Anatomy and physiology chap 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
Last updated 12:09 PM on 10/28/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
1
New cards
Chemistry
The science of change: structure of atoms, basic chemical building blocks, atoms combine to form increasingly complex structures
2
New cards
Matter
Made up of atoms; atoms join together to form chemicals with different characteristics; chemical characteristics determine physiology at the molecular and cellular levels
3
New cards
Atoms
Building blocks of matter
4
New cards
Subatomic particles
protons, neutrons, electrons
5
New cards
Proton
Positive charge, 1 mass unit
6
New cards
Neutron
Neutral, 1 mass unit
7
New cards
Electron
Negative charge, low mass
8
New cards
Atomic structure
atomic number, nucleus, electron cloud
9
New cards
Atomic number
Number of protons
10
New cards
Nucleus
Contains protons and neutrons
11
New cards
Electron cloud
Contains electrons
12
New cards
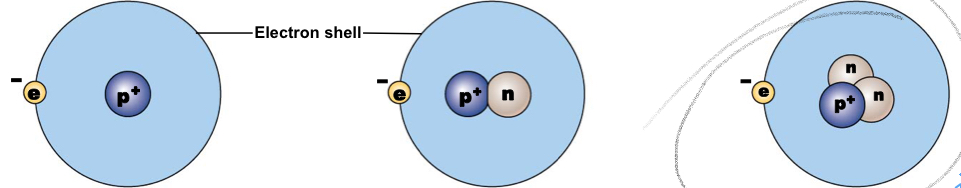
Hydrogen-1
A typical hydrogen nucleus contains a proton and no neutrons, mass number:1
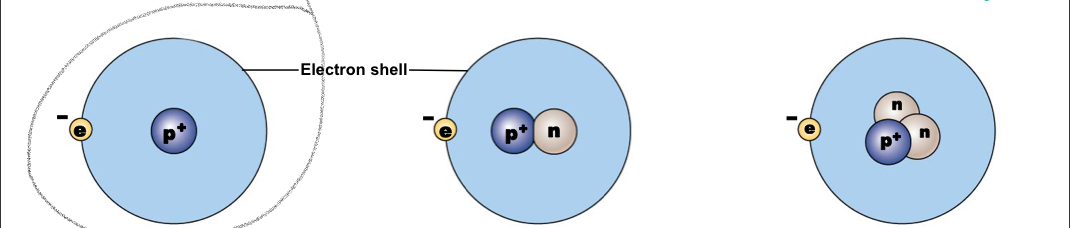
13
New cards
Hydrogen-2, deuterium
Nucleus contains a proton and a neutron, mass number: 2
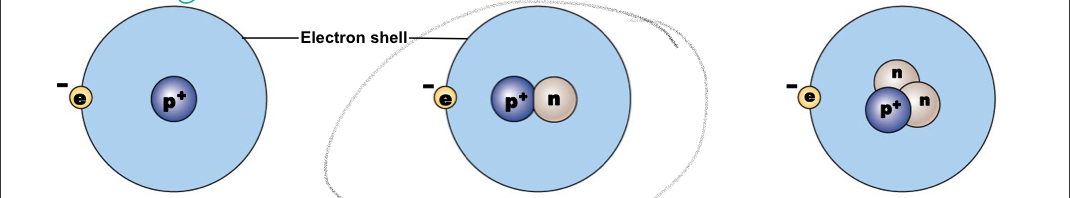
14
New cards
Hydrogen-3, tritium
Nucleus contains a proton and two neutrons, mass number: 2
15
New cards
Oxygen, O (65)
A component of water and other compounds; gaseous form is essential for respiration
16
New cards
Carbon, C (18.6)
Found in all organic molecules
17
New cards
Hydrogen, H (9.7)
A component of water and most other compounds in the body
18
New cards
Nitrogen, N (3.2)
Found in proteins, nucleic acids, and other organic compounds
19
New cards
Calcium, Ca (1.8)
Found in bones and teeth; important for membrane function, nerve impulses, muscle contraction, and blood clotting
20
New cards
Elements
Determined by atomic number of an atom; most basic chemicals
21
New cards
Isotopes
Specific version of an element based on its mass number
22
New cards
Mass number
Number of proton plus the number of neutrons
23
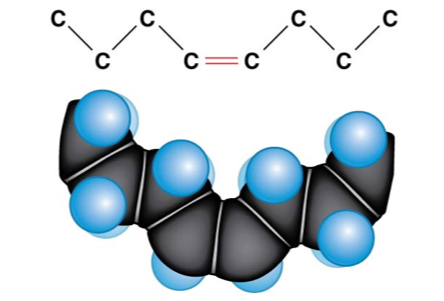
New cards
Why only are the number of neutrons different?
Because the number of protons determines the elements
24
New cards
Atomic weight
Exact mass of all particles; measured in moles; average of the mass numbers of the isotopes
25
New cards
Electrons in the electron cloud
Determine the reactivity of an atom
26
New cards
Electron cloud
Contains shells, or energy levels, that hold a maximum number of electrons
27
New cards
Valence shell
Outermost shell that determines bonding
28
New cards
Chemical bonds
Involve the sharing, gaining, and losing of electrons in the valence shell; form molecules and/or compounds
29
New cards
Three types of chemical bonds
Ionic, covalent, hydrogen
30
New cards
Ionic bonds
Attraction between cations (electron donor) and anions (electron acceptor) then draws the two ions together
31
New cards
Covalent bonds
Strong electron bonds involving shared electrons
32
New cards
Hydrogen bonds
Weak polar bonds based on partial electrical attractions; bonds between adjacent molecules, not atoms, slightly positive and negative portions of polar molecules being attracted to one another
33
New cards
Molecules
Two or more atoms joined by strong bonds
34
New cards
Compounds
Two or more atoms OF DIFFERENT ELEMENTS joined by strong or weak bonds
35
New cards
Explain: H2= Molecule only, H2O= molecule and compound
Compounds are all molecules, but not all molecules are compounds
36
New cards
Electron donor
Loses one or more electrons and becomes a cation, with a positive charge
37
New cards
Electron acceptor
Gains those same electrons from the donor and becomes an anion, with a negative charge
38
New cards
Ion
A subscript plus or minus sign following the symbol of an element
39
New cards
Single covalent bond
Sharing one pair of electrons
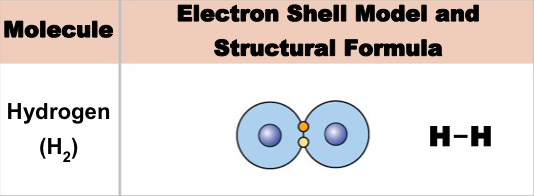
40
New cards
Double covalent bond
Sharing two pairs of electrons
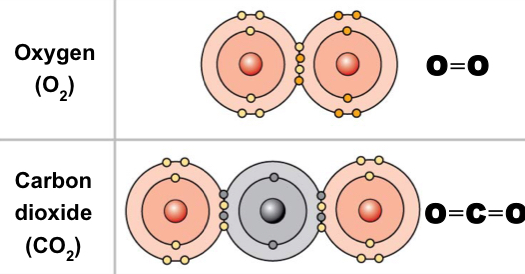
41
New cards
Triple covalent bond
Sharing three pairs of electrons
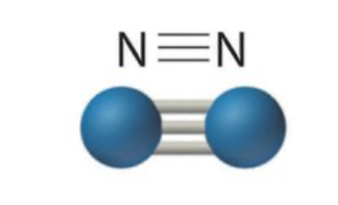
42
New cards
Nonpolar covalent bonds
Involve equal sharing of electrons because atoms involved in the bond have equal pull for the electrons
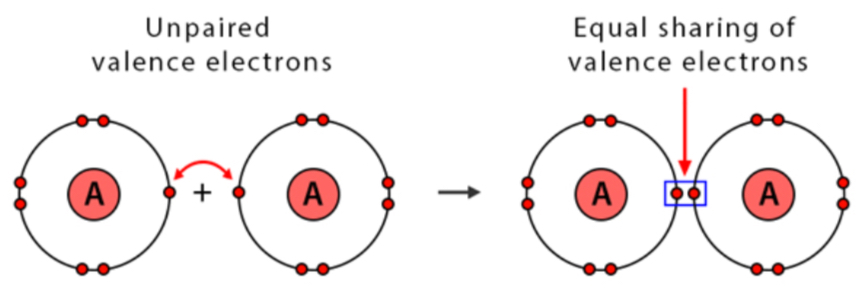
43
New cards
Polar covalent bonds
Involve unequal sharing of electrons because one of the atoms involved in the bond has a disproportionately strong pull on the electrons; ex: water
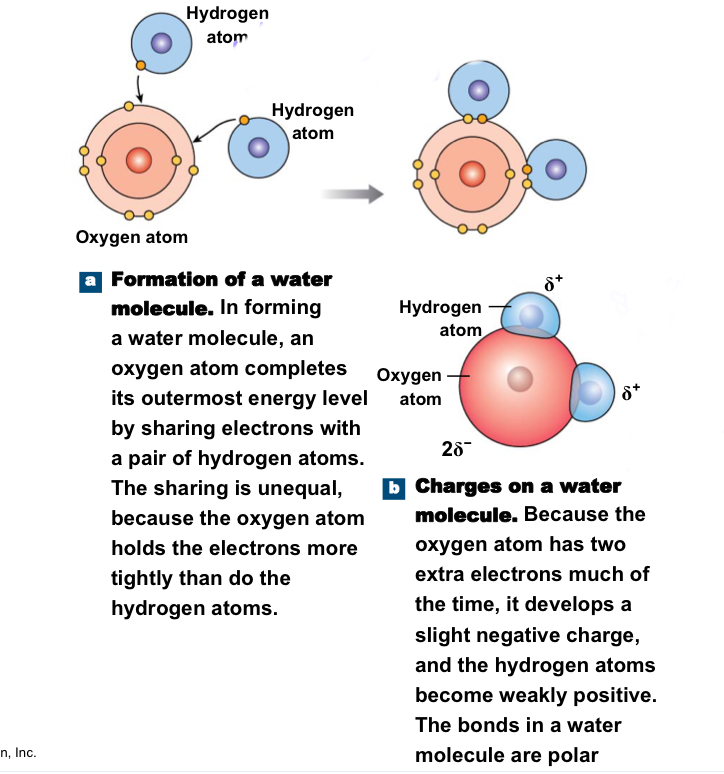
44
New cards
Hydrogen bonds between H2O molecules causes
Surface tension
45
New cards
Chemical reaction
Either new bonds are formed or existing bonds are broken; reactants, products, metabolism; in cells, cannot start without help
46
New cards
Reactants
Materials going into a reaction
47
New cards
Products
Materials coming out of a reaction
48
New cards
Metabolism
All of the reactions that are occurring at one time
49
New cards
Energy
Power to do work
50
New cards
Work
A change in mass or distance
51
New cards
Kinetic energy
Energy of motion
52
New cards
Potential energy
Stored energy
53
New cards
Chemical energy
Potential energy stored in chemical bonds
54
New cards
Types of chemical reactions
Decomposition (catabolism), synthesis (anabolism), exchange, reversible
55
New cards
Decomposition reaction (catabolism)
Breaks chemical bonds
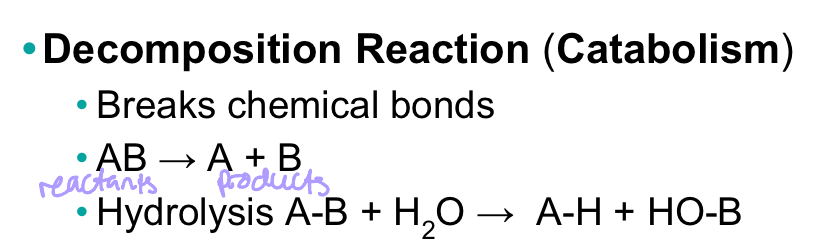
56
New cards
Synthesis reaction (anabolism)
Forms chemical bonds
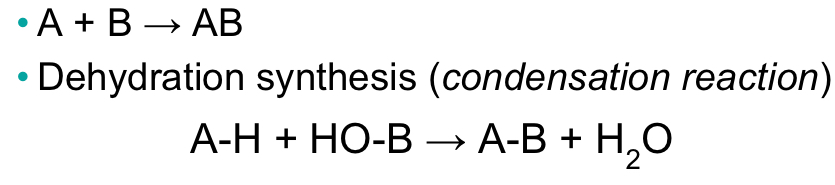
57
New cards
Exchange reaction
Involves decomposition first, then synthesis

58
New cards
Reversible reaction
At equilibrium the amounts of chemicals do not change even though the reactions are still occurring; seek equilibrium, balancing opposing reaction rates; add or remove reactants

59
New cards
Activation energy
The amount of energy needed to get a reaction started
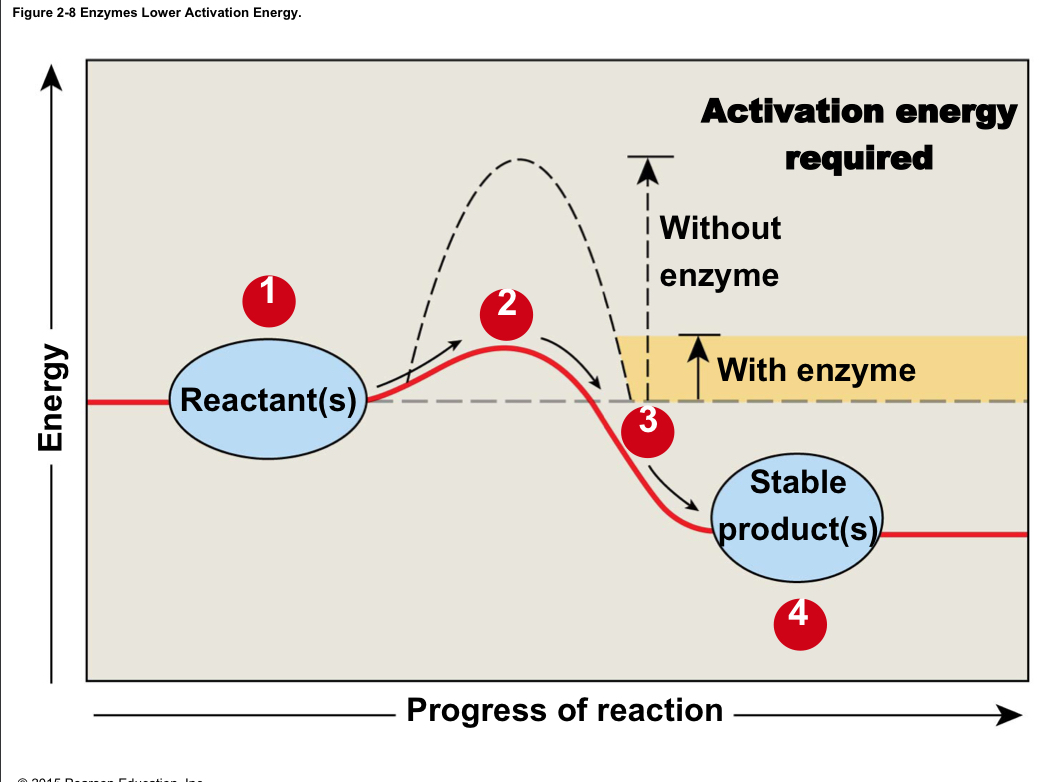
60
New cards
Enzymes
Protein catalysts that lower the activation energy of chemical reactions; are not changed or used up in the reaction
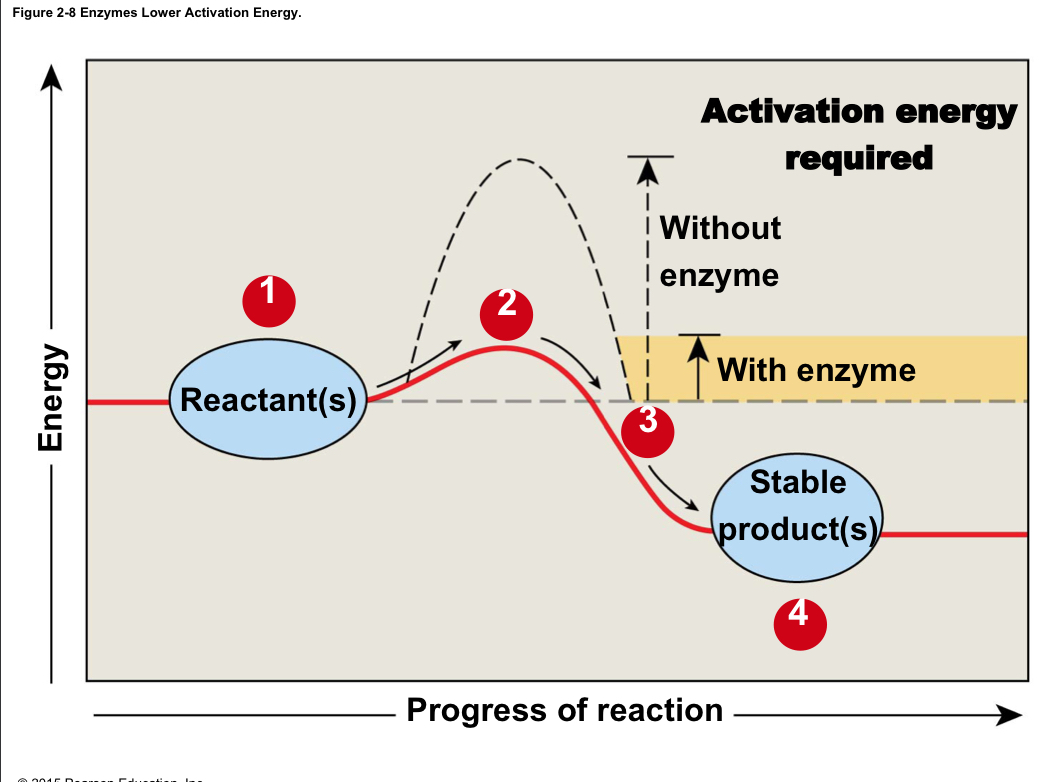
61
New cards
Exergonic (Exothermic) Reactions
Produce more energy than they use; releases energy; reaction ends with lower energy than it started with
62
New cards
Endergonic (Endothermic) Reactions
Use more energy than they produce; absorbs energy; reaction ends with higher energy than it started with
63
New cards
Nutrients
Essential molecules obtained from food
64
New cards
Metabolites
Molecules made or broken down in the body
65
New cards
Inorganic compounds
Molecules not based on carbon and hydrogen; carbon dioxide, oxygen, water, and inorganic acids, bases, and salts
66
New cards
Water
Accounts for up to two-thirds of your total body weight
67
New cards
Solution
Uniform mixture of two or more substances; consists of a solvent, or a medium, in which atoms, ions, or molecules of another substance, called a solute, are individually dispersed
68
New cards
Solubility
Water’s ability to dissolve a solute in a solvent to make a solution
69
New cards
Reactivity
Most body chemistry occurs in water
70
New cards
High heat capacity
Water’s ability to absorb and retain heat
71
New cards
Lubrication
To moisten and reduce friction
72
New cards
Colloid
A solution of very large organic molecules; ex: blood plasma
73
New cards
Suspension
A solution in which particles settle (sediment); ex: whole blood
74
New cards
Concentration
The amount of solute in a solvent (mol/L, mg/mL)
75
New cards
PH
The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution
76
New cards
Neutral pH
A balance of H+ and OH-; pure water= 7.0
77
New cards
Acidic
Lower than 7.0; high H+ concentration; low OH- concentration
78
New cards
Basic (or alkaline)
Higher than 7.0; low H+ concentration; high OH- concentration
79
New cards
pH of human blood
Ranges from 7.35 to 7.45
80
New cards
pH Scale
Has an inverse relationship with H+ concentration; more H+ ions means lower pH, fewer H+ ions means higher pH
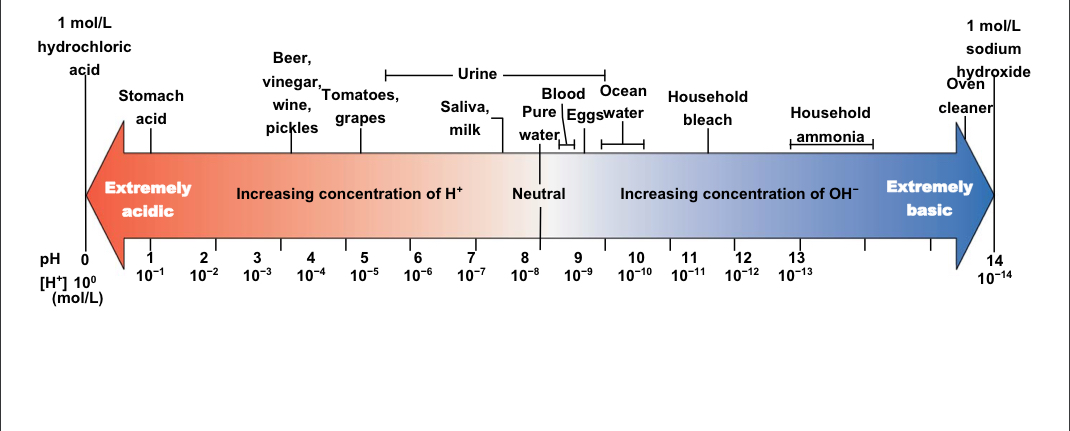
81
New cards
Acid
A solute that adds hydrogen ions to a solution; proton donor; strong ones dissociate completely in solution
82
New cards
Base
A solute that removes hydrogen ions from a solution; proton acceptor; strong ones dissociate completely in solution
83
New cards
Weak acids and weak bases
Fail to dissociate completely; help to balance the pH
84
New cards
Salts
Solutes that dissociate into cations and anions other than hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions
85
New cards
Buffers
Weak acid/salt compounds; neutralize either strong acid or strong base; sodium bicarbonate is very important in humans
86
New cards
Antacids
Basic compounds that neutralize acid and form a salt; alka-seltzer, tums, rolaids, etc
87
New cards
Organic molecules
Contain H, C, and usually O; covalently bonded; contain functional groups that determine chemistry; carbohydrates, lipids, proteins (amino acids), nucleic acids
88
New cards
Amino group— NH2
Acts as a base, accepting H+, depending on pH; can form bonds with other molecules; ex: amino acids
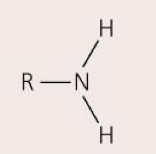
89
New cards
Carboxyl group— COOH
Acts as an acid, releasing H+ to become R—COO-; ex: fatty acids, amino acids
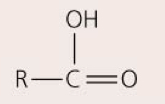
90
New cards
Hydroxyl group— OH
May link molecules through dehydration synthesis (condensation); hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl groups and water molecules affects solubility; ex: carbohydrates, fatty acids, amino acids
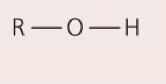
91
New cards
Phosphate group— PO4
May link other molecules to form larger structures; may store energy in high-energy bonds; ex: phospholipids, nucleic acids, high-energy compounds
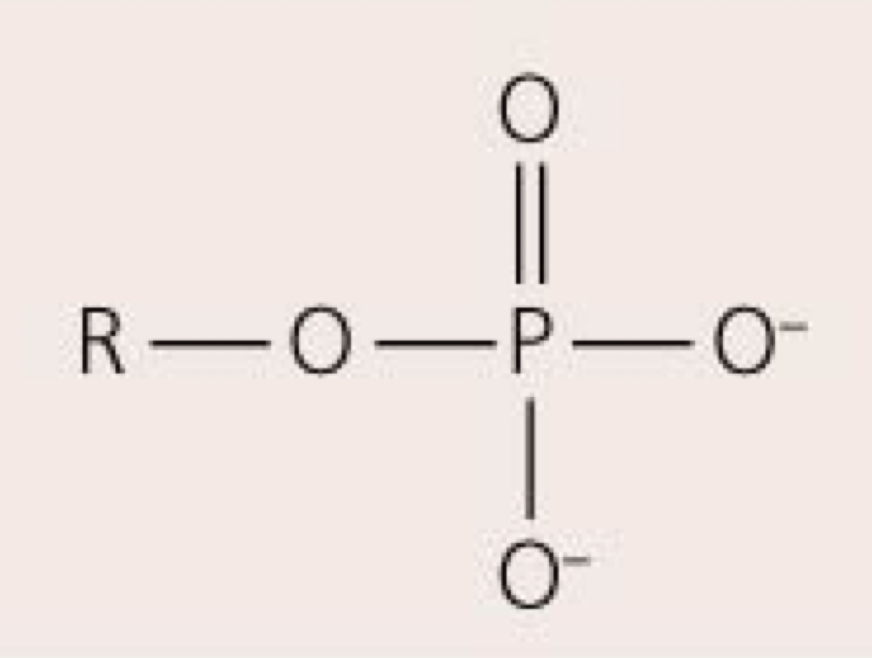
92
New cards
Carbohydrates
Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio; monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide
93
New cards
Monosaccharide
Simple sugars with 3 to 7 carbon atoms; ex: glucose, fructose, galactose
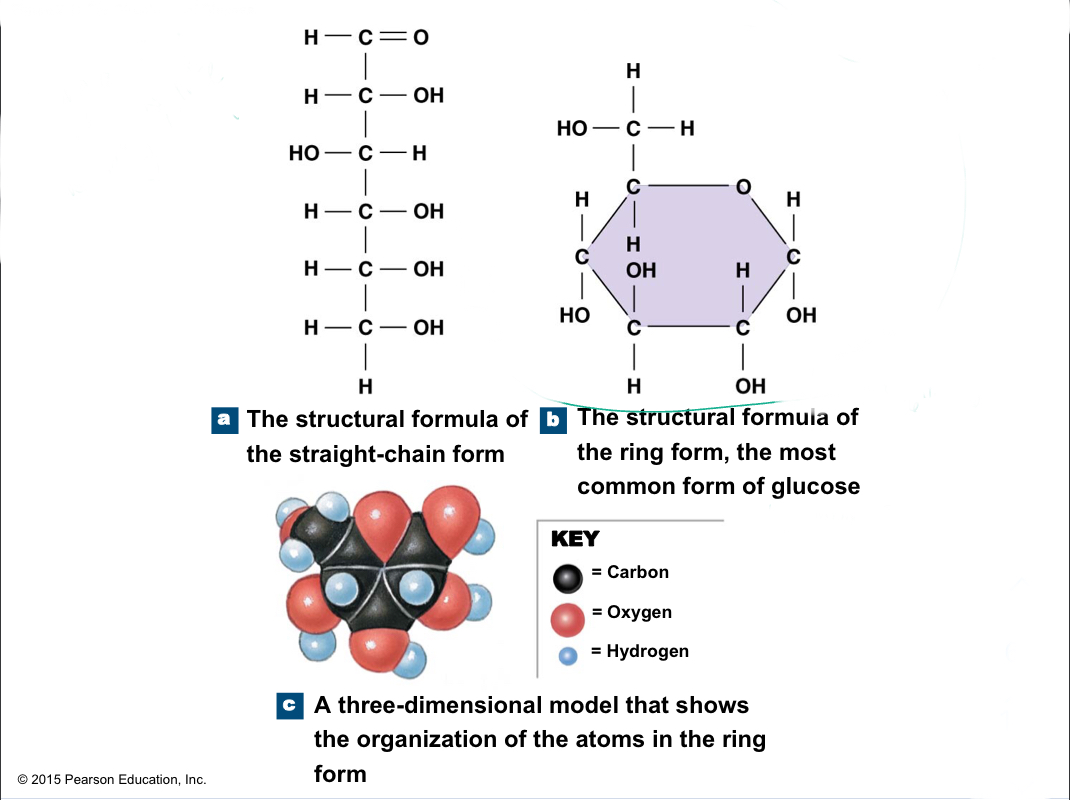
94
New cards
Disaccharide
Two simple sugars condensed by dehydration synthesis; ex: sucrose, maltose
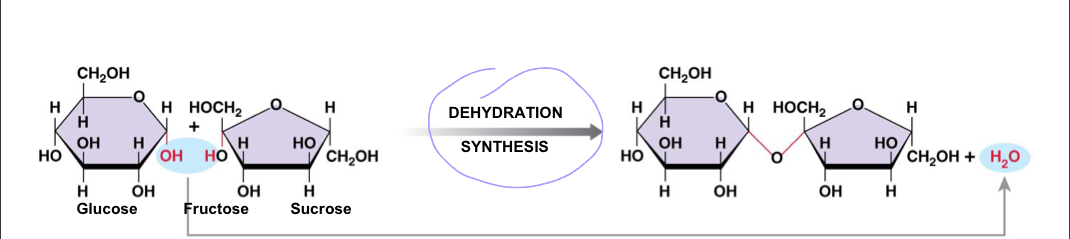
95
New cards
Polysaccharide
Many monosaccharide condensed by dehydration synthesis; ex: glycogen, starch, cellulose
96
New cards
Breakdown of sucrose into simple sugars by hydrolysis
Reverses the steps of dehydration synthesis; a complex molecule is broken down by the addition of a water molecule
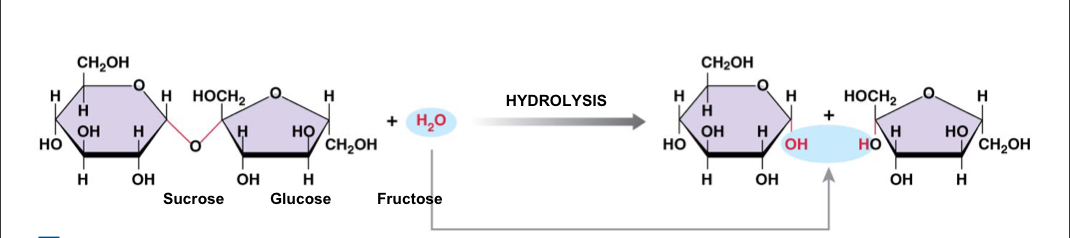
97
New cards
Lipids
Mainly hydrophobic molecules such as fats, oils, and waxes; made mostly of carbon and hydrogen atoms; fatty acids, eicosanoids, glycerides, steroids, phospholipids and glycolipids
98
New cards
Fatty acids
Long chains of carbon and hydrogen with a carboxyl group (COOH) at one end; relatively nonpolar, except the carboxyl group; saturated and unsaturated
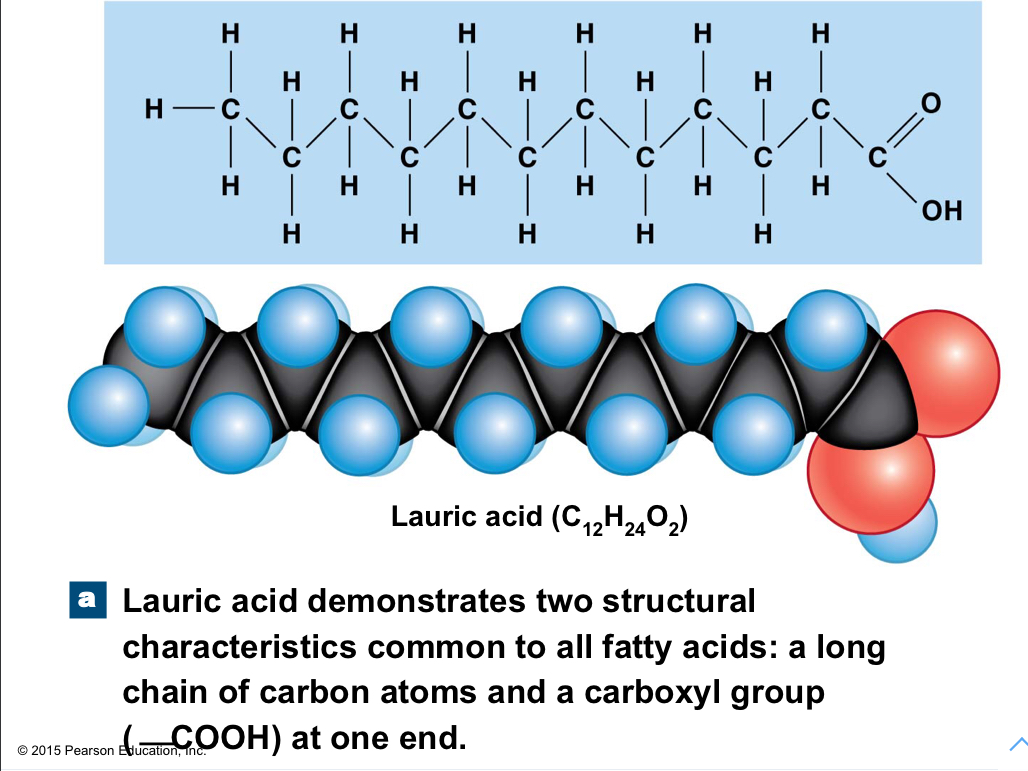
99
New cards
saturated fatty acid
With hydrogen, no covalent bonds
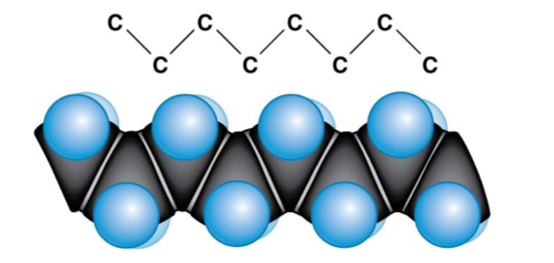
100
New cards
unsaturated fatty acid
One or more double bonds; monounsaturated, polyunsaturated