at by the public/competitors
Profits have to be shared with the other shareholders
Slower decision-making ➔ especially if all shareholders have to be consulted
advantages to Businesses of Having a Well Motivated Workforce
Increase productivity / workers produce more
per hour worked / improve performance of workers ➔ could lead to greater profits
low labour turnover ➔ workers will be happy in their work and will stay loyal ➔ reduce recruitment / training costs
Lower absenteeism ➔ workers are happy ➔ improves productivity
committed workers ➔ experienced and likely to be more efficient
Improved employer / employee relations ➔ strike action is low
Improved quality of products
Improved business reputation ➔ easier to recruit the best workers
Ways to Raise Worker Performance
Higher Pay
to encourage workers to work harder ➔ may be short-term benefit
but this will increase the business cost
Bonus / Commission
will relate pay to amount / quality of work
but may be expected by workers, targets to be set ➔ demotivation if not achieved
Longer Holidays
to provide rest / enthusiasm for work
will cost ➔ will mean work not being done ➔ dissatisfied customers
Promotion / job title
gives feeling of importance ➔ reward for work
but only limited availability ➔ envy in the workplace
Health care / insurance
encourages workers to stay
but cost
Training / better qualifications
worker feels better about self ➔ encouraged to work harder
but cost of training ➔ better qualified workers may find jobs elsewhere ➔ increased worker turnover
Rewards for best workers
employee of the week ➔ motivate employee to work harder to get the award
but may demotivate others
long chain of command
Advantages:
narrow spans of control ➔ can help to limit managers’ workloads
clear and more regular opportunities for promotion of junior employees
Disadvantages:
communication may be more difficult as it passes through many levels of hierarchy
decisions can be made slowly as information has to be passed through the organisation
short chain of command
Advantages:
fewer managers ➔ can help to reduce costs
junior employees may be motivated by being given more authority
communication can be quick and effective as fewer levels of hierarchy
Disadvantages:
managers may have spans of control that are too wide
the business may have to spend heavily on training to give junior employees the necessary skills
Primary Research
Advantages:
Up-to-date
Specific to a business’ own needs / accurate
Provides answers to exact questions that a firm may be interested in
Disadvantages:
Can be very expensive to collect
Can be very time consuming to collect
Can have problems of bias
Secondary Research
Advantages:
not expensive to collect and gather
Enables cost-effective analysis of several data sources
Disadvantages:
Often out of date
Might not be available
Little control over quality
Problems of interpretation
competitors also have access to it
Penetration Pricing
advantage:
The goods have a low price to attract customers who may then stay with the business.
disadvantage:
When prices rise people may not be willing to purchase – questions over quality
Cost Plus Pricing
advantage:
Adding profit to cost ensures that a profit is made on each good.
disadvantage:
May not work in competitive market / depends on margins.
Price Skimming
advantage:
Attracts early adopters e.g. new football boots, the latest iPhone.
disadvantage
Some customers unable to / unwilling to pay the high prices.
Psychological Pricing
advantage:
Can nudge customers to make a purchase
disadvantage:
Some may not be convinced to buy so revenue may not rise / customers may not be attracted to the business.
Competitive Pricing
advantage:
Ensures that the firm is price competitive.
disadvantage:
Customers may be used to buying from competitors so revenue might not change / customers may not switch from rivals.
e- commerce on business
advantage:
Wider market ➔ so the business will be able to attract more customers ➔ more sales
Expansion/growth possible ➔ without having to locate/fund new sites
Keep up with competitors
Convenience ➔ for customers who cannot travel to the shop
disadvantage:
Effects on current business ➔ with time ➔ efforts spent with website
Reputation may be diminished ➔ website crashes, problems with delivery
Costs of setting More storage space may be needed ➔ so higher warehouse costs
Some higher costs ➔ maintenance / special
packaging / delivery / returns
Possible fraud ➔ related to payments
no relationship with Customer
e- commerce on customer
advantage:
Can see images of products so can compare many products
Prices ➔ many sellers can be compared on one computer
No need to travel so costs saved
Wider choice from many sellers
Order 24/7
disadvantage:
Goods not inspected to see if goods meet the need
Images may be misleading so difficult to judge quality
Delays in receiving goods
If goods need to be returned there could be additional costs incurred
Possibility of fraud if goods not sent when
paying
Technical issues e.g. reliability, speed
Manufacturer to Consumer
Advantage:
All of the profit is earned by the producer
The producer controls all parts of the marketing mix
Quickest method of getting the product to the consumer
Disadvantages:
Delivery costs may be high if there are customers over a wide area
All storage costs must be paid for by the producer
All promotional activities must be carried out and financed by the producer
Manufacturer to Retailer to Consumer
Advantage:
The cost of holding inventories of the product is paid by the retailer
The retailer will pay for advertising and other promotional activities
Retailers are more conveniently located for consumers
Disadvantage:
The retailer takes some of the profit away from the producer
The producer loses some control of the marketing mix
The producer must pay for delivery of products to the retailers
Retailers usually sell competitors’ products as well
Manufacturer to Wholesaler to Retailer
to Consumer
Advantage:
Wholesalers will advertise and promote the product to retailers
Wholesalers pay for transport and storage costs
Wholesaler buys in bulk so less storage costs on producer
Disadvantage:
– Another middleman is added so more profit is taken away from the producer
– The producer loses even more control of the marketing mix
Manufacturer to Agent to Wholesaler to Retailer
to Consumer
Advantage:
The agent has specialised knowledge of the market
Disadvantage:
Another middleman is added so more profit is taken away from the producer
job production
Advantages:
Most suitable for one-off products and personal services
The product meets the exact requirement of the customer
Workers will have more varied jobs as each order is different
improving morale
very flexible method of production
Disadvantages:
Skilled labour will often be required which is expensive
Costs are higher for job production firms because they are usually labour-intensive
Production often takes a long time
Since they are made to order, any errors may be expensive to fix
Materials may have to be specially purchased for different orders, which is expensive
Batch Production
Advantages:
Flexible way of working- production can be easily switched between products
Gives some variety to workers job
more variety to consumers to choose from
Even if one product’s machinery breaks down, other products can still be made
Disadvantages:
Can be expensive since finished and semi-finished goods will need moving about
Machines have to be reset between production batches which delays production
Lots of raw materials will be needed for different product batches, which can be expensive.
Flow Production
Advantages:
There is a high output of identical products
Costs are low in the long run and so prices can be kept low
Can benefit from economies of scale in purchasing
Automated production lines can run 24×7
Goods are produced quickly and cheaply
Capital-intensive production, so reduced labour costs and increases efficiency
Disadvantages:
A very boring system for the workers, leads to low job satisfaction and motivation
Lots of raw materials and finished goods need to be held in inventory- this is expensive
Capital cost of setting up the flow line is very high
If one machinery breaks down, entire production will be affected
Technology and Production
Advantages of technology in production
Greater productivity
Greater job satisfaction among workers as boring, routine jobs are done by machines
Better quality products
More accurate demand levels are forecast since computer monitor inventory levels
New products can be introduced as new production methods are introduced
Disadvantages of technology in production
Unemployment rises as machines and computers replace human labour
Expensive to set up
frequent updating of systems will be needed- this is expensive and time-consuming.
Employees may take time to adjust to new technology or even resist it as their work practices change.
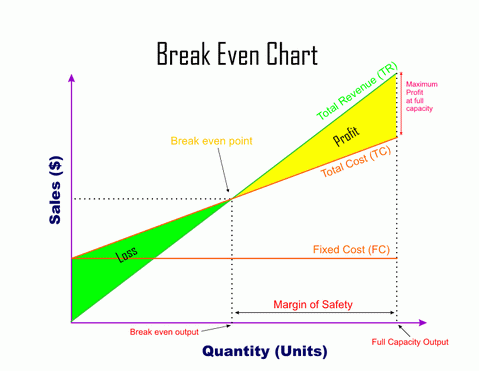
break-even charts:
Advantages of break-even charts:
Managers can find out the profit or loss at each level of output
Managers can change the costs and revenues and redraw the graph to see how that would affect profit and loss
help calculate the safety margin- the amount by which sales exceed break-even point.
Limitations of break-even charts:
assume all units of output produced are sold.
Fixed costs may not always be fixed if the scale of production changes. If more output is to be produced, an additional factory or machinery may be needed that increases fixed costs.
assume that costs can always be drawn using straight lines. Costs may increase or decrease due to various reasons. If more output is produced, workers may be given an overtime wage that increases the variable cost per unit and cause the variable cost line to steep upwards.
Quality Control
Advantages:
Eliminates the fault or defect before the customer receives it, so better customer satisfaction
Not much training required for conducting this quality check
Disadvantages:
expensive to hire employees to check for quality
may find faults and errors but doesn’t find out why the fault has occurred, so the it’s difficult to solve the problem
if product has to be replaced and reworked, then it is very expensive for the firm
Quality Assurance
Advantages:
Eliminates the fault or defect before the customer receives it, so better customer satisfaction
Since each stage of production is checked for quality, faults and errors can be easily identified and solved
Products don’t have to be scrapped or reworked as often, so less expensive than quality control
Disadvantages:
Expensive to carry out since quality checks have to be carried throughout the entire process, which will require manpower and appropriate technology at every stage.
How well will employees follow quality standards? The firm will have to ensure that every employee follows quality standards consistently and prudently, and knows how to address quality issues.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Advantages:
quality is built into every part of the production process and becomes central to the workers principles
eliminates all faults before the product gets to the final customer
no customer complaints and so improved brand image
products don’t have to be scrapped or reworked, so lesser costs
waste is removed and efficiency is improved
Disadvantages:
Expensive to train all employees
Relies on all employees following TQM– how well are they motivated to follow the procedures?
Retained Profit
Advantages:
Does not have to be repaid, unlike, a loan.
No interest has to be paid
Disadvantages:
A new business will not have retained profit
Profits may be too low to finance
Keeping more profits to be used as capital will reduce owner’s share of profit and they may resist the decision.
Sales of existing assets
Advantages:
Makes better use of capital tied up in the business
Does not become debt for the business, unlike a loan.
Disadvantages:
Surplus assets will not be available with new businesses
Takes time to sell the asset and the expected amount may not be gained for the asset
Sale of inventories
Advantage:
Reduces costs of inventory holding
Disadvantage:
If not enough inventory is kept, unexpected increase demand from customers cannot be fulfilled
Owner’s savings
Advantages:
Will be available to the firm quickly
No interest has to be paid.
Disadvantages:
Increases the risk taken by the owners.
Issue of share: only for limited companies.
Advantage:
A permanent source of capital
no need to repay the money to shareholders
no interest paid
Disadvantages:
Dividends have to be paid to the shareholders
If many shares are bought, the ownership of the business will change hands
Bank loans: money borrowed from banks
Advantages:
Quick to arrange a loan
Can be for varying lengths of time
Large companies can get very low rates of interest on their loans
Disadvantages:
Need to pay interest on the loan periodically
It has to be repaid after a specified length of time
Need to give the bank a collateral security (the bank will ask for some valued asset, as a security they can use if at all the business cannot repay the loan in the future.
Debenture issues: debentures are long-term loan certificates issued by companies.
Advantage:
Can be used to raise very long-term finance
Disadvantage:
Interest has to be paid and it has to be repaid
Debt factoring:Debt factors are specialist agents that can collect all the business’ debts from debtors.
Advantages:
Immediate cash is available to the business
Business doesn’t have to handle the debt collecting
Disadvantage:
The debt factor will get a percent of the debts collected as reward. Thus, the business doesn’t get all of their debts
Grants and subsidies
Advantage:
Do not have to be repaid, is free
Disadvantage:
Come with strings attached
Example, to locate in a particular under-developed area.
Overdrafts
Advantages:
amount overdrawn can be varied each month
Interest has to be paid only on the amount overdrawn
Overdrafts are generally cheaper than loans in the long-term
Disadvantages:
Interest rates can vary periodically, unlike loans which have a fixed interest rate.
The bank can ask for the overdraft to be repaid at a short-notice.
Trade Credits: this is when a business delays paying suppliers for some time, improving their cash position
Advantage:
No interests, repayments involved
Disadvantage:
If the payments are not made quickly, suppliers may refuse to give discounts in the future or refuse to supply at all
Hire Purchase: allows the business to buy a fixed asset and pay for it in monthly instalments that include interest charges.
Advantage:
The firms doesn’t need a large sum of cash to acquire the asset
Disadvantage:
A cash deposit has to be paid in the beginning
Can carry large interest charges.
globalisation
Advantages of globalisation
Allows businesses to start selling in new foreign markets- increasing sales and profits
Can open factories and production units in other countries, at a cheaper rate (cheaper materials and labour can be available in other countries)
Import products from other countries and sell it to customers in the domestic market- this could be more profitable than producing and selling the good themselves
Import materials and components for production from foreign countries at a cheaper rate.
Disadvantages of globalisation
now that foreign firms can compete in other countries, it puts up much competition for domestic firms. If these domestic firms cannot compete with the foreign goods’ cheap prices and high quality, they may be forced to close down operations.
Increasing investment by multinationals in home country- this could further add to competition in the domestic market
Employees may leave domestic firms if they don’t pay as well as the foreign multinationals in the country- businesses will have to increase pay and conditions to recruit and retain employees.
Leasing
Advantages:
The firm doesn’t need a large sum of money to use the asset
The care and maintenance of the asset is done by the leasing company
Disadvantage:
The total costs of leasing the asset could finally end up being more than the cost of purchasing the asset!
Multinational Companies (MNCs) in domestic countries (where they go to)
Advantages:
More jobs created
Increases GDP of the country
The technology that the multinational brings in can bring in new ideas and methods into the country
imports will be reduced and some output can even be exported
Multinationals will also pay taxes, thereby increasing the government’s tax revenue
More product choice for consumers
Disadvantages :
The jobs created are often for unskilled tasks. The unskilled workers may also be exploited with very low wages and unhygienic working conditions.
local firms may be forced out of industry, unable to survive the competition
Multinationals can use up the scarce, non-renewable resources in the country
Repatriation of profit- profits earned by the multinational could be sent back to their home country
As multinationals are large, they can influence the government and economy. They could threaten the government that they will close down and make workers unemployed if they are not given financial grants and so on.
Environmental factors
advantages of business meeting sustainable development:
Meeting government targets ➔ avoids having to pay fines ➔ reducing costs and potentially increasing profits ➔ avoids bad publicity
Showing concern for the environment ➔ important for the image of the business ➔ leading to increased sales with those that share concerns
Consumer pressures ➔ more likely to recommend business ➔ all important for the image of business ➔ leads to increased sales
Pressure groups ➔ less likely to give unfavourable attention to businesses who employ environmental policies
disadvantages of business meeting sustainable development:
Business costs of being environmentally friendly impact negatively on profit margins
Packaging issues such as cost / finding alternatives ➔ increased business costs ➔ impacting negatively on profits or pricing flexibility