Topic 1: core concepts
1/355
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
356 Terms
role of the nucleus
contains DNA which codes for proteins
site of transcription where mRNA is made
a channel protein spans the membrane what type of r groups will be found near the pore that molecules can pass through
polar or charged that are hydrophilic
as they are near the water environment inside and outside of the cell
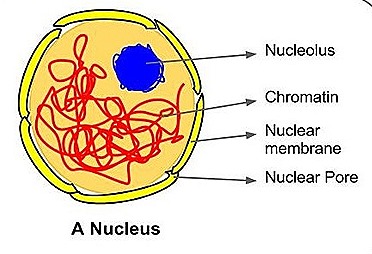
what does a nucleus contain
nuclear pore
nuclear envelope
chromatin
nucleoplasm
nucleolus
nuclear envelope
double membrane with pores
nuclear pore
allows mRNA and ribosomes to leave the nucleus
chromatin
DNA coiled around histone proteins for protein synthesis
nucleolus
rRNA synthesis
structure of a nucleus
mitochondria role
produces ATP in aerobic respiration
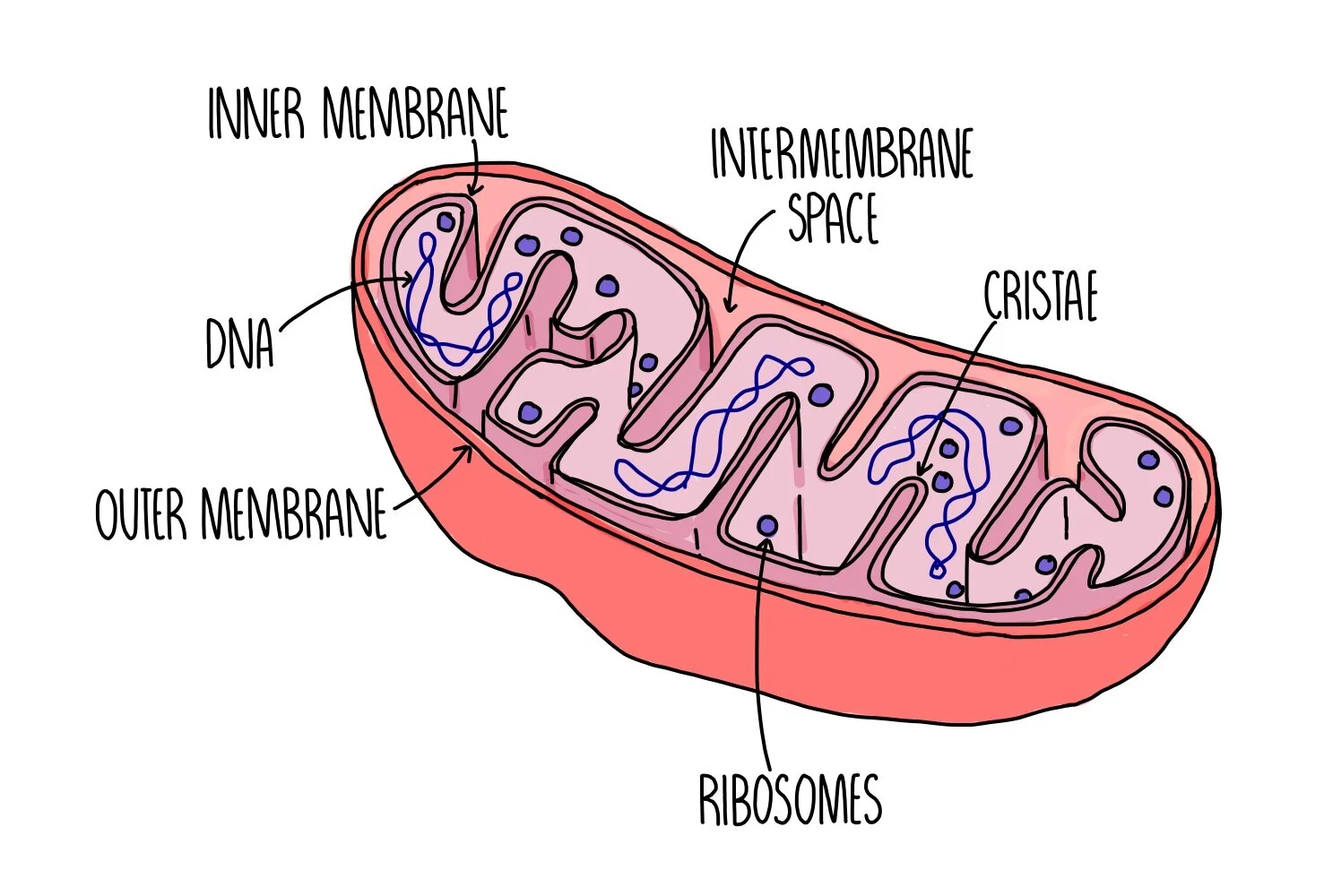
what does a mitochondria contain
matrix
cristae
70S ribosomes
DNA
outer/ inner membrane
matrix
jelly like substance containing lipids and proteins
cristae
folding of the inner membrane
site of ATP synthesis
increase the surface area
advantage of mitochondria being cylindrical
increases surface area to volume ratio, reducing diffusion distance for aerobic respiration
structure of a mitochondria
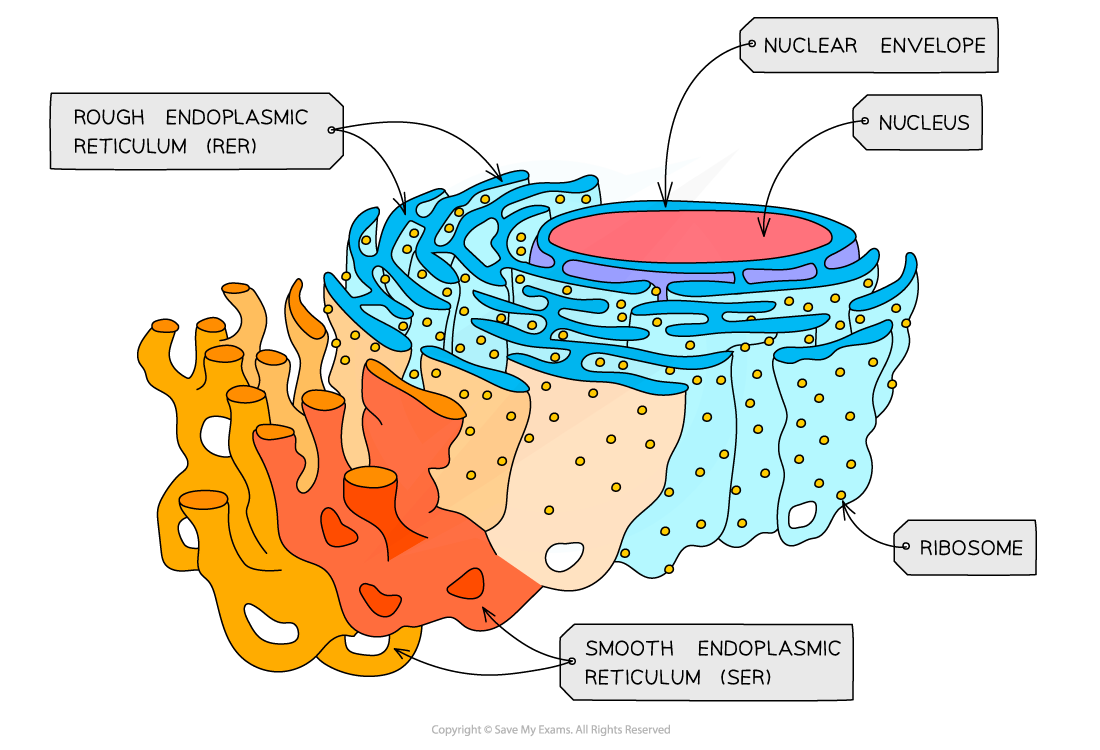
rough endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes on outer surface making it bumpy and cisternae transport proteins made
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
made of membranes that lack ribosomes
endoplasmic reticulum
flattened sacs
double membraned cisternae leading on from nuclear envelope
endoplasmic reticulum structure
ribosomes role
site of protein synthesis
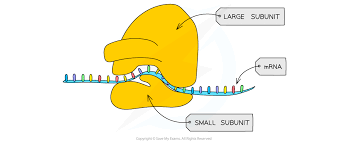
2 different sizes 70s and 80S
ribosome structure
made up of large and small subunit
made up of rRNA and proteins
lysosmes role
waste disposal unit
lyosome structure
vesicles with double membrane and proteins and digestive enzymes
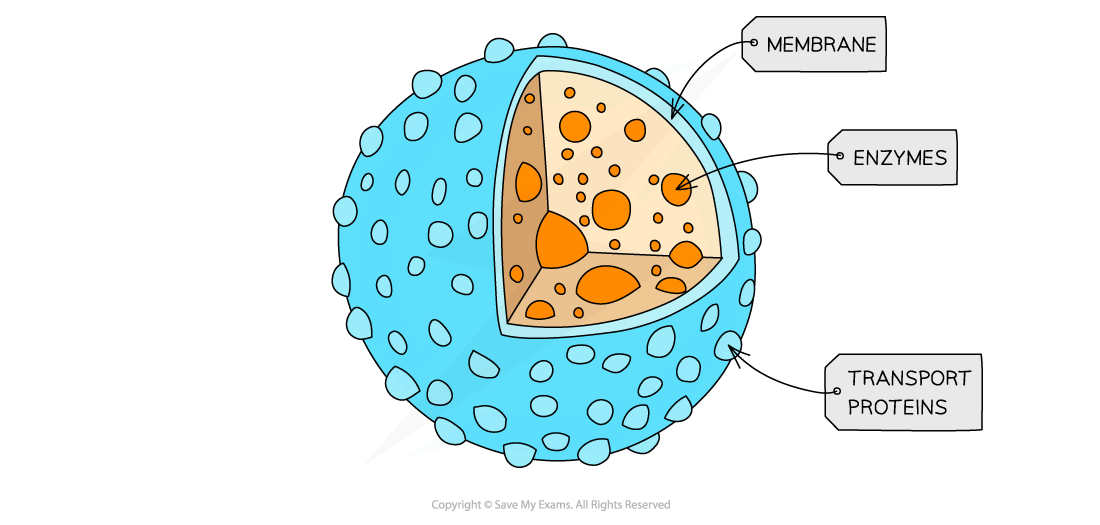
chloroplast role
site of photosynthesis
what does chloroplasts contain
outer membrane, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid, lamella, granum, inter membrane space, 70S ribosomes
stroma
fluid filled containing products of photosynthesis
thylakoids
membrane bound disks where photosynthesis takes place
granum
stack of thylakoids
lamella
connects thylakoids
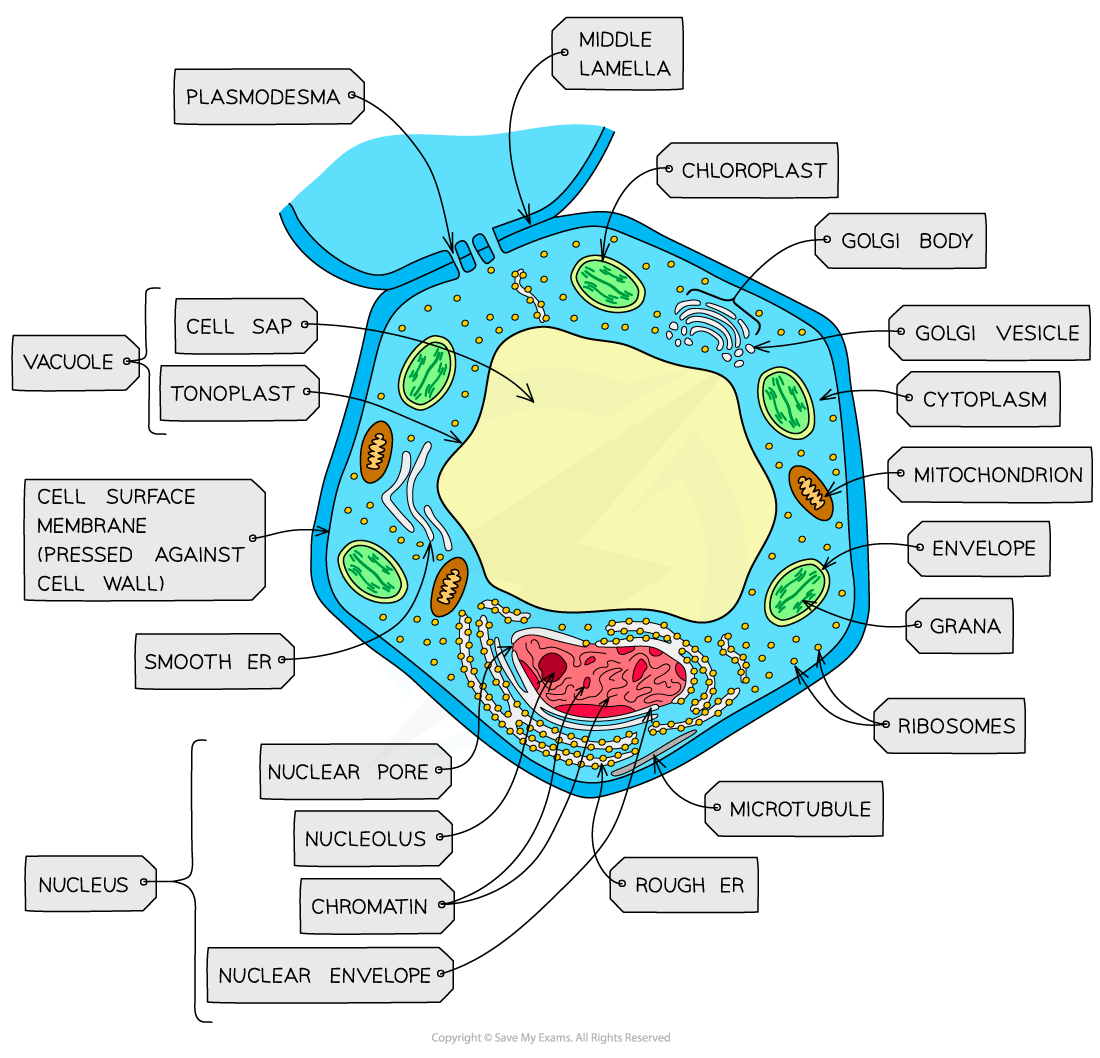
plasmodesmata
hole in cell wall and membrane filled with cytoplasm
allows diffusion between cells
plant cell structure
animal cell structure
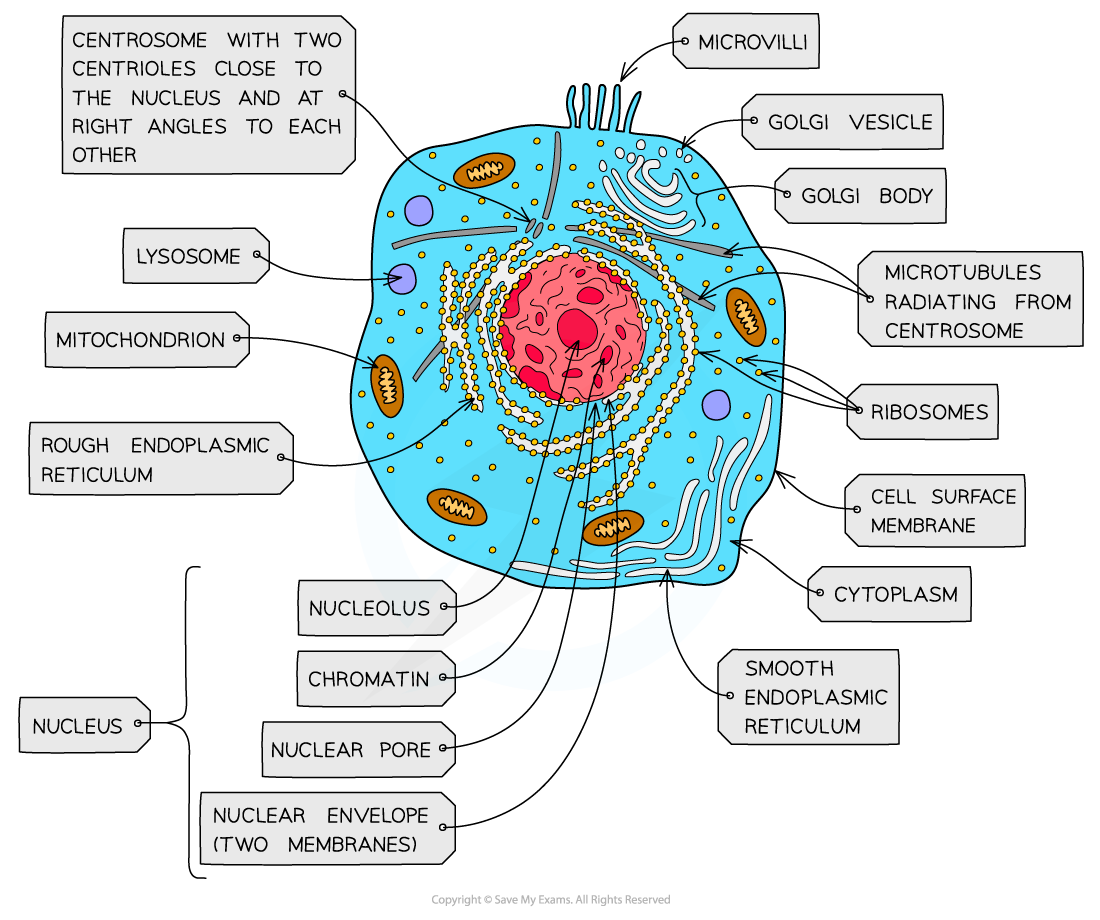
centrioles
2 rings of micro tubules outside nucleus, organise micro tubules that make the spindle in cell division
not present in plants
vacuole
fluid filled sap surrounded by tonoplast membrane
cell wall for prokaryotes made of
peptidoglycan
prokaryotes
DNA not membrane bound
cell wall for fungi
chitin
what ion is cell wall strengthened by
calcium
mesosmes
make ATP in prokaryotes
name 4 structures that some prokaryotes contain but not all
slime capsule, plasmids, flagellum, pili
smooth endoplasmic reticulum function
to produce and transport lipids
how are products of photosynthesis stored in chloroplasts
as starch grains and lipid droplets
plasmodesmata
gap in cell walls and cell membranes of adjacent plant cells filled with cytoplasm
what nucleic acids may be found in a virus
DNA or RNA
stroma
contains enzymes for light independent reactions of photosynthesis
mesome
folding of cell membrane found only in prokaryotes
structure of DNA in prokaryotes
circular and not bound to proteins
structure of rough endoplasmic reticulum
flattened sacs called cisternae attached to the nuclear envelope, 80s ribosomes are attached to the cisternae
describe structure of a virus
nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
describe the structure and function of the nuclear envelope
double membrane that separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasmk
key characteristics of all prokaryotic cells
free DNA in the cytoplasm called nucleoid
describe the structure of ribosomes
2 subunits made of rRNA and proteins
structure of permanent vacuole
fluid filled sac surrounded by membrane called the tonoplast
what does the matrix in the mitochondria contain
enzymes
function of the golgi body
modify proteins and pack them into vesicles to either export to cell membrane surface or to use in cell
cell theory
new cells form from existing cells which are the fundamental unit of organisms
what is the prokaryote cell wall made from
peptidoglycan
why are cristae needed
to increase surface area of inner membrane
which 2 parts of mitochondria indicate organelle was once bacteria
circular DNA to self replicate
70S ribosomes to make own proteins
explain how you would identify cardiac muscle tissue
cells are found only in the heart, they are striated but don’t form long fibres
explain how you would identify skeletal muscle tissue
made of long parallel cells arranged to form fibres, striated, found attached to bones
in the endosymbiotic theory what is the benefit to the eukaryotic cell
gains the function of aerobic respiration and photosynthesis
explain how you would identify smooth muscle tissue
cells form no uniform shape and are unstriated, they are found throughout the body
golgi body structure
cisternae, lumen, transface, cisface, newly forming vessicle, secretory vessicle
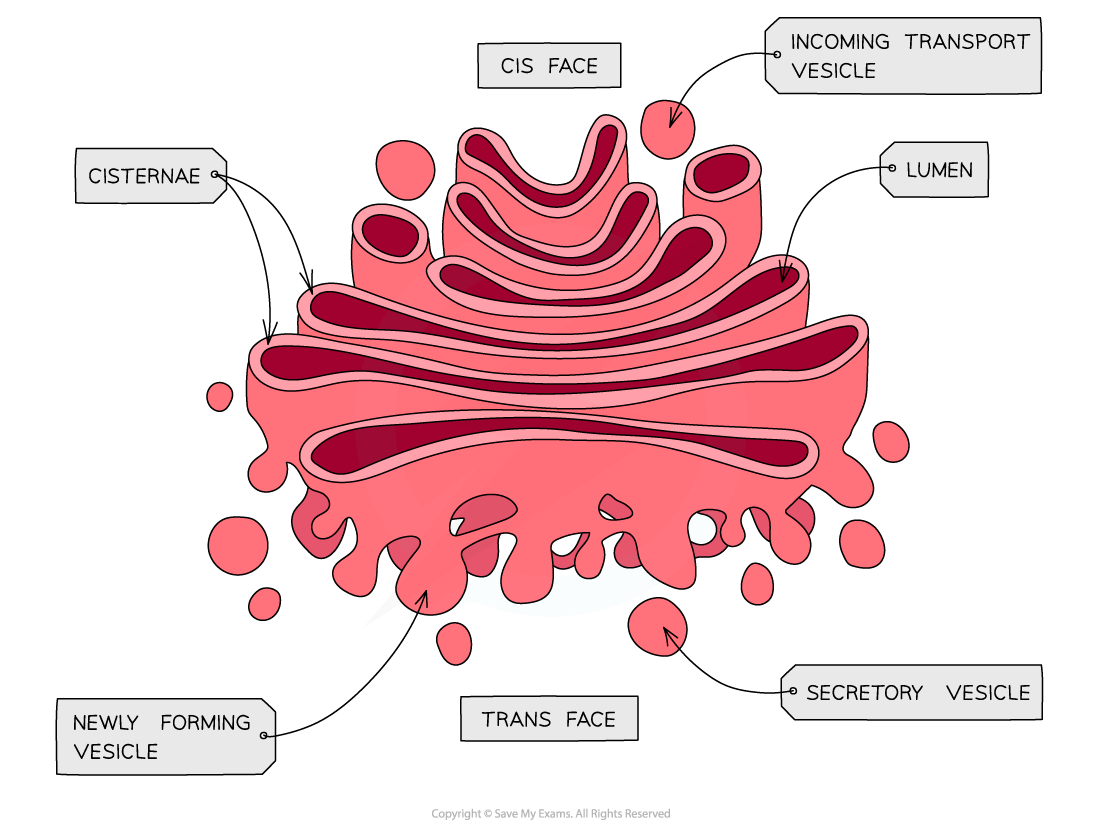
what does golgi body do to vessicle
receives them from endoplasmic reticulum
role of pilli
lets prokaryotes stick to eachother or a host
endosymbiotic theory
eukaryotes are evolved from prokaryotes
cell theory
all living organisms are composed of cells, a cell is the basic unit and cells arise from pre-existing cells
endocytosis
enveloping the membrane of other organelles
how does endosymbiosis work overview
variation in prokaryotes means that 1 may be aerobic bacteria
endocytosis occurs and a large cell engulfs the aerobic bacteria but isn’t digested so they work together
over time bacteria becomes mitochondria
advantage of endosymbiosis to chloroplasts/mitochondria
protection
raw materials supplied to them
provides ideal conditions for reactions
advantage of endosymbiosis to eukaryote
initially temporary benefit but evolutionary advantage
provided ATP so internalised energy store
photosynthesis so internalised nutrient supply
endosymbiosis method
extensions of membrane forms vesicles
organelles engulfed
bacteria cell membrane surrounds organelles membrane forming double membrane
vessicle formed and moved through the cell taking in organelles
organelles eventually permanent feature of cell
to find the overall magnification
eyepiece lens X objective lens
why may 2 pictures of a mitochondria look different
they are cut across different planes
they vary in shape
magnification equation
magnification= image/ actual
how would you identify squamous epithelial tissue
cells are thin and found lining organs
how would you identify smooth muscle tissue
cells form no uniform shape, are unstriated, found throughout the body
facts that support mitochondria and chloroplasts
like prokaryotes they :
have free DNA
have 70s ribosomes
divide by binary fission
affected by antibiotics
link the properties of cardiac muscle to its function
cardiac muscle allows heart to contract so doesn’t tire and acts involuntary
striated so have medium power
3 categories of tissue found in animals
epithelial, muscle, connective
in the endosymbiotic theory what is the benefit to the eukaryotic cell
protection from external environment, substances can flow from the mitochondria to the chloroplast
link the properties of skeletal muscle to its function
skeletal muscles allow bones to move, therefore there are voluntary muscles
due to long bands of cells it has a high power
due to high power it tires easily
describe the structure of connective tissue
contains fibres of collagen and elastic
cells
basic unit of a living thing
tissues
different cells work together for a specific function
organs
different tissues that work together for a specific function
organ systems
different organs that work together to support a whole system
organism
different systems work together to support the whole organism
different types of epithelial tissue
squamous, cuboildal, cilliated
epithelial tissue
continuous layers that line external/ internal surface
cells sit on basement membrane of collagen and other proteins
maybe have protective/ secretory functions and nerve endings
squamous tissue
e.g walls of alveoli
flattened cells used for diffusion
cuboidal epithelial tissue
e.g salivary glands
1 cell thick
ciliated columnar epithelial tissue
e.g in trachea
substances move through them
columnar epithelial tissue with micro villi
for absorption in the small intestine
protein
biological molecules, all complex polymers made from amino acids and monomers
polypeptides
chain of amino acids
zwitterion
at a pH of 7 the amino group is positively charged and the carboxyl group is negatively charged so overall neutral
what happens to the amino group of a protein at pH7
as it is basic it gains a H+ ion becomes positively charged
what happens to the carboxyl group of a protein at pH7
as it is acidic it looses a H+ ion becomes negatively charged
diapeptide
formed from 2 amino acids during a condensation reaction