Particle model of matter (paper 1-physics)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
How are particles arranged in a solid and its density?
High density
Particles are tightly packed in a fixed,regular arrangement
Lots of mass in a small volume → density is high
Particles vibrate but do not move from place to place.
How are particles arrange in a liquid and its density ?
Medium density
Particles close together but not arrange in a regular pattern→ slightly more space between particles→ lower density than solids
Particles can move around each other.
How are particles arrange in a gas and its density ?
Lowest density
Particles are very far apart and arranged in any pattern.→ move freely
very little mass in a large volume → gases are much less dense
Particles move rapidly.
Required practical :Density → how to determine the densities of regular & irregular solid objects
Regular objects → have dimensions easy to measure e.g: solid :
Measure the mass using a balance . Then measure length, width, & height of object using a ruler
Calculate volume using : Volume = L * W *H
Use the density formula = Density = mass/volume
Irregular objects→ can’t measure its dimensions easily
measure the ass using a balance.
Find its volume using a displacement method : fill a eureka can with water just below the spout & place a measuring cylinder underneath - the volume of water displaced = volume of object
Use the density formula again
Use consistent units → E.g: grams & cm3 / kg / m3
Calculating liquid:
place measuring cylinder on a balance &zero the balance
Pour 10ml of the liquid into measuring cylinder & record the total volume & mass → repeat process until measuring cylinder is full
For each measurement use the formula to find the density
Take an average of calculated densities to get an accurate value for the density of the liquid
What does density mean?
The mass of a given volume.
Formula for density
density= mass/volume
kg/m³ or g/cm³
Why does the solid polystyrene have a low density?
It has a very open structure and is full of air spaces so it has a very small mass for it’s volume.
Internal energy
The total energy stored inside a system due to its kinetic energy (Movement) and the Potential energy(intermolecular forces& chemical bonds)
Energy stored inside a system by particles
Changes of state: Effect of heating & Cooling on internal energy
Heat a solid → Increases internal energy → melting → into liquid
Further heat →continues increasing internal energy → boiling state → into gas
Cool gas→ reduces internal energy → condensation→ becomes liquid
Cool further →reduce internal energy even more → freezing → becomes solid
SUBLIMATION : solid → gas
Mass is always conserved during changes of state → no gain/loss of particles
Chanegs of state = physical changes → if reverse → recovers to original properties
EVAPORATION : liquid → gas (only on surface particles )
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1 degrees Celsius.
Formula for specific heat capacity
Q=m ×c×AT
Change in thermal energy (J)= mass (kg) × specific heat capacity (J/kg degrees Celsius) × temperature change (degrees Celsius)
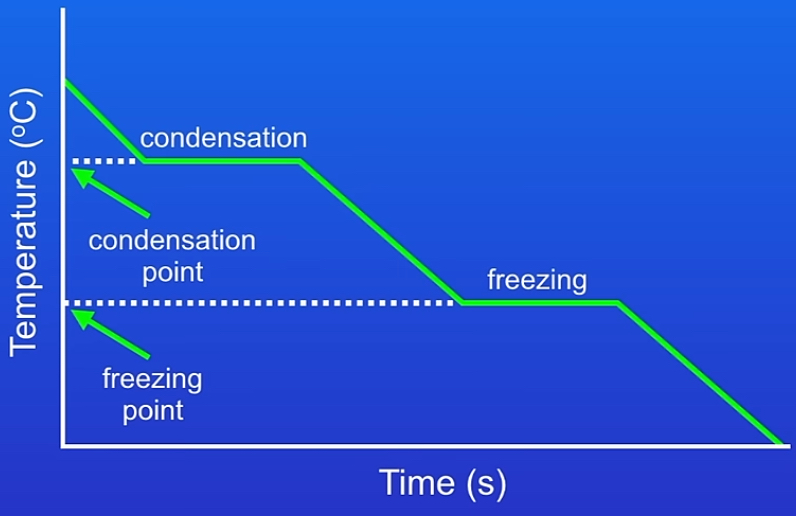
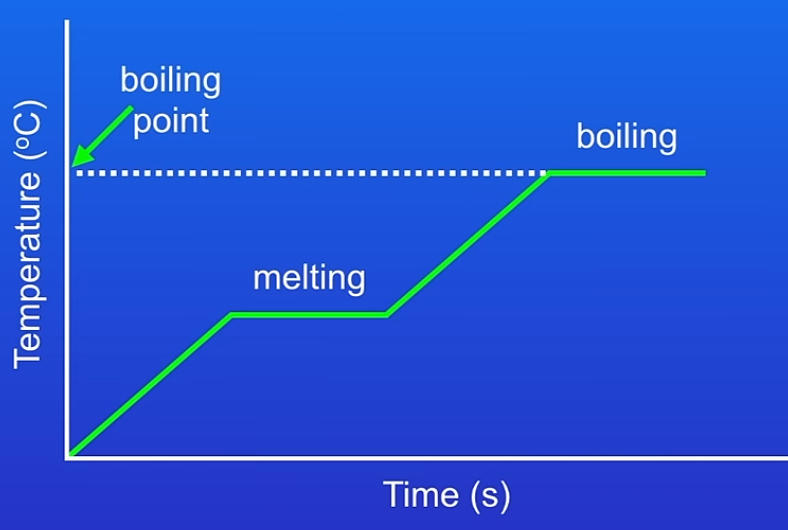
Heating & cooling graphs
x-axis → time or energy added
Y-axis → temperature of the substance
Heating :
Solid heating → temperature rises & particles move faster → reaches melting point = temperature constant plateau & energy breaks bond → temp. Stays same → until liquid heating → temperature rises & particles move even faster → reaches boiling point = hits plateau & energy breaks intermolecular forces→ gas heating → temp. Rises & particles moving faster
Cooling :
Gas cooling → temperature decreases & particles move slower → condensation = temp. Constant plateau & energy released as bonds form →until liquid cooling → temp. Decreases again & particles slow down → reaches freezing point = constant plateau → temp stays constant & energy released as bonds form → solid cooling → temp. Falls as solids vibrate less
Why does temperature stay the same during the change of state?
(When a change of state occurs, the internal energy increases but not the temperature.)
This is because the energy is being used to weaken or break the forces of attraction between the particles.
REMEMBER: During flat plateaus (melting,boiling,freezing,condensing) , temperature stays constant while the state changes → energy is sued to break / for bonds , not change temperature
What is specific latent heat?
The amount of energy required to change the state of 1 kilogram of the substance with no change in temperature.
Specific latent heat of fusion
The energy required to change 1kg of a substance from a solid to a liquid with no change in temperature.
Specific latent heat of vaporisation
The energy required to change 1kg of a substance from a liquid to a gas with no change in temperature.
Specific latent heat formula
E= m × L
Energy for change of state (J) = mass (kg)× specific latent heat (J/kg)
Temperature & particle energy & gas pressure
Temperature & particle energy:
Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of gas particles
Higher temperature→ particles move faster
Temperature & pressure:
increasing temperature→ particles hit container walls more often & with more force→ pressure increases (if volume constant)
Decreasing temperature→ particles move slower→ pressure decreases