Modern Physics Lecture 1 - Waves
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Why is the particle model ruled out?
Light arriving at screen has to “know” about both slits
Give two things that phase shift can be caused by
Difference in path length
Passage through a crystal
What is the definition of the classsical theory of light?
A wave distrubance in the electric and magnetic fields in space
How do you calculate intensity for a wave?
I = A² (where A = amplitude)
Give 3 important properties of intesity
It is never negative but can be zero
The “intensity” of lighr is an average over time
It is carried by both electric an magnetic fields
What is an advantage of using an interferometer?
It has a very high degree of accuracy
What is a beam splitter?
A beam splitter transmits 50% and reflects 50% of light intensity
Define doping
Adding impurities to change the % of transmission
What did interferometers help discover
Helped discover gravitational waves
What does reflection from a beam splitter cause and why?
Phase shift - arises because of energy conservations
Desribe a symmetric beam splitter
Transmission causes no phase shift
Reflection causes ¼ wavelength phase shift
Describe the detector
Indicates the intensity(power) of incident light
Units: Watts
Describe the mirror
No transmission
No phase shift on reflection
Give 3 problems with the wave picture
Black body radiation
Photoelectric effect
Compton scatterring
Define black body
An idealised object which absorbs all light incident on it and re-emits it having brought it into equilibrium with matter
Give Stefan’s law

Give Wien’s law
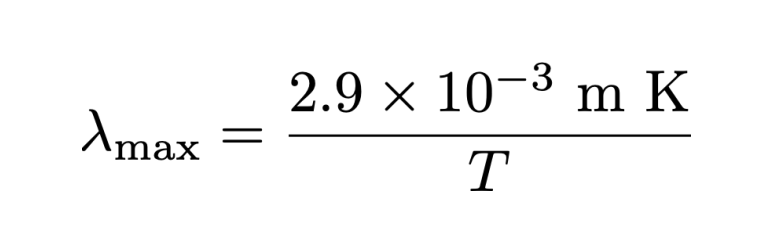
Give the Rayleigh-Jeans law
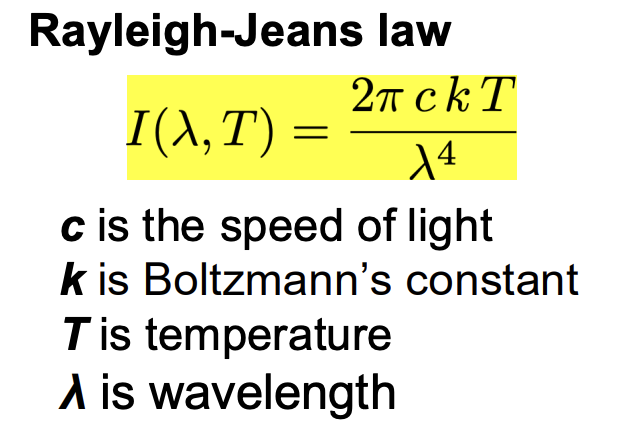
What is the key assumption in deriving the Rayleigh-Jeans law?
At all wavelengths ligth energy is absorbed and emitted continuously
What is the problem with the Rayleigh-Jeans law?
Didn’t fit the data
Diverges for small wavelengths, prediciting infinite intensity for very small wavelengths.
Known for ultra-violet catastrophe.
Give Planck’s law
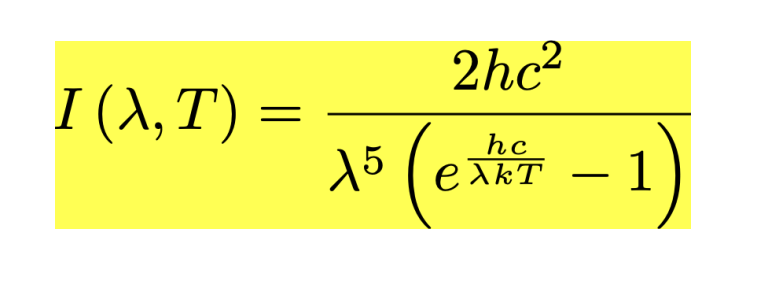
What is hbar?
hbar = h/2pi
Give two experimental observations for the photoelectric effect
When incident light is above a threshold frequency, current flowa, proportional to intensity.
When incident light is below the threshold frequency, no current flows, irrespective of intensity
What is binding energy
Energy needed for electron to escape from the metal
What is the wavevector?
k = 2pi/lambda
What is compton scattering?
When x-rays are incident on a metal, they scatter from the free electrons in the metal
What is Thomson scattering?
A theory for how electromagnetic waves should scatter from charged particles
What are the key elements of Thomson scattering?
Incoming wave induces the charged particle to oscillate at the same frequenc f as the wave.
Oscillating particle emits light at the same frequency f in all directions
Why did high energy x-ray scattering experients not match Thomson’s predictions:
Back-scattered light was weaker than Thomson predicted
Scattered light experienced an angle-dependant wavelength wavelnegth shift
What did compoton model scattering as?
An elastic collision between electron and photon
Give compton scattering formula:
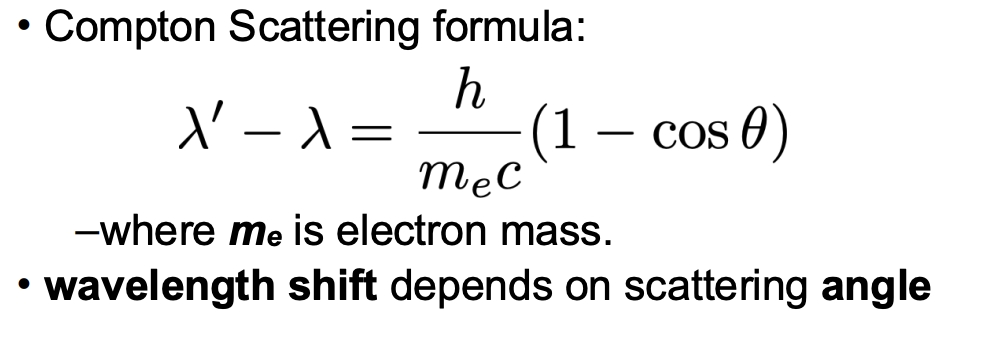
When is the shift only measurable?
When photon wavelength is not enormous relative to a picometre
What happens when a very very weak beam is projected at a screen?
Detection is no longer continuous
“clicks” at random intervals, on average once per second
Why does measurement have a profound effect on the sustem,?
When not observed the photon behaves like a wave
When measured, the photon behaves like a particle