Lecture 5: Screening and sampling
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
define precision
o Refers to the ability of a measuring instrument to give consistent results on repeated trials
o Synonym: reliability
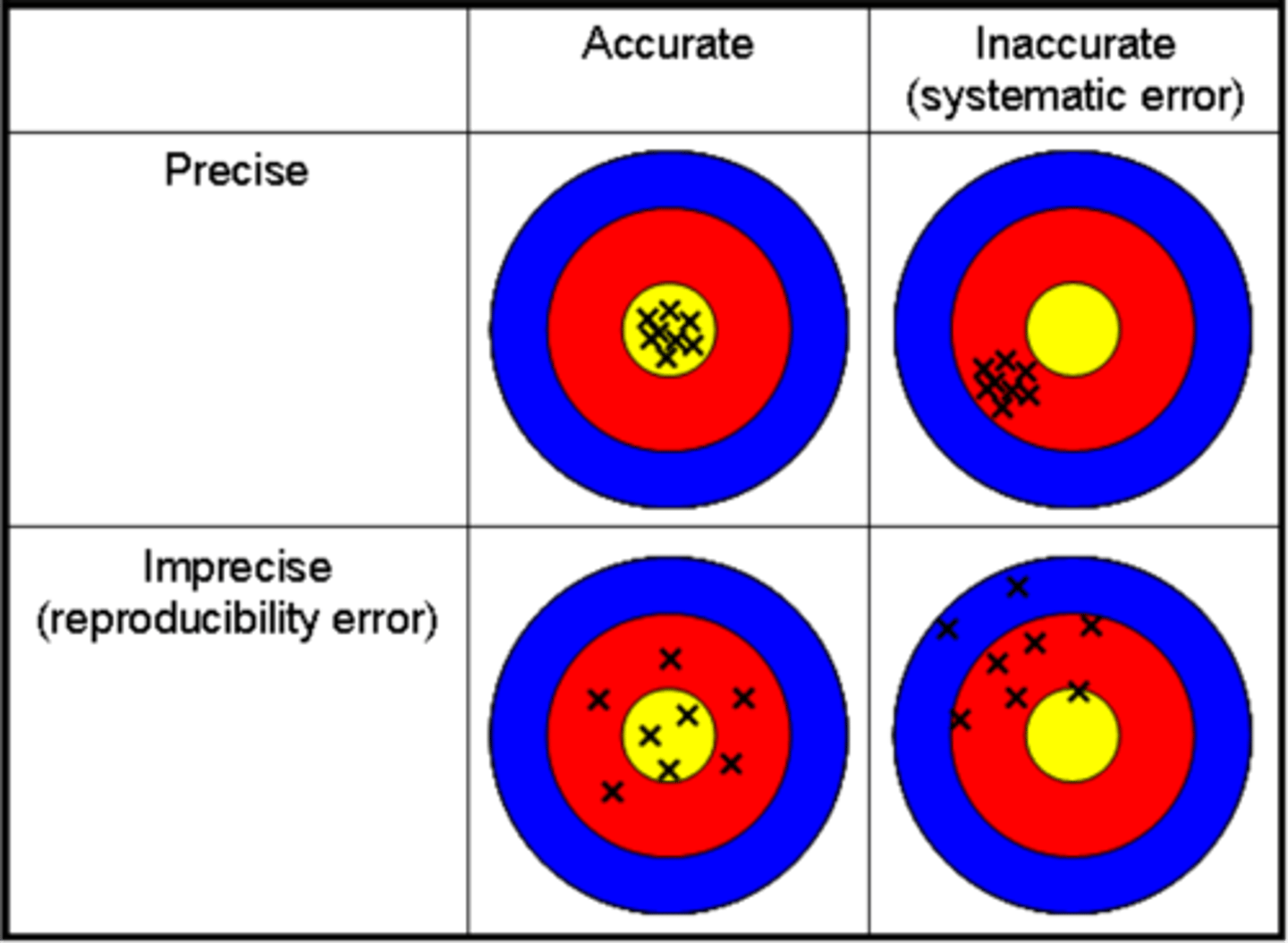
define accuracy
o The ability of the measuring instrument to give a true interpretation of reality
o Synonym: validity
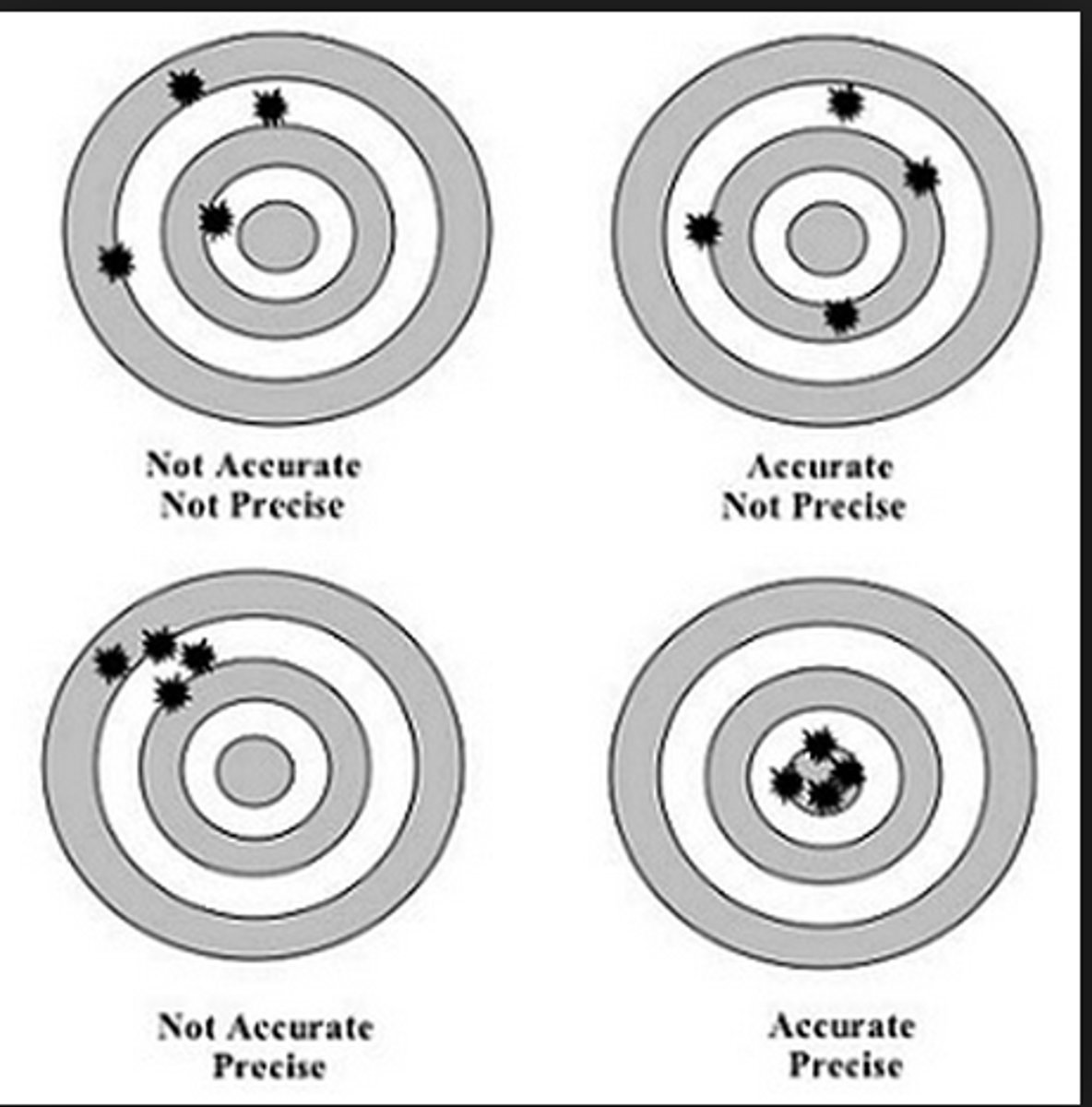
What is precision in the context of screening tests?
Precision refers to how consistently a test produces the same result under the same conditions, or its repeatability.
What is accuracy in the context of screening tests?
Accuracy refers to how close the result is to the true value or accepted standard.
How is precision different from accuracy?
Precision is about consistency and repeatability of measurements, while accuracy is about how close the measurement is to the true value.
Why is it important for a screening test to be both precise and accurate?
For reliable and valid measurements in diagnostics or treatment monitoring, ensuring both precision (consistency) and accuracy (truthfulness) is essential.
what are the measures of accuracy?
- sensitivity
- specificity
- positive predictive value
- negative predictive value
define sensitivity
o Positive in disease
o The probability of the test being positive when the disease is actually present
define gold standard
o The 'truth' against which we compare our tests
o A definitive diagnostic test that is considered the best available
E.g., biopsy/clinpath, surgery, necropsy, etc.
o Provides a standard against which sensitivity and specificity are evaluated
how do you calculate sensitivity?
True positives divided by (true positives + false negatives)
a/(a+c)
Highly sensitive test allows you to trust a negative result more than a positive result
Minimizes type II error (that of obtaining a 'false negative')
define specificity
o Negative in health
o The probability of a test correctly classifying an individual as 'disease free'
how do you calculate specificity?
True negatives divided by (true negatives + false positives)
d/(b+d)
Highly specific test allows you to trust a positive result more than a negative result
Minimizes type I error (that of obtaining a 'false positive')
define positive predictive value
The probability of a patient actually having a disease when the test is positive
define negative predictive value
The probability of a patient being healthy when the test is negative
how do you calculate positive predictive value?
a/(a+b)
(true positives)/((true positives + false positives))
how do you calculate negative predictive value?
d/(c+d)
(true negatives)/(true negatives + false negatives)
Types of random sampling
o Simple random sampling
o Systematic random sampling
o Stratified sampling
o Cluster sampling
o Multi-stage sampling
o Much more common and desirable in medical/public health applications
Determination of error/bias is possible
Given a positive heartworm test in a dog with normal behavior and normal PE, what is the PPV of this test, and how confident should you be in the result?
1. Prevalence: 1.7% means 17 out of 1,000 dogs are truly positive.
2. Sensitivity: 98% sensitivity means 98% of the true positives are correctly identified.
True Positives (TP) = 98% of 17 = 16.7
3. False Negatives (FN): 17 - 16.7 = 0.3
4. Specificity: 98% specificity means 98% of true negatives are correctly identified.
True Negatives (TN) = 98% of 983 = 963.3
5. False Positives (FP): 983 - 963.3 = 19.7
PPV calculation:
PPV = True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives)
PPV = 16.7 / (16.7 + 19.7) = 45.9%
Thus, the PPV is 45.9%, meaning you are only about 46% confident that this positive test result is correct.
What should you do next given a positive heartworm test with a low PPV?
1. Test blood for microfilariae: If positive, the result is likely correct. If negative, uncertainty remains.
2. Use a confirmatory test: Consider Western blot or a different antigen test to confirm the result.
3. Treat as if the result is accurate: If confident enough, proceed with treatment.
4. Do not treat and continue preventative: In cases of uncertainty, hold off on treatment and maintain preventive care.
What is random sampling?
Random Sampling (Probability Sampling):
Every element in the population has an equal chance of being selected.
Statistically advantageous because it's unbiased and allows for generalization to the population.
What is non-random sampling (non-probability sampling)?
Probability of selection is unknown.
Easier and less expensive but makes it harder to identify errors or conduct statistical analysis.
What are some types of non-random sampling methods?
1. Convenience Sampling: Samples are selected because they are easily accessible.
2. Snowball Sampling: Sampling starts with one person and grows as others refer their friends or contacts.
3. Purposive Sampling (Judgmental Sampling): You choose participants based on your judgment, selecting individuals who are thought to be representative of the population.
4. Quota Sampling: Selecting a specific number of participants from each subgroup of the population based on predefined characteristics.
Why is random sampling considered more scientifically advantageous over non-random sampling?
Random Sampling eliminates bias, ensuring that each member of the population has an equal chance of being selected, which leads to more reliable and generalizable results.
Non-Random Sampling does not provide equal chances for every member to be included, which can introduce bias and make it harder to extrapolate findings to the broader population.
What is sampling bias?
Sampling Bias occurs when the sampled population is not representative of the overall population.
Example: Fast-growing fish are more likely to be sampled than slower-growing fish in a non-random, non-size-selective method.
when does sampling bias arise?
It arises when certain groups are more or less likely to be selected for the sample, leading to an inaccurate representation of the population.
What is sampling error?
Sampling Error is the difference between the survey result and the actual population value due to the random nature of sampling.
is sampling error avoidable?
It is unavoidable unless you sample the entire population.
what is sampling error influenced by?
Influenced by sample size and the sampling scheme.
how is sampling error different from sampling bias?
Unlike sampling bias, it can be predicted, calculated, and accounted for.
what are some measures of sampling error?
Confidence limits
Standard error
Coefficient of variance
P-values
Compare and contrast sampling bias and sampling error
Sampling Bias: Results from flawed sampling methods or unequal probabilities in selecting participants. It leads to misrepresentation and cannot be avoided without careful attention to method.
Sampling Error: A natural occurrence in any sample, due to randomness, which can be quantified and accounted for by using statistical measures like confidence limits or standard error.
How can sampling error be controlled?
Sampling error can be controlled by:
1. Selecting an appropriate sample size.
2. Using a suitable sampling method.
After the sample is taken, sampling error can be calculated and adjusted for.
what do the measures of sampling error help quantify?
These help quantify the degree of uncertainty in the sample estimate and are useful for determining sample size and the accuracy of the results.