Intestinal Polyps & Neoplasia
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Hamartoma
Benign tumor that is the same type of tissue as the organ of biopsy
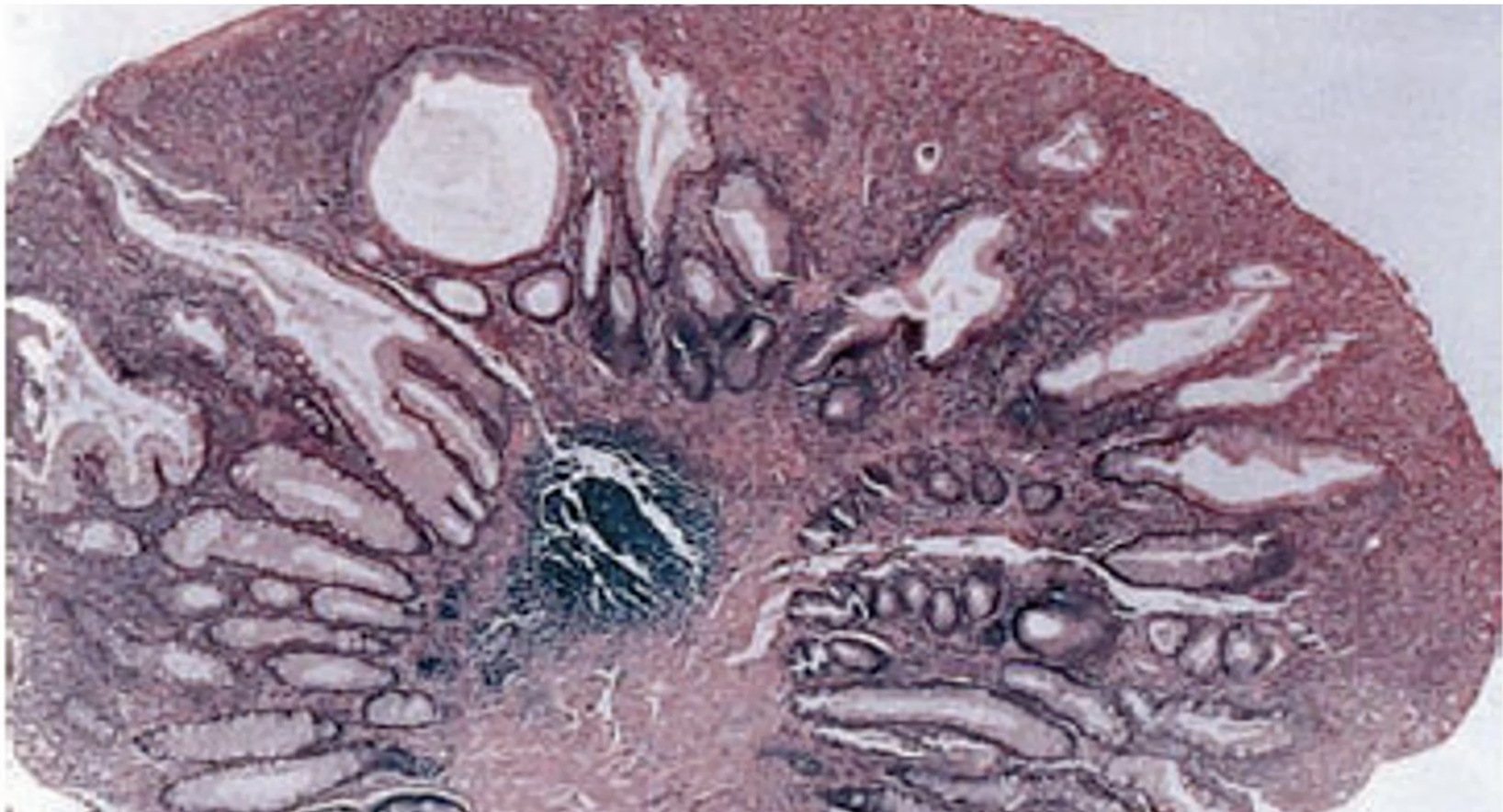
Juvenile Polyp
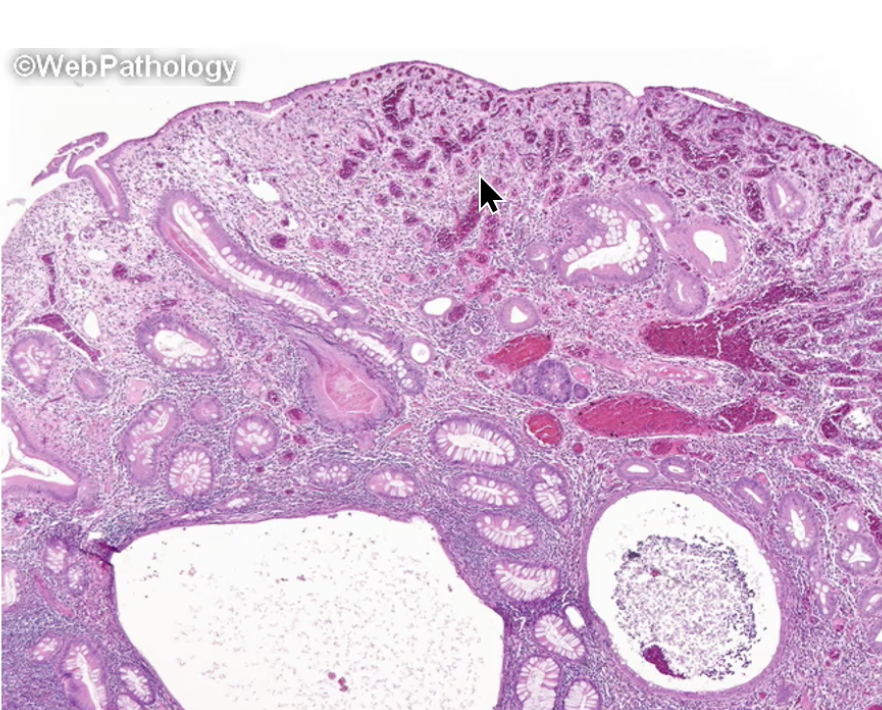
Juvenile Polyposis
Juvenile Polyposis
is a genetic condition with multiple juvenile polyps in the GI tract which increases the risk of colorectal cancer.
Common presentation for Juvenile Polyposis
<5 years old with rectal bleeding or anemia
SMAD4, BMPR1A
Juvenile Polyposis Genes
Peutz-Jegher Syndrome
is a genetic disorder with hamartomatous polyps in the GI tract and mucocutaneous pigmentation, increasing the risk of various cancers.
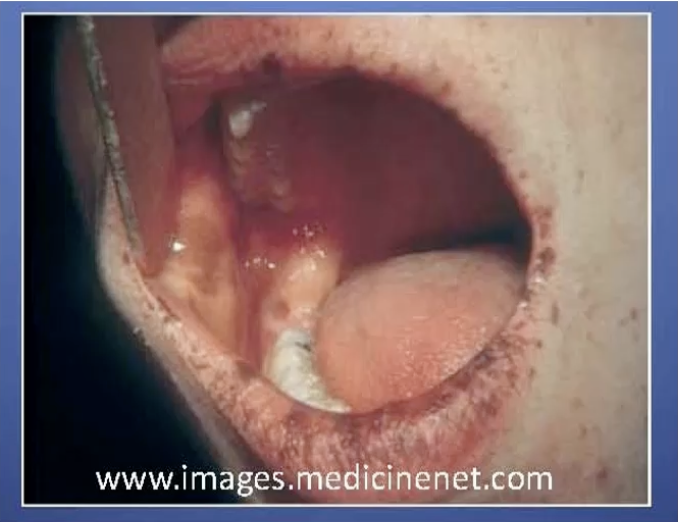
Peutz-Jegher Syndrome
STK11
Gene associated with Peutz-Jegher Syndrome
STK11 inheritance?
Autosomal Dominant
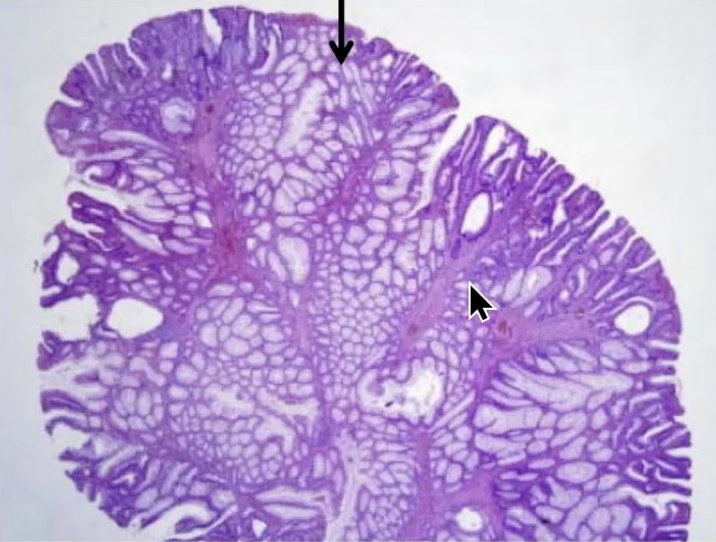
Peutz-Jhegers Polyp with arterizing smooth muscle
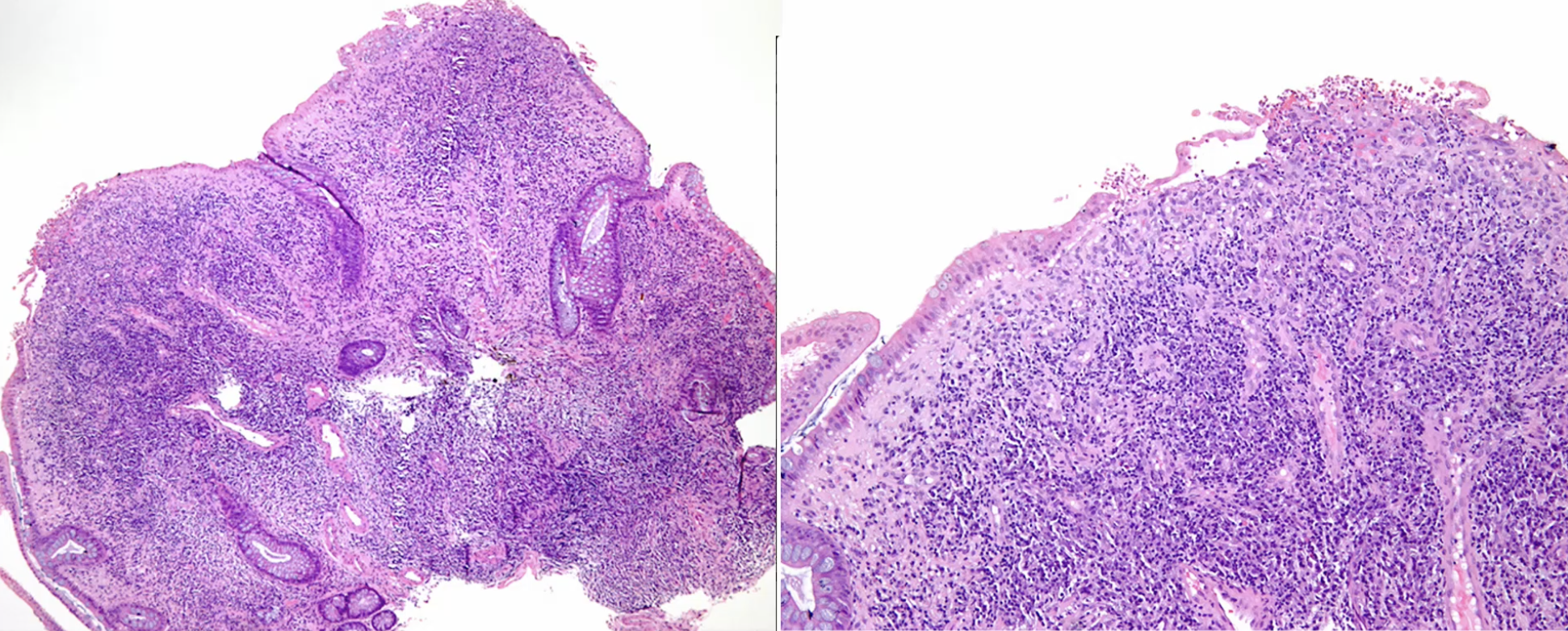
Characterize this Polyp
Inflammatory polyp without dysplasia
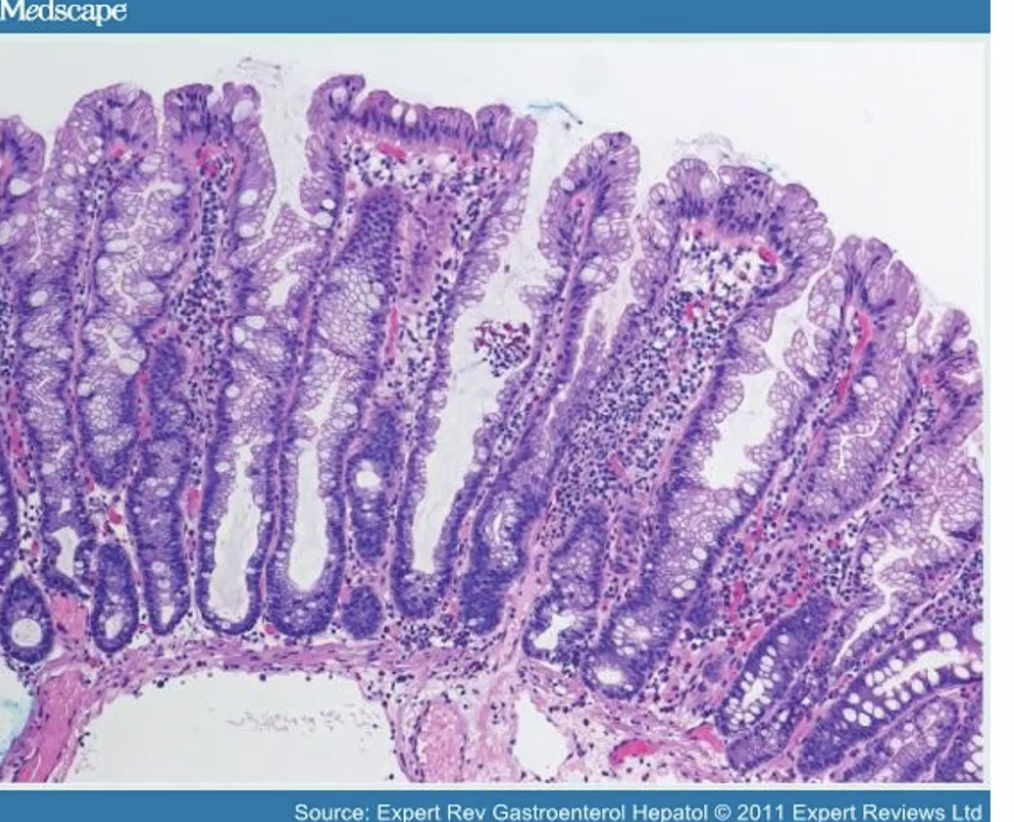
Characterize this Polyp
Hyperplastic polyp
Small polyp on the left side of the distal colon in >50 year old that is benign is most likely
Hyperplastic Polyp
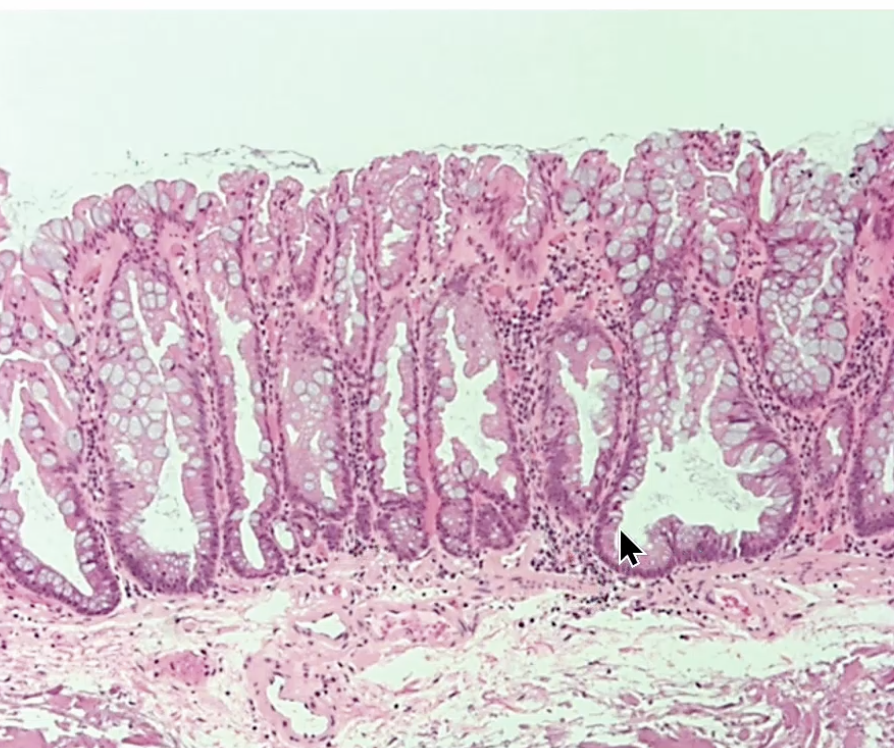
Sessile Serrated Adenoma
Polyp that is easily confused with hyperplastic but is premalignant and on the right side of the colon (proximal)
Sessile serrated adenoma
The precursor to most colorectal cancers is
adenomatous polyp.
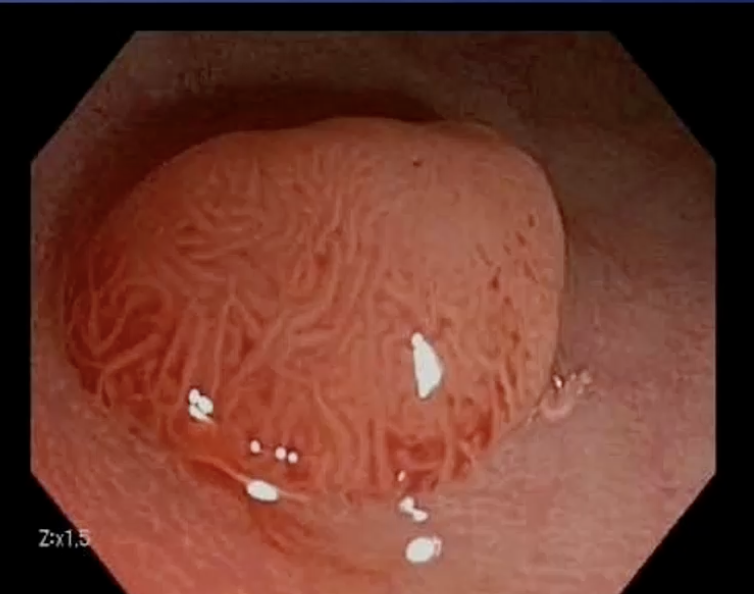
Adenoma Polyp
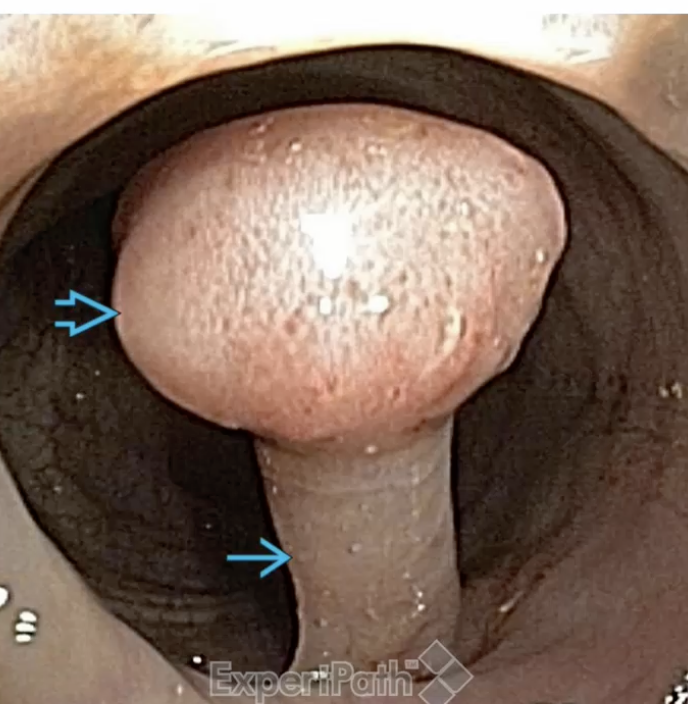
Pedunculated Adenoma Polyp
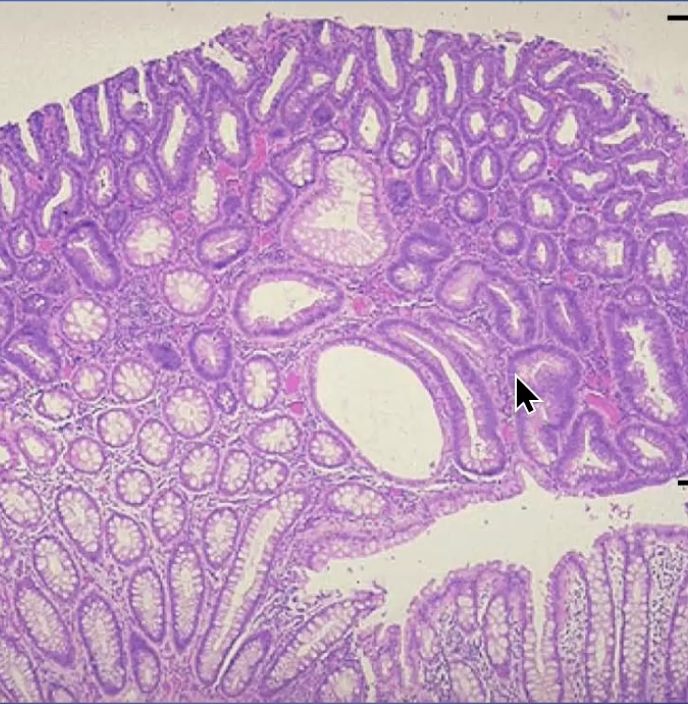
Tubular Adenoma
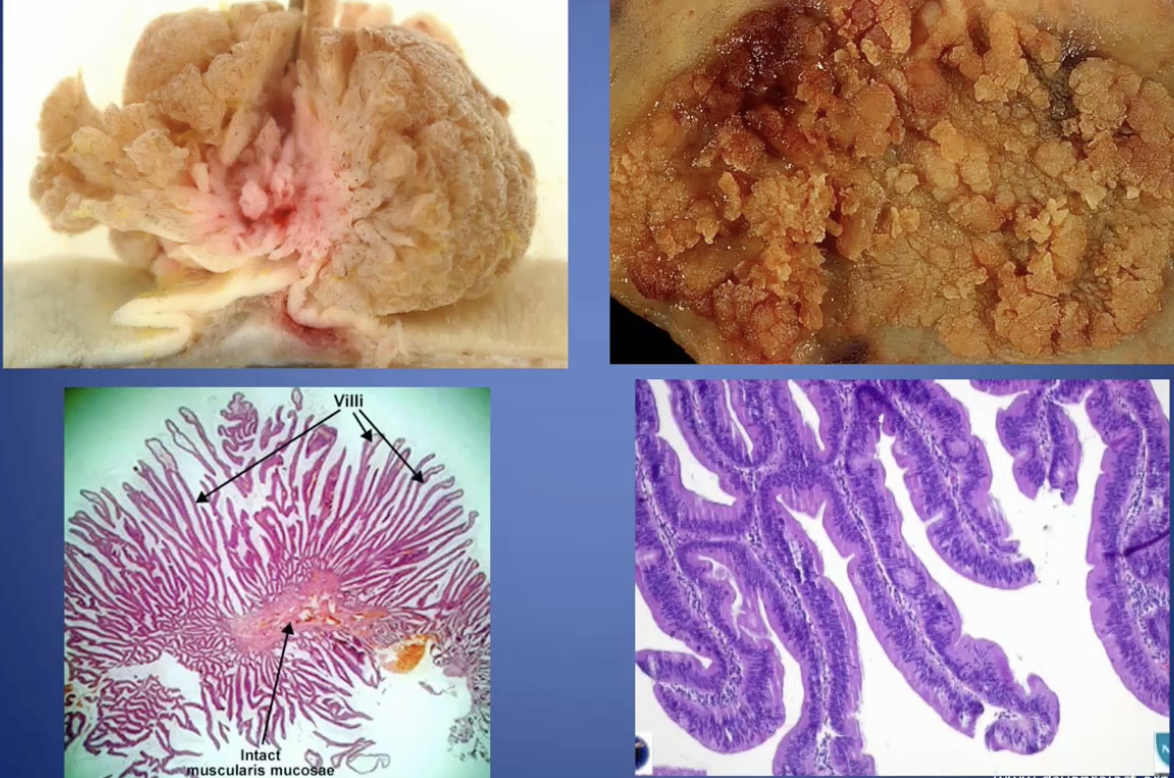
Villous Adenoma
Histology features of adenomatous epithelium
Blue (Hyperchromatic), Pencil shaped nuclei, pseudo stratified (jumping off basement membrane), lack of surface maturation (no goblet cells)
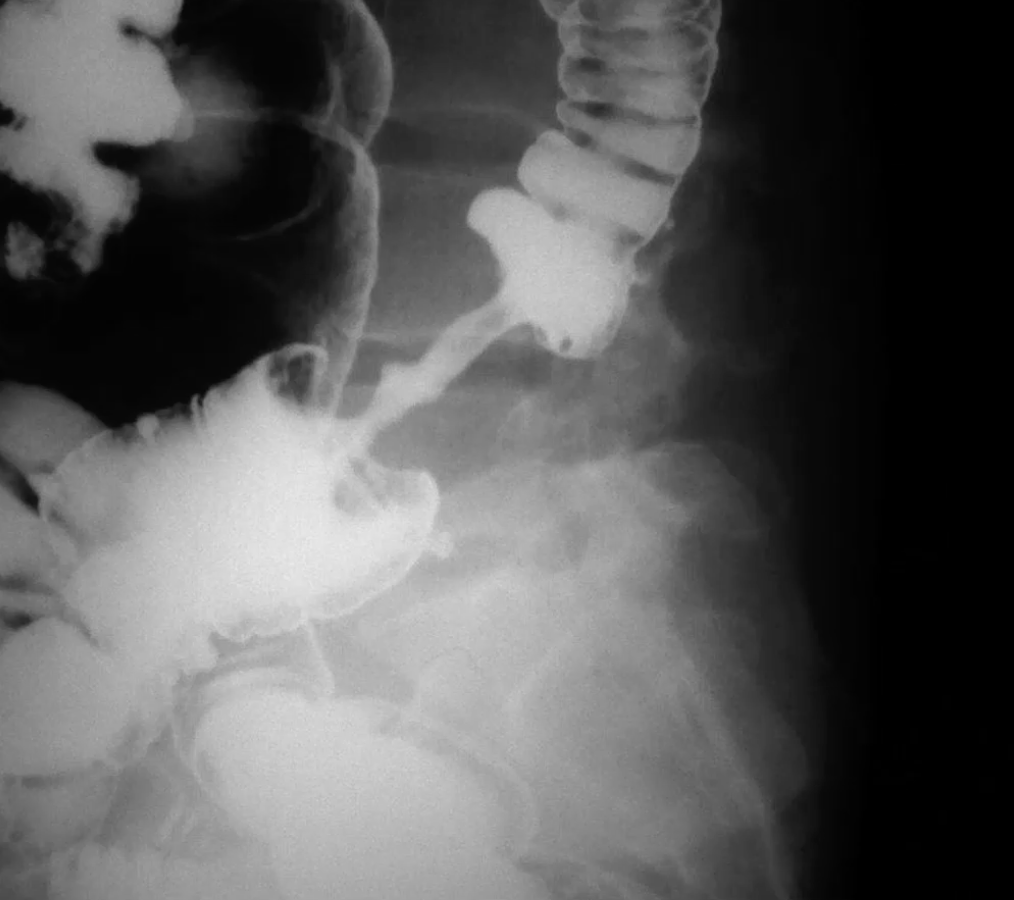
Colorectal cancer apple core sign
APC at 5q21
the “gate keeper” one of the first genes to get mutated on the development to colorectal cancer
Sessile serrated adenoma gene pathway -
Micro satellite instability (MSI) with mutations in MLH1-PMS2 or MHS2-MHS6
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
Autosomal dominant , mutation in APC with multiple polyps in the colon
Lynch Syndrome
Mutation in mismatch repair genes, inherited autosomal dominant, and leads to colon polyps
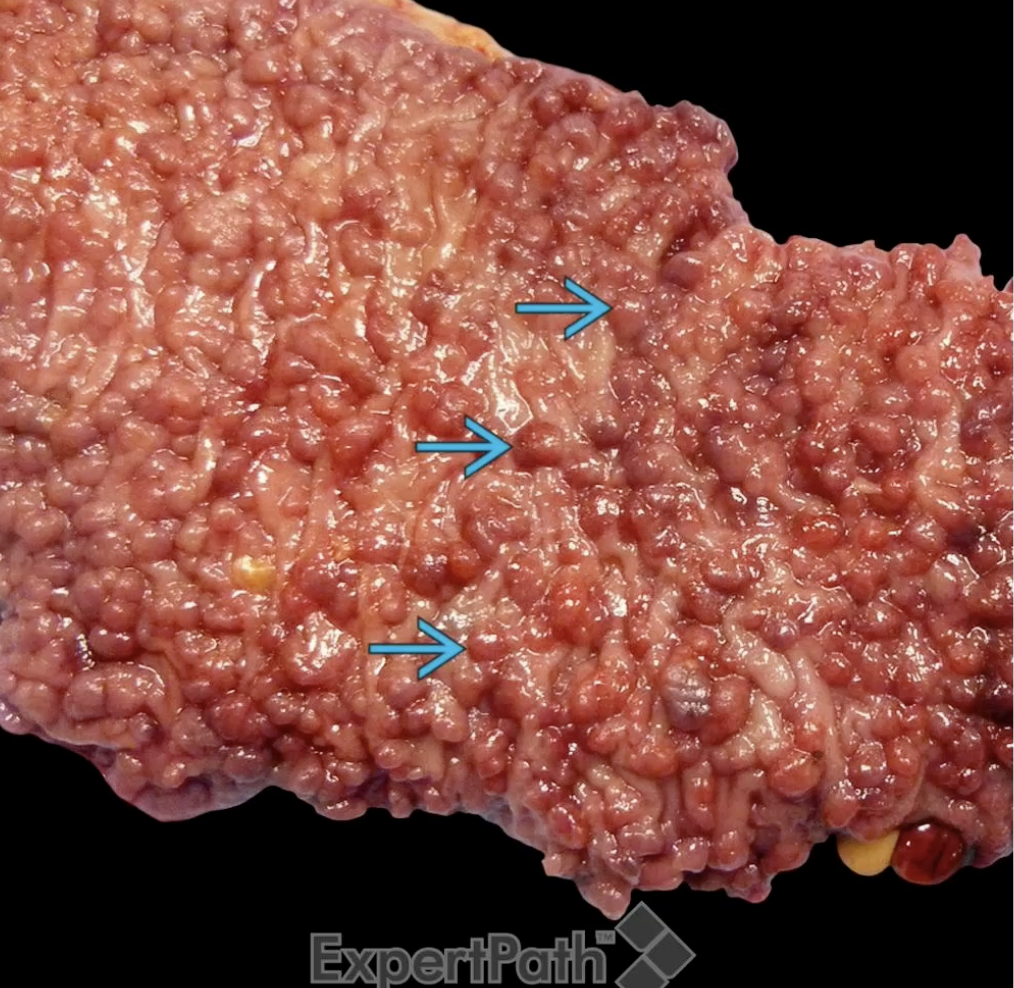
FAP
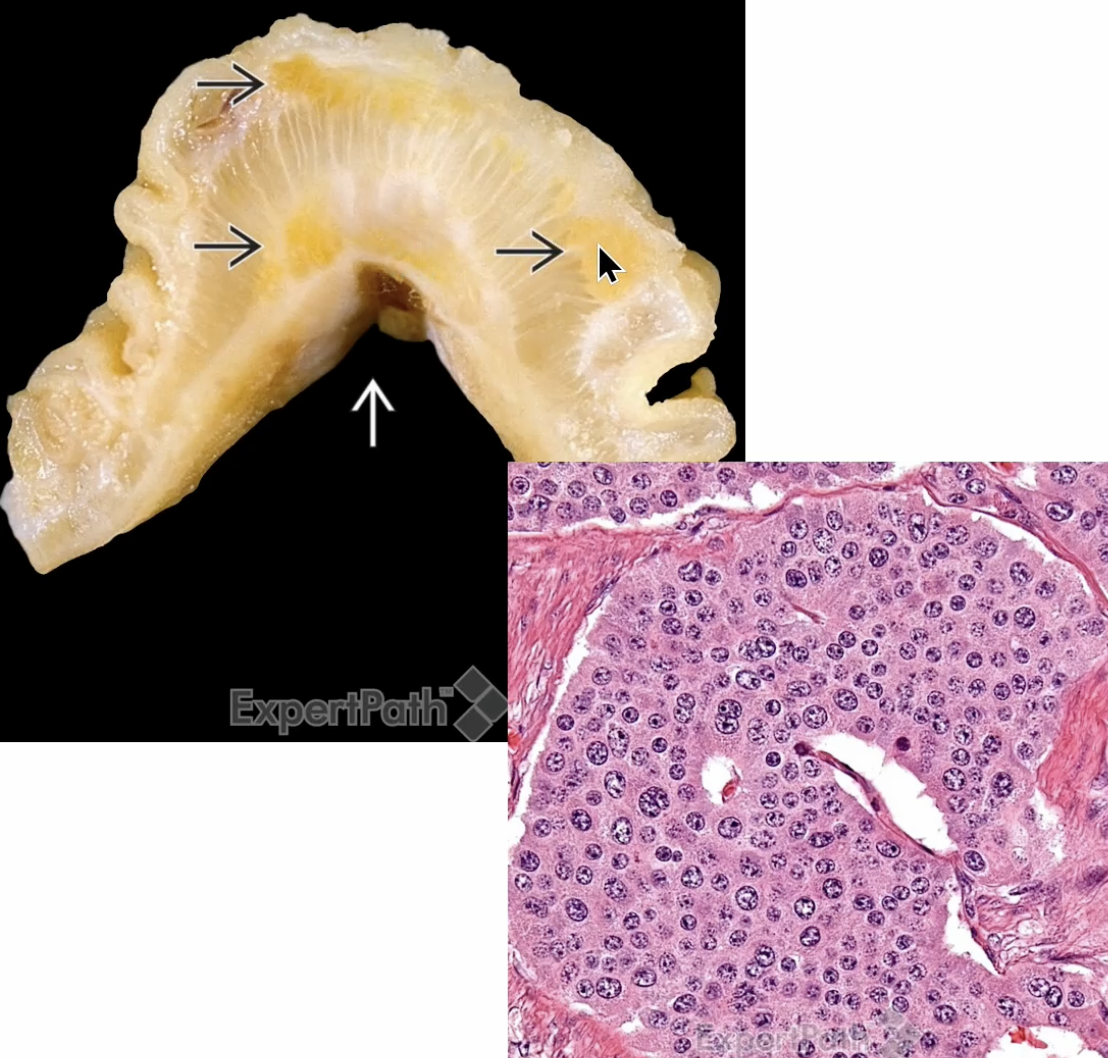
Neuroendocrine Tumor
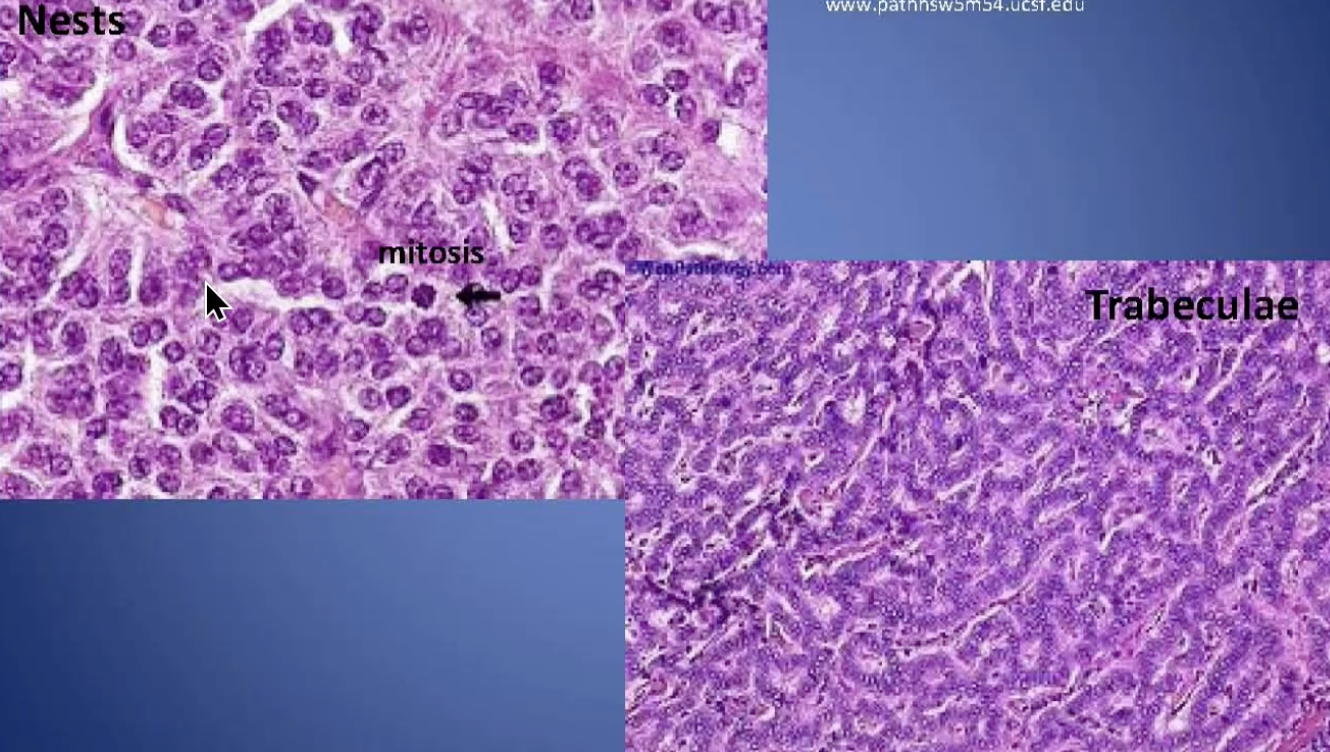
Neuroendocrine/Carcinoid Tumor
Carcinoid Syndrome
A group of symptoms resulting from hormone-like substances released by carcinoid tumors — but requires metastasis to the liver
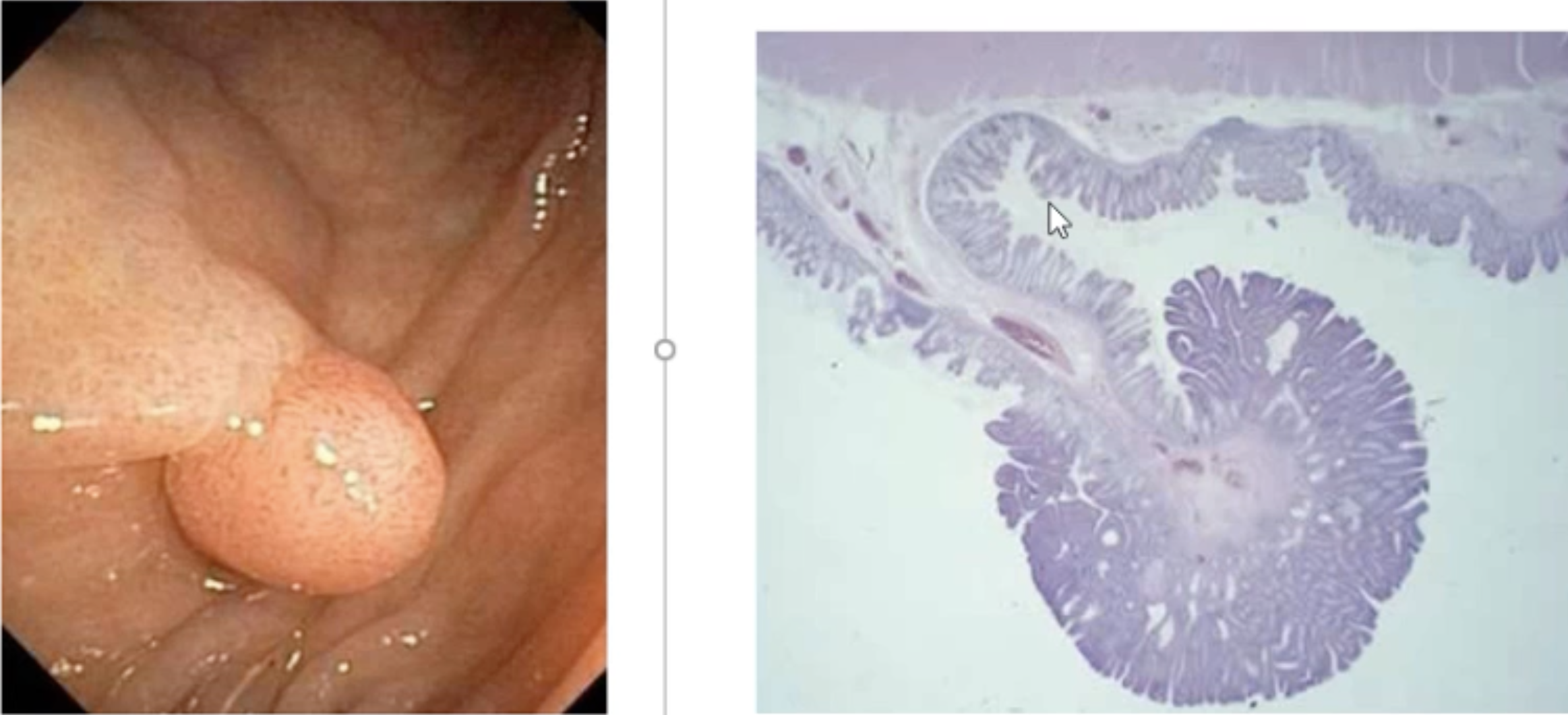
Tubular Adenoma
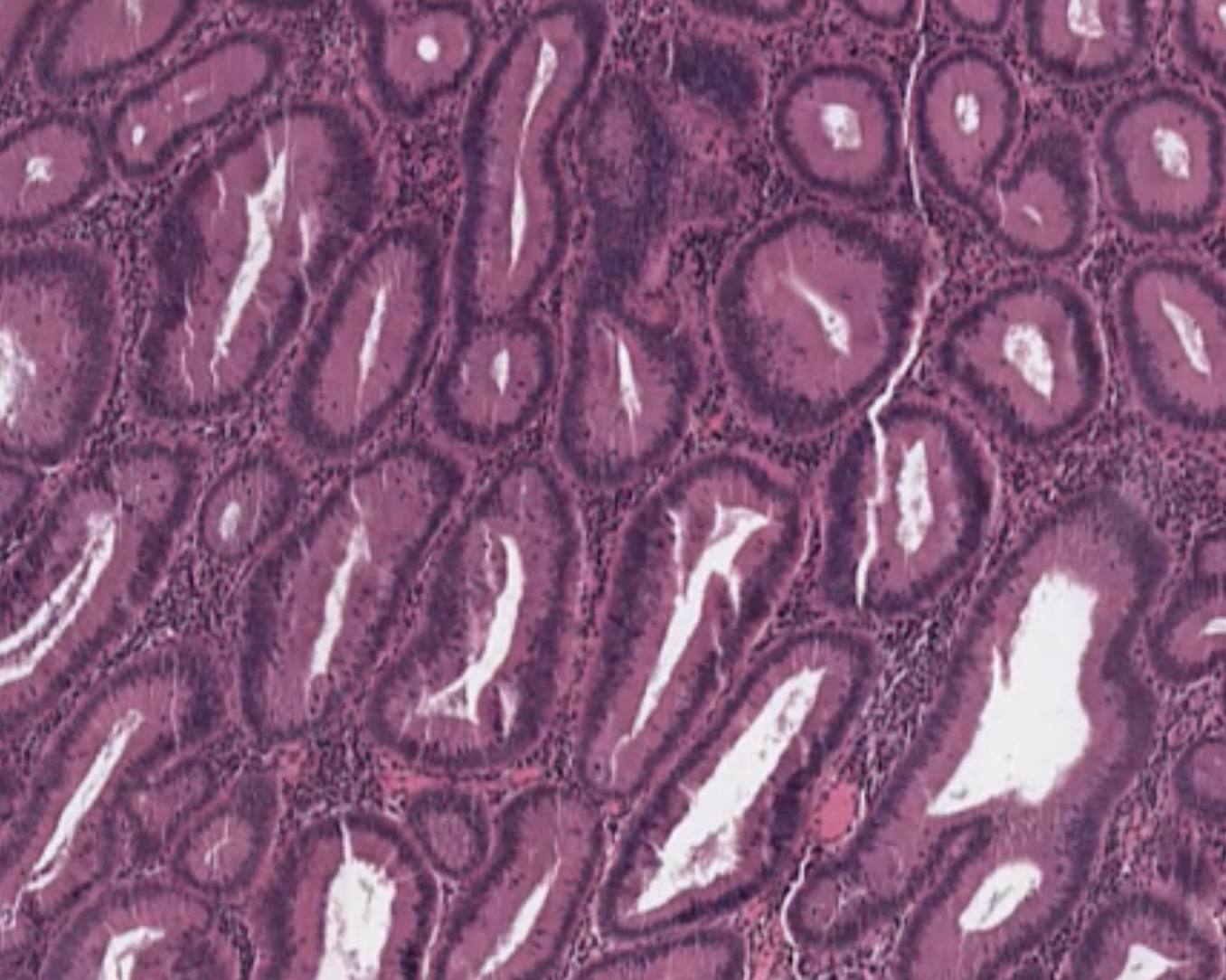
Tubular Adenoma
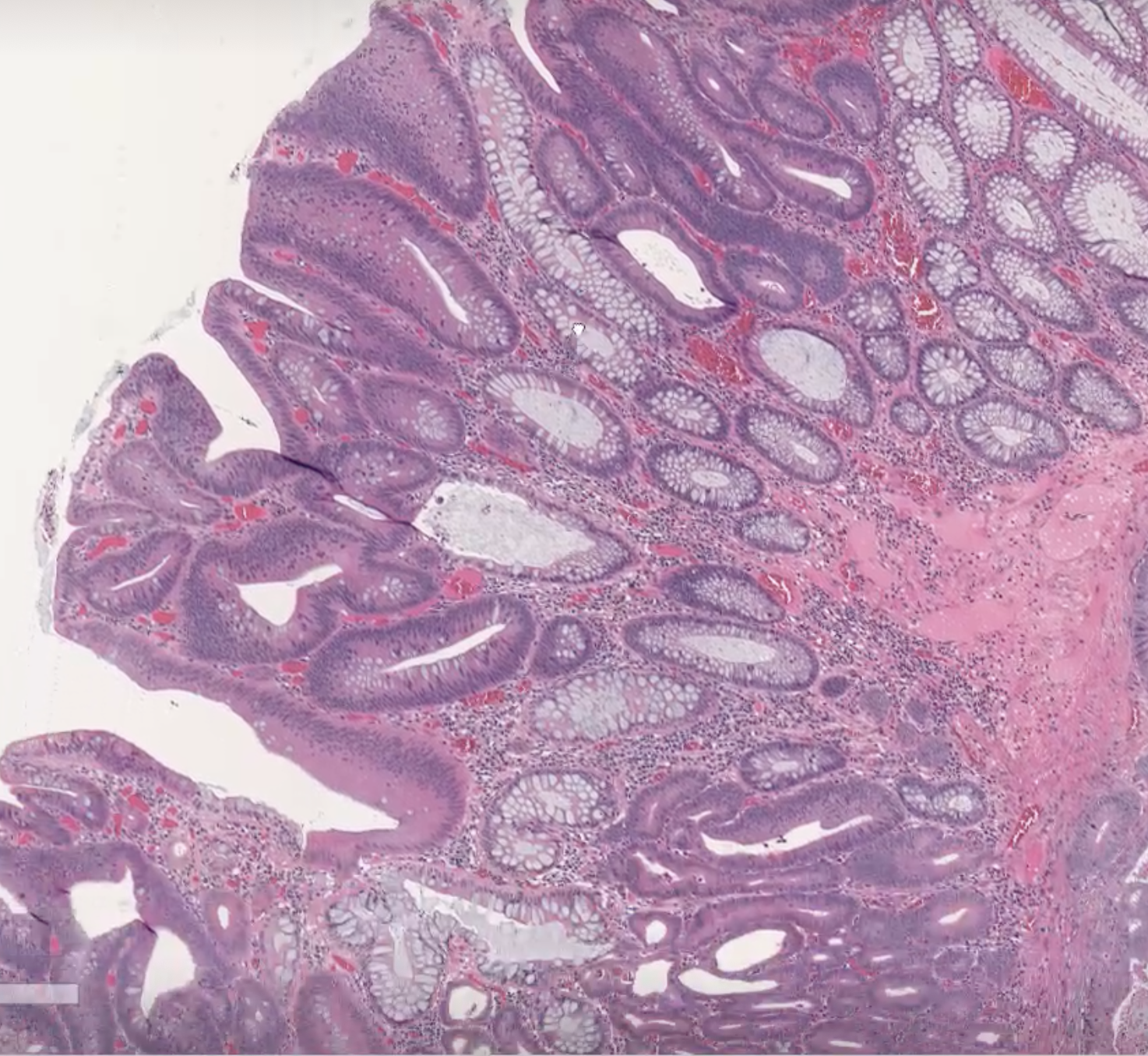
Tubulovillous Adenoma
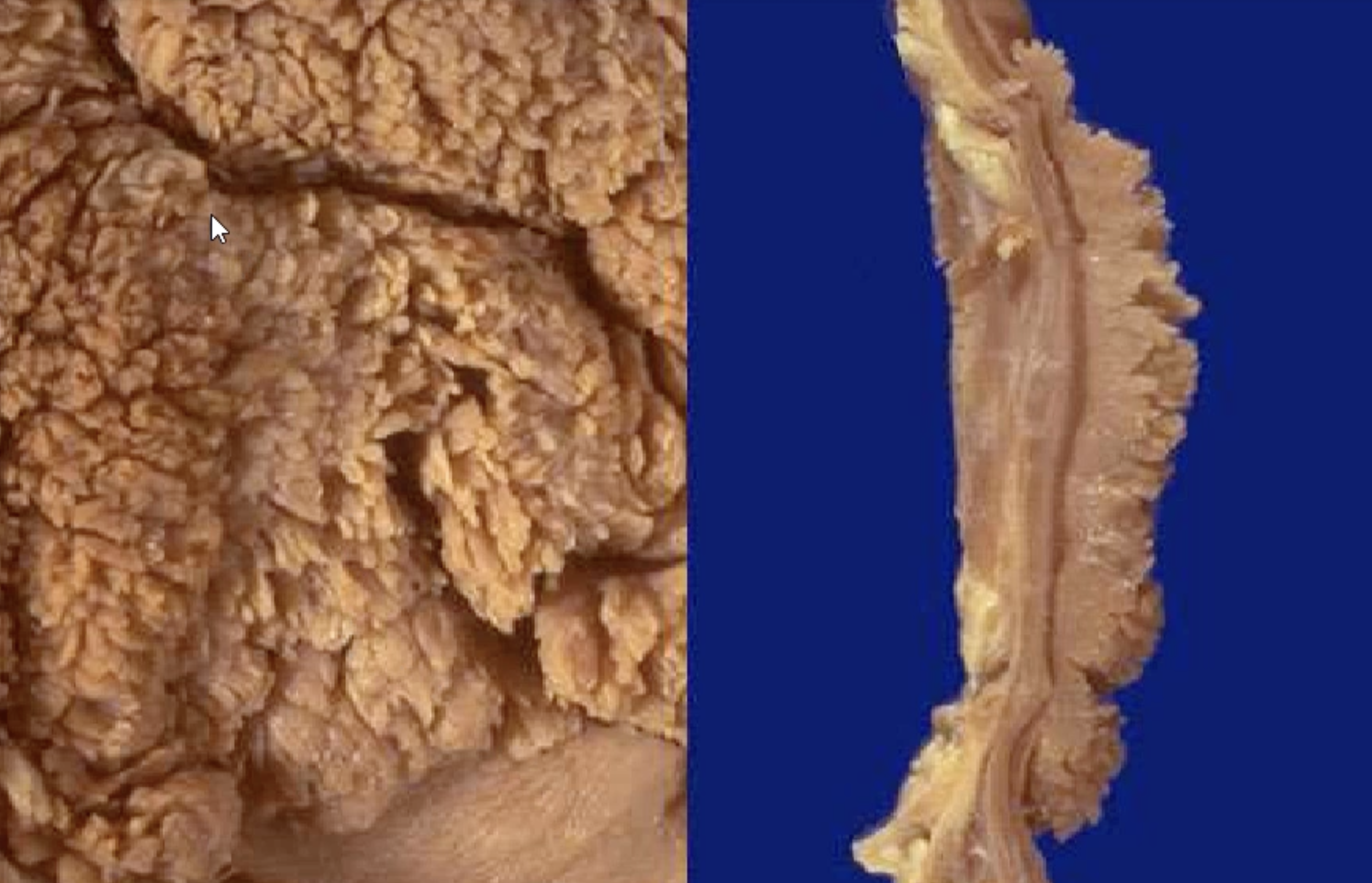
Villous Adenoma
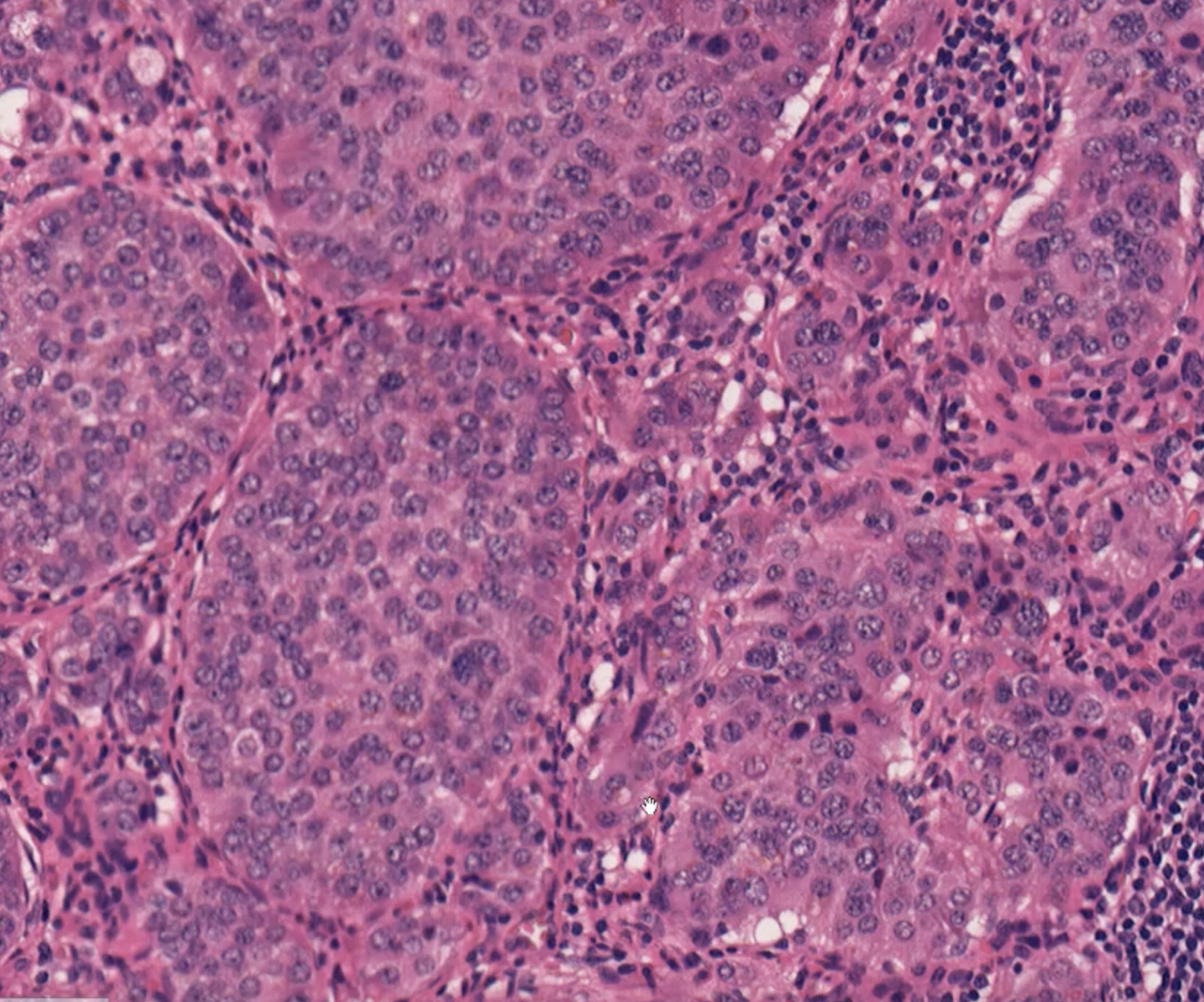
Neuroendocrine neoplasm of the intestine
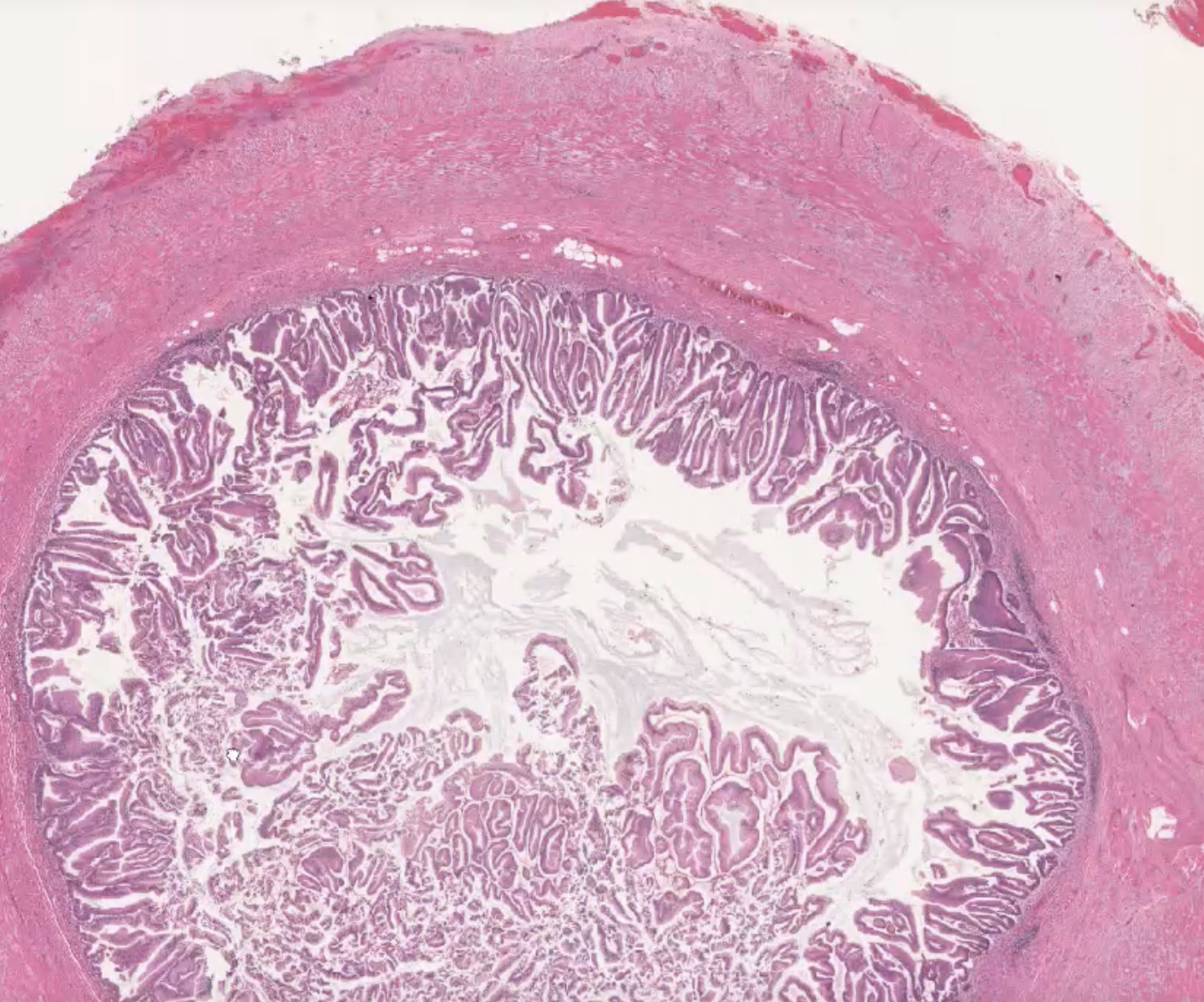
Low grade apendocele mucinous neoplasm