7.1-7.3 Exchange surfaces and breathing
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
why do single-celled organisms not need specialised exchange surfaces
1) low metabolic activity = low O2 and CO2 demands
2) large SA:V
4 characteristics of an efficient exchange surface
increased surface area
thin layers
good blood supply
ventilation
increased surface area as a feature of an efficient exchange surface
provides area needed for exchange and overcomes the limitation of a small SA:V
thin layers as a feature of a specialised exchange surface
short diffusion distances = fast and efficient
good blood supply as a feature of a specialised exchange surface
maintains a steep concentration gradient = faster diffusion
ventilation as a feature of a specialised exchange surface
maintains concentration gradient = faster diffusion
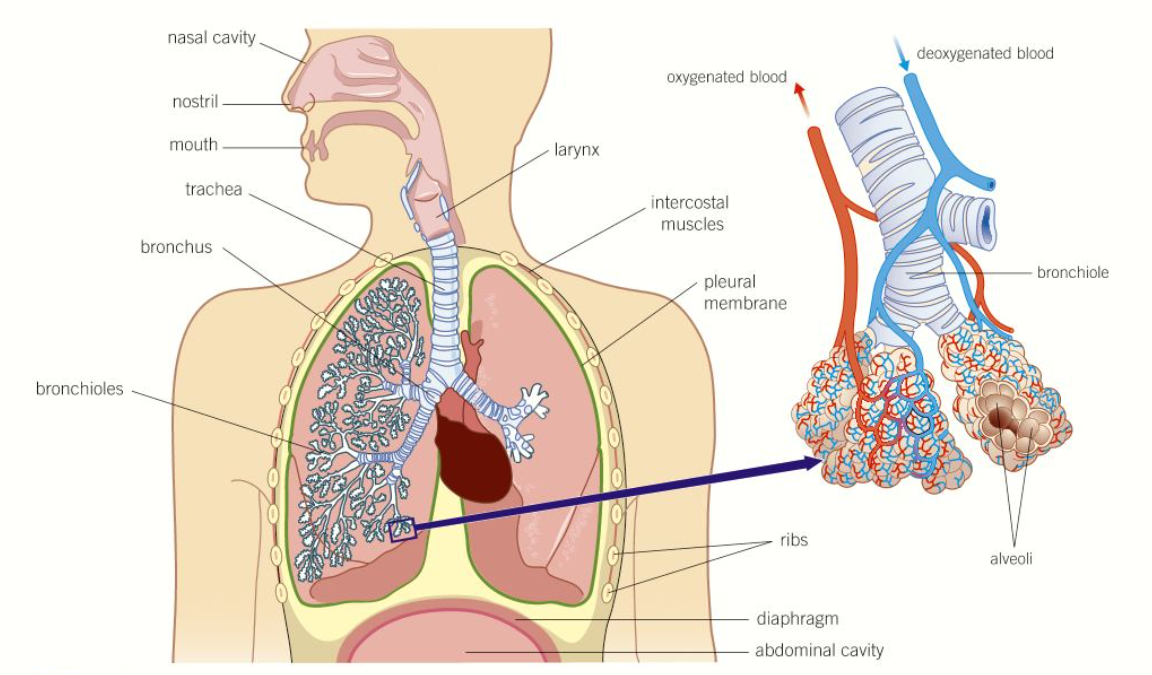
diagram of the structure of the human gaseous exchange system
3 features of the nasal cavity
1) a large surface area with a good blood supply = warms the air to body temperature
2) a hairy lining = secretes mucus to trap dust and bacteria = protects lung tissue from irritation and infection
3) moist surfaces = increase humidity of incoming air = reducing evaporation from the exchange surfaces
why are the cartilage rings supporting the trachea incomplete
allows food to move easily down the oesophagus behind the trachea
goblet cells
secrete mucus onto the lining of the trachea to trap dust and microorganisms that have escaped the nose lining
cilia
beat and move mucus, trapped dirt, and microorganisms away from the lungs
inspiration
diaphragm contracts and lowers
external intercoastal muscle contract moving ribs upwards and outwards
vol of thorax increases so pressure decreases
expiration
diaphragm relaxes and moves up
external intercoastal muscles relax moving ribs down and inwards
vol of thorax decreases
forceful expiration
internal intercoastal muscles contract which pulls the ribs down hard and fast
abdominal muscles contract forcing diaphragm up
pressure in lungs increases
peak flow meter
device that measures the rate at which air can be expelled from the lungs
vitalograph
version of the peak flow meter
patient breathes out as quickly as they can through a mouthpiece and a graph of the forced expiratory volume in one second is produced
spirometer
used to measure different aspects of lung volume
tidal volume
the vol of air that moves into and out of the lungs with each resting breath
vital capacity
the vol of air that can be breathed in when the strongest possible exhalation is followed by the deepest possible intake of breath
inspiratory reserve volume
the max vol of air that can be breathed in over and above a normal inhalation
expiratory reserve volume
the extra amount of air that can be forced out of the lungs over and above the normal tidal vol of air that is breathed out
residual volume
the vol of air that is left in the lungs after exhaling as hard as possible
total lung capacity
the sum of the vital capacity and the residual volume
breathing rate
the number of breaths taken per minute
ventilation rate
the total vol of air inhaled in one minute
tidal volume x breathing rate
trachea
the main airway carrying clean, warm, moist air from the nose down to the chest
wide tube supported by incomplete rings of strong, flexible cartilage = stop trachea from collapsing
lined with a ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
walls contain smooth muscle and elastic fibres
describe the structure of the bronchi
goblet cells and ciliated cells to filter out dust and pathogens
incomplete rings of cartilage
smaller than trachea
divide into smaller bronchioles
walls contain smooth muscle and elastic fibres
describe the structure of the bronchioles
walls contain smooth muscle = contraction and relaxation = control amount of air reaching the lungs
lined with ciliated epithelium, but contain no goblet cells
walls contain elastic fibres
walls contain smooth muscle (not in smallest bronchioles)
describe the structure of alveoli
tiny air sacs
squamous epithelium lining = very thin, permeable for easy diffusion of gases
walls contain elastic fibres = elastic recoil
some collagen
describe adaptations of the alveoli for effective gas exchange
1) large surface area = increases SA:V
2) thin layers = only single epithelial cell thick = very short diffusion distance
3) good blood supply = alveoli are supplied with an extensive network of capillaries = maintain steep concentration gradient
4) good ventilation = breathing air moves in and out of alveoli = maintains steep concentration gradients
5) inner surface of alveoli is covered in a thin layer of lung surfactant = keeps alveoli inflated