Chapter 12 - Transcription and RNA Modification
1/28
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Gene
A segment of DNA used to make a functional product, either an RNA or a polypeptide. Transcription is the first step in expressing this chromosomal DNA.
Transcription
The act or process of making a copy. In genetics, it refers to the copying of a DNA sequence into an RNA sequence. The structure of DNA is not altered as a result of this process, so it can continue to store information. The second process in the central dogma of genetics.
Structural Genes
Also called protein-encoding genes, these encode the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Transcription of a protein-encoding gene produces this product. The sequence of bases in this product determines the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide during translation.
Polypeptides / traits
Fill in the blank…
One or more ( ) constitute a protein. The synthesis of functional proteins determines an organism’s ( ).
DNA Replication
Makes DNA copies that are transmitted from cell to cell and from parent to offspring. The first process in the central dogma of genetics.
Translation
The final process in the central dogma of genetics that produces a polypeptide using the information in mRNA. This polypeptide becomes part of a functional protein that contributes to an organism’s traits.
Gene Expression
The overall process by which the information within a gene is used to produce a function product which can, in concert with environmental factors, determine a trait.
DNA base sequences define the beginning and end of a gene and regulate the level of RNA synthesis. Proteins must recognize and act on DNA for transcription to occur.
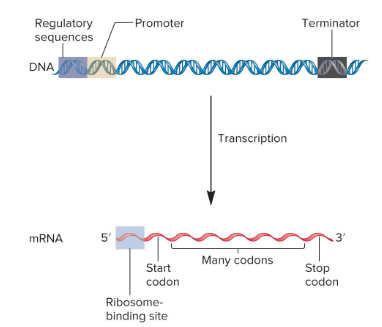
Regulatory Sequences
Sites for the binding of regulatory proteins, which influence the rate of transcription. These can be found in a variety of locations.
Promoter
The site for RNA polymerase binding; it signals the beginning of transcription.
Terminator
A site that signals the end of transcription.
Ribosome-Binding Site
The site for ribosome binding to mRNA in bacteria; translation begins near this site in the mRNA.
In eukaryotes, the ribosome binds to a 7-methylguanosine cap in the mRNA and scans the RNA for a start codon.
Codons
3-nucleotide sequences within the mRNA that specify particular amino acids. The sequence of codons within mRNA determines the sequence of amino acids within a polypeptide.
Start Codon
Specifies the first amino acid in a polypeptide sequence, usually a formylmethionine in bacteria or a methionine in eukaryotes.
Stop Codon
Specifies the end of polypeptide synthesis.
Polycistronic
A bacterial mRNA that encodes two or more polypeptides.
Template Strand
The DNA strand that is actually transcribed. The RNA transcript is complementary to this strand. It is also called the anti-sense strand.
Coding Strand
Also called the sense strand or the non-template strand, this strand’s base sequence is identical to the RNA transcript, except for the substitution of uracil in RNA for thymine in DNA.
Transcription Factors
Recognize the promoter and regulatory sequences to control transcription.
Translation
Fill in the blank…
mRNA sequences such as the ribosomal-binding site and codons direct ( ).
1) Initiation
2) Elongation
3) Termination
What are the three stages of transcription? These steps involve protein-DNA interactions.
Initiation
In this stage of transcription, the promoter functions as a recognition site for transcription factors. The transcription factors enable RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter. Following binding, the DNA is denatured into a bubble known as the open complex.
Elongation
During this stage of transcription, RNA polymerase slides along the DNA in an open complex to synthesize RNA.
Termination
During this process of transcription, a terminator is reached that causes RNA polymerase and the RNA transcript to dissociate from the DNA.
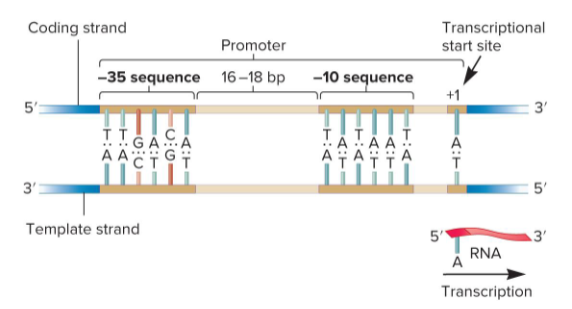
Promoters
DNA sequences that “promote” gene expression. They direct the exact location for the initiation of transcription. They are typically located just upstream of the site where transcription of a gene actually begins. The bases here are numbered in relation to the transcriptional start site.
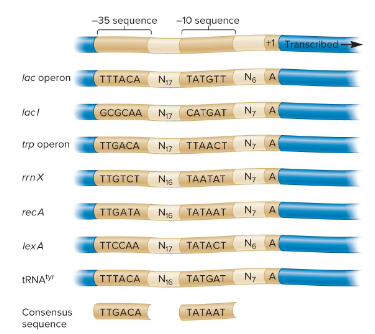
Consensus Sequence
The most common sequence in the -35 and -10 promoter regions. It is likely to result in a high level of transcription. Sequences that deviate from this sequence typically result in lower levels of transcription.
RNA Polymerase
The enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA. In E.coli, the holoenzyme is composed of a core enzyme with five subunits and a sigma factor, which all play distinct functional roles.
Closed Complex
This complex forms when RNA polymerase binds to the promoter.
Open Complex
This complex forms when the TATAAT box in the -10 region is unwound since A-T bonds are more easily separated.