ap psych - unit three study guide
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:39 PM on 12/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
1
New cards
sensation
how an organism receives stimuli and information from the surrounding world via sensory organs
2
New cards
perception
cognitive processes of receiving, encoding, storing, and organizing sensations
3
New cards
bottom-up processing
starts with sensory receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory info for processing
\
ex: stubbing your toe
\
ex: stubbing your toe
4
New cards
top-down processing
the construction of perceptions from sensations (coming from bottom-up) and on our own experiences/experiences
\
ex: if you’re in a bad mood and eating, the food might taste bad
\
ex: if you’re in a bad mood and eating, the food might taste bad
5
New cards
psychophysics
study of the links between physical stimuli and psychological experience
6
New cards
absolute threshold
weakest amount of a stimulus that a person can detect 50% of the time
7
New cards
signal detection theory
ability to identify a stimulus (signal) when it is embedded in a distraction background
8
New cards
subliminal stimulation
stimulus which is below one’s threshold for conscious awareness
9
New cards
difference threshold
smallest difference between two stimuli which a person can detect 50% of the time or more
\
aka: just noticeable difference (jnd)
\
aka: just noticeable difference (jnd)
10
New cards
weber’s law
the principle that two stimuli must differ by a constant proportion, not a constant amount, for a difference between them to be connected
\
just noticeable difference (jnd)
\
about 2% for everything
\
just noticeable difference (jnd)
\
about 2% for everything
11
New cards
transduction
conversion of one form of energy into another; receptor cells take incoming energy and change it into neural impulses
\
in hearing: cochlea
in vision: retina
in olfaction: cilia
in gustation: taste receptors
in touch: touch receptors
\
in hearing: cochlea
in vision: retina
in olfaction: cilia
in gustation: taste receptors
in touch: touch receptors
12
New cards
cocktail party effect
phenomenon of being able to focus one's auditory attention on a particular stimulus while filtering out a range of other stimuli, much the same way that a partygoer can focus on a single conversation in a noisy room
13
New cards
sensory adaptation
reduction in sensitivity a stimulus after constant exposure to it
\
physiological adaptation
\
self-regulated
\
physiological adaptation
\
self-regulated
14
New cards
habituation
kind of learning; nervous system selectively filters out stimuli
\
psychological adaptation - decreased response
\
conscious
\
psychological adaptation - decreased response
\
conscious
15
New cards
selective attention
process of directing our awareness to relevant stimuli while ignoring irrelevant stimuli in the environment
16
New cards
wavelength
distance from the peak of one light/sound wave to the peak of the next
\
in light: color/hue
in sound: pitch
\
in light: color/hue
in sound: pitch
17
New cards
amplitude
top to bottom of a wave
\
in light: intensity
in sound: intensity/volume
\
in light: intensity
in sound: intensity/volume
18
New cards
pupil
adjustable opening in the center of the eye
19
New cards
iris
muscle that controls pupil size
20
New cards
lens
changes shape to help focus, accommodates
21
New cards
retina
light sensitive surface with rods and cones
\
rods and cones → bipolar cells → ganglion cells → optic nerve
\
rods and cones → bipolar cells → ganglion cells → optic nerve
22
New cards
acuity
sharpness of vision
23
New cards
nearsightedness/myopia
light focuses in front of the retina
\
objects near are clear and objects far are blurry
\
objects near are clear and objects far are blurry
24
New cards
farsightedness/hyperopia
light focuses behind the retina
\
objects far are clear and objects near are blurry
\
much rarer
\
objects far are clear and objects near are blurry
\
much rarer
25
New cards
rods
periphery of retina
\
120 million
\
no color vision
\
sensitive to light and give twilight vision
\
120 million
\
no color vision
\
sensitive to light and give twilight vision
26
New cards
cones
clustered in the fovea
\
fewer than rod cells (6-7 million)
\
center of the retina
\
color and daylight vision
\
fewer than rod cells (6-7 million)
\
center of the retina
\
color and daylight vision
27
New cards
optic nerve
carries neural impulses to the thalamus
28
New cards
blind spot
where optic nerve leaves the eyeball
29
New cards
blindsight
condition in which a person can respond to a visual stimulis without consciously experiencing it
30
New cards
fovea
center focus point
31
New cards
malleus
another name for hammer
\
^^a small bone in the middle ear that transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus (anvil)^^
\
^^a small bone in the middle ear that transmits vibrations of the eardrum to the incus (anvil)^^
32
New cards
incus
another name for anvil
\
^^a small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations between the malleus (hammer) and stapes (stirrup)^^
\
^^a small anvil-shaped bone in the middle ear, transmitting vibrations between the malleus (hammer) and stapes (stirrup)^^
33
New cards
stapes
another name for stirrup
\
^^a tiny, U shaped bone that passes vibrations from the anvil (incus) to the cochlea^^
\
^^a tiny, U shaped bone that passes vibrations from the anvil (incus) to the cochlea^^
34
New cards
stroop effect
\n brains recognize color first, interfering with our ability to read aloud
\
need selective attention to identify the color of the word
\
need selective attention to identify the color of the word
35
New cards
feature detectors
respond to visual aspects of the environment (shape, angle, movement)
\
visual cortex
\
send information to neural networks (supercell clusters) that can perform tasks like visualizing faces
\
cube, triangle (gestalt)
\
visual cortex
\
send information to neural networks (supercell clusters) that can perform tasks like visualizing faces
\
cube, triangle (gestalt)
36
New cards
parallel processing
brain processes many aspects simultaneously
\
divides a visual scene into sub-dimensions
\
divides a visual scene into sub-dimensions
37
New cards
young-holtzman trichromatic theory
retina has three receptors sensitive to red, green, and blue
38
New cards
opponent-process theory
opposing retinal processes enable color vision
\
red and green, blue and yellow, white and black
\
red and green, blue and yellow, white and black
39
New cards
color constancy
\n perceiving familiar objects as having consistent color under different conditions of illumination
\
ex: black and blue or white and gold dress
\
ex: black and blue or white and gold dress
40
New cards
audition
sense/act of hearing
41
New cards
frequency theory
rate of nerve impulses travelling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, enabling us to sense its pitch
\
^^explains how we sense low pitches^^
\
^^explains how we sense low pitches^^
42
New cards
place theory
\n links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea's membrane is stimulated
\
^^explains how we sense high pitches^^
\
^^explains how we sense high pitches^^
43
New cards
pinna
external part of the ear
44
New cards
auditory canal
tube that runs from outer ear to middle
45
New cards
eardrum
tympanic membrane that vibrates with sound waves
\
middle ear
\
middle ear
46
New cards
hammer, anvil, sitrrup
smallest bones; vibrate from the eardrum
\
middle ear
\
middle ear
47
New cards
cochlea
where transduction occurs
\
coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube where sound waves trigger neural impulses
\
filled with hair cells
\
inner ear
\
coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube where sound waves trigger neural impulses
\
filled with hair cells
\
inner ear
48
New cards
semicircular canals
fluid filled tubes to help keep balance; connect to vestibular sacs
\
inner ear
\
inner ear
49
New cards
basilar membrane
a fibrous membrane within the cochlea that supports the organ of corti
50
New cards
synesthesia
to perceive together; perceptual phenomenon in which stimulation of one sensory or cognitive pathway leads to involuntary experiences in a second cognitive or sensory pathway
51
New cards
conduction hearing loss
damage to the system that conducts sound waves to the cochlea
\
most likely due to a punctured eardrum
\
most likely due to a punctured eardrum
52
New cards
sensorineural hearing loss
damage to the cochlea’s receptor cells or to the auditory nerves
53
New cards
gate-control theory
neurological “gate” in the spinal cord which opens to allow small fibers of pain through but large fibers can override small fibers to stop pain
\
a-delta fibers: small myelination; sharp, immediate pain
c-fibers: dull, aching pain (chronic)
beta fibers: sense touch
\
a-delta fibers: small myelination; sharp, immediate pain
c-fibers: dull, aching pain (chronic)
beta fibers: sense touch
54
New cards
sensory interaction
experiences result in two or more senses working together because one sense can influence another
55
New cards
kinesthesis
system for sensing the position and movement of individual body parts
\
aka: proprioception
\
aka: proprioception
56
New cards
vestibular
sense of body movement, position, and spatial orientation; including sense of balance
\
located in the semicircular canal
\
located in the semicircular canal
57
New cards
gustation
taste, chemical sense
\
5 basic sensations:
sweet - energy source
salty - sodium essential to psychological processes
sour - potentially toxic acid
bitter - potential poisons
umami - proteins to grow and repair tissue
\
5 basic sensations:
sweet - energy source
salty - sodium essential to psychological processes
sour - potentially toxic acid
bitter - potential poisons
umami - proteins to grow and repair tissue
58
New cards
fungiform papillae
swellings on the anterior surface (front) of the tongue, in humans numbering about 200 and each shaped like a mushroom
\
taste buds
\
decrease with age
\
taste buds
\
decrease with age
59
New cards
taste process
1. molecules enter taste pores of taste buds and stimulate taste cells
2. nerve impulses travel via the facial/glossopharyngeal nerve to the brain
3. impulse reaches the thalamus, where it is rerouted to the temporal lobe
4. taste stimuli is processed by the gustatory cortex
60
New cards
olfaction
smell, chemical sense
\
odorants enter the nasal cavity to stimulate five million receptors in the mucous membranes
\
odorants enter the nasal cavity to stimulate five million receptors in the mucous membranes
61
New cards
phermones
chemical message sent by a chemical
62
New cards
smell process
1. olfactory receptors
2. olfactory bulb (below frontal lobe)
3. olfactory areas in the temporal lobe
4. limbic system
\
hippocampus and amygdala can create strong emotional responses and memories associated to smell
63
New cards
nociceptors
sensory receptors that detect pain
64
New cards
pain → brain process
1. nociceptors
2. nerve fibers
65
New cards
inattentional blindness
selectively attending to one part of the environment and missing another
66
New cards
change blindness
specific form of inattentional blindness
\
fail to notice changes in our environment
\
fail to notice changes in our environment
67
New cards
prosopagnosia
neurological disorder characterized by the inability to recognize faces
68
New cards
gestalt
an organized whole, tendency to integrate meaningful pieces of info into meaningful wholes
69
New cards
figure-ground
organization of the visual field onto objects that stand out from their surroundings
70
New cards
grouping
after distinguishing the figure from the ground, our perception needs to organize the figure into a meaningful form using grouping rules (proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, and connectedness)
71
New cards
convergence
neuromuscular cue to tell brain the closeness of an object
\
binocular
\
binocular
72
New cards
retinal disparity
difference between how each retina experiences the world
\
binocular
\
binocular
73
New cards
relative height
vertical dimensions seem longer than identical horizontal
\
monocular
\
monocular
74
New cards
relative size
allows you to determine how close objects are to an object of known size
\
monocular
\
monocular
75
New cards
relative motion (parallax)
as we’re moving, objects that are actually stable seem to move
\
monocular
\
monocular
76
New cards
interposition
if one object partially blocks our view of another, we percevie it as closer
\
monocular
\
monocular
77
New cards
relative clarity
hazy/blurry objects seem farther away than sharp, clear ones
\
monocular
\
monocular
78
New cards
texture gradient
gradual change from coarse, distinct texture to a fine, indistinct texture signals increasing distances
\
monocular
\
monocular
79
New cards
linear perspective
as lines converge, greater distance is perceived
\
monnocular
\
monnocular
80
New cards
light/shadows
using light and shadows to perceive depth
\
monocular
\
monocular
81
New cards
stroboscopic movement
the apparent motion of a series of separate stimuli occurring in close consecutive order, as in motion pictures
82
New cards
depth perception
ability to see objects in 3d although the images that strike the retina are 2d
83
New cards
ponzo effet
visual illusion in which the upper of two parallel horizontal lines of equal length appears to be longer than the bottom of the two lines when they are flanked by oblique lines that are closer together at the top than they are at the bottom
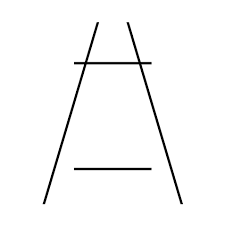
84
New cards
distal stimuli
stimuli that lie outside of the body
85
New cards
proximal stimuli
stimulus energies that impinge directly on our sensory receptors
86
New cards
muller-lyer illusion
optical illusion in which two lines of the same length appear to be of different lengths
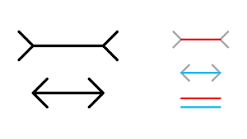
87
New cards
ames room illusion
an irregularly shaped but apparently rectangular room in which cues for depth perception are used experimentally to distort the viewer's perception of the relative size of objects within the room
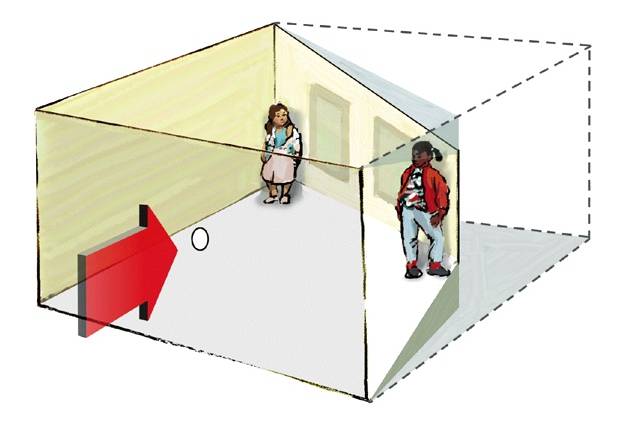
88
New cards
lightness constancy
perceiving objects with the same level of brightness, even though the illumination may change
89
New cards
perceptual adaptation
adjust to artificially displaced or even inverted visual field
90
New cards
perceptual set
mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another
91
New cards
mcgurk effect
occurs when a person perceives that another's lip movements do not correspond to what that individual is saying
92
New cards
gustav fechner
coined the term “absolute threshold”
93
New cards
david hubel
demonstrated that neurons in the occipital lobe's visual cortex receive information from individual ganglion cells in the retina (feature detector cells)
\
also proved that the brain divides a visual scene into several subdimensions (color, movement, etc.) and processes each separately
\
also proved that the brain divides a visual scene into several subdimensions (color, movement, etc.) and processes each separately
94
New cards
ernst weber
created “weber’s law”
95
New cards
daniel kahneman
conducted research to discover factors that influence human judgment and decision making
96
New cards
torsten wiesel
discovered feature detectors