Topic E - Introduction to Model View Controller
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
separation of concerns (SoC)
a design principle for separating a computer program into distinct sections such that each section addresses a separate concern.
recall class diagrams and how each class has its own unique set of behaviours
related to the “single responsibility principle”
exampl: suppose we have two classes BankAccount and Client, BankAccount would only be concerned with data relating to an account
concern (in computer programming)
set of information that affects the code of a computer program
single responsibility principle
the idea that every method, class, attribute should only be responsible for ONE thing
ex: a class that contains methods calculateData(), formatAsPDF(), and sendByEmail(). bad design bc this class would have three full-fledged responsibilities (data, formatting, and communication). therefore, it’s better to have THREE classes that are responsible for each of those three things.
encapsulation design principle
closely related to single responsibility principle and separation of concerns
encapsulation: group the data (fields) and the methods that operate on the data in the same module (aka, class)
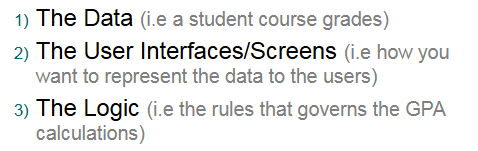
the three main components of user interfaces
so for MODEL VIEW CONTROLLER:
data = model
user interface/screen = view
logic = controller
main purposes of MVC (model view controller)
make maintenance for the application easier
reduce effort to add new features
provides a logical and simple code structure
enables the presentation of the same info in different ways (for example, view in desktop, website, mobile, etc)
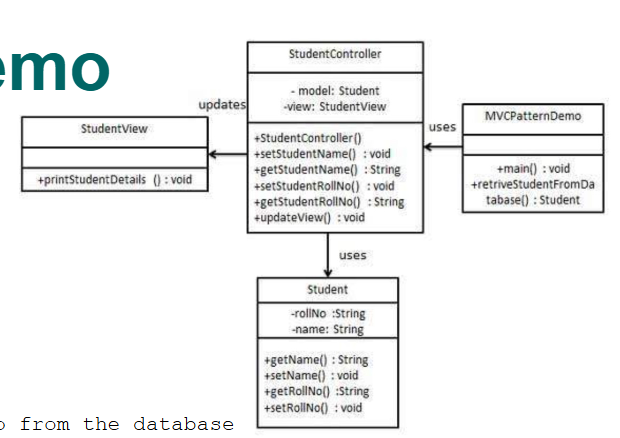
class diagram of a system designed following MVC
note: the MVC DEMO is not considered part of MVC; it’s the “main” method that allows you to see how things are ran and executed