Final Exam: H Chemistry (2024-2025)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
A strong electrolyte is one that ________ completely in solution.
Ionizes
Of the species below, only ________ is not an electrolyte
Ar
Which one of the following compounds is insoluble in water?
ZnS
With which of the following will the Potassium ion form an insoluble salt?
Potassium will form soluble salts with all choices
With which of the following will the ammonium ion form an insoluble salt?
None of the above
Aqueous potassium chloride will react with which one of the following in an exchange (metathesis) reaction?
Lead Nitrate
Which combination will produce a precipitate?
NaOH (aq) and Fe(NO₃)₂ (aq)
The balanced molecular equation for complete neutralization of H₂SO₄ by KOH in aqueous solution is
H₂SO₄ (aq) + 2KOH (aq) → 2H₂O (l) + K₂SO₄ (aq)
What are the spectator ions in the reaction between KCl (aq) and AgNO3 (aq)?
K+ and NO3-
What are the spectator ions in the reaction between Ba(OH)₂ (aq) and HCl (aq)?
H⁺ and OH⁻
When aqueous solutions of AgNO3 and KI are mixed, silver iodide precipitates. The balanced net ionic equation is
Ag+ (aq) + I ⁻(aq) → AgI (s)
A neutralization reaction between an acid and a metal hydroxide produces
Water and a salt
Which one of the following is a weak acid?
HF
The balanced reaction between aqueous nitric acid and aqueous strontium hydroxide is
2HNO₃ (aq) + Sr(OH)₂ (aq) → 2H₂O (l) + Sr(NO₃)₂ (aq)
The net ionic equation for the reaction between aqueous nitric acid and aqueous sodium hydroxide is
H⁺(aq) + OH⁻ (aq) → H₂O (l)
The following diagrams represent aqueous solutions of acids HX, HY, and HZ, with water molecules omitted for clarity. Rank the acids from strongest to weakest.
HY, HZ, HX
Of the choices below, which would be the best for the lining of a tank intended for use in the storage of hydrochloric acid?
Copper
Reduction is the ________ and oxidation is the ________.
gain of electrons, loss of electrons
Oxidation cannot occur without ________.
Reduction
In which species does oxygen have an oxidation number of zero?
O₂
In which species does nitrogen have the highest oxidation number?
NH₃
In which reaction does the oxidation number of oxygen increase?
2H₂O (l) → 2H₂ (g) + O₂ (g)
Based on the equations below, which metal is the most active? Sn(NO₃)₂ (aq) + Co (s) → Co(NO₃)₂ (aq) + Sn (s) Cu(NO₃)₂ (aq) + Ag (s) → No reaction Cu(NO₃)₂ (aq) + co (s) → Co(NO₃)₂ (aq) + Cu (s)
Co
Which of the following reactions will not occur as written?
Pb (s) + Zn(NO₃)₂ (aq) → Zn (s) + Pb(NO₃)₂ (aq)
The net ionic equation for the dissolution of barium metal in aqueous hydrochloric acid is ________.
Ba (s) + 2H⁺ (aq) → Ba²⁺ (aq) + H₂ (g)
Which element is oxidized in the reaction below?Au(s) + 3NO₃⁻(aq) + 6H⁺(aq) → Au³⁺(aq) + NO(g) + 3H₂O (l)
Au
Which one of the following is a correct expression for molarity?
mol solute/ L solution
Which solution has the same number of moles of HCl as 25.0 mL of 0.200 M solution of HCl?
12.5 mL of 0.400 M solution of HCl
Which of the following 0.300 M solutions would contain the highest concentration of sodium ions?
Sodium phosphate
What volume (mL) of a concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide (6.00 M) must be diluted to 200.0 mL to make a 0.880 M solution of sodium hydroxide?
29.3
What volume (mL) of a concentrated solution of magnesium chloride (9.00 M) must be diluted to 350. mL to make a 2.75 M solution of magnesium chloride?
107 mL
A 650 mL sodium bromide solution has a bromide ion concentration of 0.245 M. What is the mass (g) of sodium bromide in solution?
16.4
The molarity (M) of an aqueous solution containing 129 g of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) in 200 mL of solution is ________.
3.58
How many grams of CH₃OH must be added to water to prepare 150 mL of a solution that is 2.0 M CH₃OH?
9.6
The point in a titration at which the indicator changes is called the ________.
End point
Which one of the following substances is produced during the reaction of an acid with a metal hydroxide?
Water
What is the molarity of a NaOH solution if 15.5 mL of a 0.220 M H₂SO₄ solution is required to neutralize a 25.0-mL sample of the NaOH solution?
0.273
The internal energy of a system is always increased by ________.
Adding heat to the system
Which one of the following conditions would always result in an increase in the internal energy of a system?
The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings.
When a system ________, ΔE is always negative.
Gives off heat and does work
Which one of the following is an exothermic process?
Condensation of water vapor
Of the following, which one is a state function?
H
ΔH for an endothermic process is ________ while ΔH for an exothermic process is ________.
Positive, negative
A chemical reaction that absorbs heat from the surroundings is said to be ________ and has a ________ ΔH at constant pressure.
Endothermic, positive
Calculate the work (kJ) done during a reaction in which the internal volume expands from 14L to 50L against a vacuum (an outside pressure of 0 atm.)
0 kJ; no work is done
Which one of the following statements is true?
Enthalpy is a state function
Which of the following is a statement of Hess's law?
If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, the ΔH for the reaction will equal the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps.
For which one of the following reactions is ΔH°rxn equal to the heat of formation of the product?
(1/2)N₂ (g) + O₂ (g) → NO₂(g)
For the combustion reaction of methane, ΔH°f is zero for ________. CH₄ (g) + O₂ (g) → 2H₂O(g) + CO₂ (g)
O₂ (g)
The term standard conditions with respect to enthalpy change means ________.
1 atm and 298 K
The ΔE of a system that releases 12.4 J of heat and does 4.2 J of work on the surroundings is ________ J.
-16.6
The change in the internal energy of a system that absorbs 2,500 J of heat and that does 7,655 J of work on the surroundings is ________ J.
-5,155
The value of ΔH° for the reaction below is -126 kJ. ________ kj are released when 2.00 mol of NaOH is formed in the reaction? 2Na₂O₂ (s) + 2H₂O (l) → 4NaOH (s) + O₂ (g)
-63
The value of ΔH° for the reaction below is -336 kJ. Calculate the heat (kJ) released to the surroundings when 23.0 g of HCl is formed. CH₄ (g) + 3Cl₂ (g) → CHCl₃ (l) + 3HCl (g)
-70.7 kJ
The specific heat capacity of lead is 0.13 J/g-K. How much heat (in J) is required to raise the temperature of 15g of lead from 22 °C to 37 °C?
29 J
What is the molar heat capacity (in J/mol-K) of liquid bromine (Br₂)? The specific heat of liquid bromine is 0.226 J/g-K.
36.1 J/mol-K
ΔH for the reaction IF₅ (g) → IF₃ (g) + F₂ (g) is ________ kJ, given the data below.
+355
Given the reactions in the table below, the enthalpy of reaction is ________ kJ.
17.5
Given the data in the table below, ΔH°rxn for the reaction C₂H₅OH (l) + O₂ (g) → CH₃CO₂H (l) + H₂O (l) is ________ kJ.
-492.6
Determine the energy change for the following reaction:
-125 kJ/mol
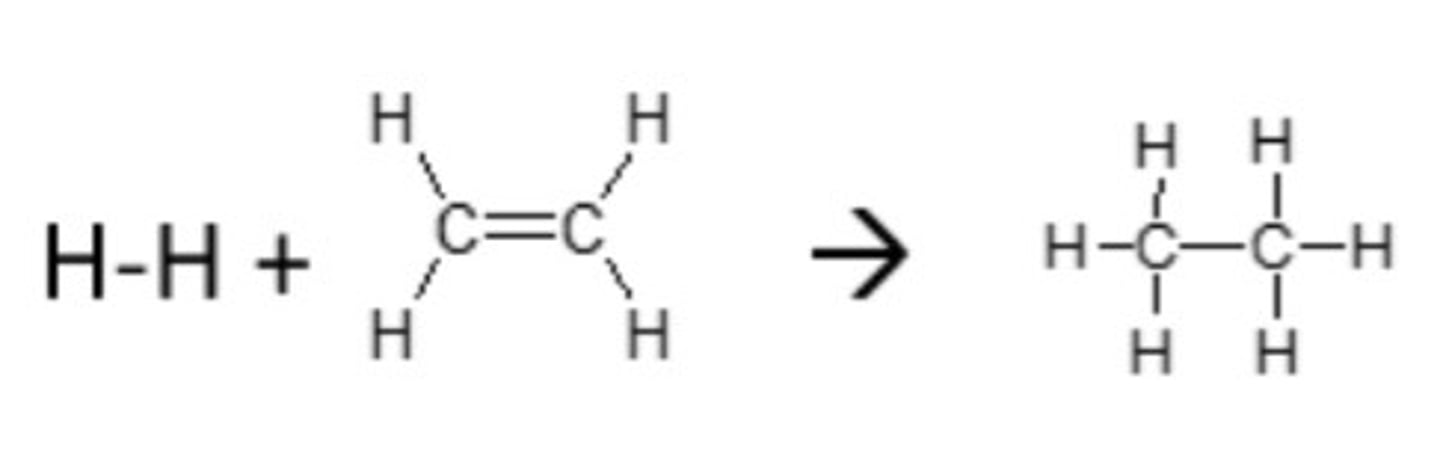
Which one of the following is correct?
νλ = c
Of the following, ________ radiation has the shortest wavelength
X-ray
The photoelectric effect is ________.
the ejection of electrons by a metal when struck with light of sufficient energy
Visible light with a wavelength of 550 nm has a frequency of ________ Hz.
5.5 × 10¹⁴
The energy of a photon of light is ________ proportional to its frequency and ________ proportional to its wavelength.
directly, inversely
The energy of a photon that has a wavelength of 8.33 × 10⁻⁶ m is ________ J.
2.39 × 10⁻²⁰
The frequency of electromagnetic radiation required to promote an electron from n = 2 to n = 4 in a Bohr hydrogen atom is ________ Hz.
6.17 × 10¹⁴
A spectrum containing only ________ wavelengths is called a line spectrum.
Specific
When the electron in a hydrogen atom moves from n = 6 to n = 1, light with a wavelength of ________ nm is emitted.
93.8
In the Bohr model of the atom, ________.
electron energies are quantized
According to the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, it is impossible to know precisely both the position and the ________ of an electron.
Momentum
All of the orbitals in a given electron shell have the same value as the ________ quantum number.
Principal
All of the orbitals in a given subshell have the same value as the ________ quantum number.
Principal
Which one of the following is not a valid value for the magnetic quantum number of an electron in a 5d subshell?
3
Which of the subshells below do not exist due to the constraints upon the angular momentum quantum number?
2d
An electron cannot have the quantum numbers n = ________, l = ________, ml = ________.
1, 1, 1
All of the following are a result from the solution of the Schrodinger equation except ________.
Spin
In a px orbital, the subscript x denotes the ________.
Axis along which the orbital is aligned
A 4pz orbital in a many-electron atom is degenerate with ________.
4px
Which one of the following orbitals can hold two electrons?
All of the above
Which of the quantum number(s) below represent the principal quantum number?
N only
Which of the following is not a valid set of four quantum numbers? (n, l, ml, ms)
1, 1, 0, +1/2
Which of the following is a valid set of four quantum numbers? (n, l, ml, ms)
2, 1, 0, +1/2
No two electrons within the same orbital can have the same set of quantum numbers. This statement describes ________.
Pauli Exclusion Principle
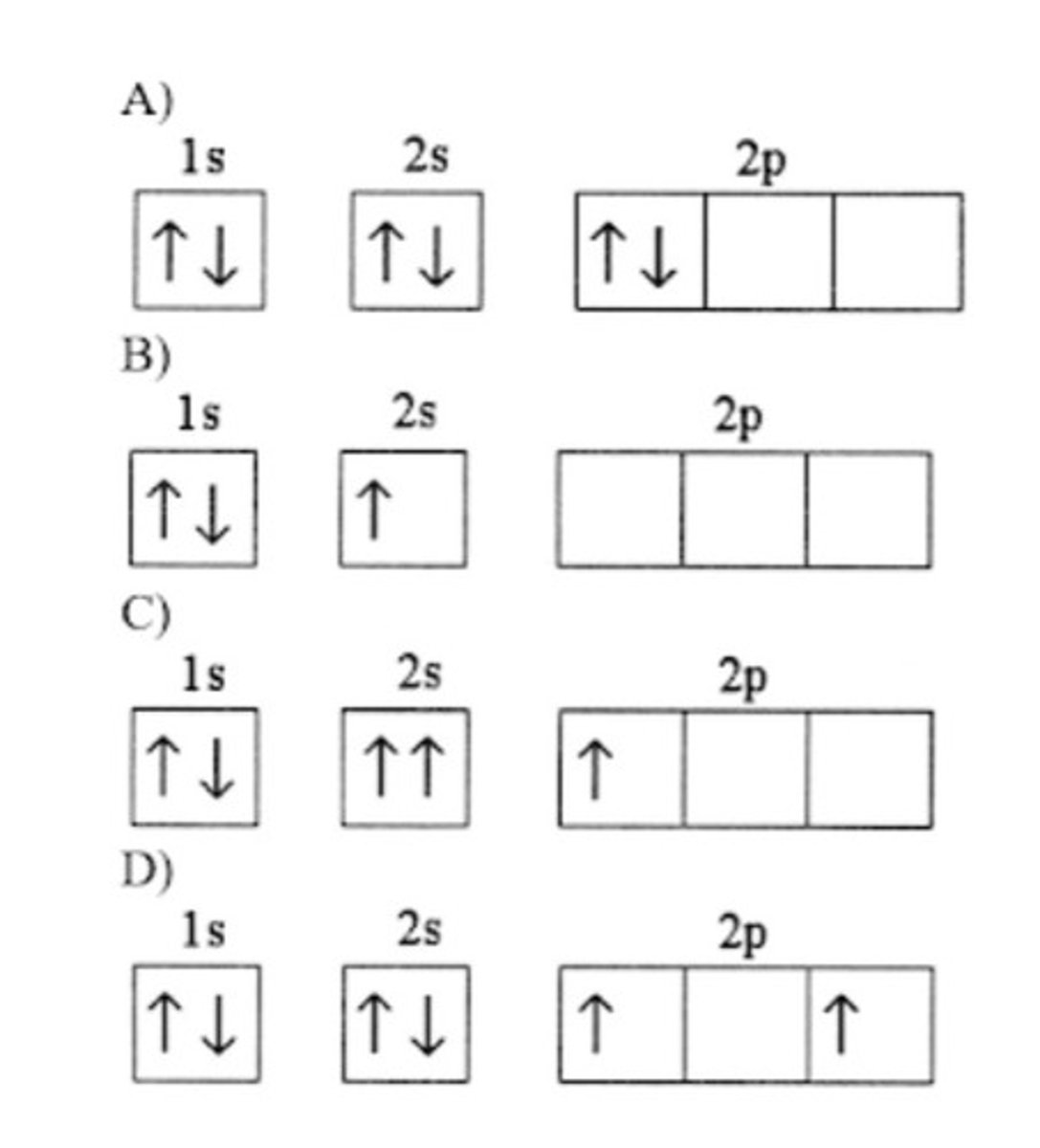
Which electron configuration represents a violation of the Pauli exclusion principle?
C
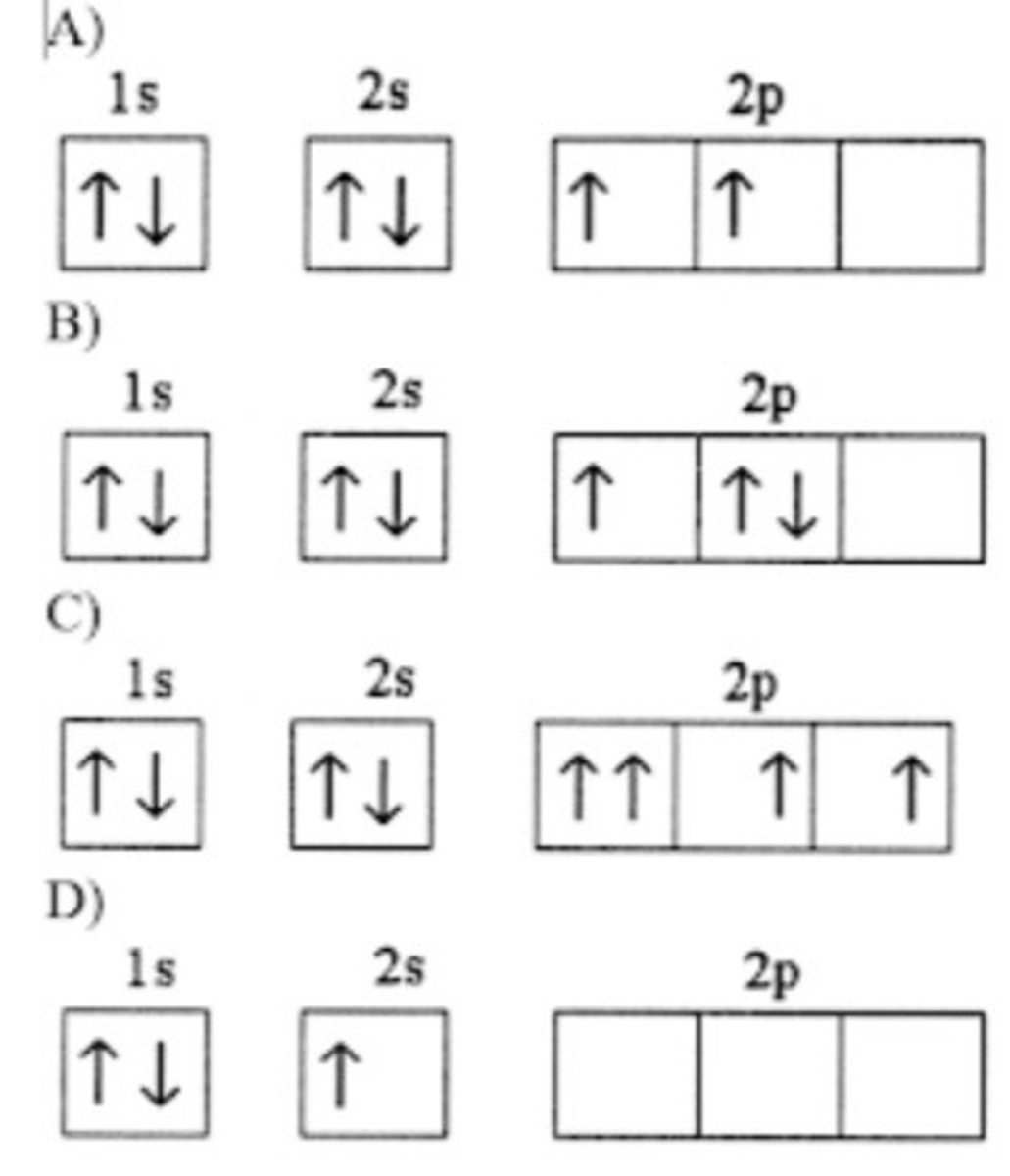
Which electron configuration represents a violation of Hund's rule for an atom in its ground state?
C
The ground-state configuration of fluorine is ________.
D
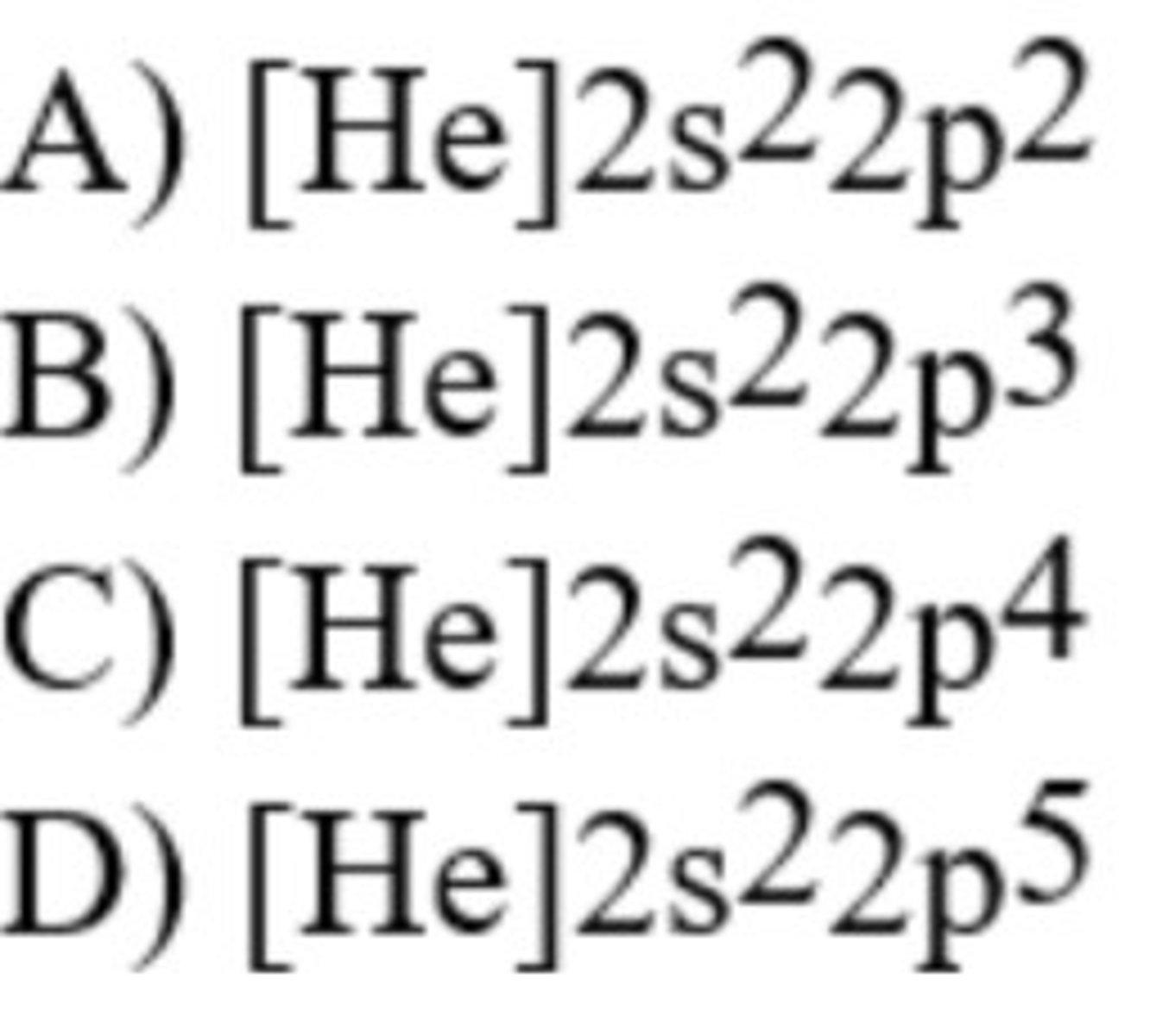
The ground-state configuration of tungsten is ________.
B: [Xe]6s24f15d4
Which two elements have the same ground-state electron configuration?
Cu and Ag
In which set of elements would all members be expected to have very similar chemical properties?
Br, I, At
________ is credited with developing the concept of atomic numbers.
Henry Moseley
Which element would be expected to have chemical and physical properties closest to those of rubidium?
K
In which orbital does an electron in a copper atom experience the greatest effective nuclear charge?
1s
Electrons in the 1s subshell are much closer to the nucleus in Ar than in He due to the larger ________ in Ar.
Nuclear charge
Screening of the nuclear charge by core electrons in atoms is ________.
More efficient than that by valence electrons
The effective nuclear charge of an atom is primarily affected by ________.
Inner electrons
The atomic radius of main-group elements generally increases down a group because ________.
The principal quantum number of the valence orbitals increases
Atomic radius generally increases as we move ________.
Down a group and from right to left across a period
Of the following, which gives the correct order for atomic radius for Mg, Na, P, Si and Ar?
Na > Mg > Si > P > Ar
Which of the following is an isoelectronic series?
O²⁻, F⁻, Ne, Na⁺