Anatomy exam 1 UCF Dow
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
anterior
front of the body
posterior
back of body
superior
Higher on the body, nearer to the head
inferior
Lower on the body, farther from the head
proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
distal
away from the point of attachment
Rostral
toward the nose
caudal
toward the tail
Astrocytes (neuroglia cell)
-CNS
-most abundant glial cell type
-extract blood sugar from capillaries for energy
-take up and release ion to control environment around neurons
-involved in synapse formation in developing neural tissue
microglial (neuroglia cells)
-CNS
-smallest and least abundant glial cell
-defensive cells
-phagocytes-- the macro phages of the CNS
-engulf invading microorganisms and dead neuron
-derive from blood cells called monocytes
-migrate to CNS during embryonic and fetal periods
ependymal cells (neuroglial)
-CNS
-line the central activity of the spinal cord and the brain
-bear cilia- help circulate the cerebrospinal fluid
Oligodendrocytes (neuroglial)
-CNS
-have few branches
-wrap their processes around axons in CNS
**produce myelin sheaths in the CNS
satellite cells (neuroglial)
-PNS
-surround neuron cell bodies w/in ganglia
Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes)
(neuroglia)
-PNS
-surround axons in the PNS
**form myelin sheath around axons of the PNS
organizational structure of skeletal muscles
Each skeletal muscle is composed of individual muscle cells called muscle fibers. Muscle fibers are arranged into a bundle called a fascicle that is surrounded by connective tissue. Many fascicles are bundled together to make up the muscle
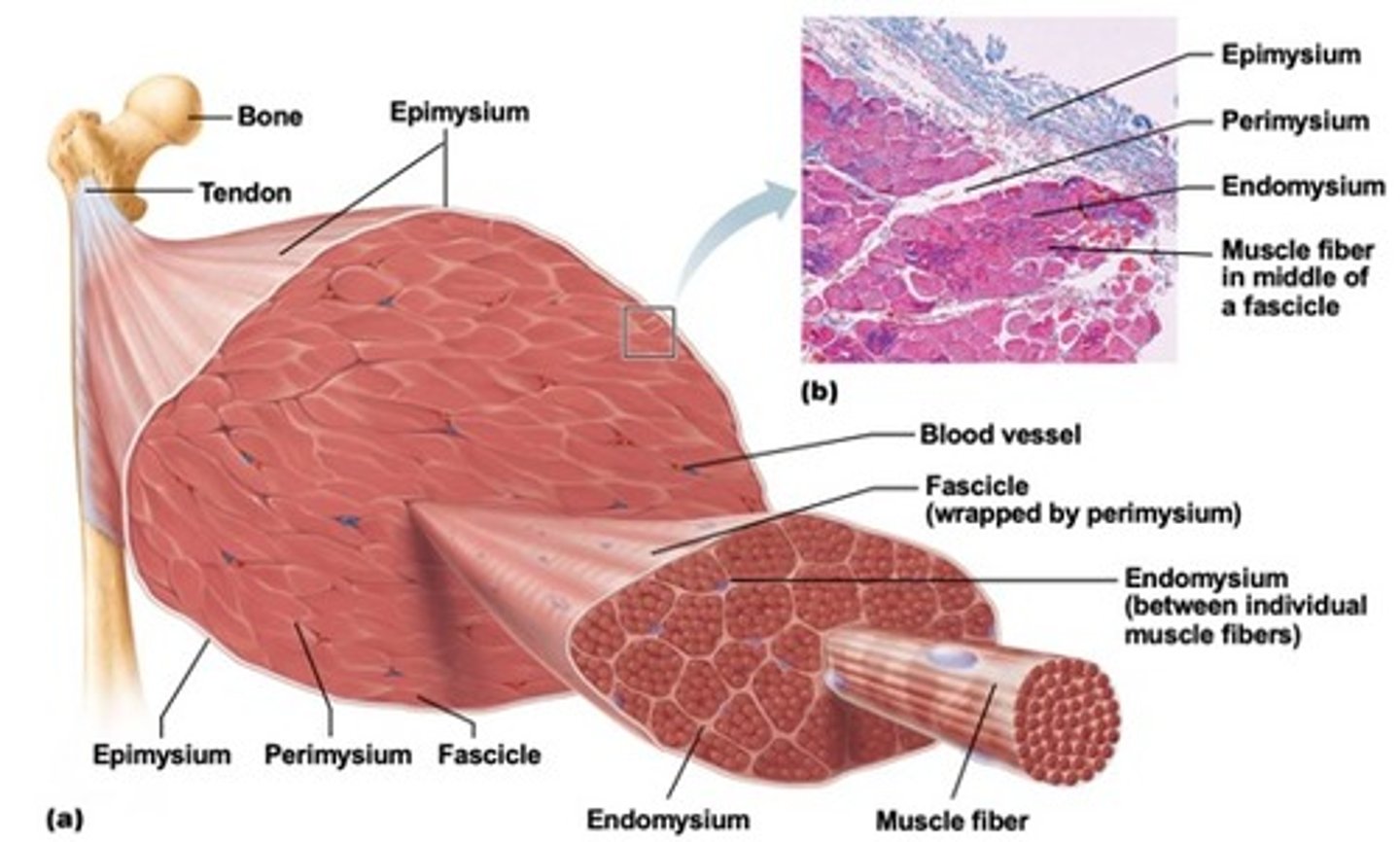
types of neurons
sensory- bring messages to CNS
motor- listen to sensory neurons; take message from CNS and bring to specific muscle
interneurons- acts on messages and tells motor neurons what to do; enables communication between sensory/motor neuron and CNS
structural classification of neurons
multipolar- possess more than 2 processes, numerous dendrites and 1 axon
bipolar- possess 2 processes, rare neurons, found in some special sensory organs
unipolar (pseudounipolar)- possess 1 short single process, start as bipolar neurons during development
how a neuron interacts w/ a skeletal muscle fiber to cause contraction
-indirect communication
-action potential
importance of the neuromuscular junction
-where nerve ending and muscle fiber meet (motor unit)
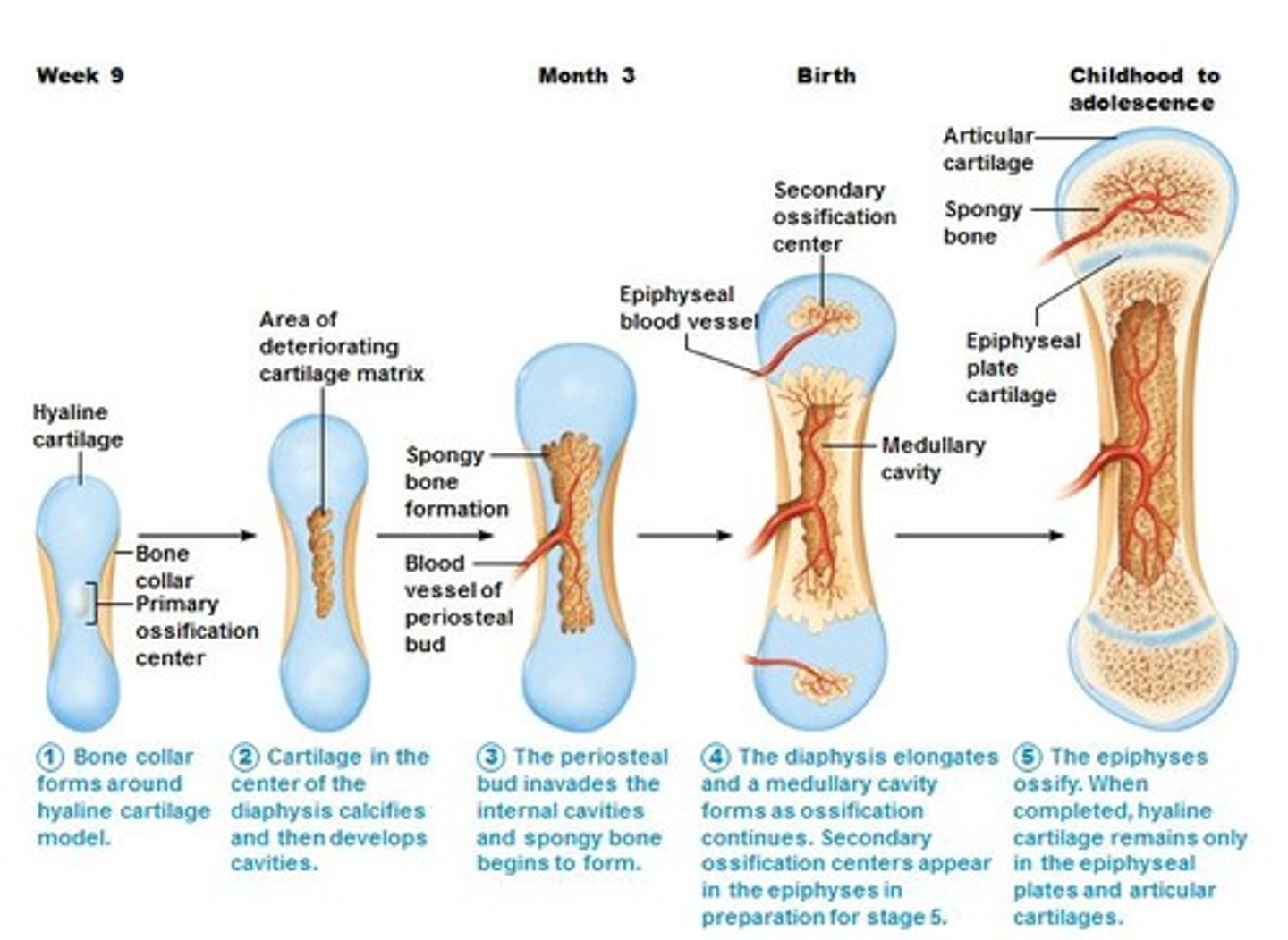
Ossification (osteogenesis)
-bone tissue formation
membrane bones (ossification)
-intramembranous ossification
-formed directly from mesenchyme w/in mesenchyme mb
-only happens during embryonic development
-specific bones: skull, mandible (jaw), clavicle
other bones (ossification)
-endochondral ossification
-w/in cartilage in embryonic development and rest of life
-w/ all bones except skull jaw and clavicle
-what is done when bones break
intamembranous ossification
bone develops from a fibrous membrane
-during embryonic development
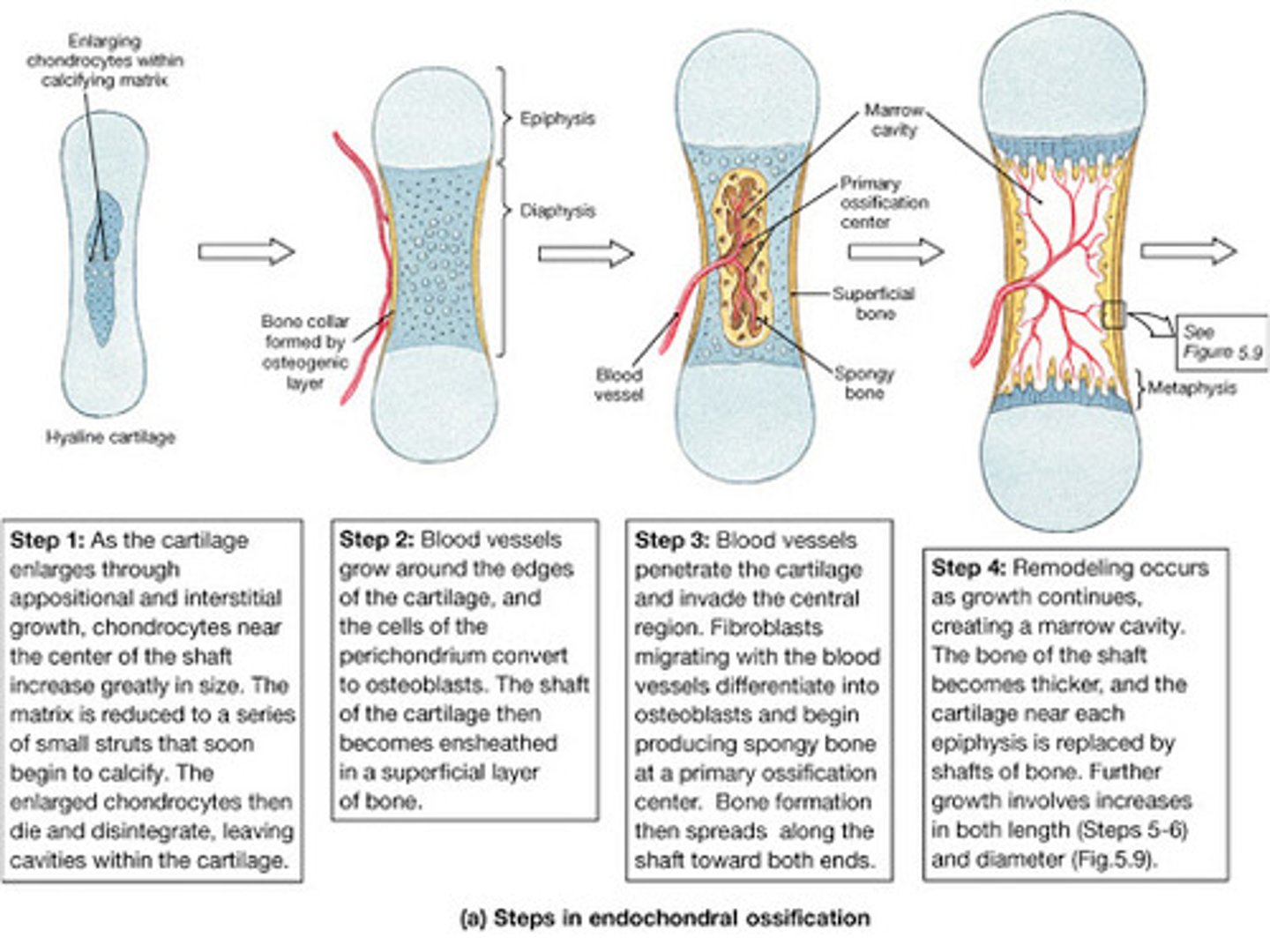
endochondral ossification
bone forms by replacing hyaline cartilage
-during late in second month of embryonic development and continues to early adulthood
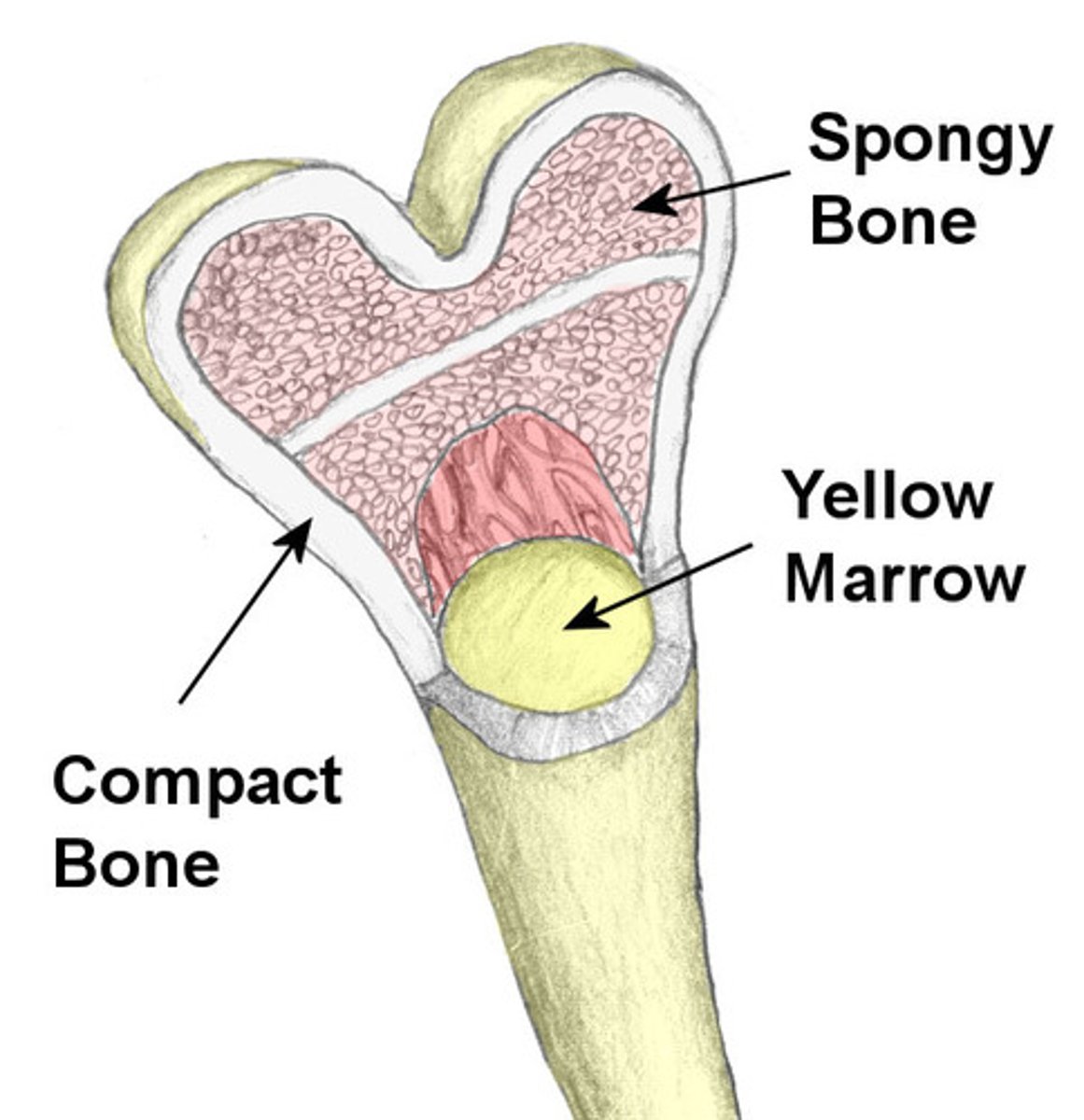
compact bone
dense outer layer of bone
spongy (cancellous) bone
-internal network of bone
-trabeculae: little "beams" of bone
-open spaces btwn trabeculae are filled with yellow bone marrow
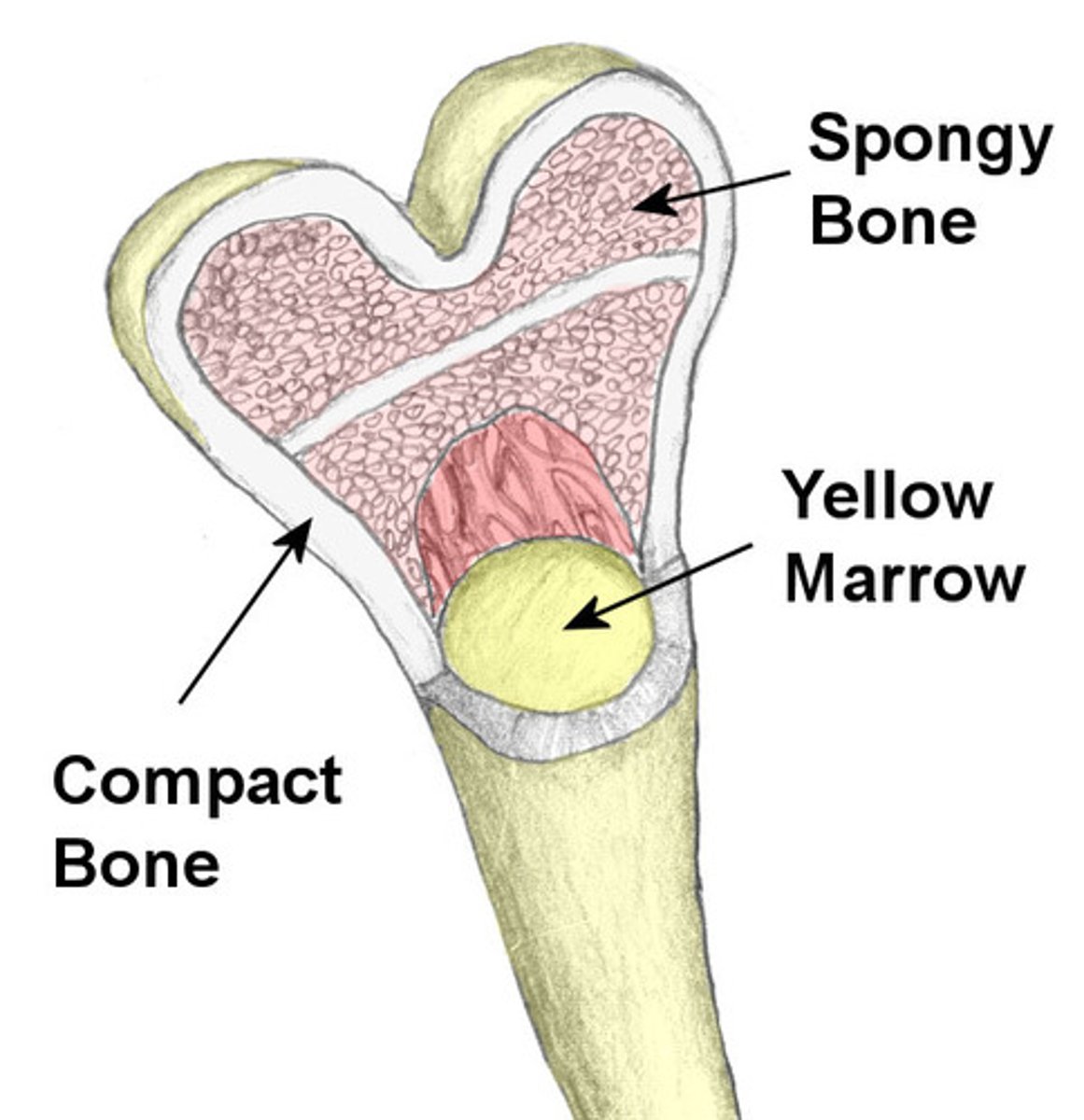
Where is red bone marrow found?
found mainly in flat bones such as hip, breast, skull, ribs, vertebral, and shoulder blades and in spongy bone at proximal ends of femur and humerus
osteoporosis
-A condition in which the body's bones become weak and break easily.
-characterized by low bone mass, bone reabsorption outpaces bone deposition, occurs in most of women after menopause (secretion of estrogens helps maintain bone density)
osteomalacia
-abnormal softening of bones in adults
-bones are inadequately mineralized
osteosarcoma
form of bone cancer
arthritis
painful inflammation and stiffness of the joints
-osteoarthritis: most common type, "wear and tear" arthritis
-rheumatoid arthritis: chronic inflammation disorder, normally paired w/ autoimmune disorders
-gout: uric acid build up causes pain in joints, based on diet
Atherosclerosis
condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries
-can restrict blood flow, if plaque bursts blood clot will form, considered a heart problem, can affect arteries
unpaired cranial bones
frontal
occipital
sphenoid
ethmoid
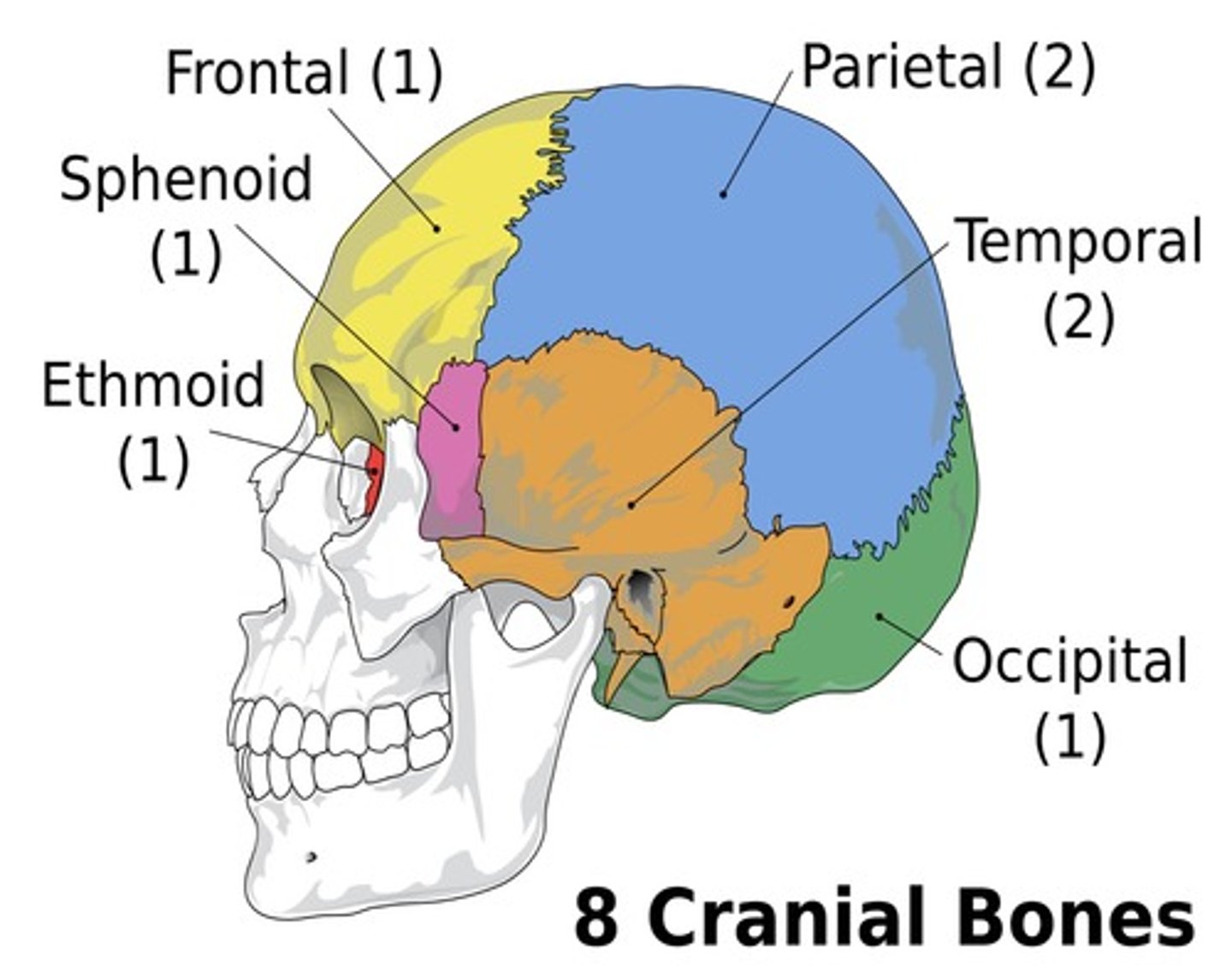
paired cranial bones
temporal
parietal
unpaired facial bones
mandible (jaw)
vomer
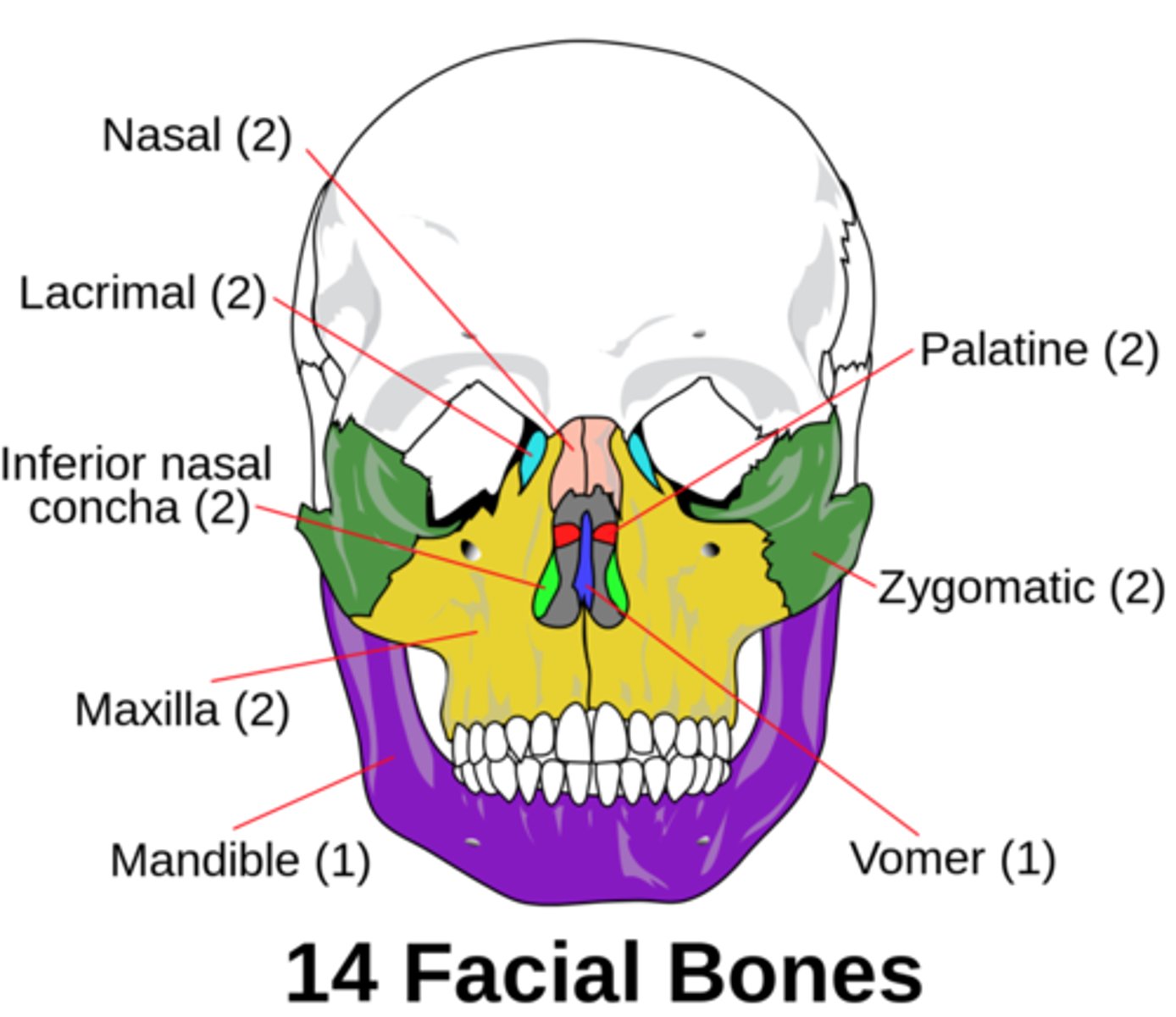
paired facial bones
maxillae
zygomatic
nasal
lacrimal
palatine
inferior nasal conchae
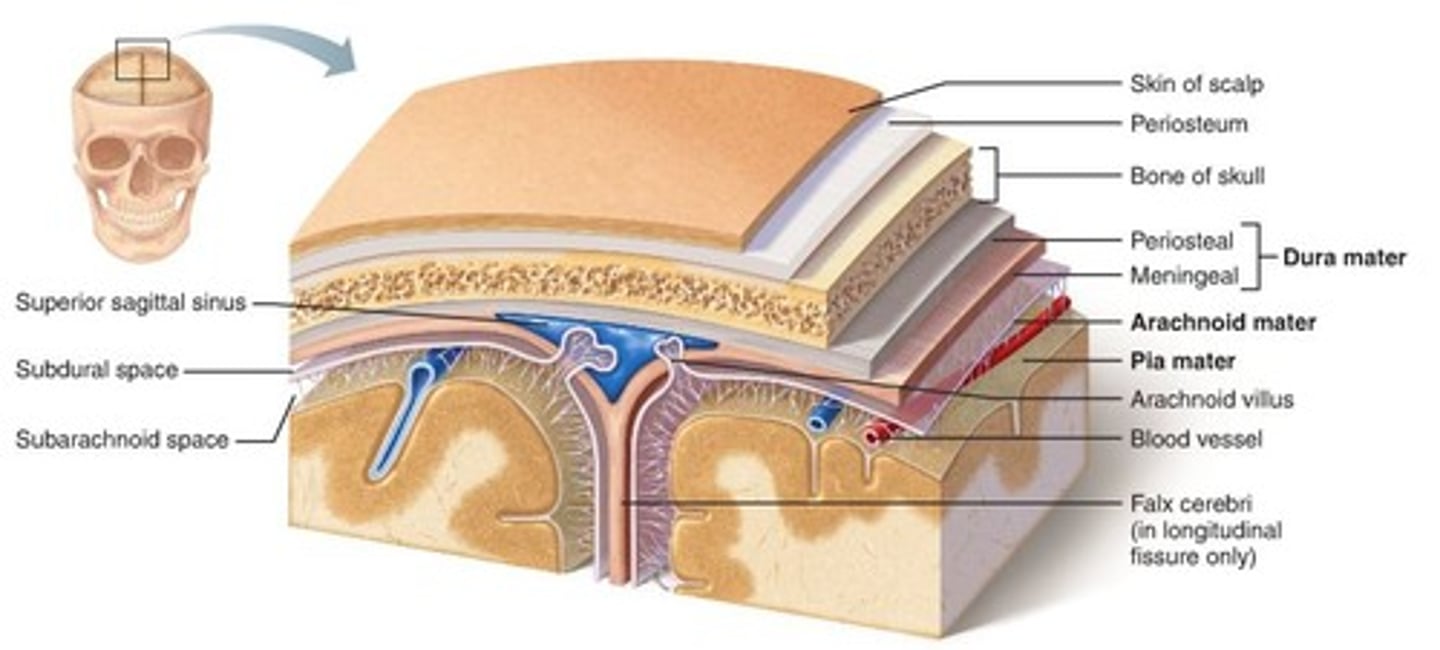
Within the meninges, where would you find cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)?
-both brain and spinal cord are covered by meninges: dura, arachnoid, and pia matters
-CSF is found inside the subarachnoid layer
How is CSF produced?
-plasma is drawn from the choroid plexuses through ependymal cells into the ventricles to produce CSF
-produced from arterial blood by the choroid plexuses of the lateral and fourth ventricles by a combined process of diffusion, pinocytosis and active transfer. A small amount is also produced by ependymal cells
How is CSF recycled back into the blood?
-CSF is absorbed through blood vessels over the surface of the brain back into the bloodstream
-Some absorption also occurs through the lymphatic system
-recycled back into the blood through the dural sinuses via sagittal sinus
What is the importance of the choroid plexus? Where is it located?
-primary functions is to produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) via the ependymal cells that line the ventricles of the brain
-resides in the innermost layer of the meninges (pia mater) which is in close contact with the cerebral cortex and spinal cord
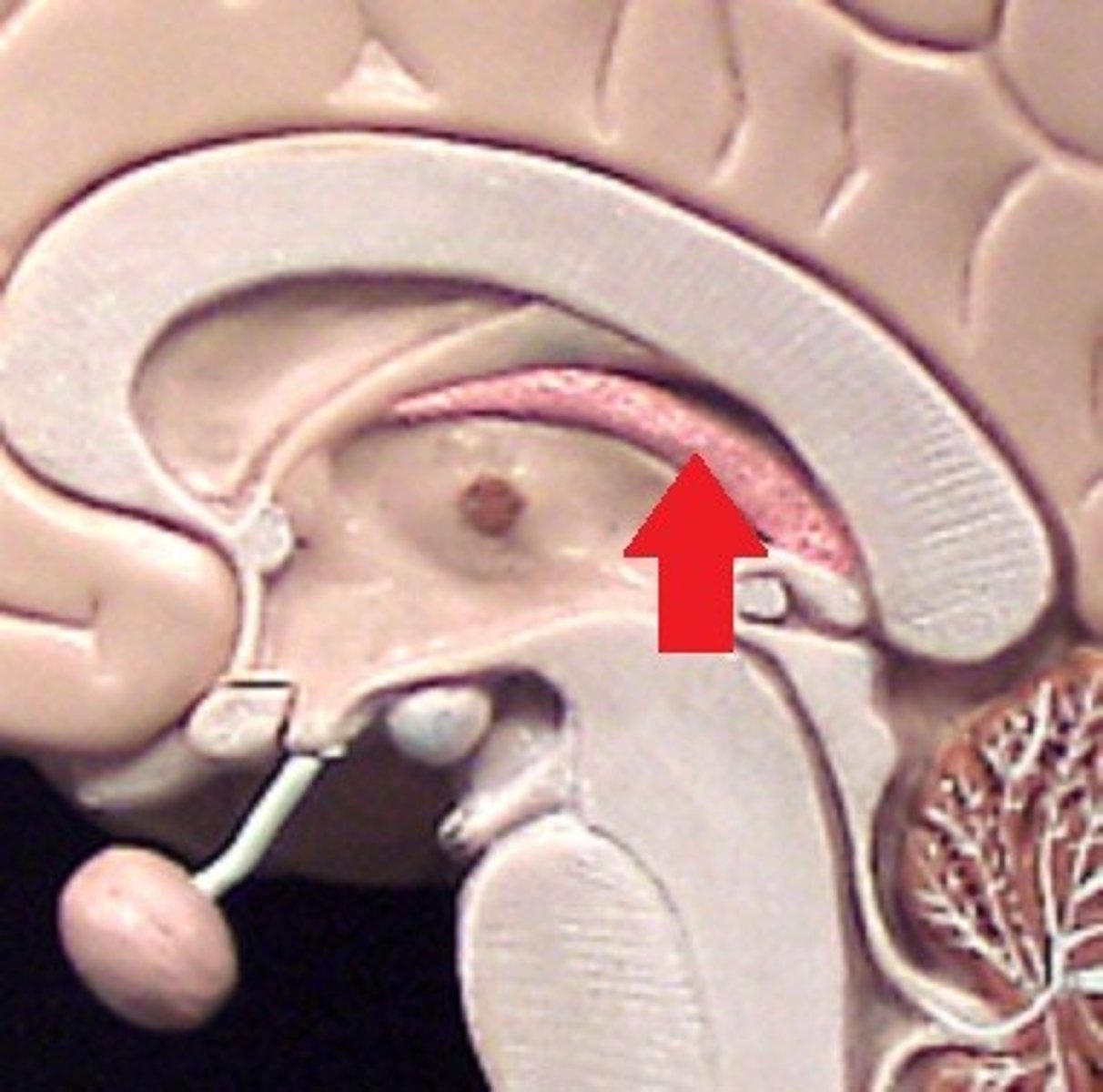
hydrocephalus
-accumulation of excess CSF w/in ventricular system
-either from overproduction of CSF or decreases reabsorption
-diagnosed with fetal MRI
-treated by a surgical insertion of drainage system called shunt
Meningitis
-inflammation of the meninges
-diagnosed by collection CSF by lumbar puncture
-treated with antibiotics
brain tumors
-can grow in several locations
-symptoms depend on size and location
-most do not metastasize
How could the facial artery and cavernous sinus be involved in the development of encephalitis or meningitis?
the facial vein anastomoses (drains into/ is connected to) angular vein and the anastomoses is directly connected to the cavernous sinus which is where the brain sits on top of
-so if bacteria is picked up in the facial artery there is a possibility of that contaminated blood instead of being brought to the internal jugular vein, being brought into to the cavernous sinus which is what the brain is sitting on
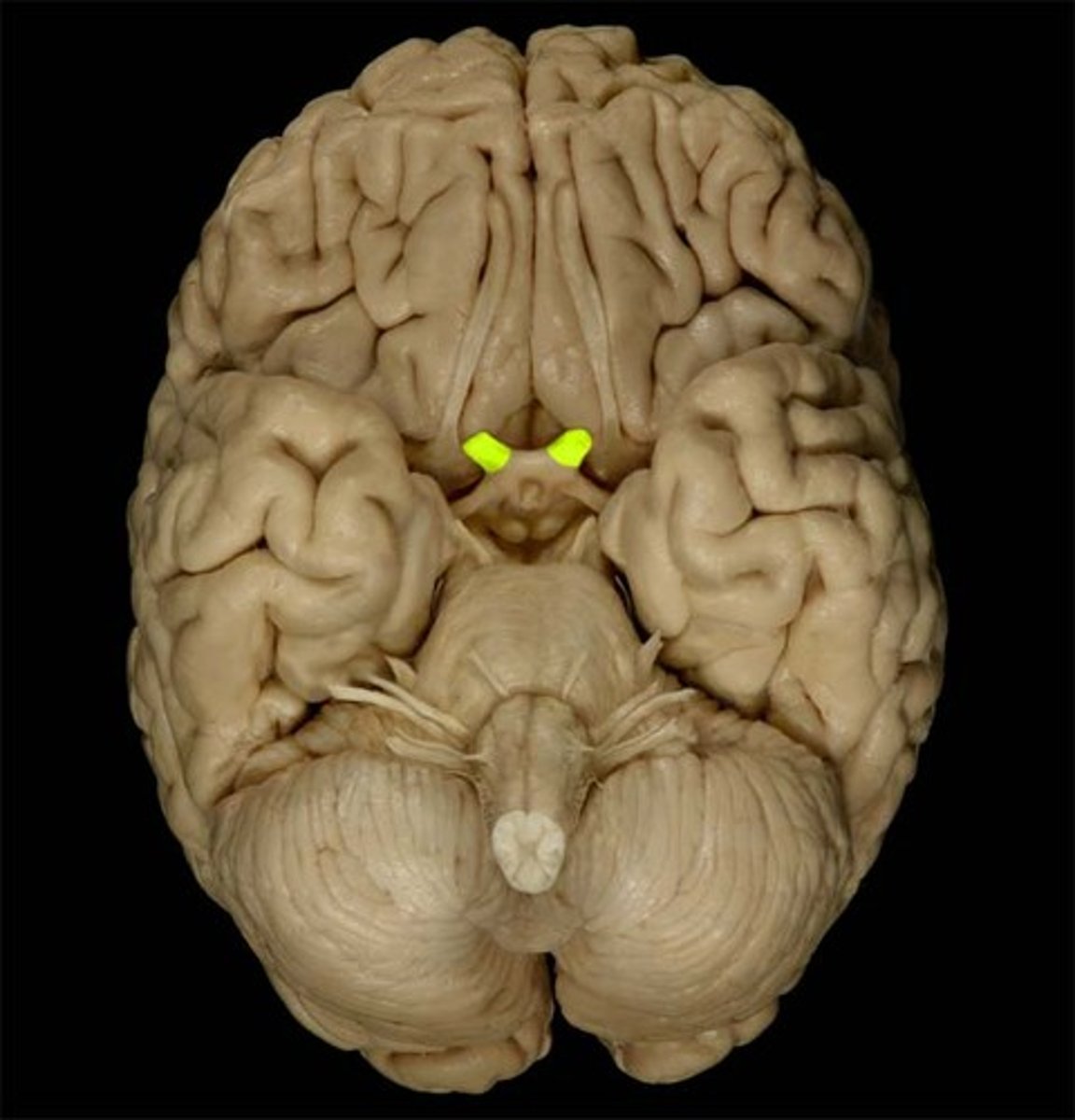
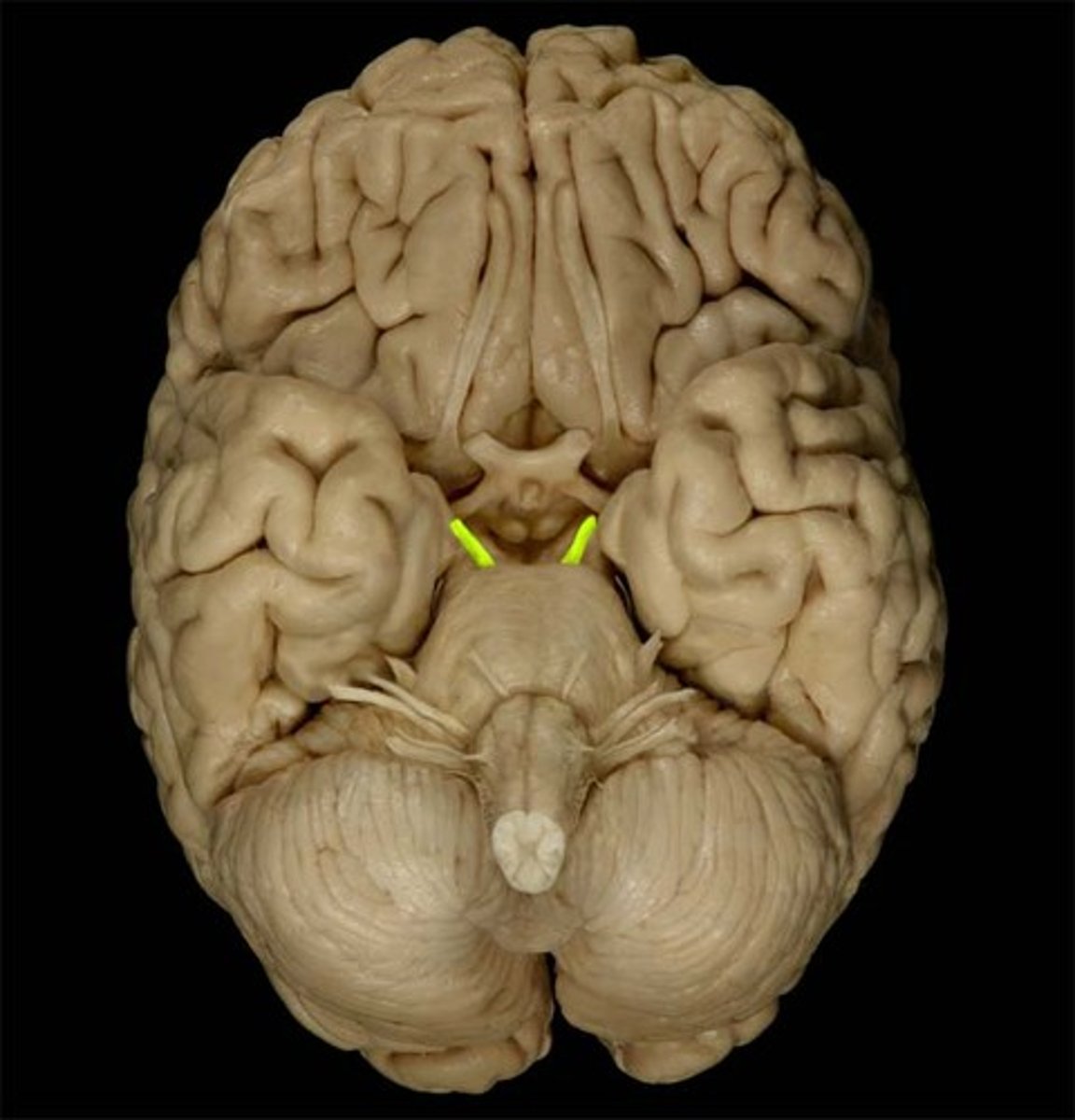
*CN I
-Olfactory
-sensory
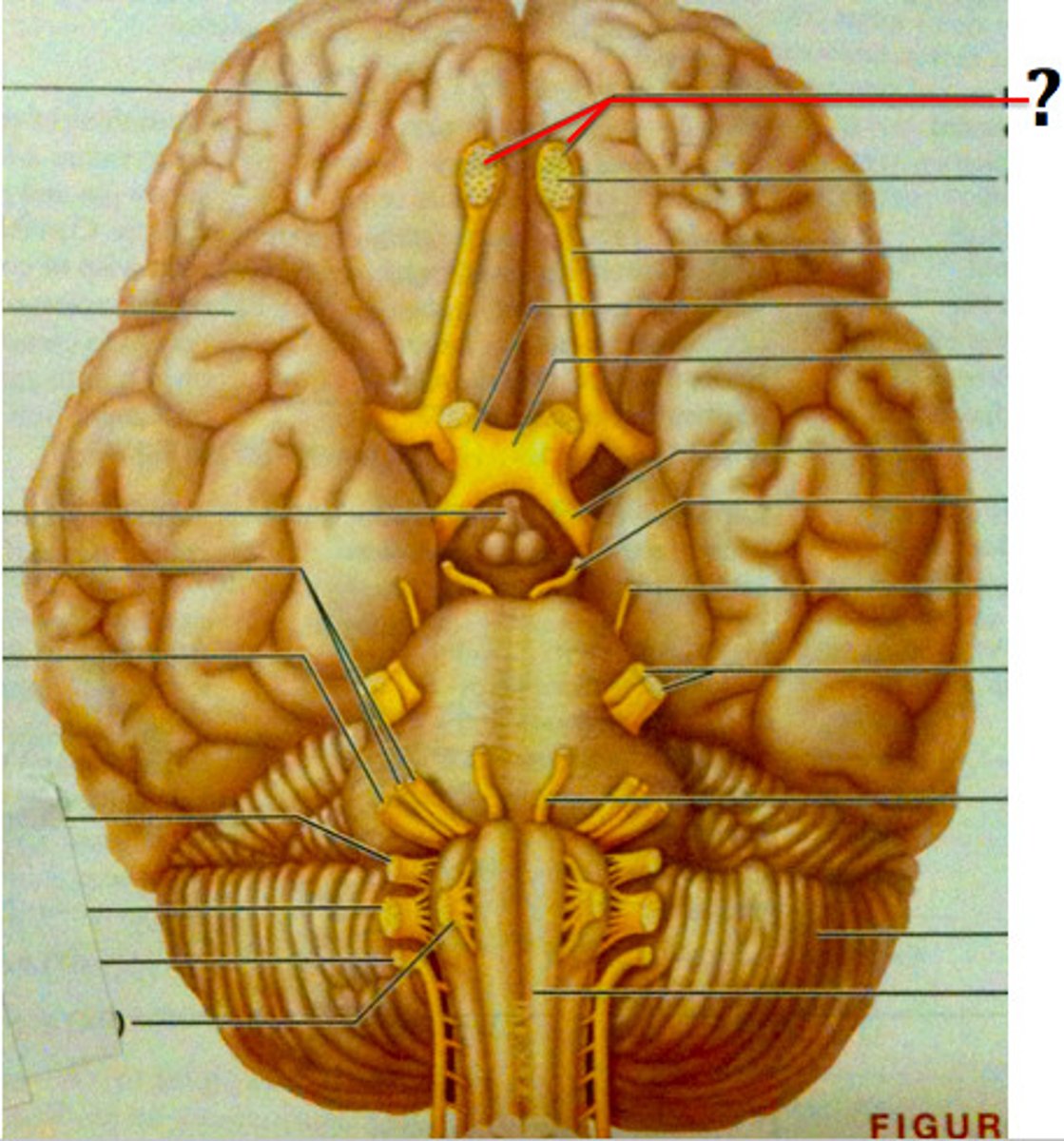
*CN II
-optic
-Sensory
*CN III
-oculomotor
-motor
*CN IV
-trochlear
-motor
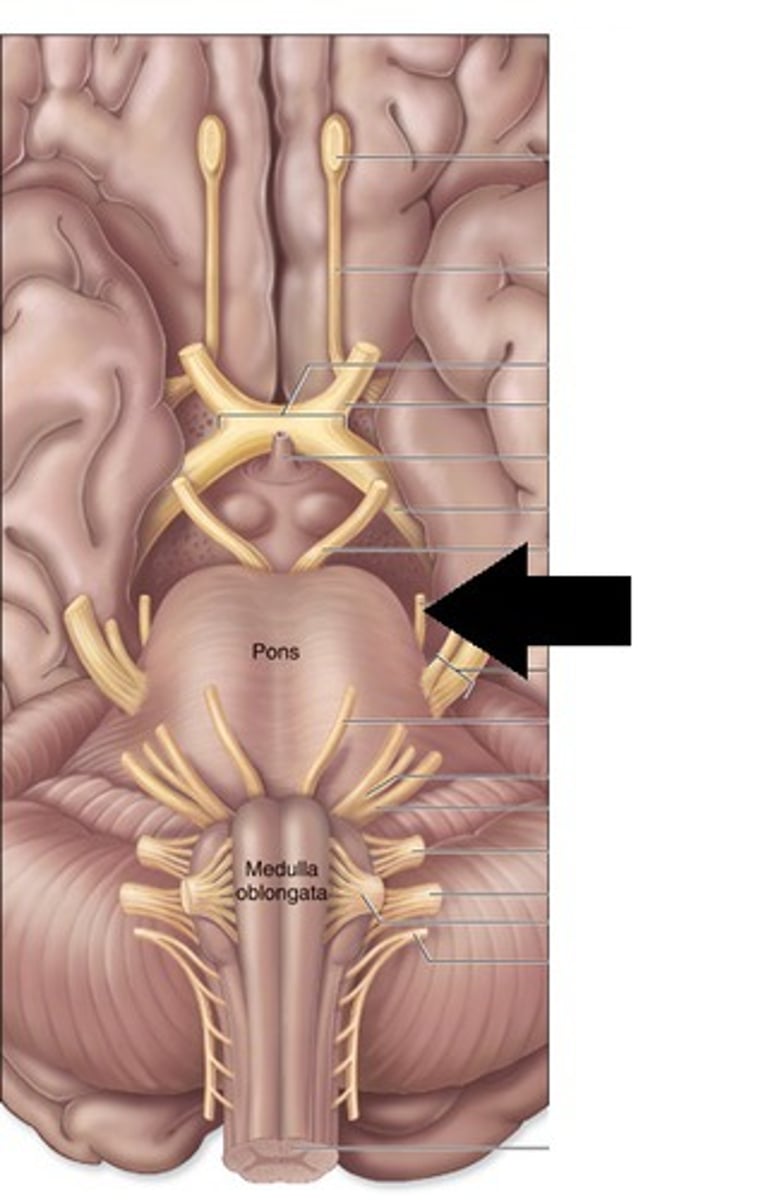
*CN V
-trigeminal
-Sentory and motor
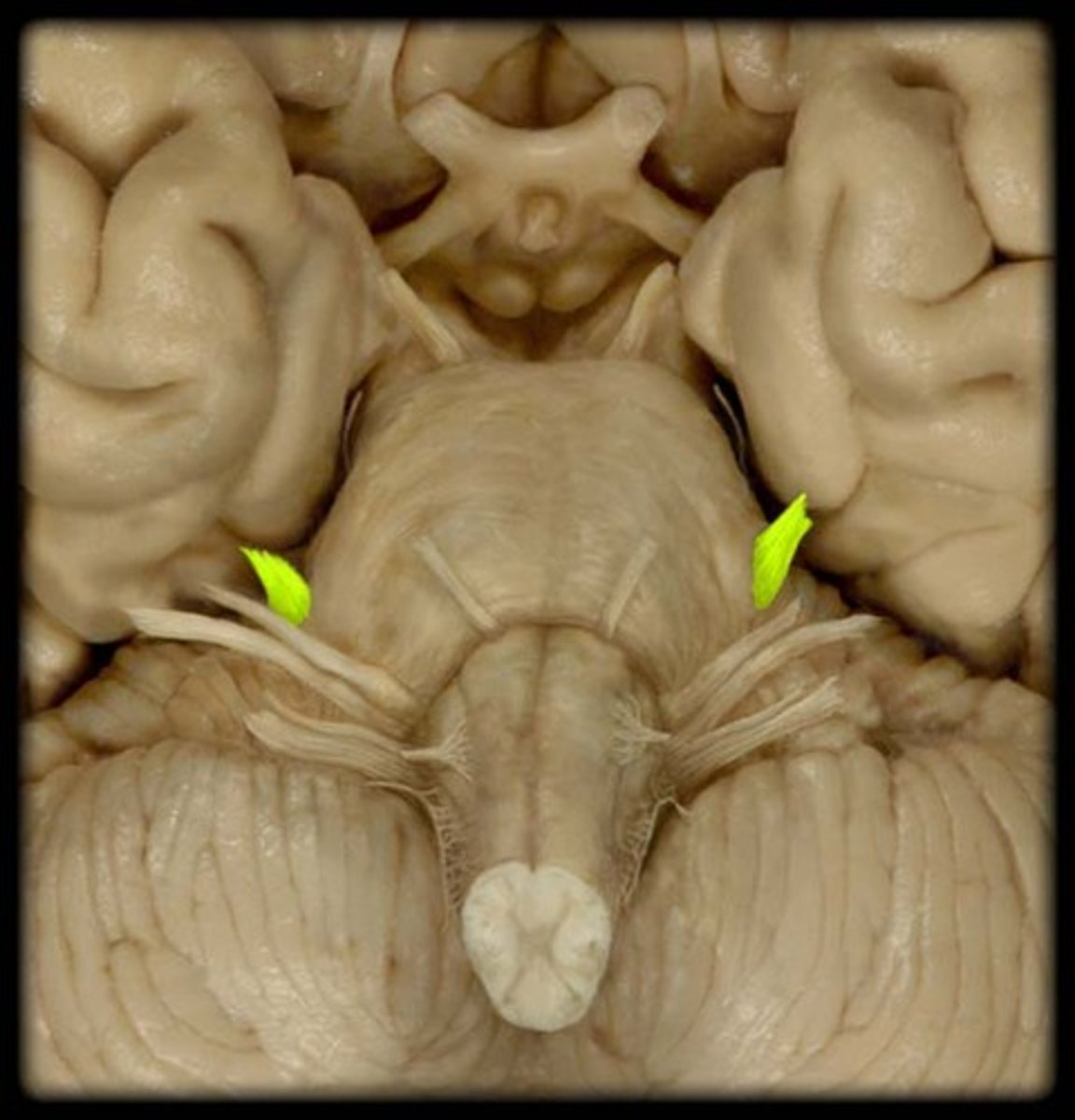
*CN VI
-abducent
-motor
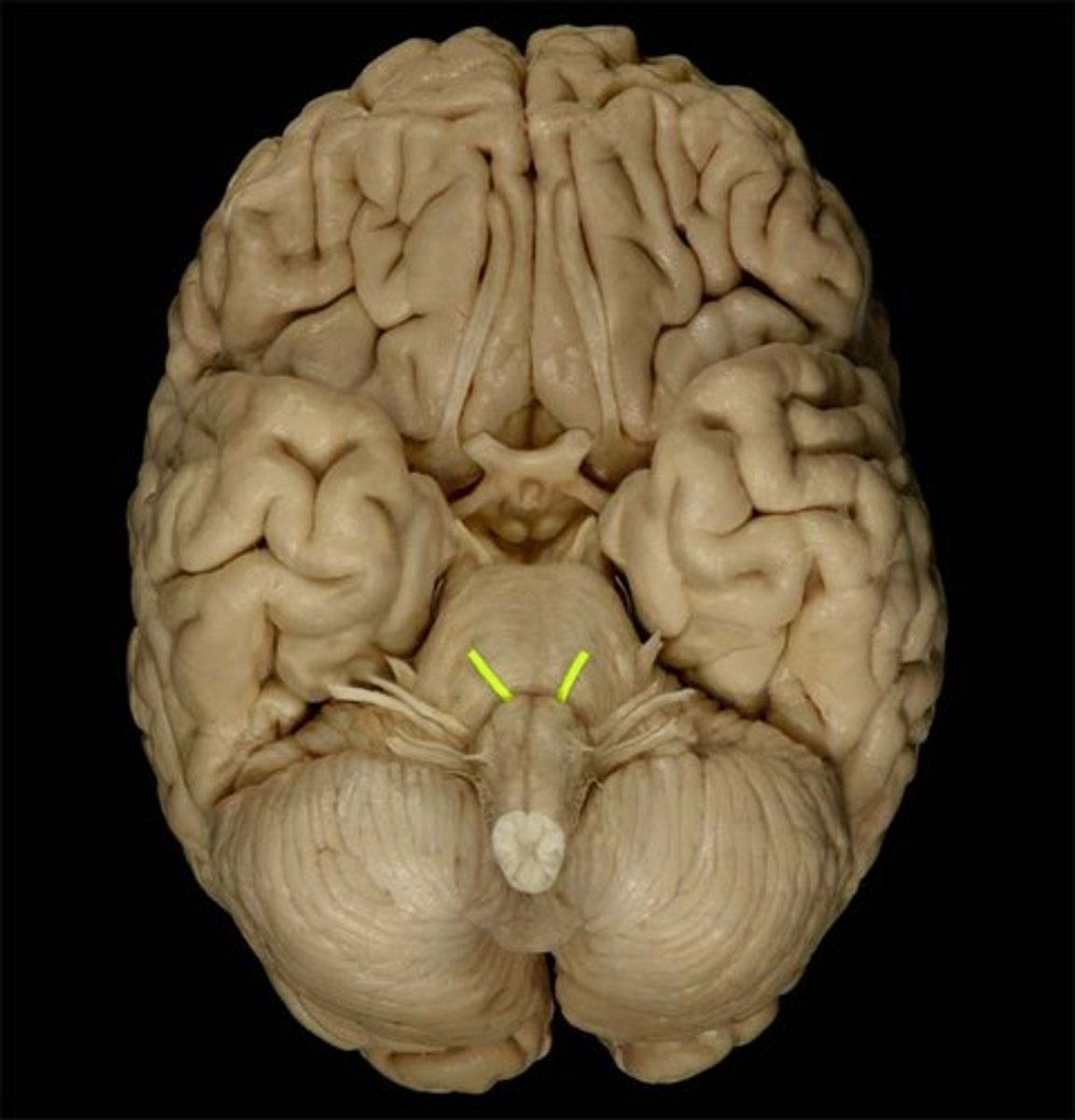
*CN VII
-facial
-sensory and motor
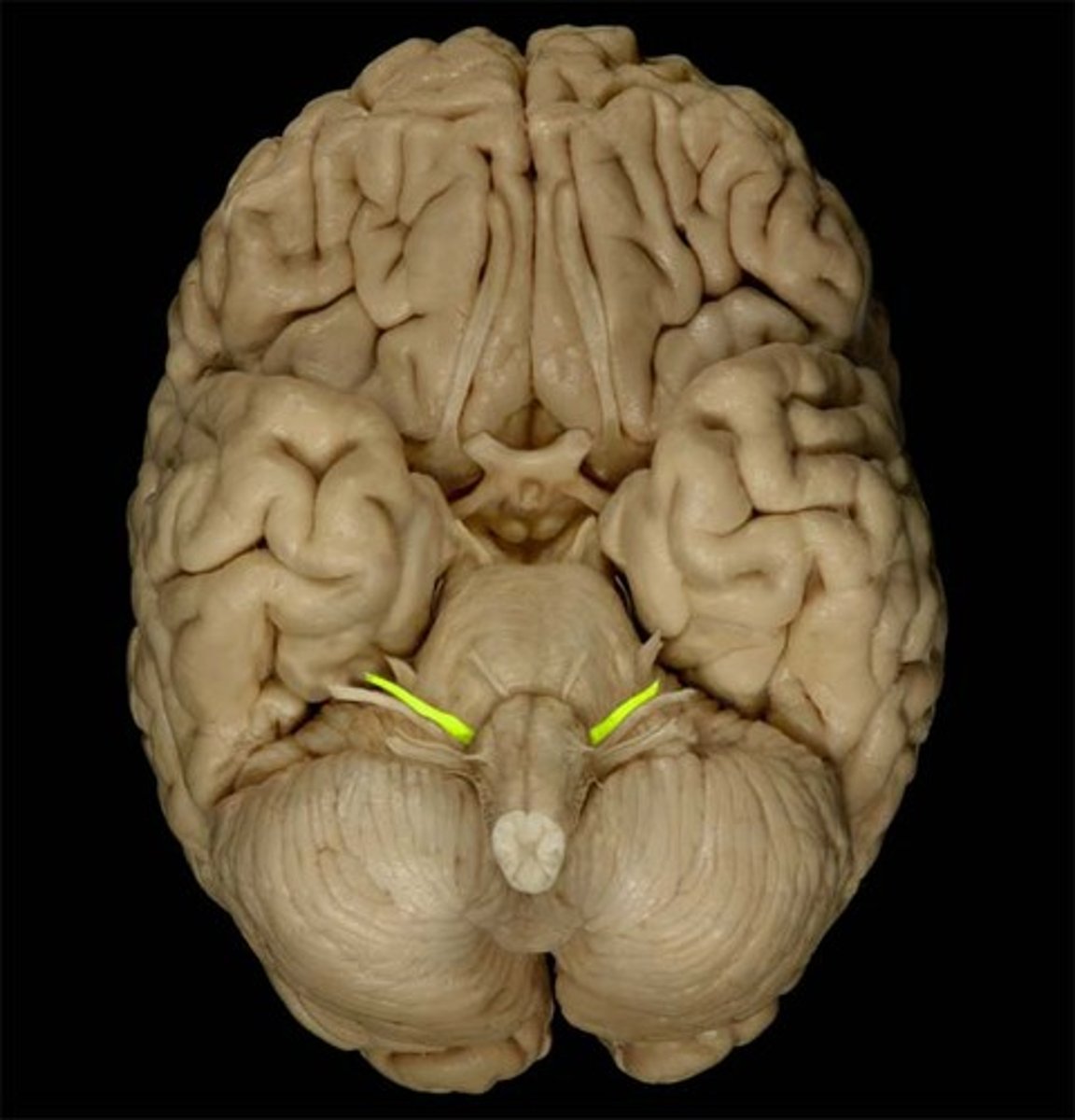
*CN VIII
-vestibulocochlear
-sensory
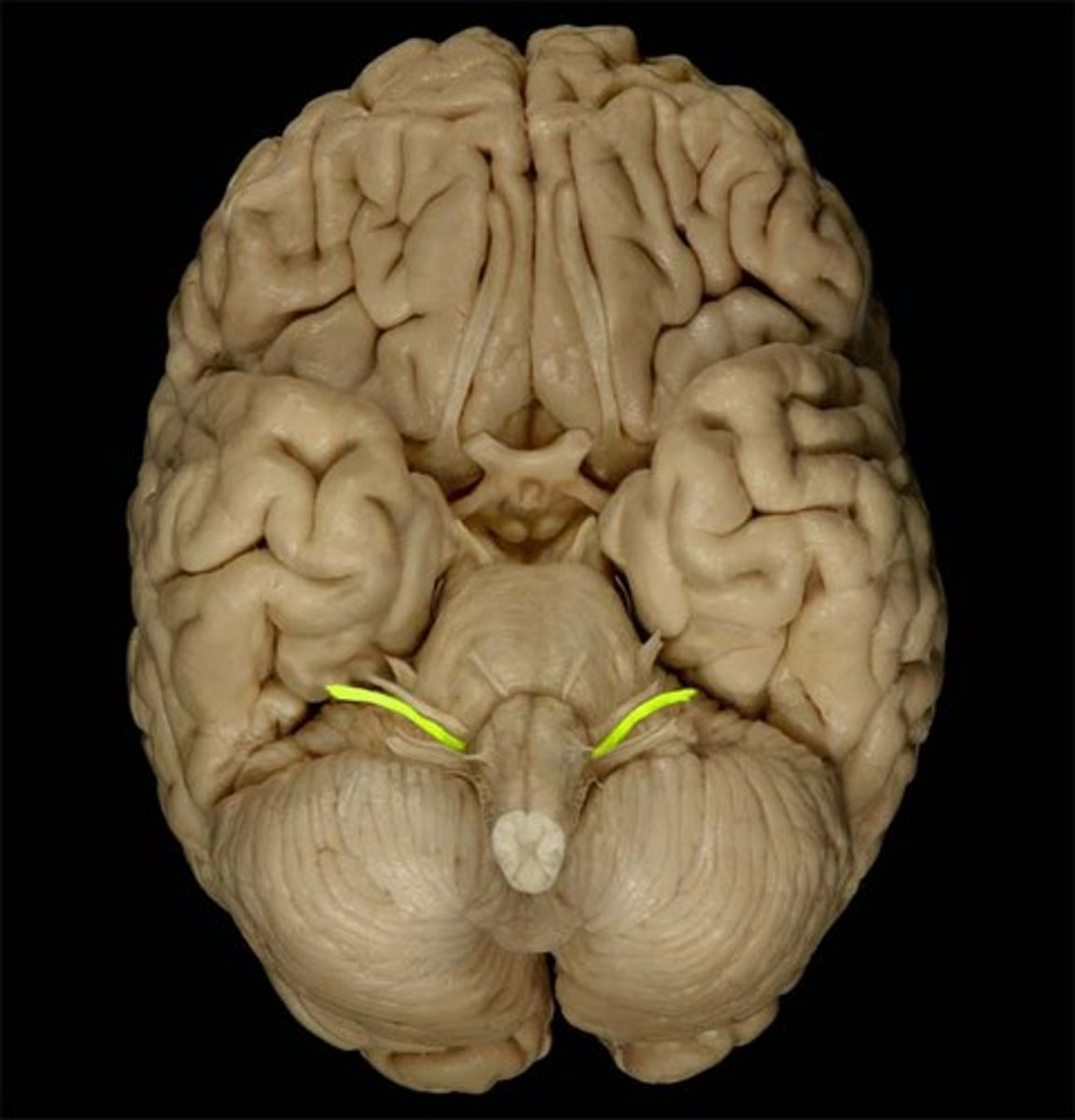
*CN IX
-glossopharyngeal
-sensory and motor
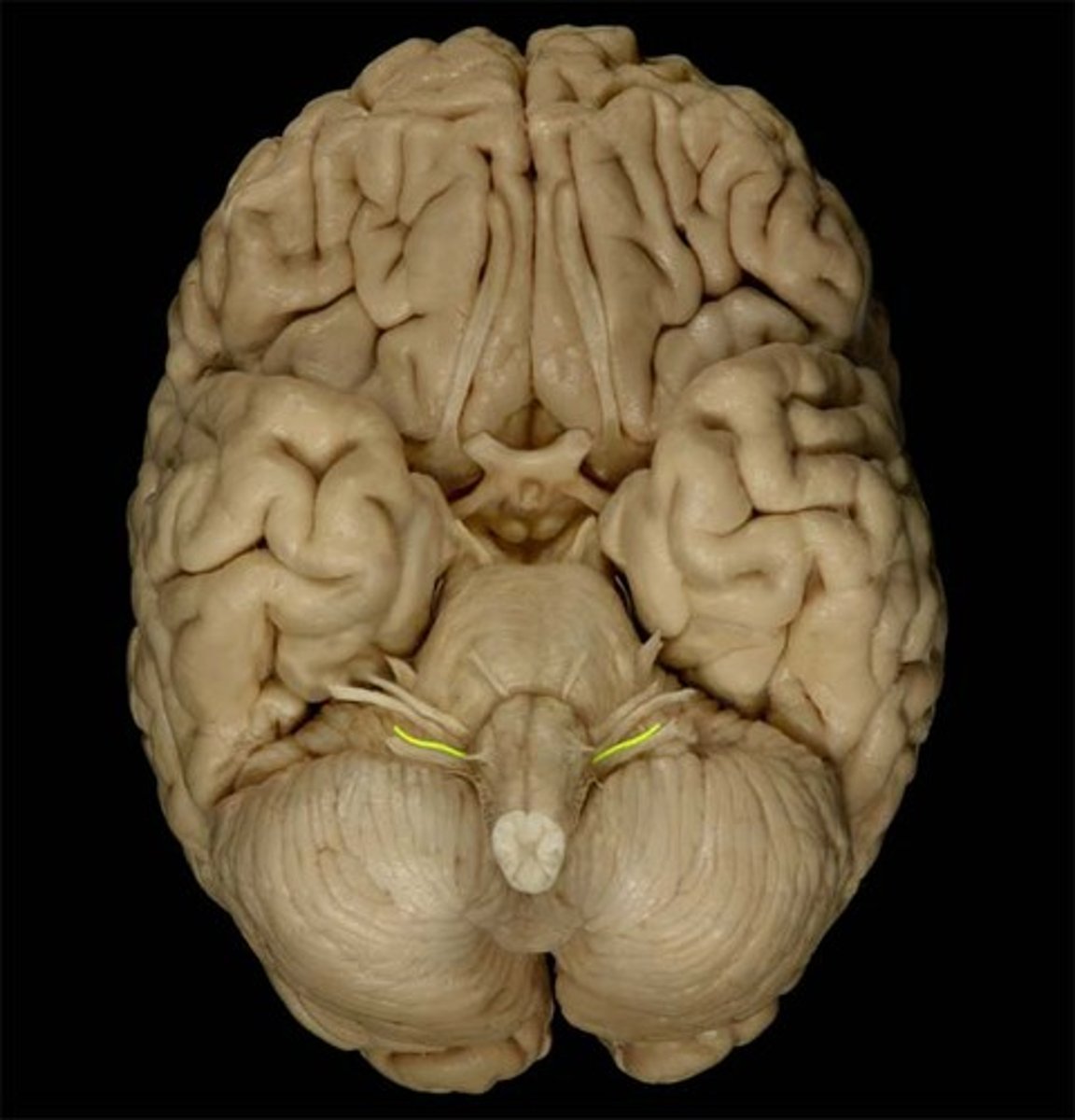
*CN X
-vagus
-sensory and motor
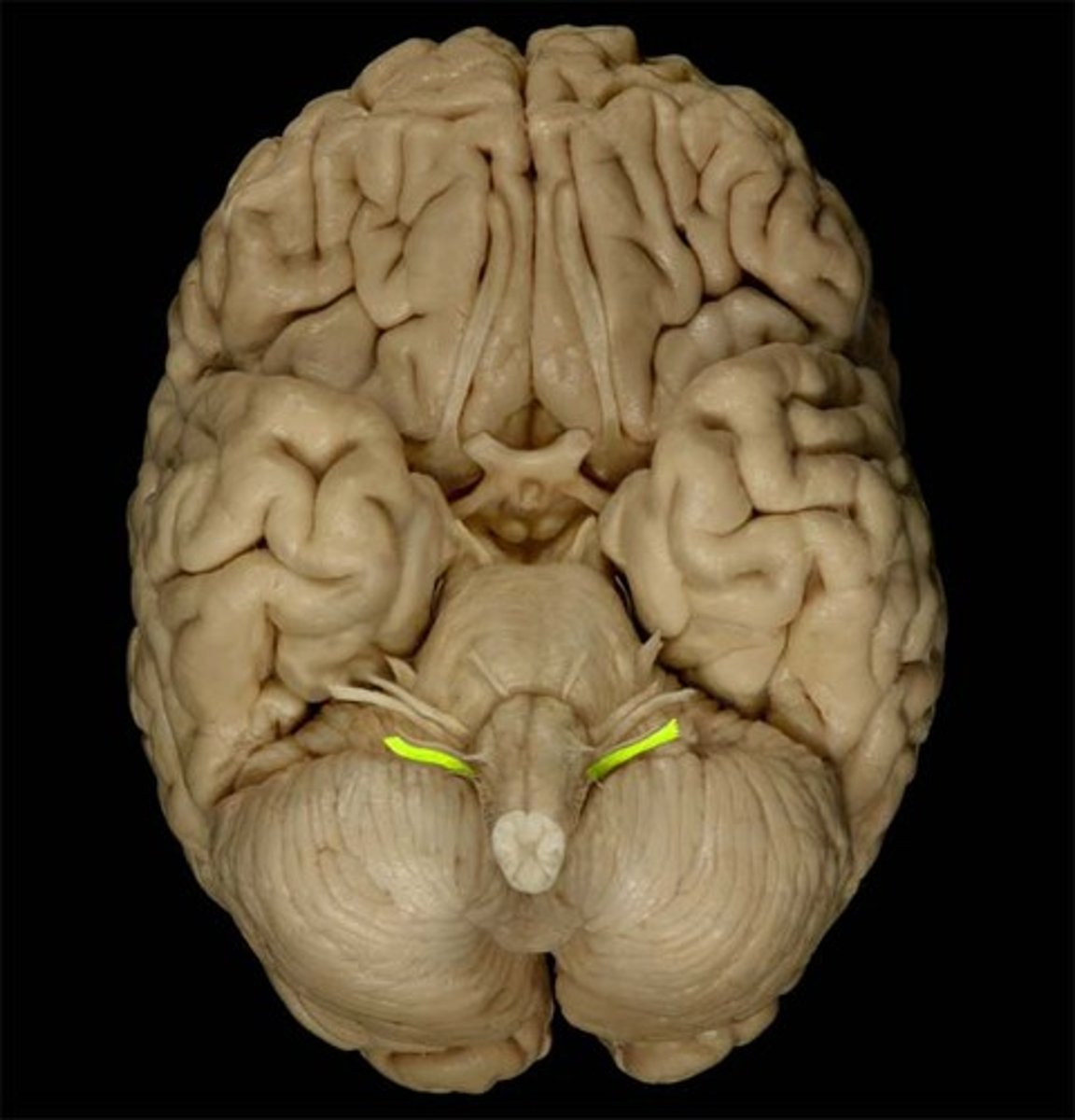
*CN XI
-accessory
-motor
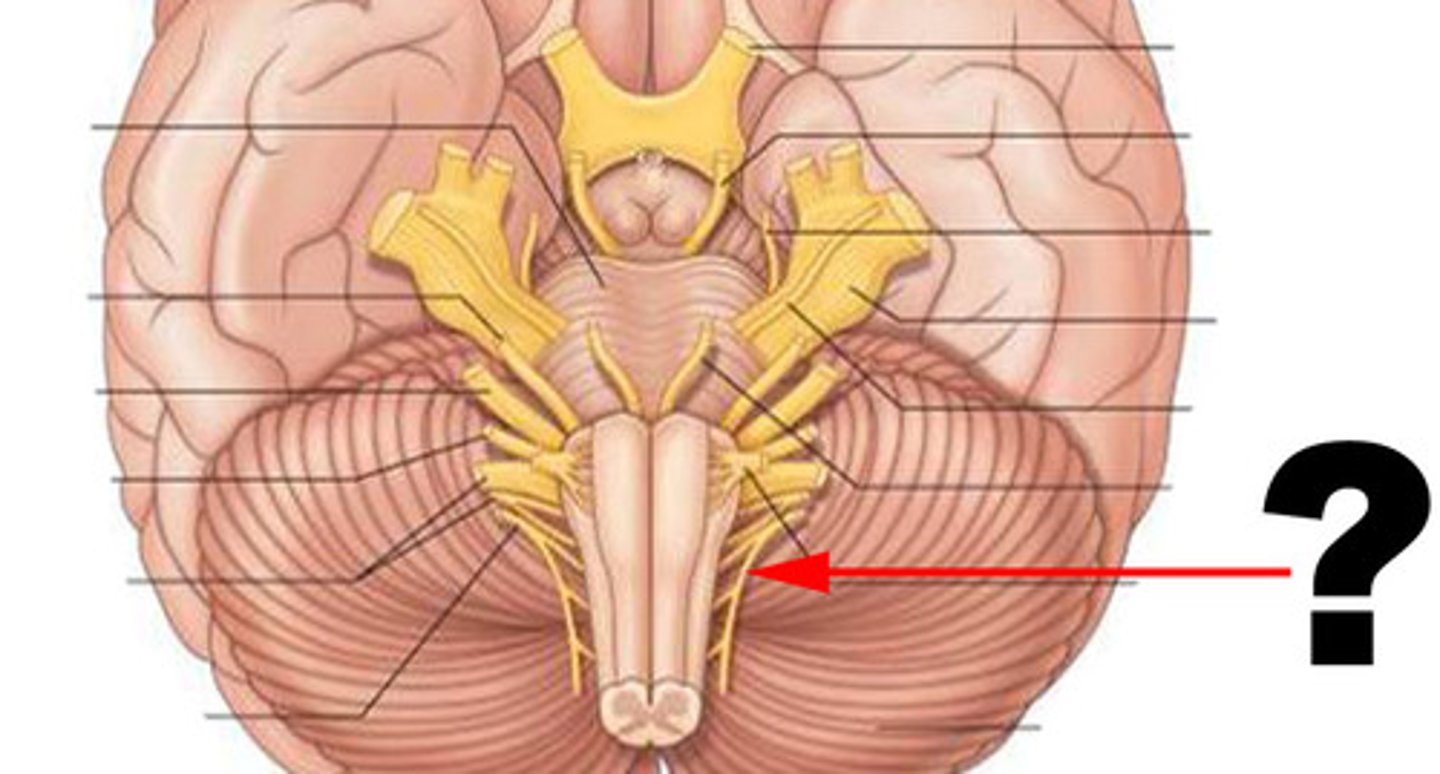
*CN XII
-hypoglossal
-motor
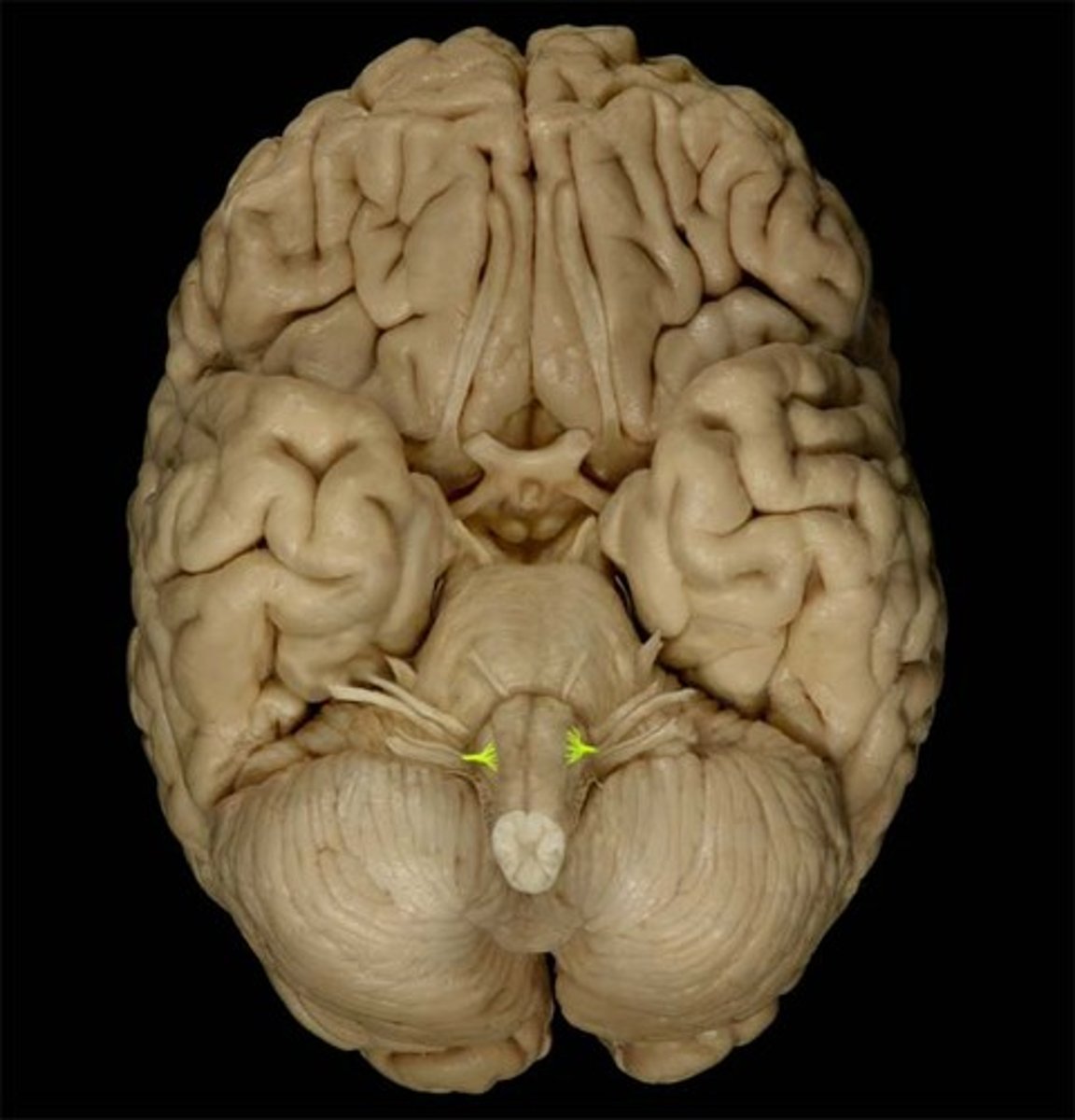
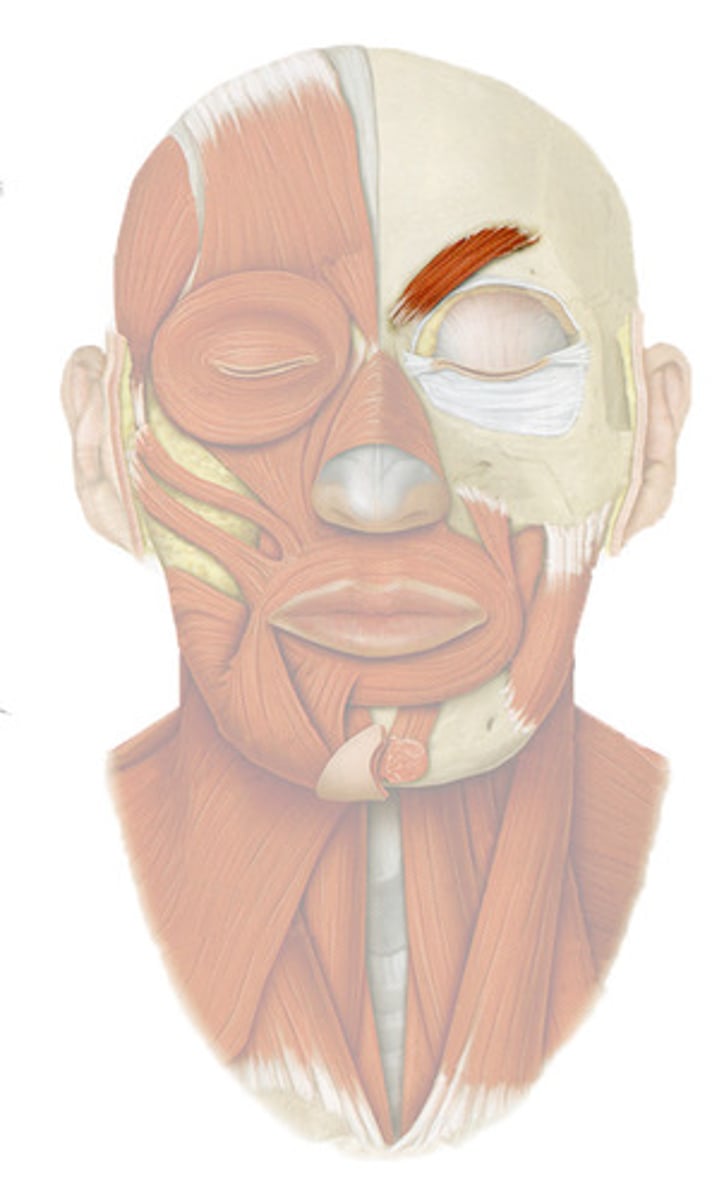
mimetic muscles
facial muscles; called mimetic because they convey meaning in speech through "mimes" and also function to shape the oral and nasal cavities
*ALL mimetic muscles are innervated by CN VII*
-4 group: scalp, region of eyelid, nasal region, mouth region
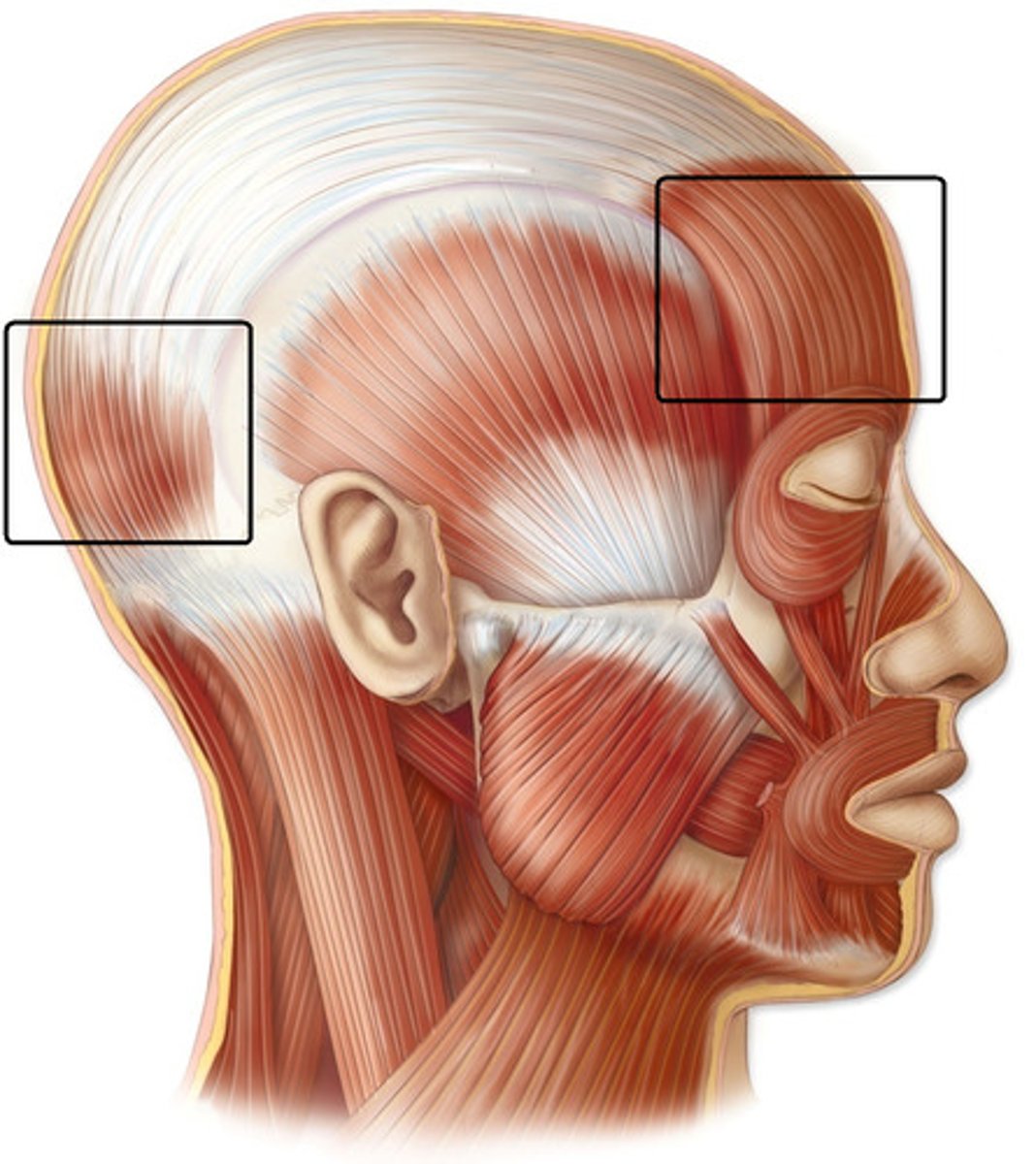
Epicranius
-has 2 bellies: frontal and occipital, connected by an aponeurosis (flat tendon)
-fxn: produces wrinkles in forehead and gives facial expressions of astonishment
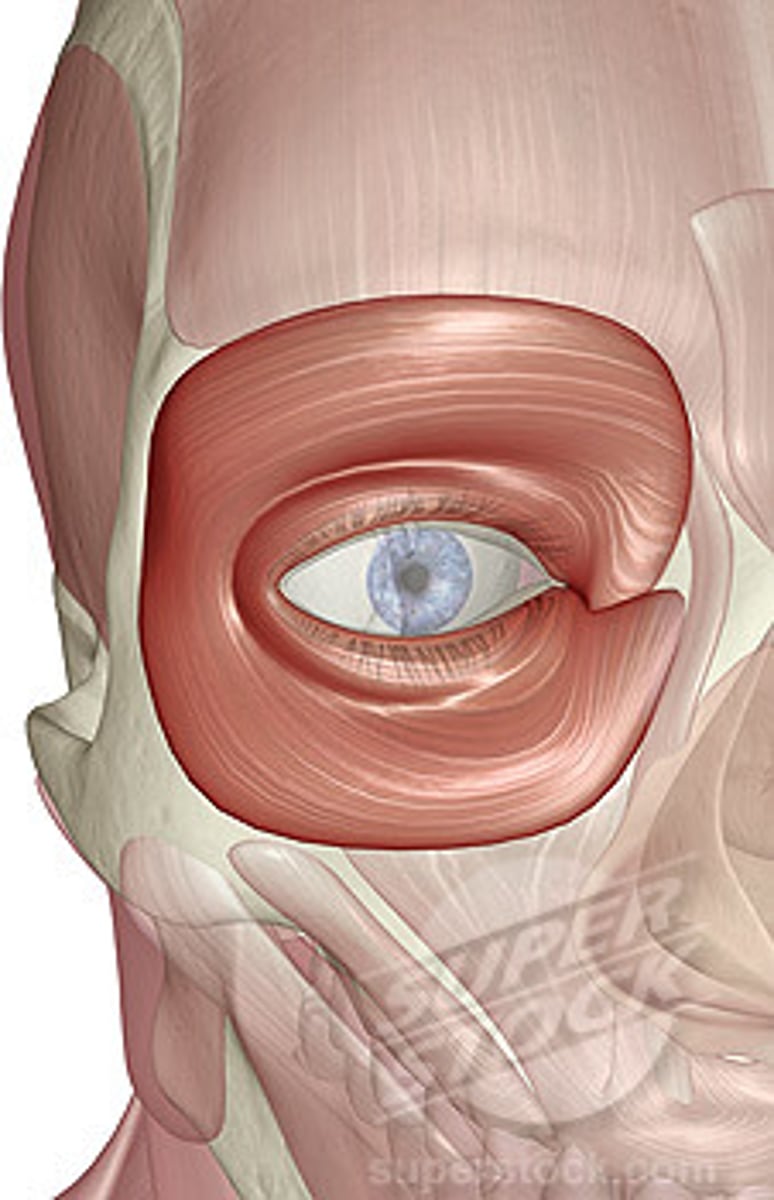
orbicularis oculi
-3 parts: orbital, palpebral, and lacrimal
-fxn: produces folds in lateral angle of the eye, expression of worry and concern
corrugator supercilii
-fxn: pulls the skin and eyebrows down and medially, produces vertical folds, protects against light
-thinkers brow expression
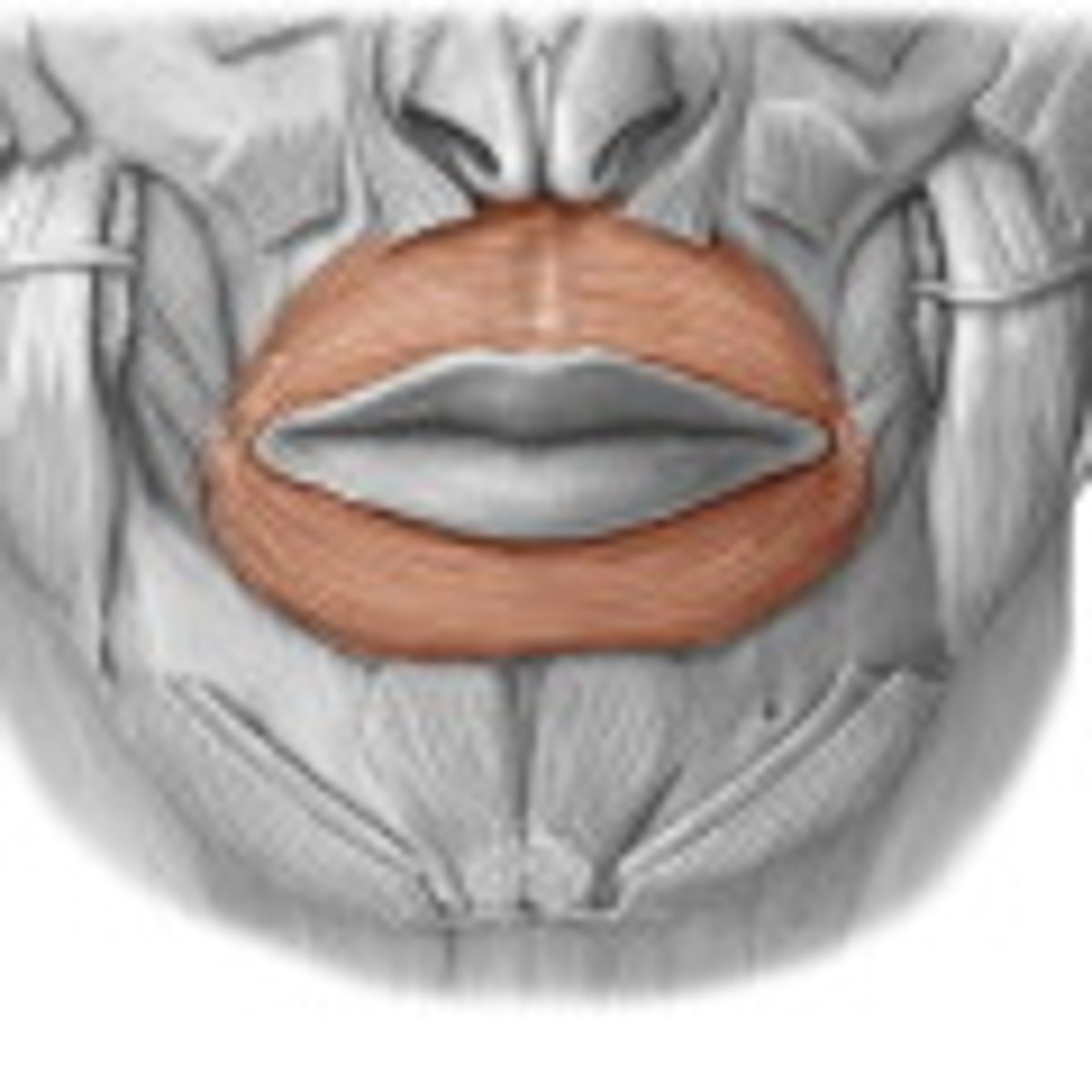
obicularis oris
fxn- contraction closes the mouth, strong contraction giving sucking shape
buccinator
quadrilateral in shape
-fxn: enables air to be blown out of the mouth, keeps the mucous mb of the cheek free of folds
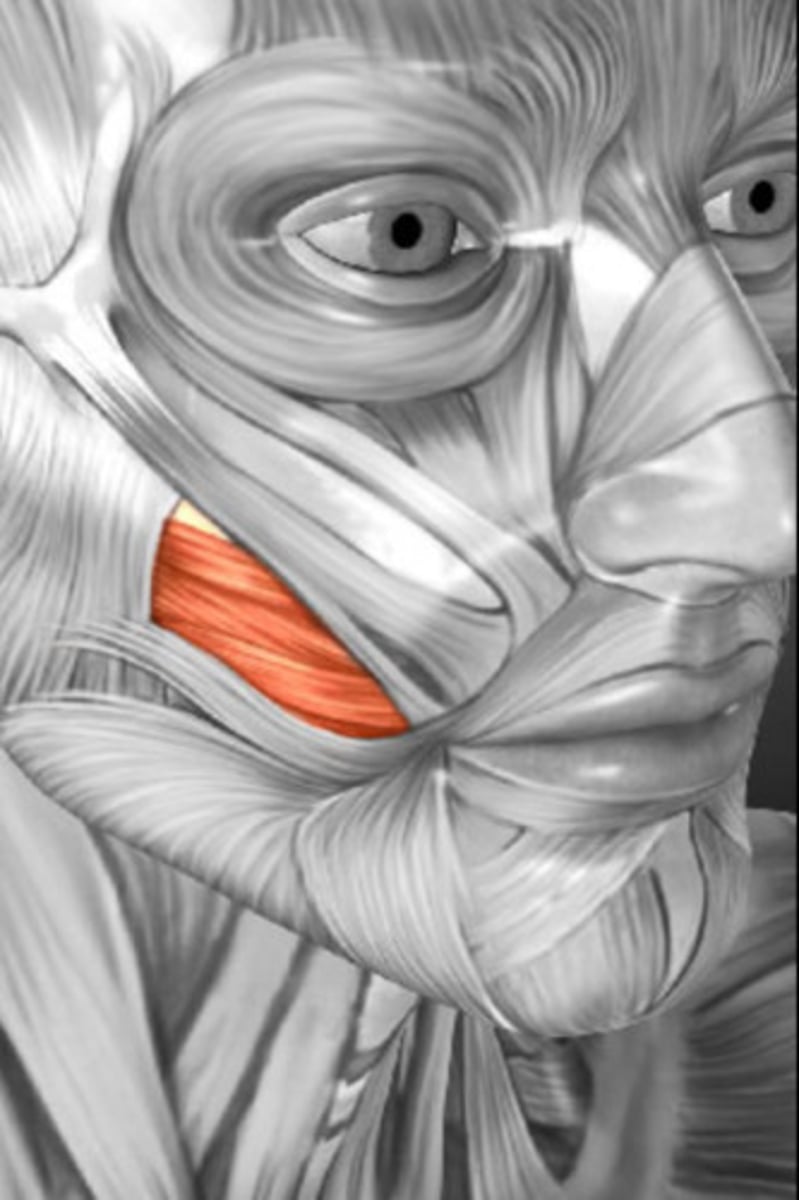
zygomaticus major
fxn- lifts the corner of the mouth upward, giving expression of laughter or pleasure
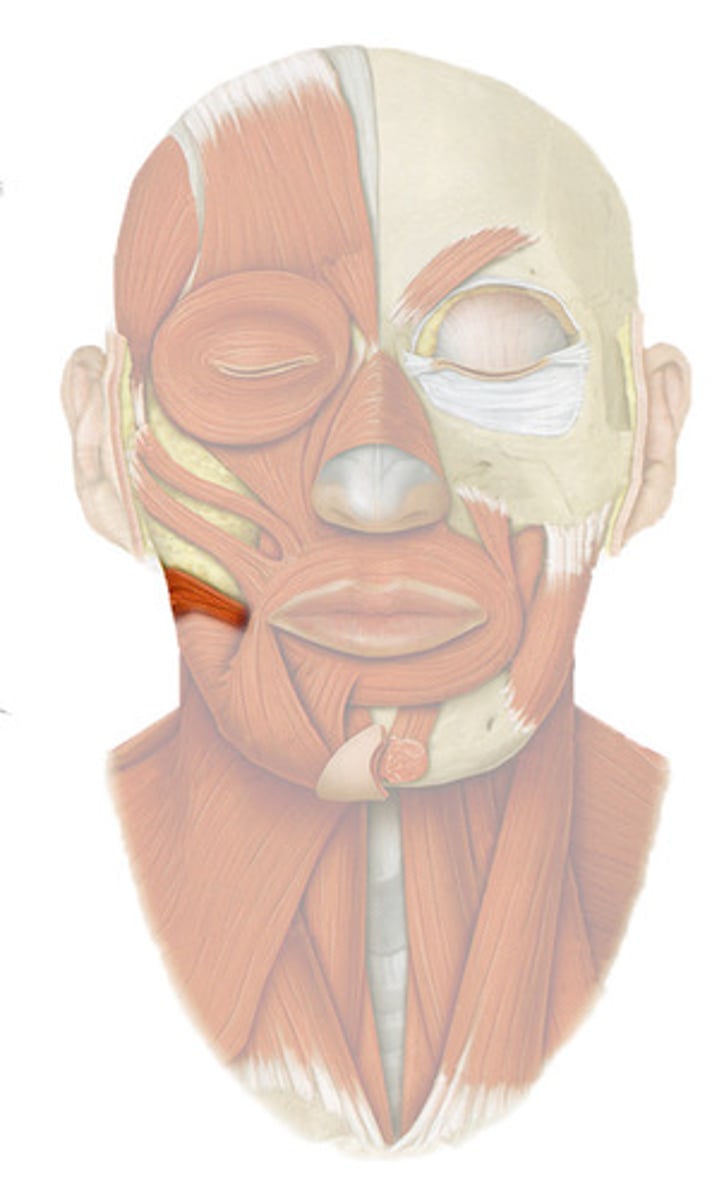
zygomaticus minor
retracts and elevates upper lip
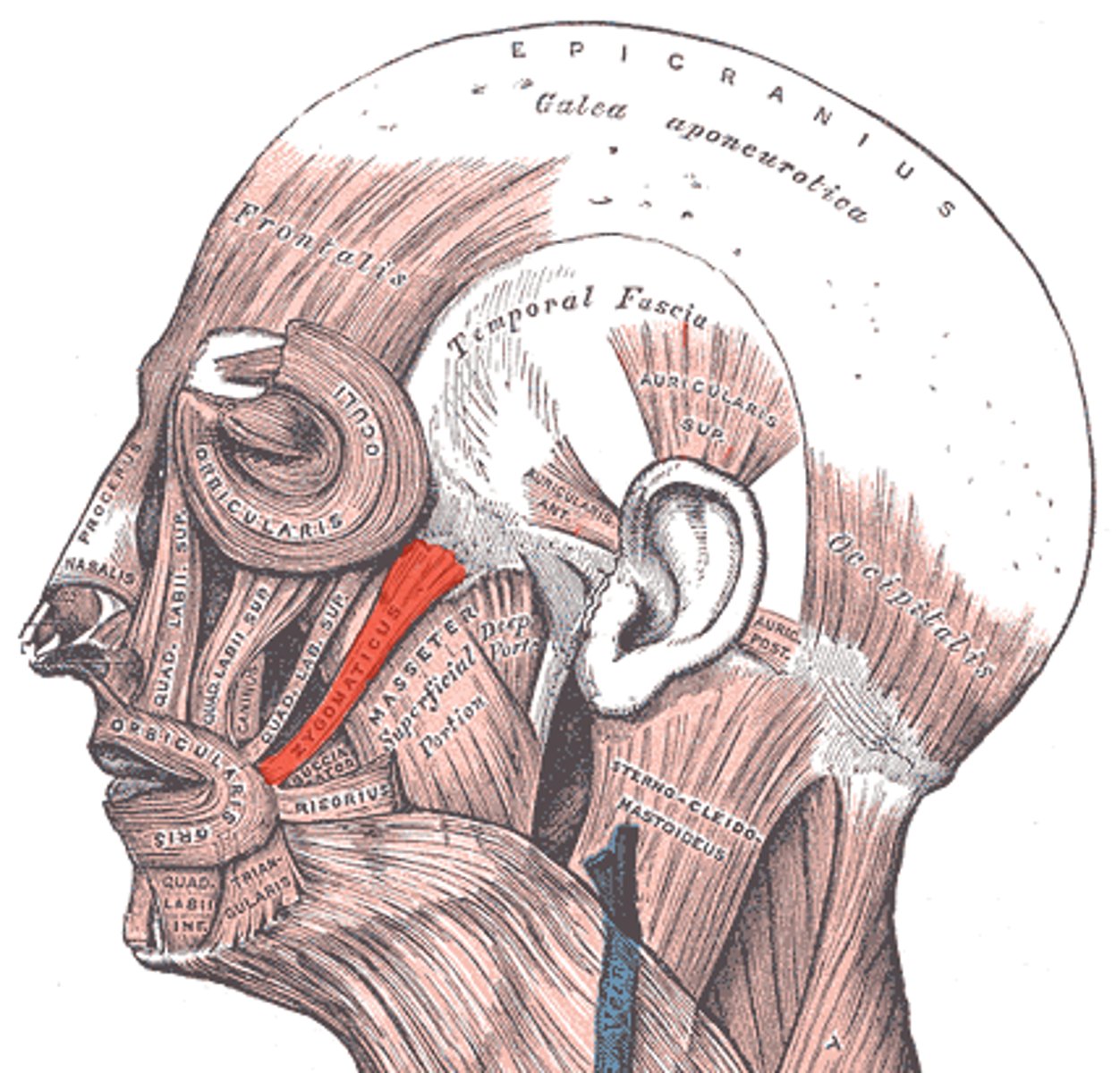
risorius (laughing muscle)
fxn- together w/ zygomatic major it produces the nasolabial folds
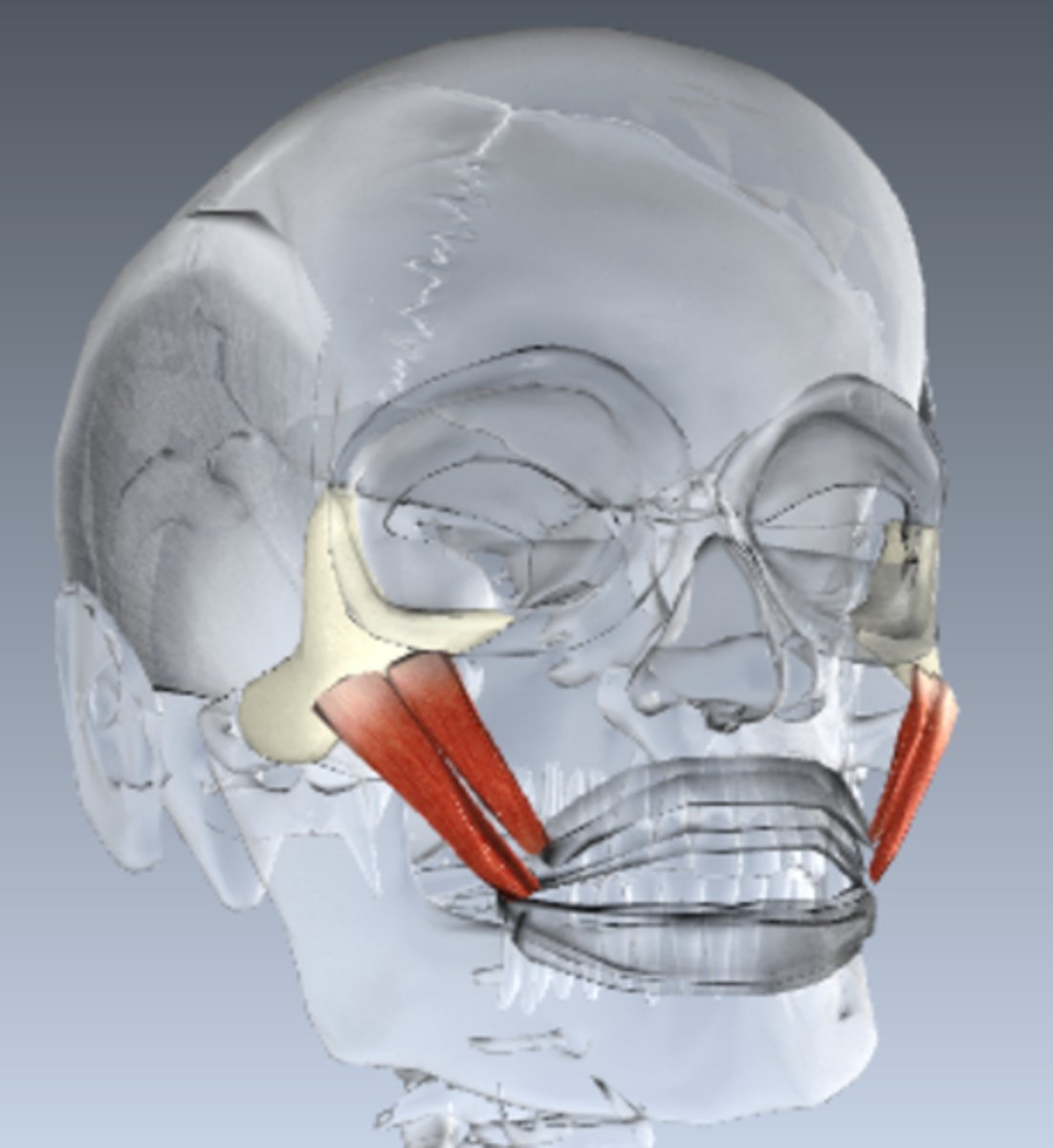
levator labii superioris
elevates upper lip
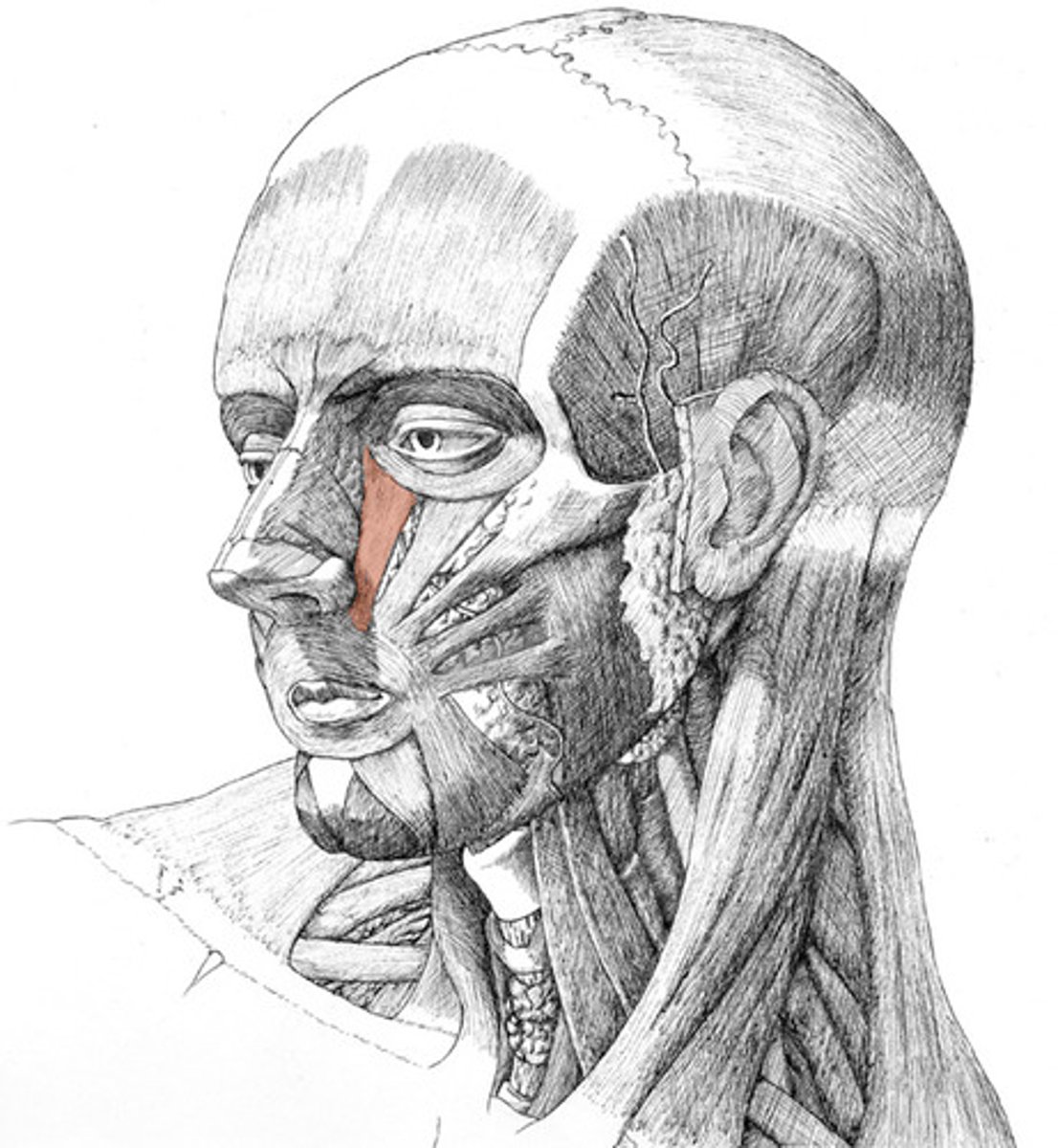
Lavator anguli oris
fxn- lifts the angle of the mouth giving expression of self confidence
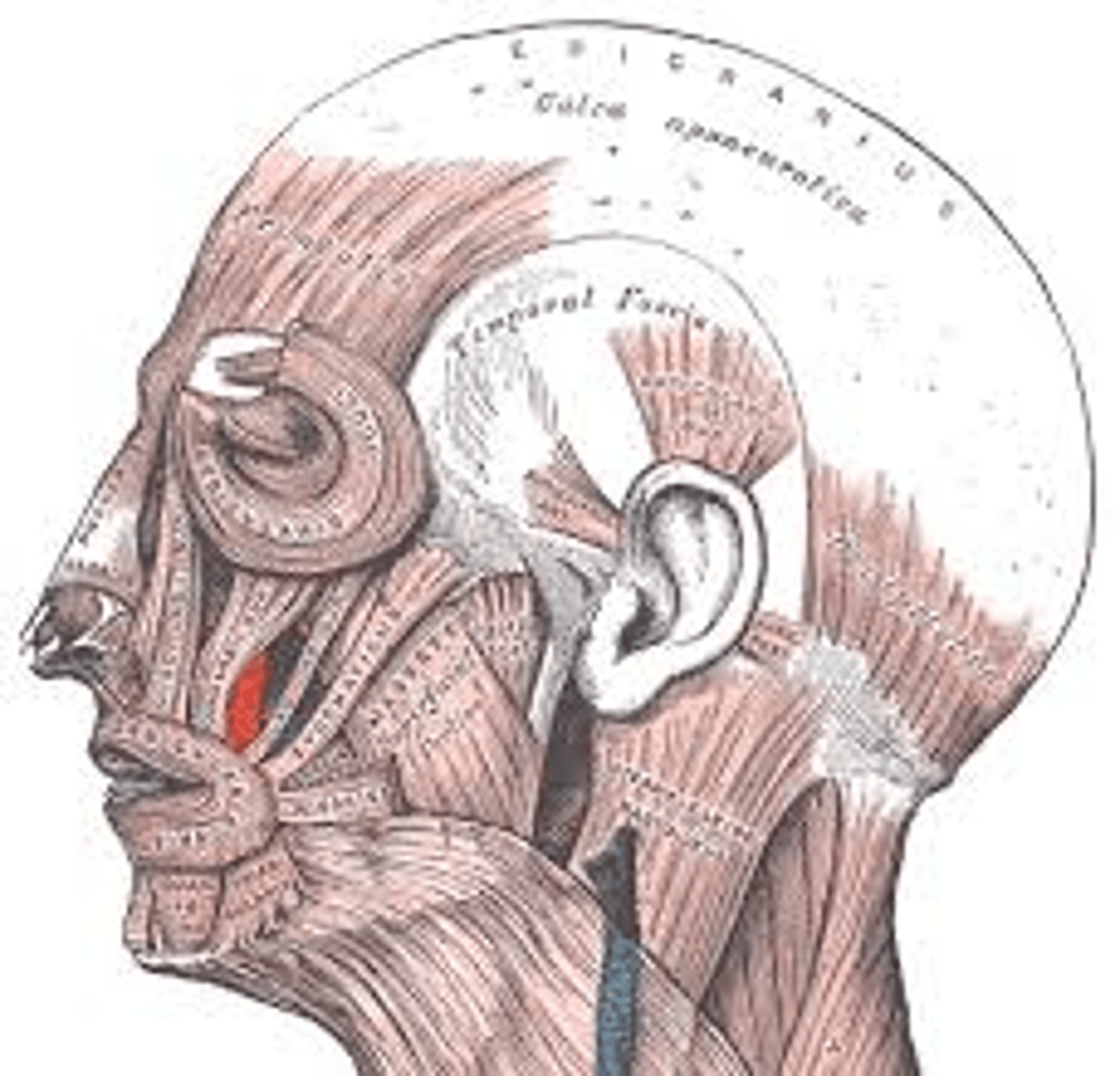
depressor anguli oris
fxn- pulls the angle of the mouth downwards and produces expression of sadness
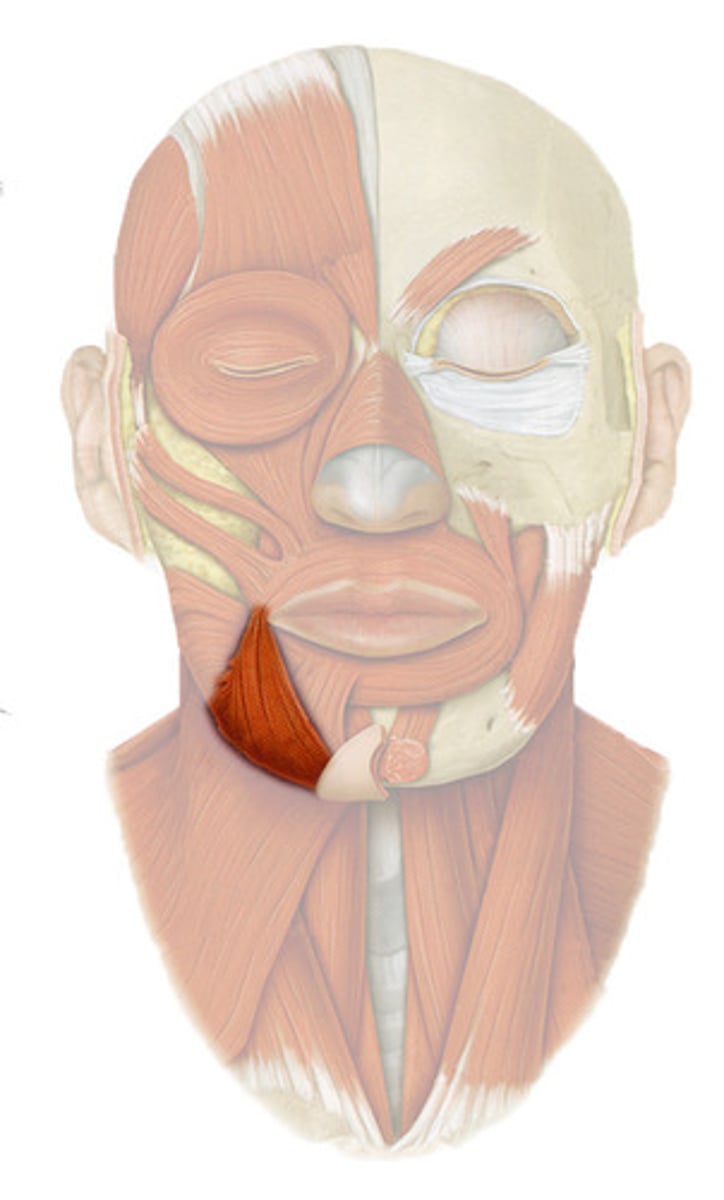
depressor labii inferioris
fxn- pulls the lower lip down giving the expression of perseverance
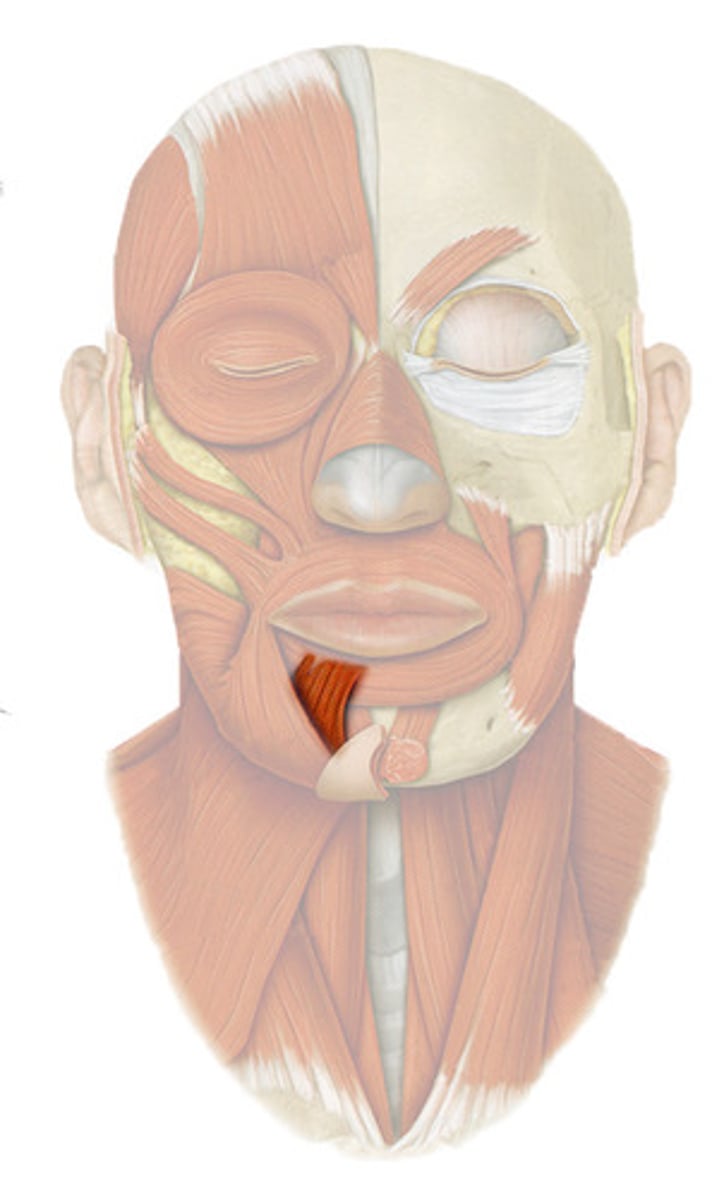
mentalis
fxn- chin lip furrow giving expression of doubt and indecision
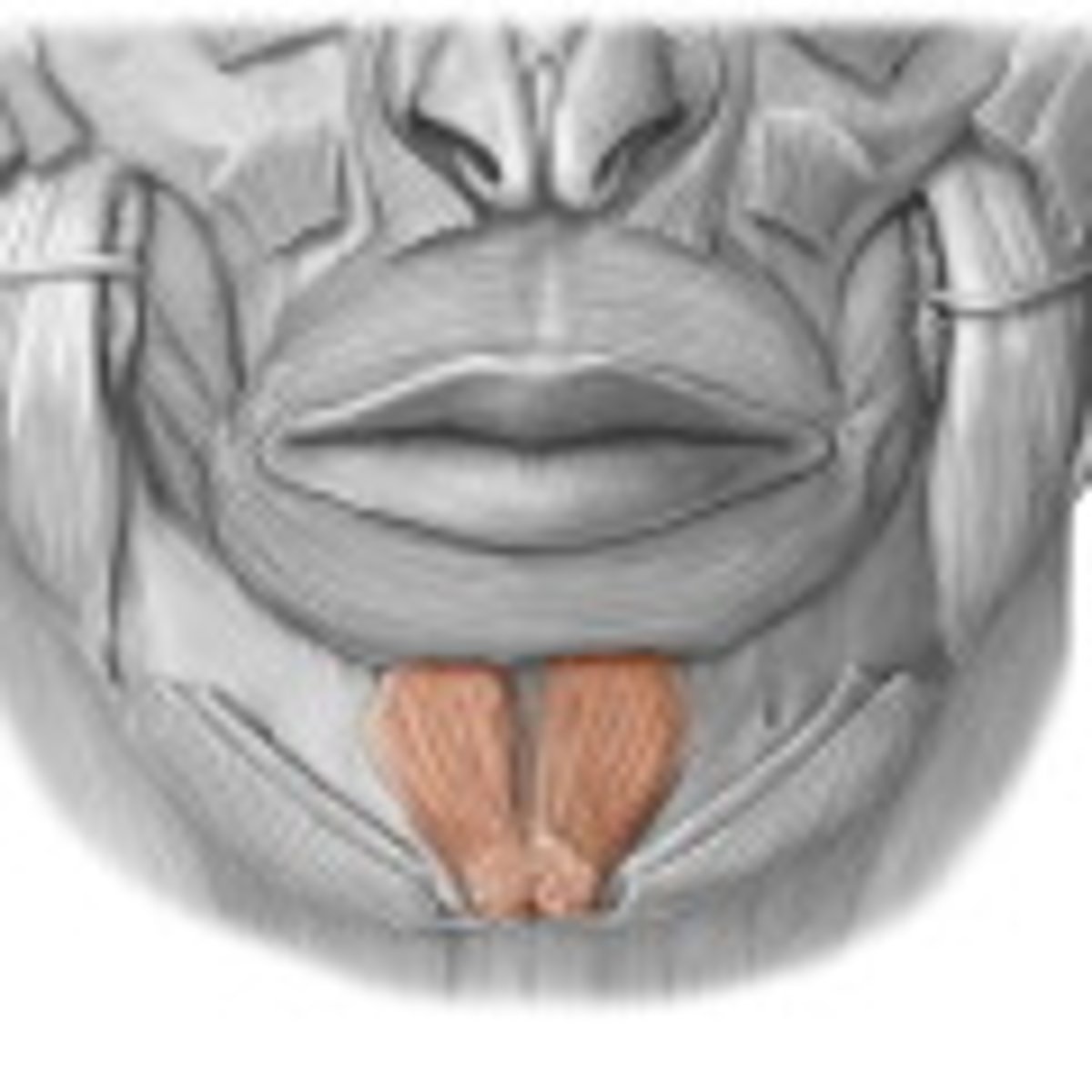
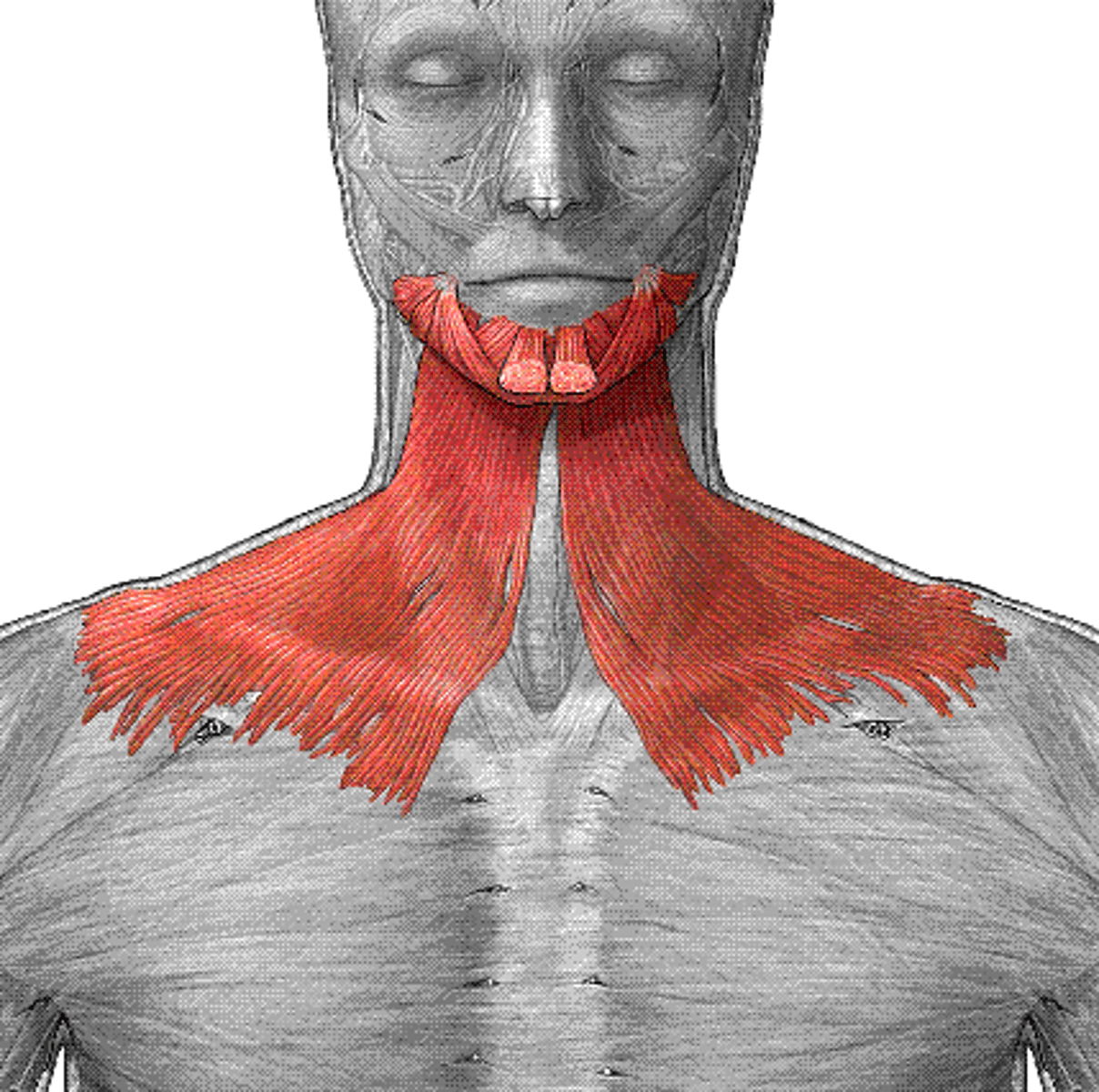
platysma
fxn- tenses skin in the anterior neck
TMJ syndrome
an unbrella term used to describe acute or chronic pain in the mastication muscle or the temporomandibular joint
salivary glands
parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands
-produce saliva, releasing it into the oral cavity through ducts like parotid (stensens) duct
-receive parasympathetic innervation from superior and inferior salivatory nuclei, through CN VII and CN IX
What is the sensory innervation of the face?
Sensation on the face is innervated by the trigeminal nerves (V) as are the muscles of mastication, but the muscles of facial expression are innervated mainly by the facial nerve (VII) as is the sensation of taste.
What are the seven bones that form the eye orbit?
frontal bone
sphenoid bone
zygomatic bone
ethmoid bone
maxilla
lacrimal bone
nasal bone
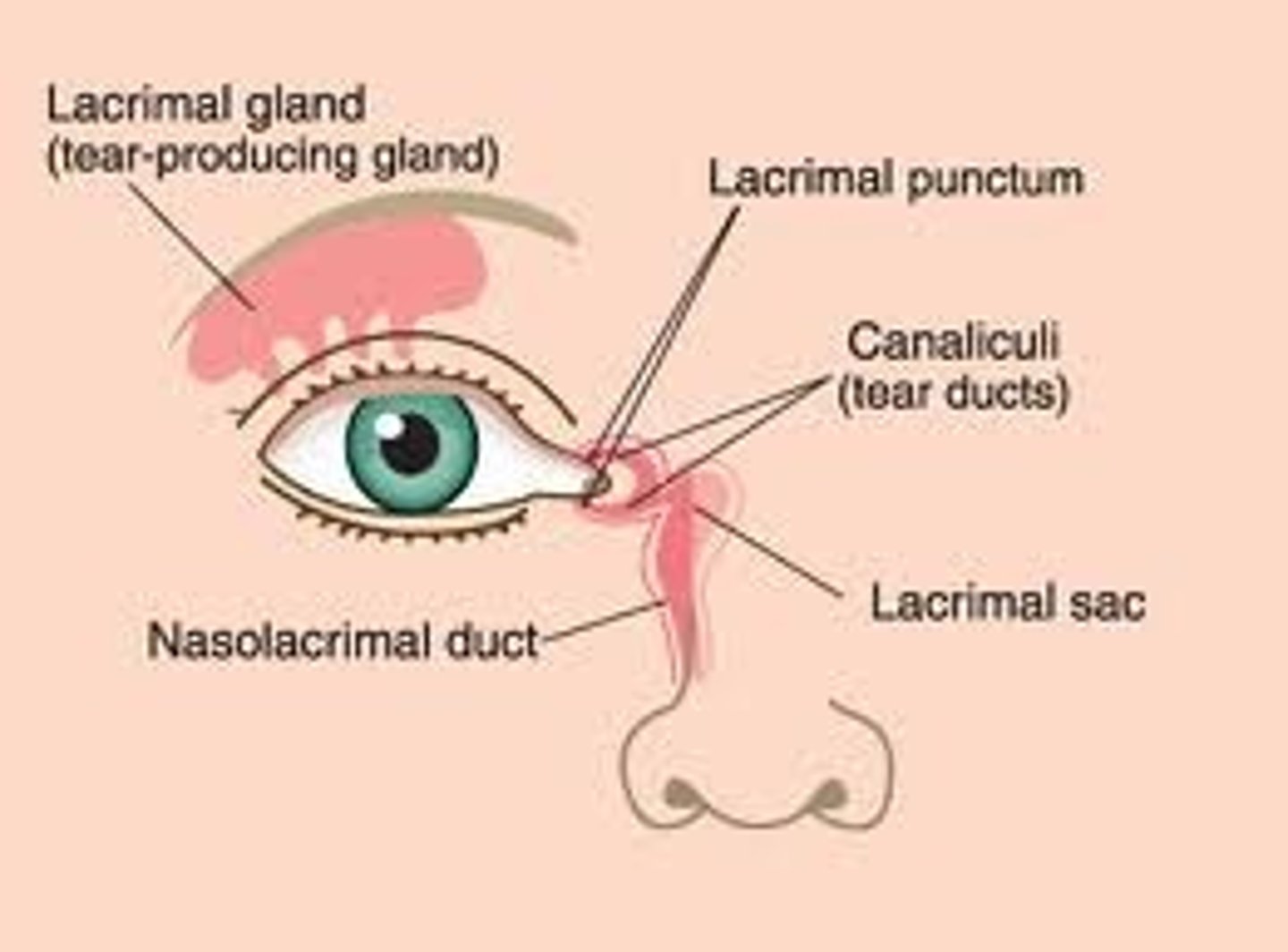
What is the lacrimal apparatus, and where is it located?
lacrimal gland (located anterolateral) produces tears which collect on the medial side of the eye, through puncta lacrimalia (openings on the inner side of the lids), passing into the lacrimal canal
-collected tears flow into the lacrimal sac which extends from nasolacrimal duct to the inferior meatus of the nose
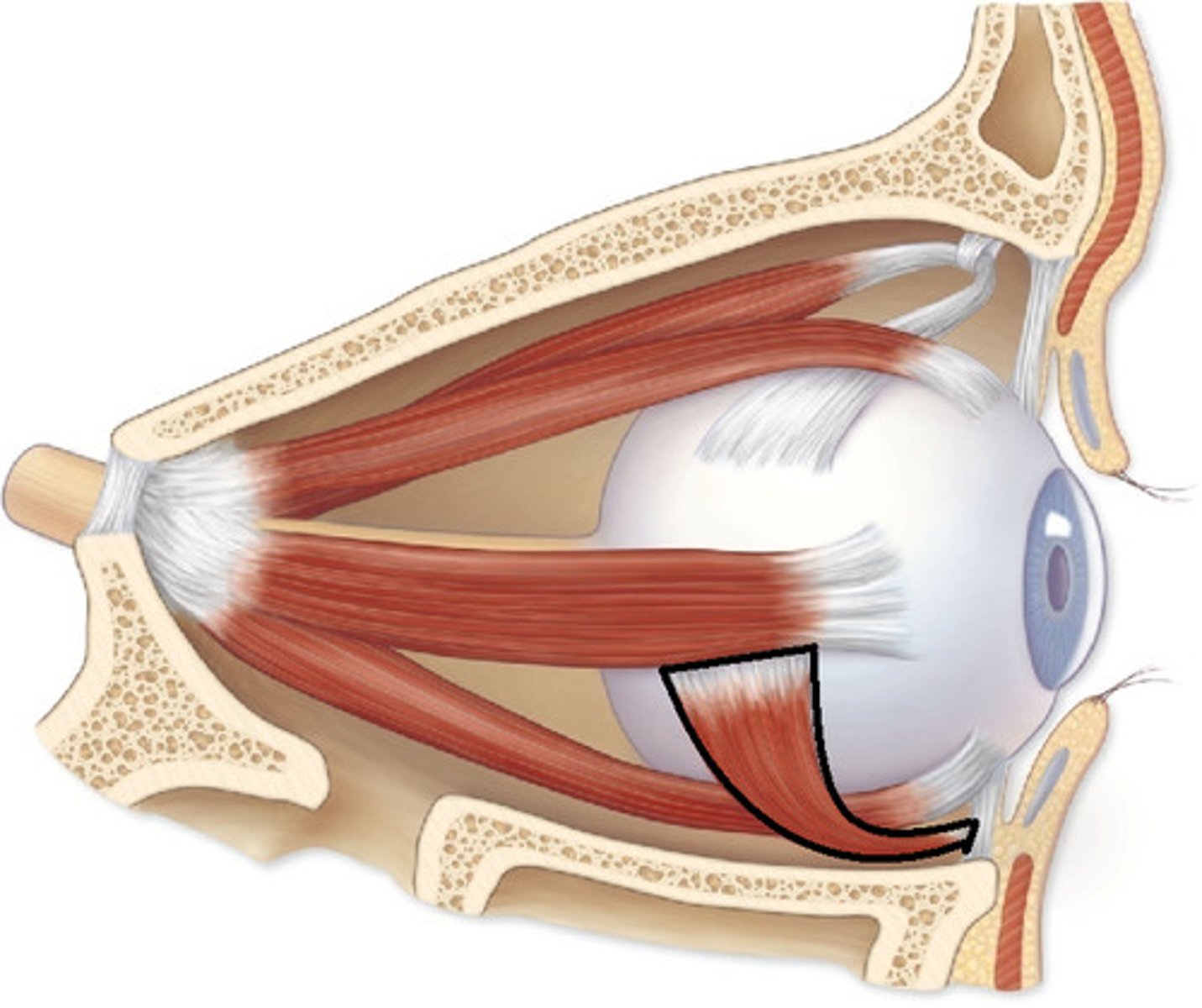
extraocular muscles of the eye
superior rectus
inferior rectus
inferior oblique
medial rectus
superior oblique
lateral rectus
superior rectus
CN III
-lifts the eye, adduction, rotation
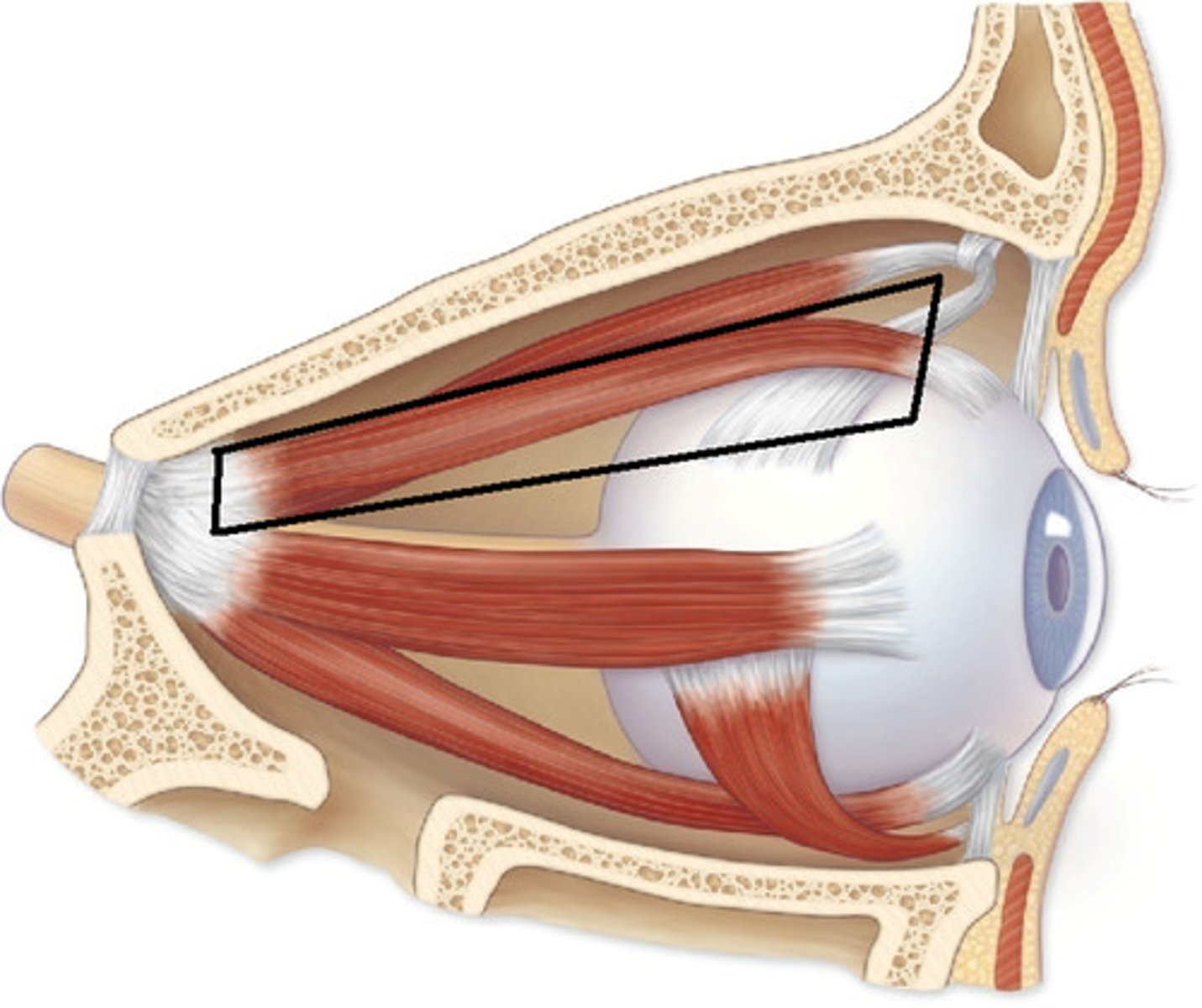
inferior rectus
CN III
-depresses the eye, adduction, external rotation
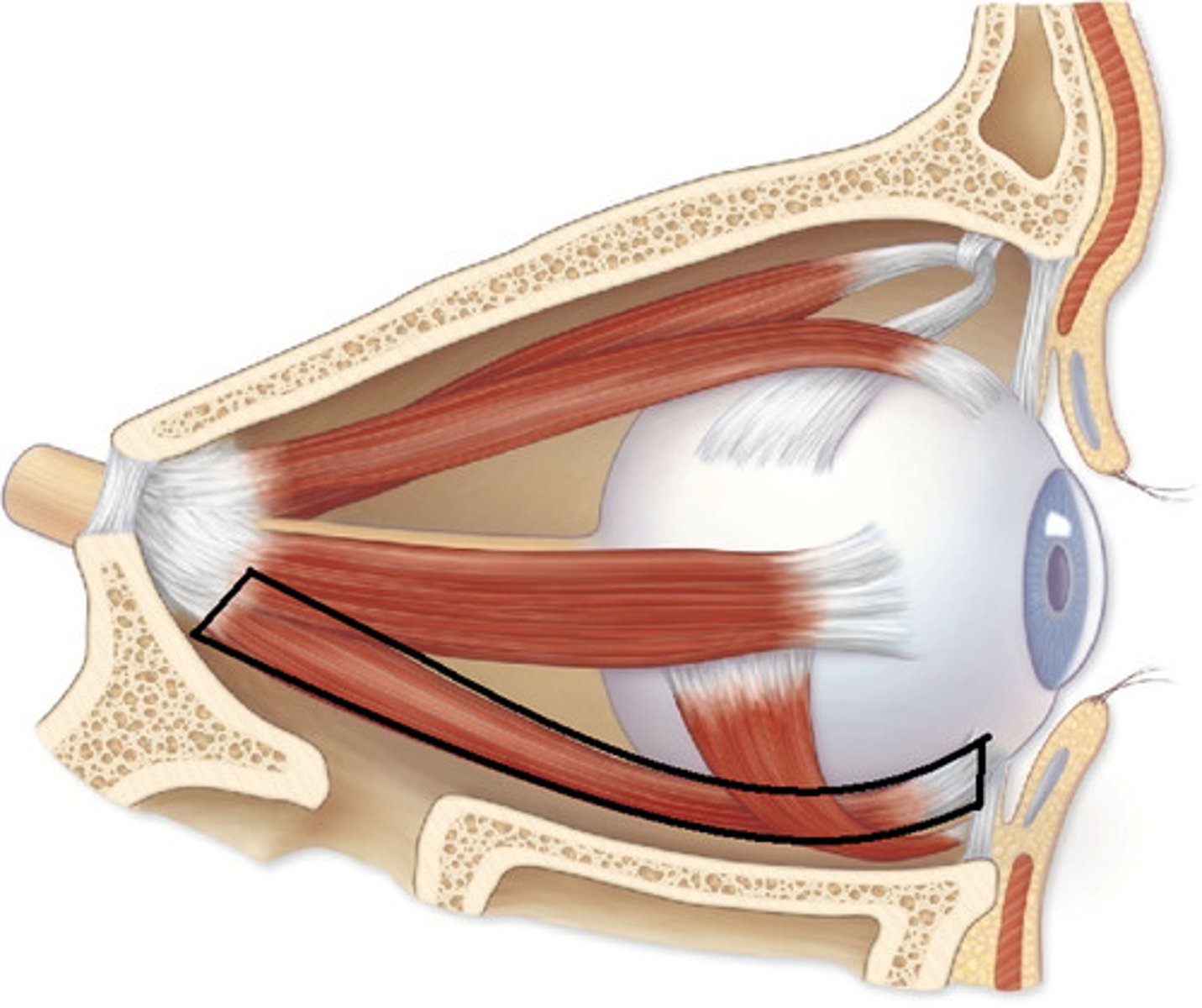
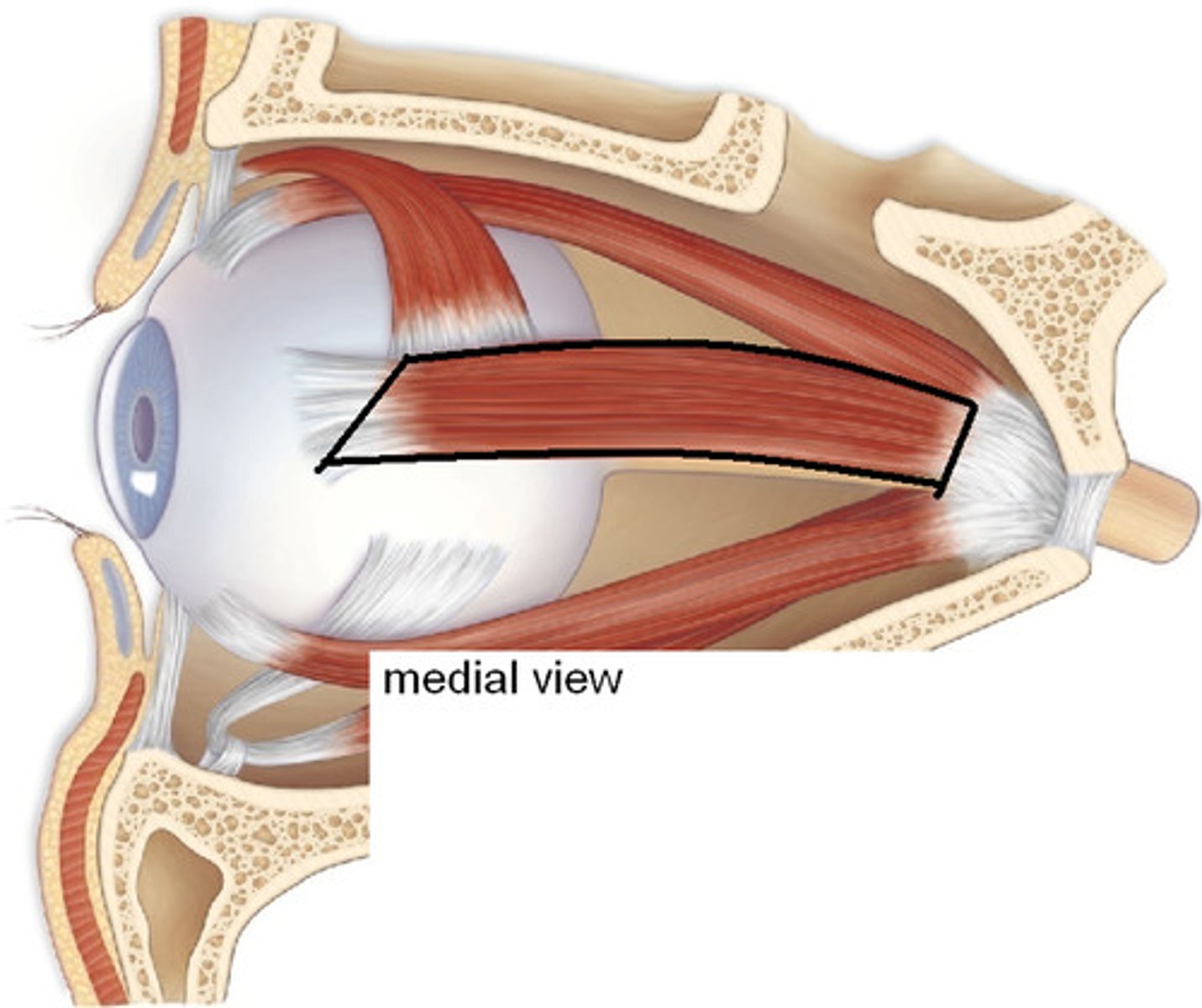
medial rectus
CN III
-adduction
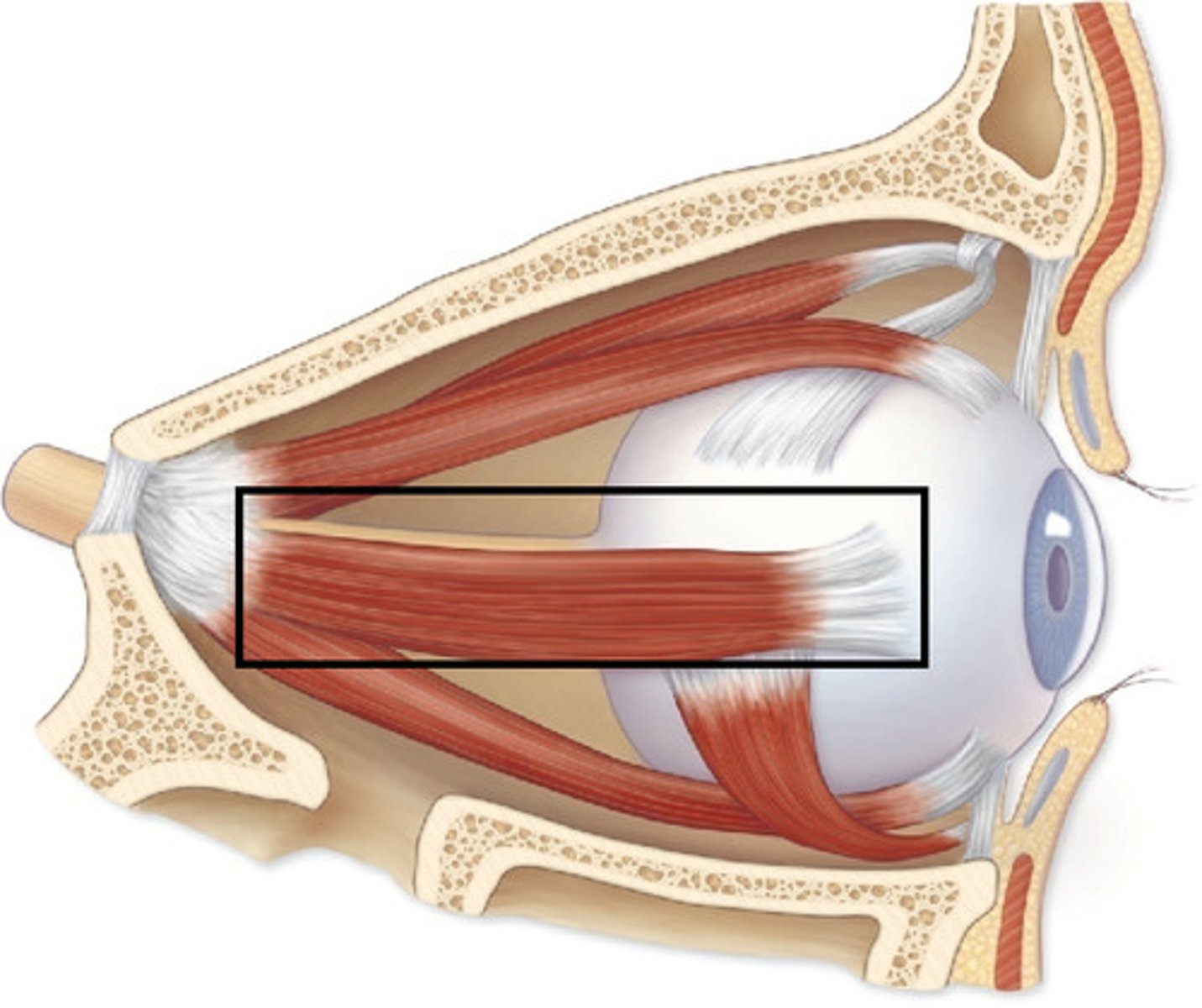
lateral rectus
CN VI
-adduction
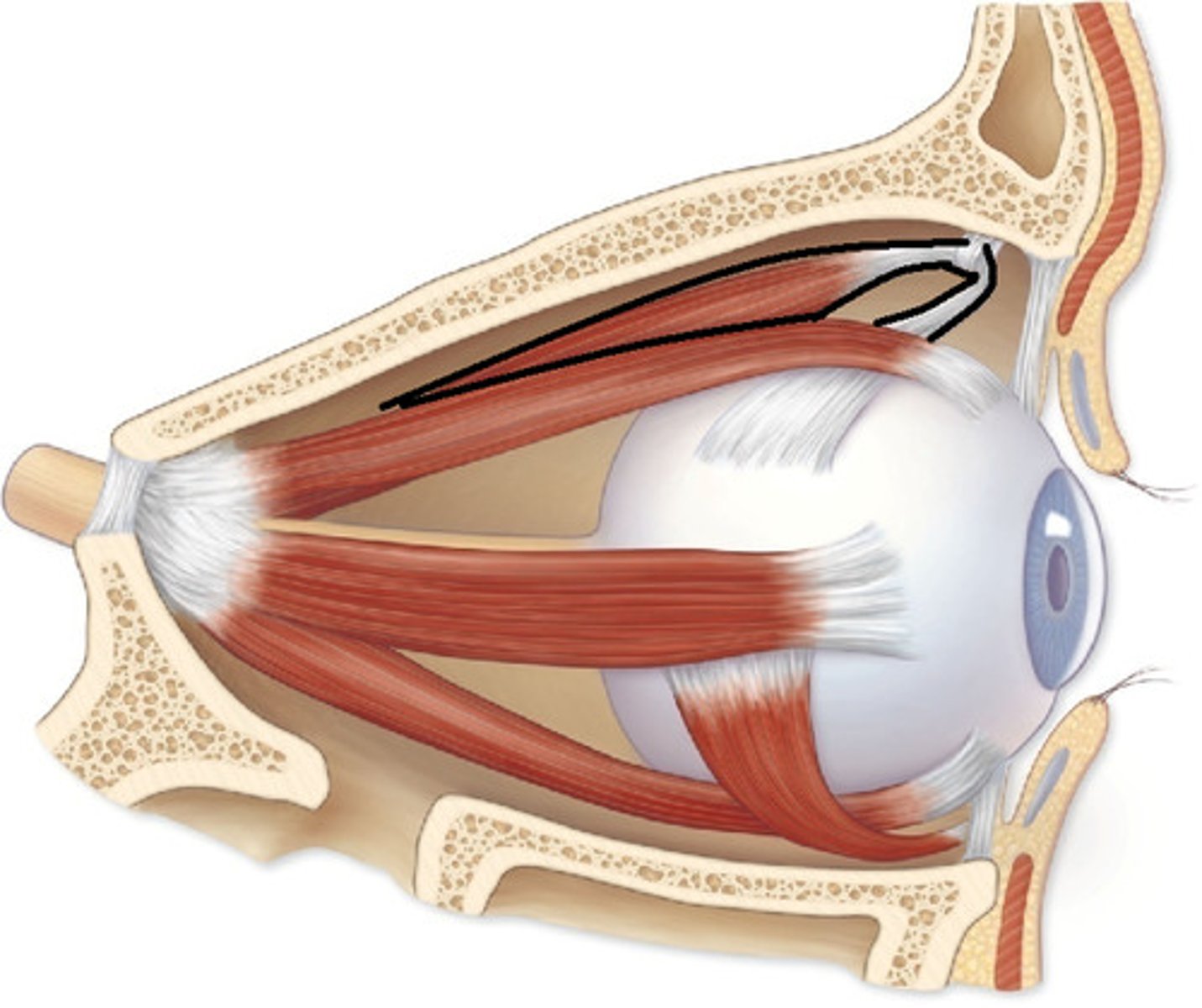
superior oblique
CN IV
-rotates upper half of of eye ball towards the nose
inferior oblique
CN III
-rotates the upper half of the eye ball towards the temporal side
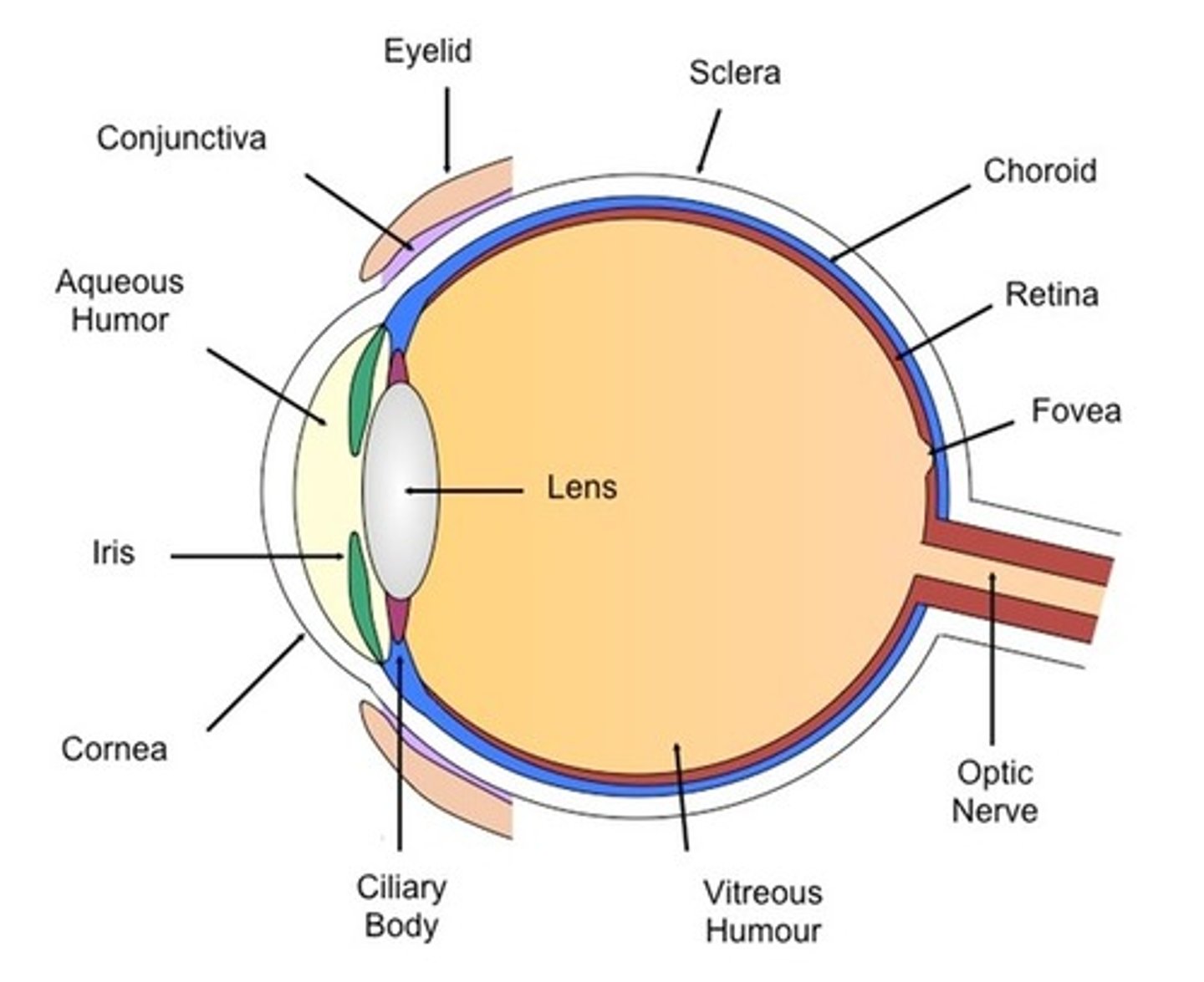
cornea
anterior surface, transparent
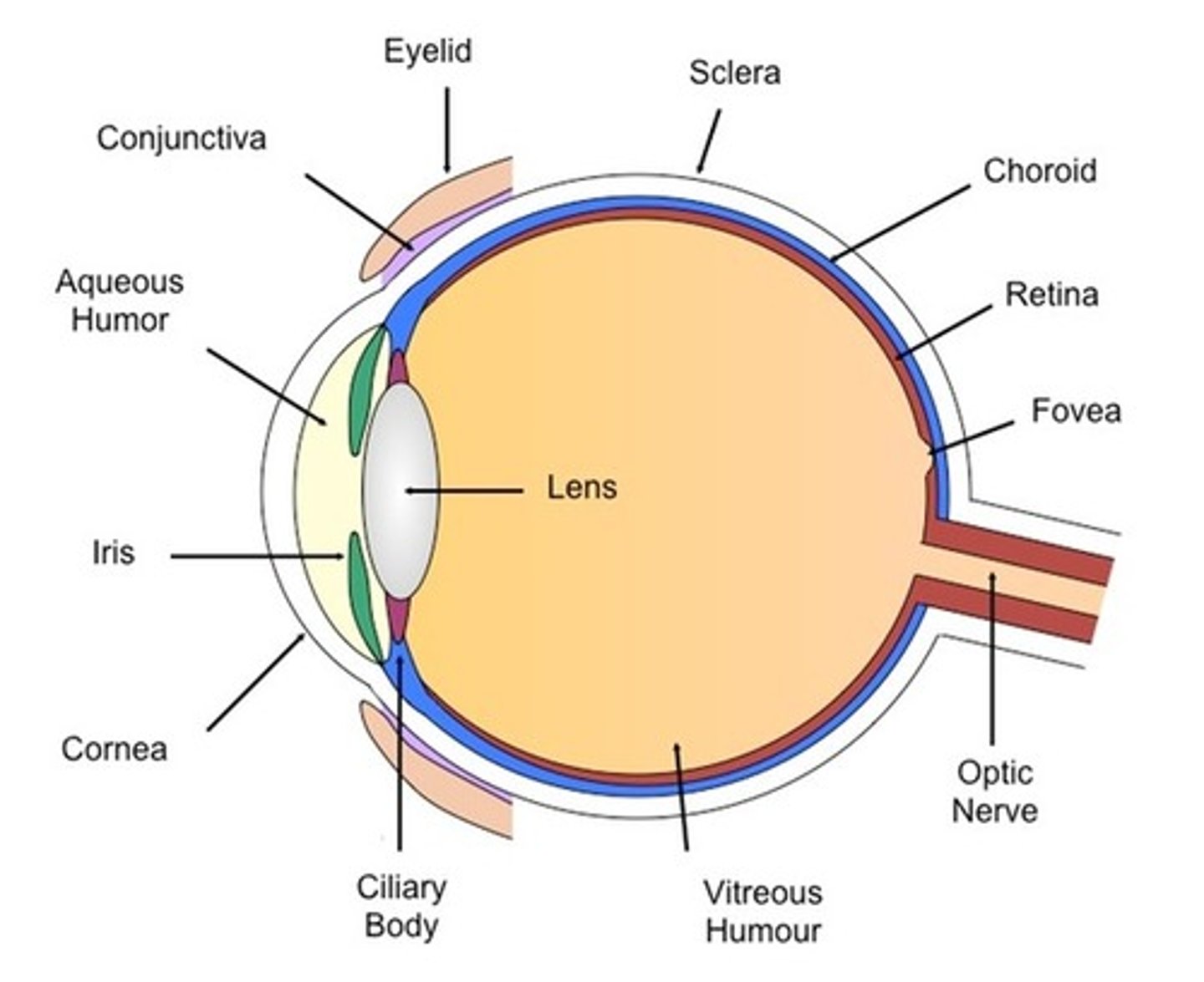
lens
posterior to the iris which has a central opening, the pupil
optic nerve
posterior, medial to the optic axis
anterior chamber of eye
bordered by cornea, iris, and lens, which has a clear fluid called aqueous humor
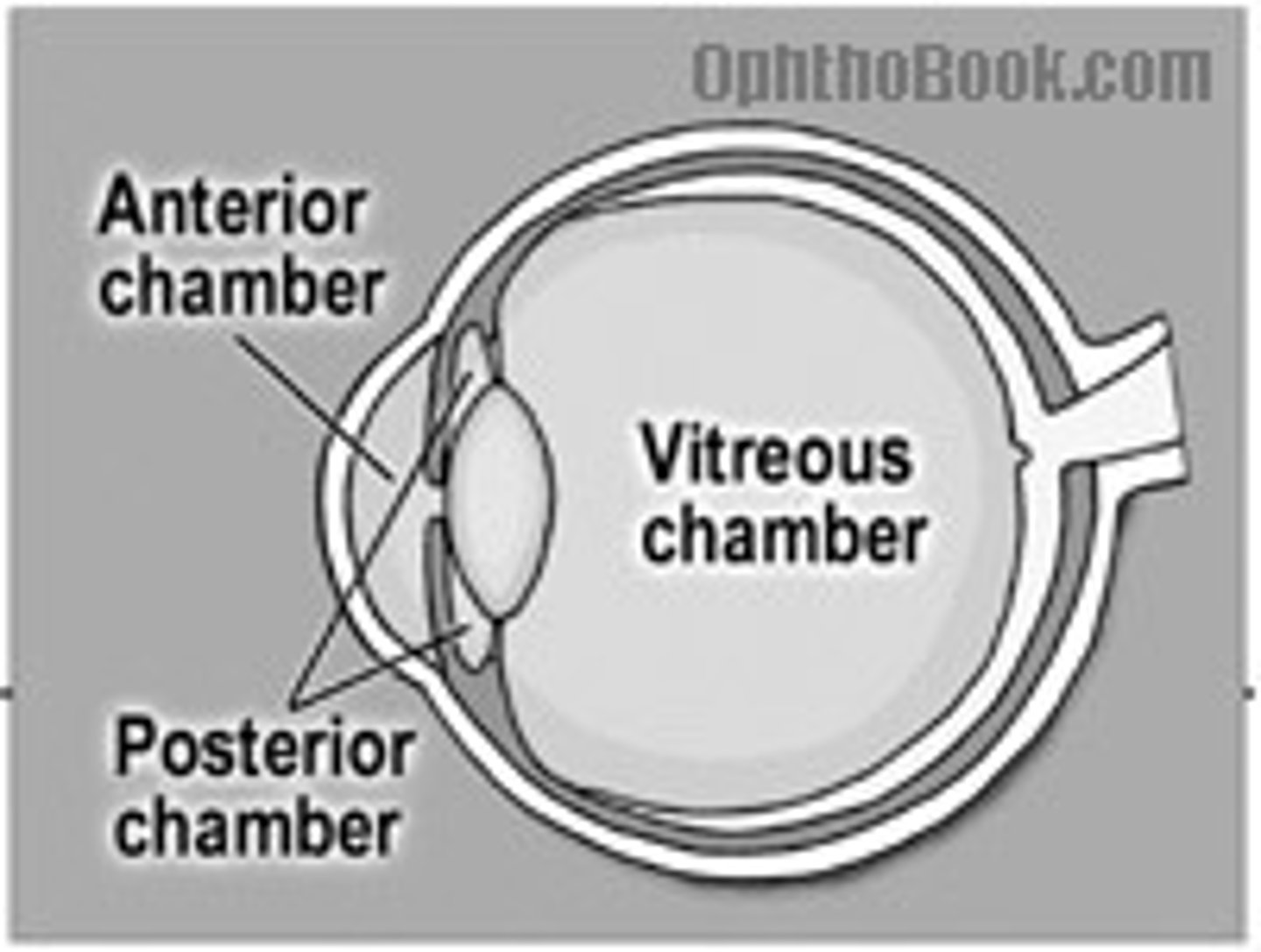
posterior chamber of eye
lies in a ring around lens, also contains the aqueous humor
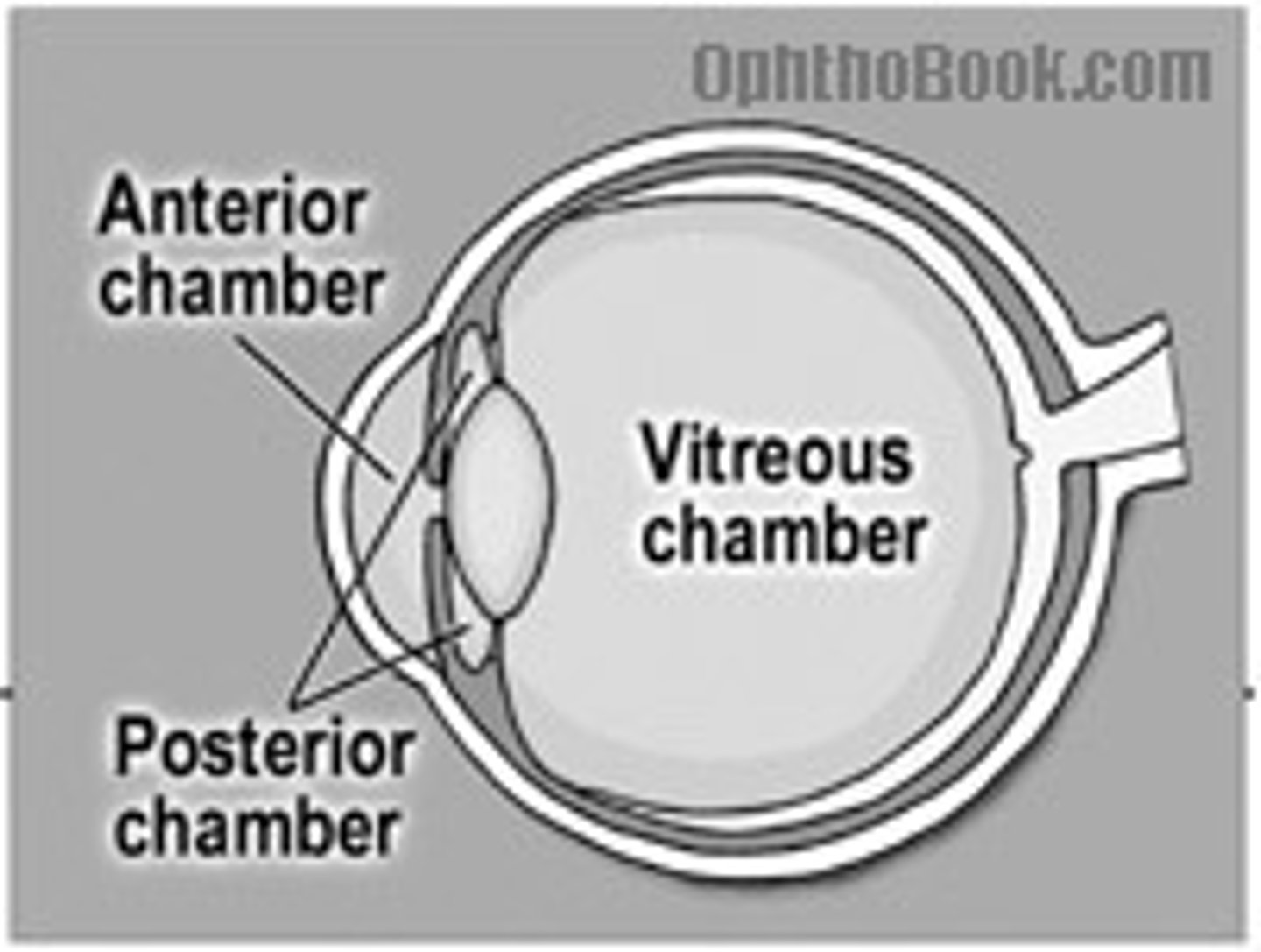
interior (vitreous) chamber
contains vitreous body, a jelly like substance containing water
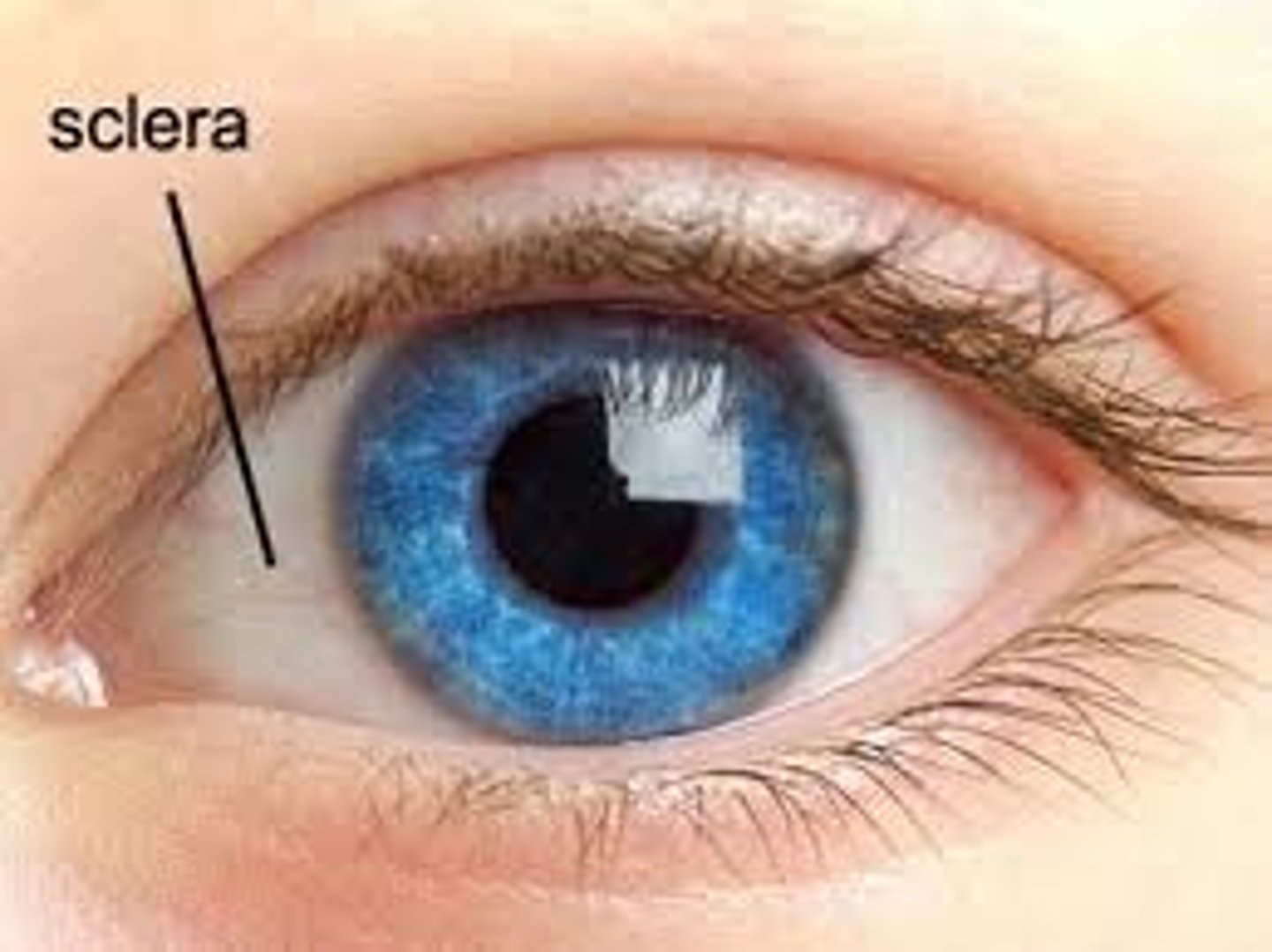
sclera
dense taut connective tissue capsule of collagen and elastic fibers
-maintains the shape of eyeball along with intraocular pressure
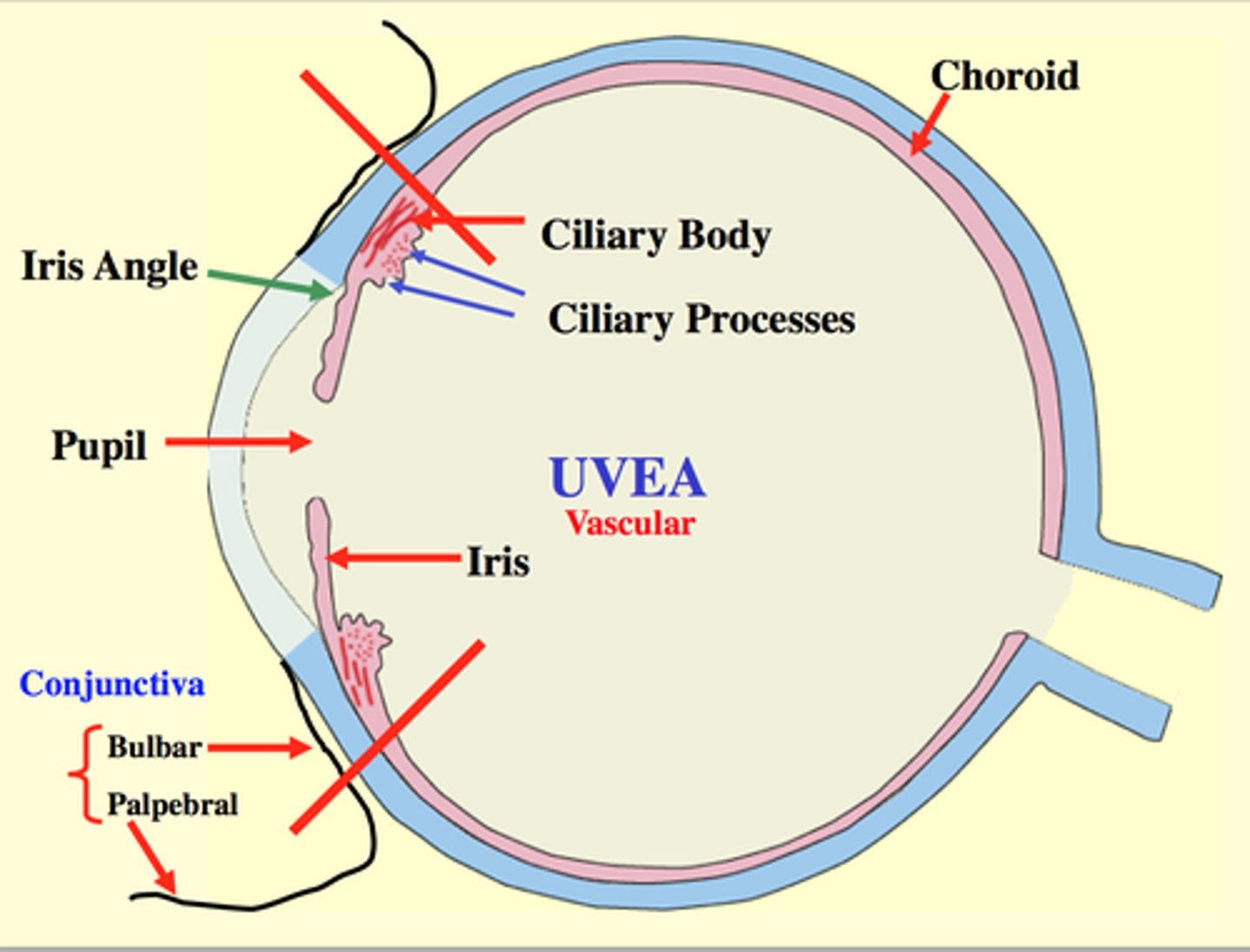
uvea
contains blood vessels, forms iris and ciliary body in the anterior chamber and the choroid in the interior chamber
-high pigment in iris= brown iris
-low pigment=blue or green eyes
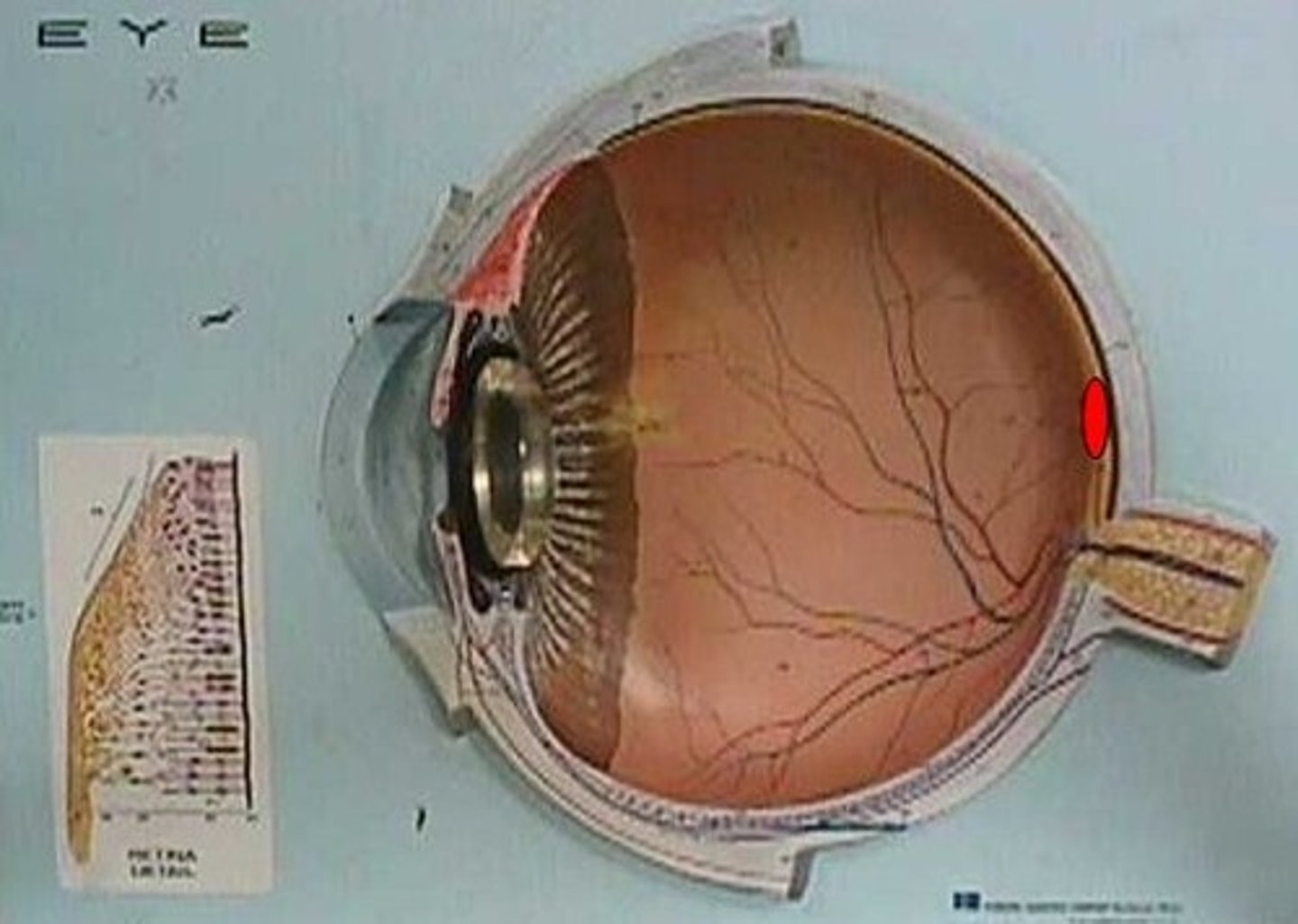
retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
macula
region of greatest visual activity, yellowish in color and has a central pit (fovea centralis)
Horner's syndrome
characterized by the classic triad of: miosis (constricted pupil), partial ptosis (drooping eyelid), loss of hemifacial sweating (anhidrosis)
Direct and consensual light reflex
constriction of ipsilateral and contralateral pupil when a light is shone into one eye
-it shows the function of CN III and also the optic pathway
-these reflexes may be lost in head trauma
glaucoma
optic neuropathy, retinal ganglion cell loss, and blindness due to impaired drainage of the aqueous humor from the schlemms canal
-leads to incresed intraocular pressure and increased retinal blood flow
cataracts
progressive degeneration and opacity of the lens which leads to impaired vision and blindness
-due to the deposition of aggregated proteins
muscles of mastication
ALL innervated by mandibular nerve CN V
-CN V= trigeminal nerve, 3 branches: ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular
masseter
mandibular division of CN V
-fxn: powerfully closes the jaw by elevating the mandible
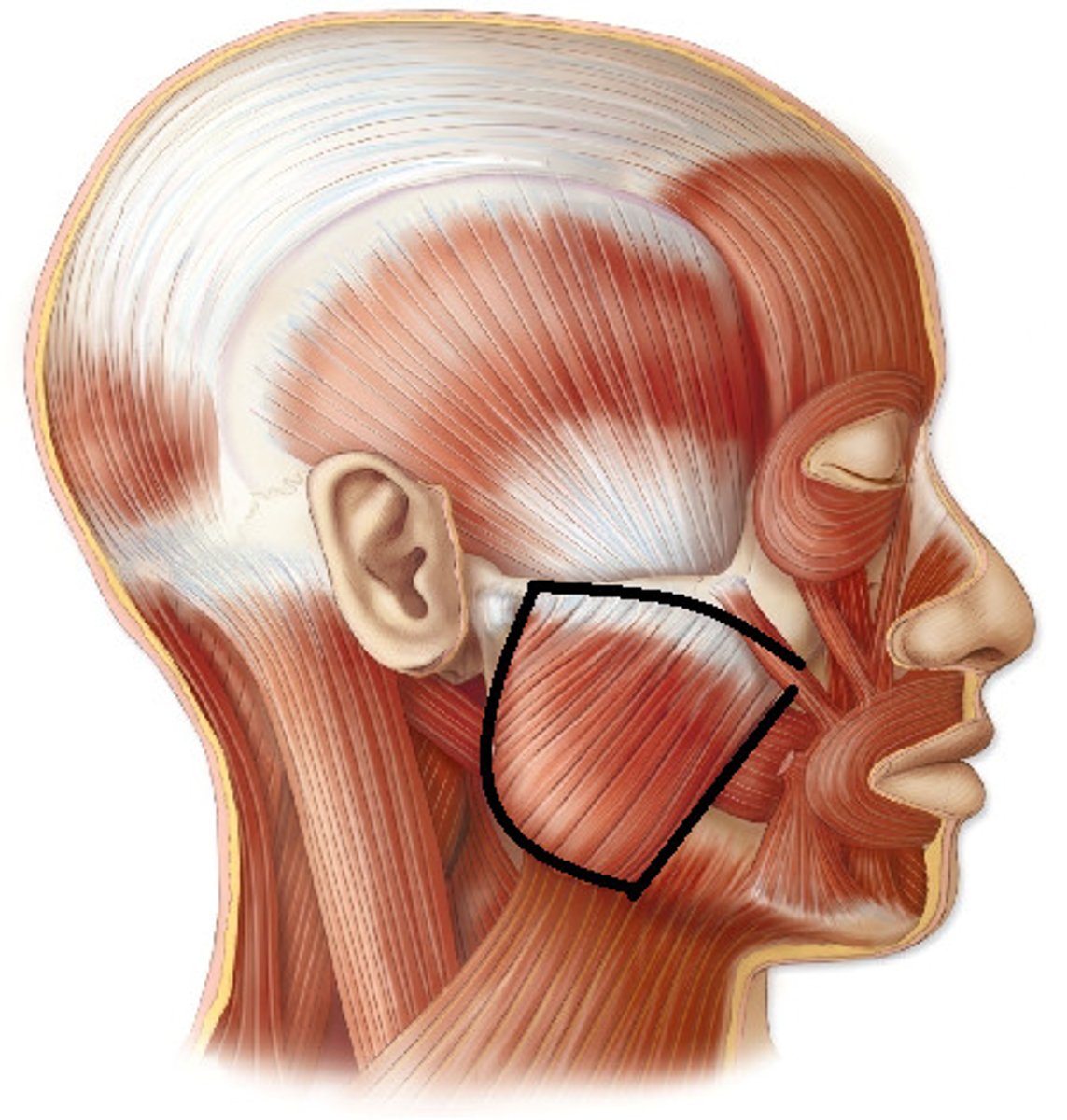
temporalis
mandibular division of CN V
-fxn: strongest elevator of lower jaw