BIO 201: Chapter 4.6 and 4.7 Special Senses and Autonomic Nervous System
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
sensation
detection of changes in the internal and external environments which may be conscious or subconscious
perception
integration and interpretation of information that one is consciously aware of
vision, hearing, equilibrium, taste, and olfaction
special senses
touch, pain, and temperature
general senses
chemosenses
olfaction and taste are sometimes referred to as _____ because they rely on chemoreceptors to relay information about the environment to the brain
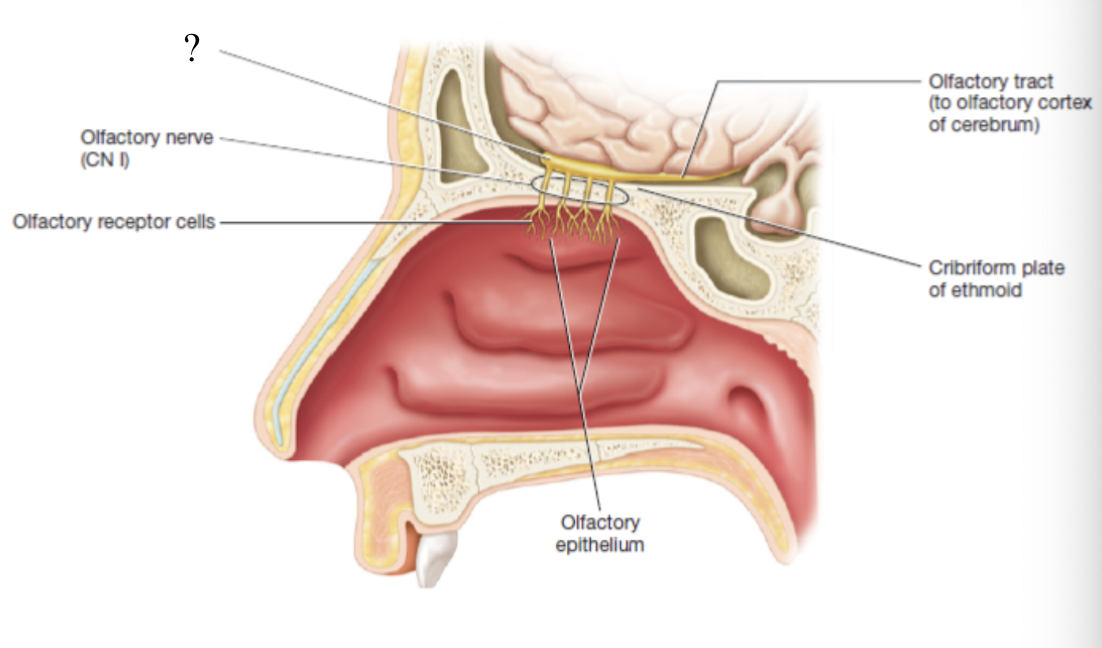
olfactory epithelium
small patch in the roof of the nasal cavity in which chemoreceptor of olfaction can be found
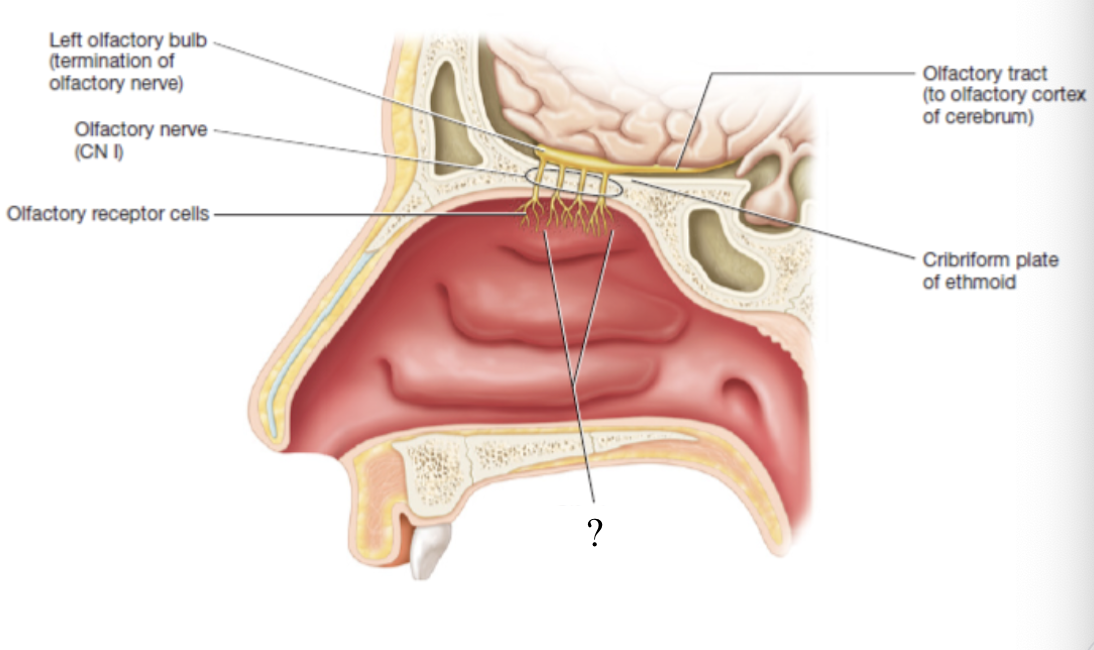
olfactory receptor cells
about 10-20 million bipolar neurons contained in the olfactory epithelium
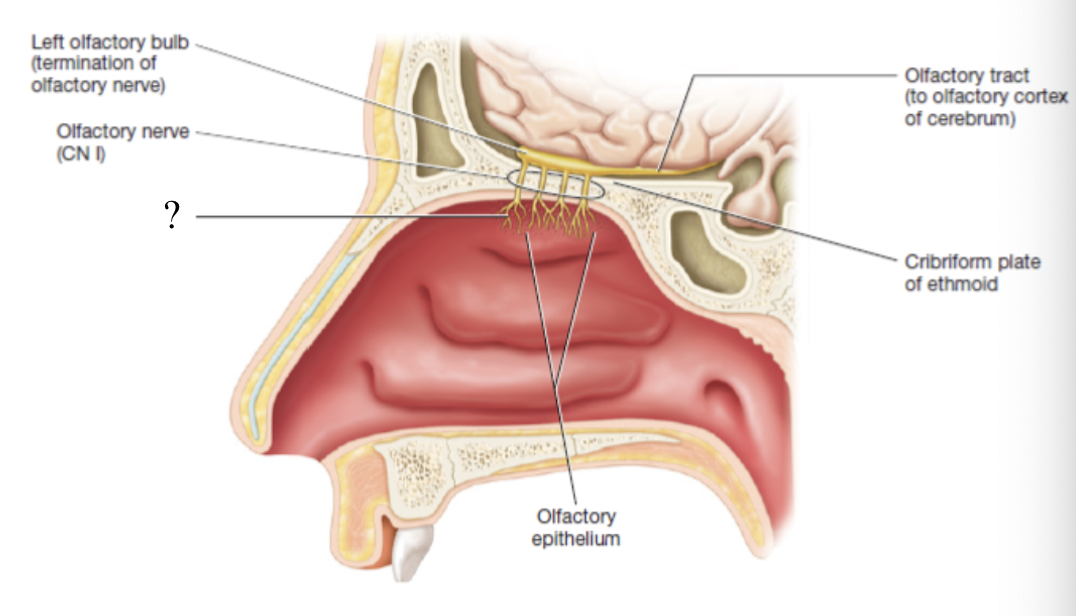
CN I olfactory nerve
made up of the axons of olfactory receptor cells that penetrate holes in the cribriform plate
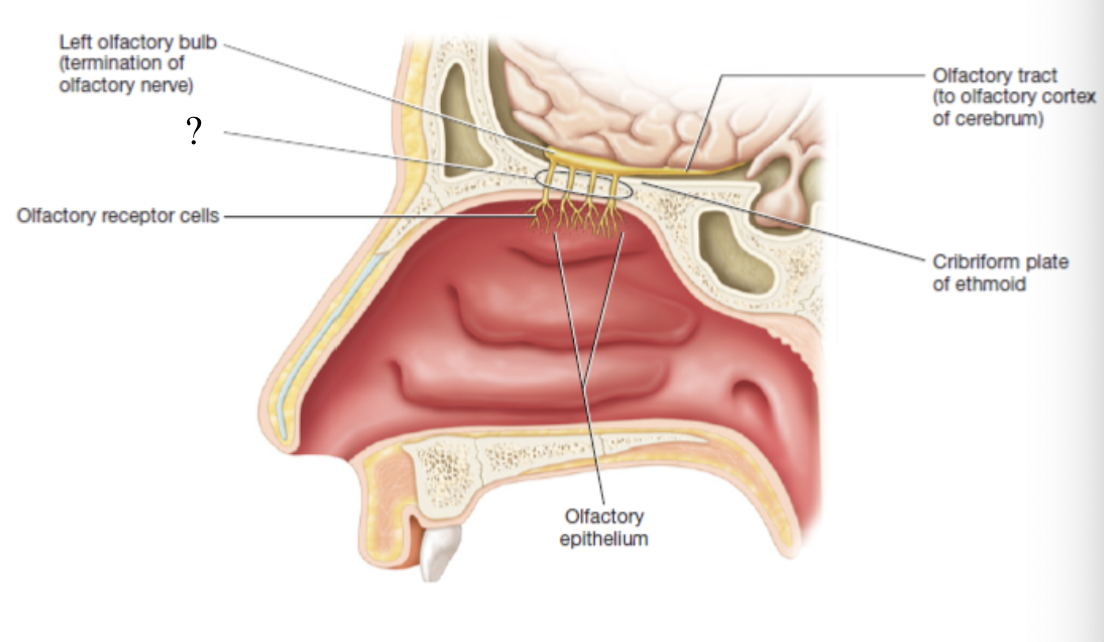
olfactory bulb
sends the impulses down the axons of the olfactory tract to the olfactory cerebral cortex
taste buds
taste receptors are located on about 4000 of these
lingual papillae
projections from the tongue which include 4 types
filiform papillae
most numerous, located on the surface of the tongue, its spiky surface gives the tongue its rough appearance
plays role in sensing if food is chewed enough to shallow and senses food texture
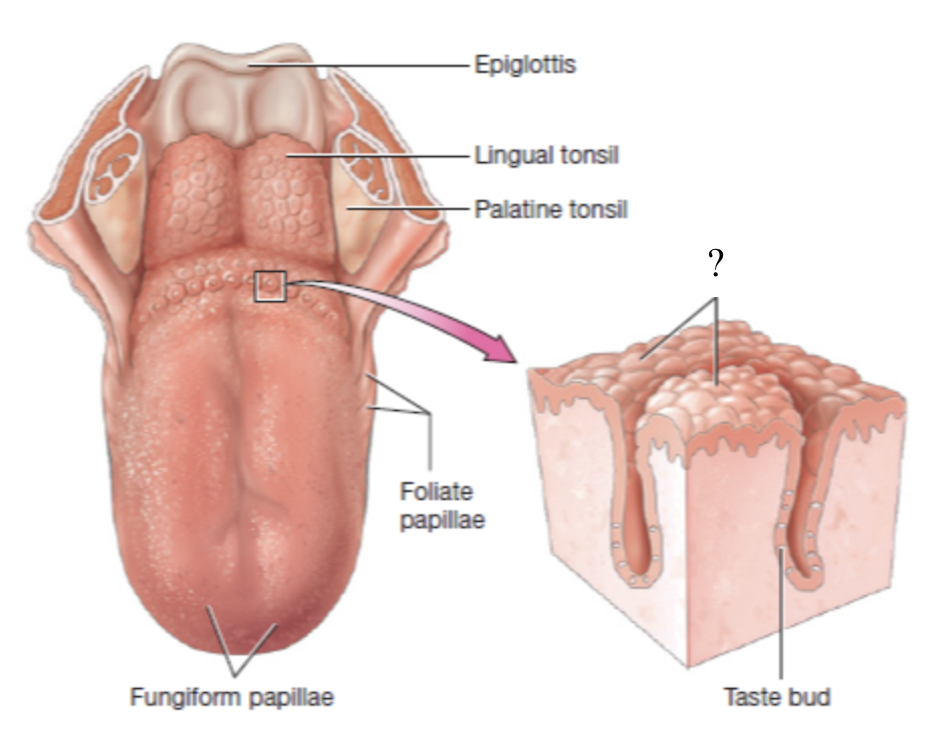
fungiform papillae
sporadically scattered over the surface of the tongue and kind of resembles a mushroom
plays role in sensing food texture
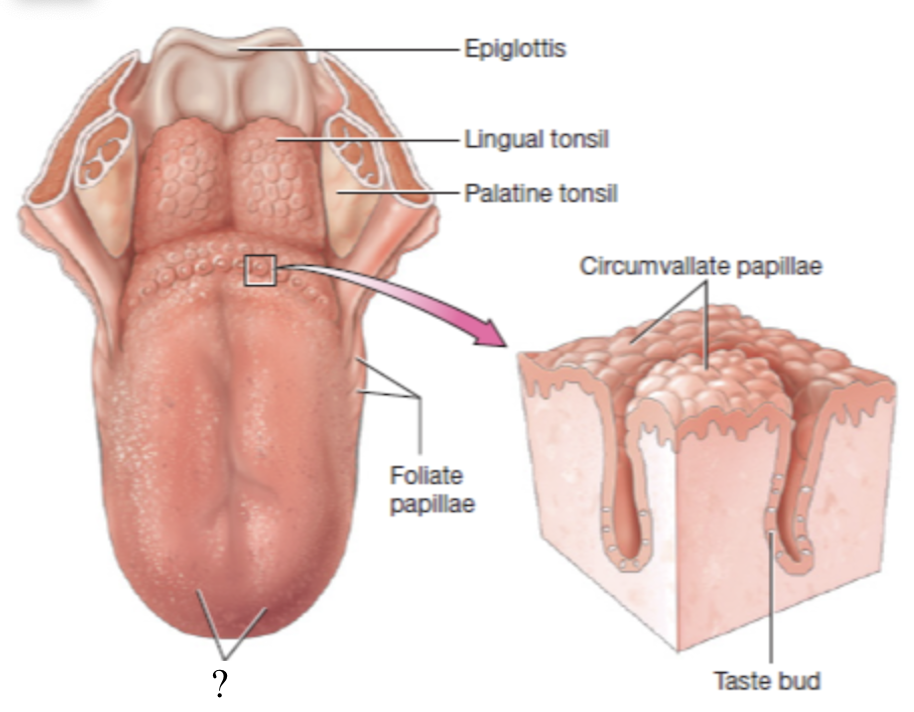
circumvallate papillae
large papillae located at the posterior aspect of the tongue in a V shape arrangement
contains most of the tastebuds
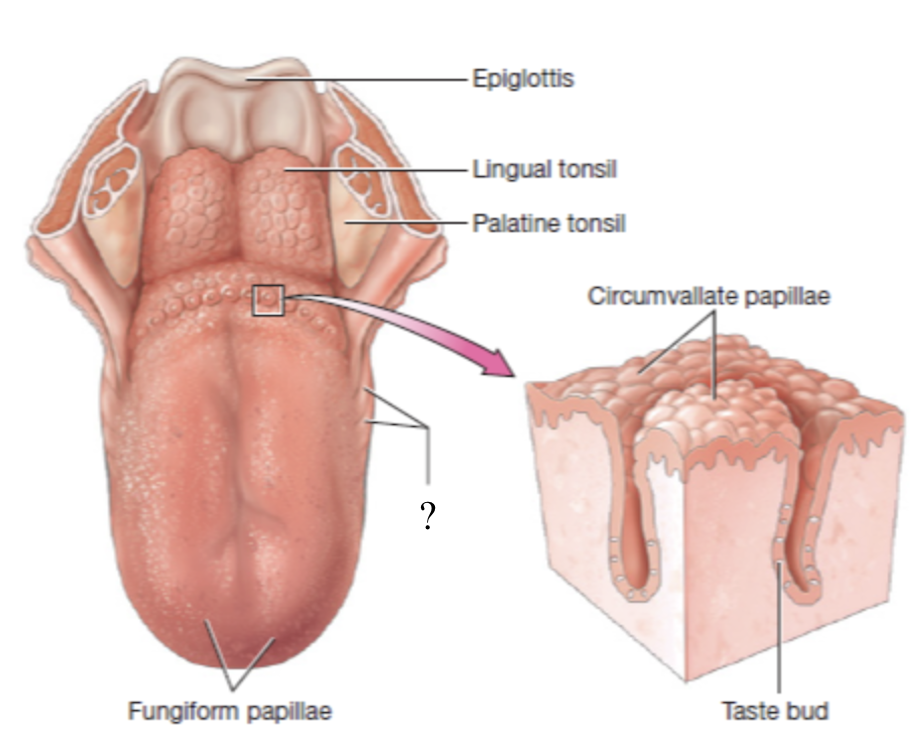
foliate papillae
translate to “leaf-like” and are parallel ridges located on the lateral aspects of the tongue
contain taste buds primarily during childhood
true
true or false: of the four types of papillae, all but filiform papillae house taste buds
salty, sweet, sour, bitter, and umami
primary tastes sensed by the taste buds
outer ear
begins with the auricle/pinna and includes the external auditory canal and the tympanic membrane
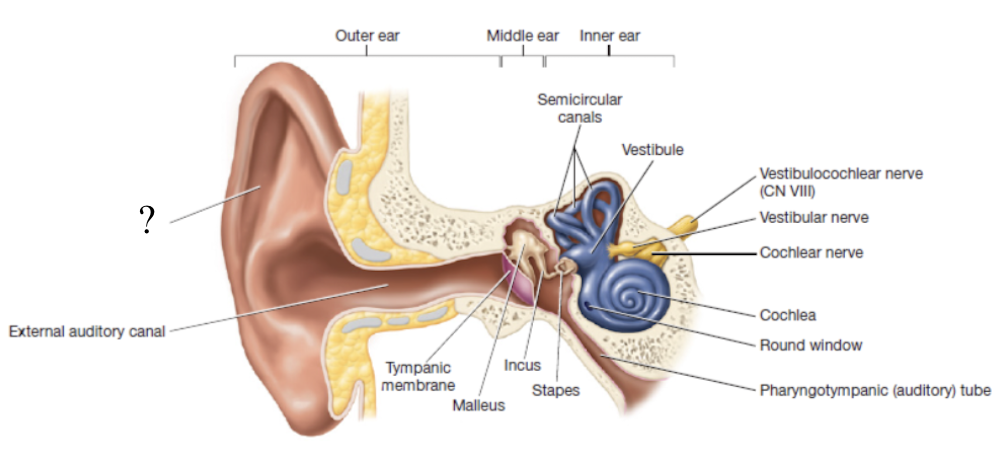
auricle/pinna
shell-shaped structure composed primarily of elastic cartilage that surrounds the opening to the external auditory canal
external auditory canal
extends about 2.5 cm into the temporal lobe and ends in the tympanic membrane
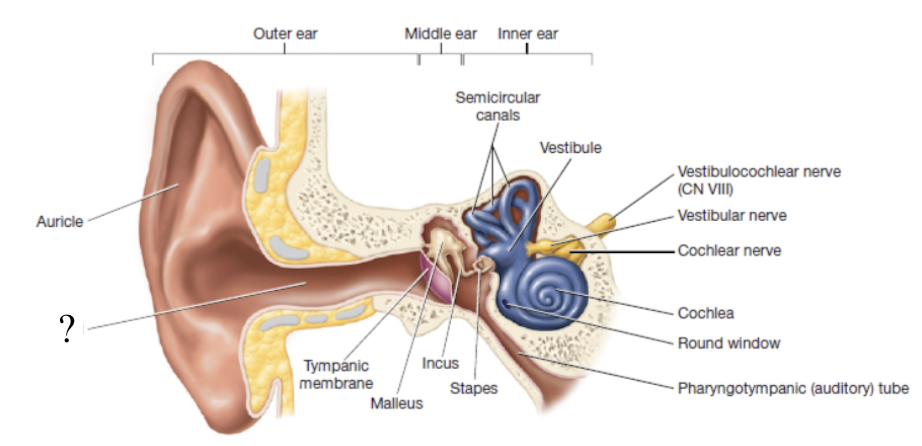
tympanic membrane
thin sheet of pearly gray epithelium and connective tissue that separates the outer ear from the middle ear
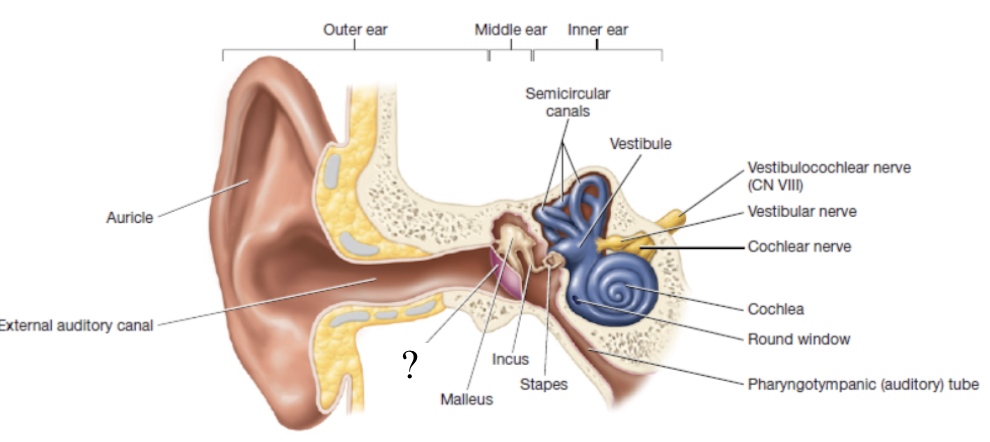
middle ear
small air-filled cavity within the temporal bone that houses the auditory ossicles
auditory ossicles
tiny bones that include the malleus, incus, and stapes which all transmit vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear
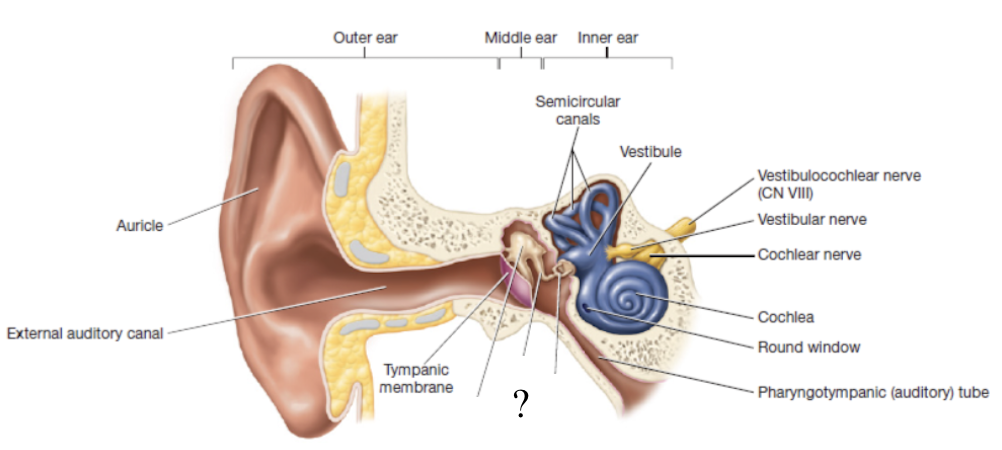
oval window
opening to the inner ear where ossicles transmit vibrations
stapes is attached here
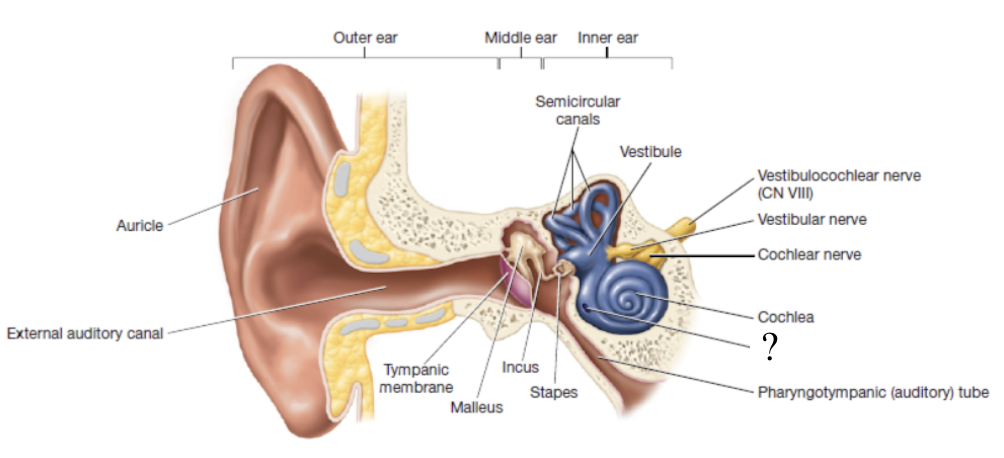
pharyngotympanic tube
also known as the auditory tube and functions to connect the middle ear to the pharynx and equalizes pressure in the middle ear
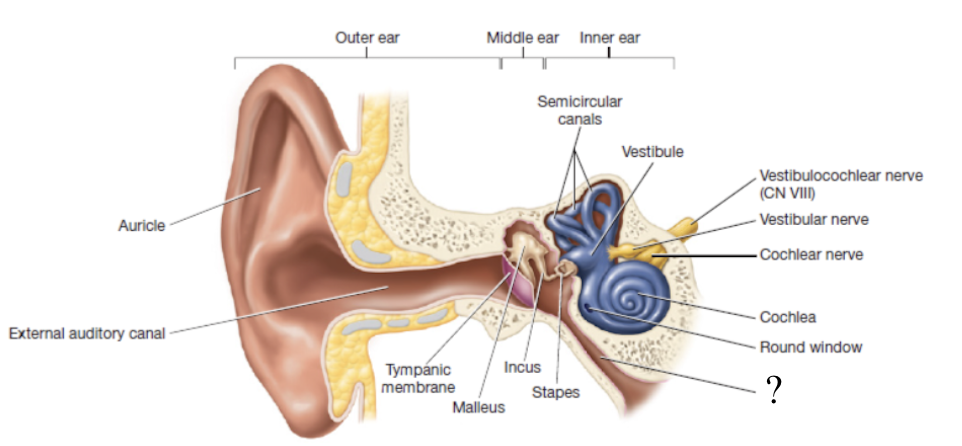
inner ear
contains the sense organs for hearing and equilibrium
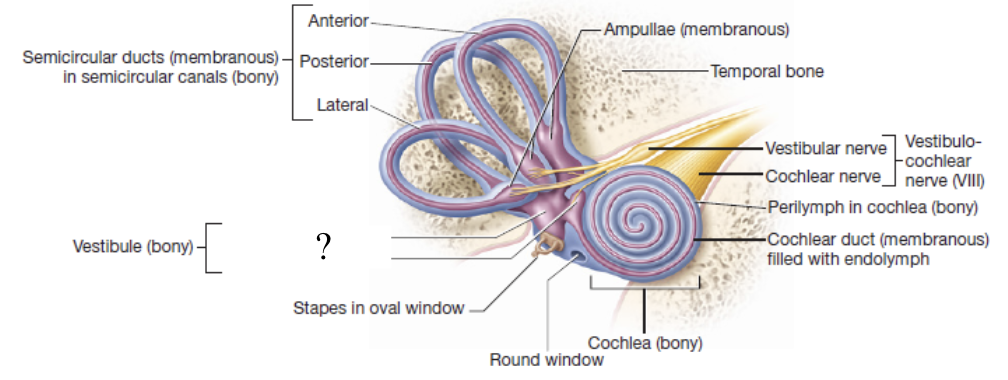
bony labyrinth
cavities of the inner ear that are filled with a fluid called perilymph
has 3 regions: vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea
membranous labyrinth
series of membranes within the perilymph that contain a thicker fluid called endolymph
vestibule
egg shaped bony cavity that houses two membranous structures responsible for equilibrium:
saccule (sac)
utricle (bag)
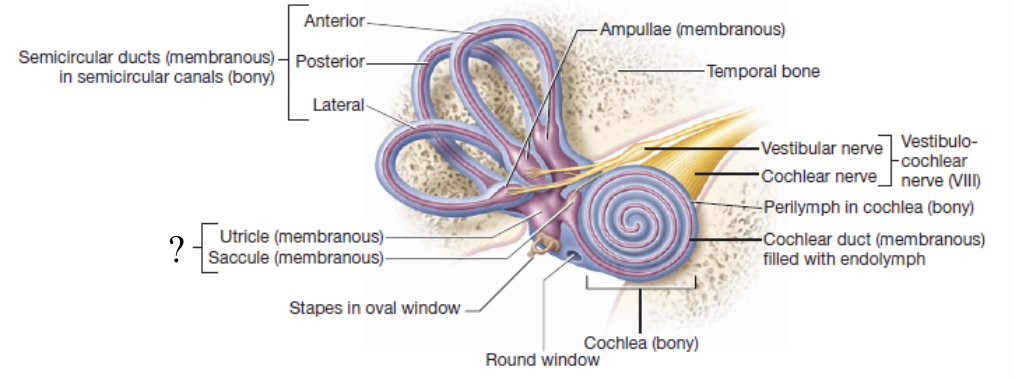
saccule and utricle
structures in the vestibule that transmit impulses down the vestibular nerve and are responsible for static equilibrium
static equilibrium
refers to maintaining balance when the body is not moving
semicircular canals
3 round and bony canals that house the semicircular ducts and ampullae
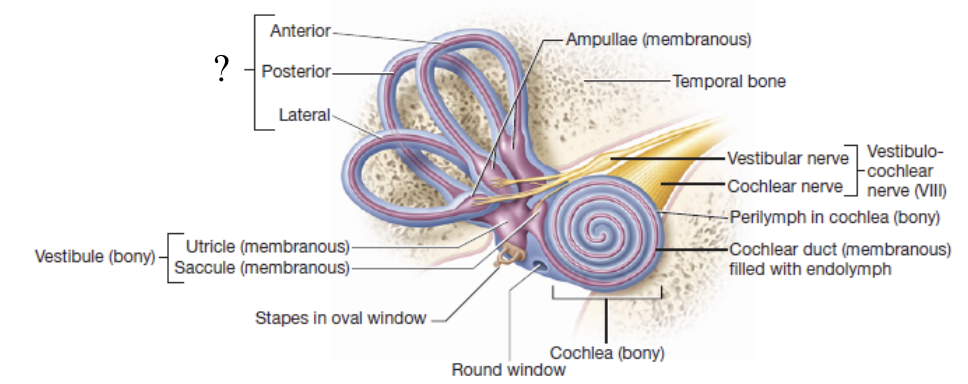
semicircular ducts and ampullae
membranous structures that transmit impulses down the vestibular nerve and work together with the organs of the vestibule to maintain rotational/dynamic equilibrium
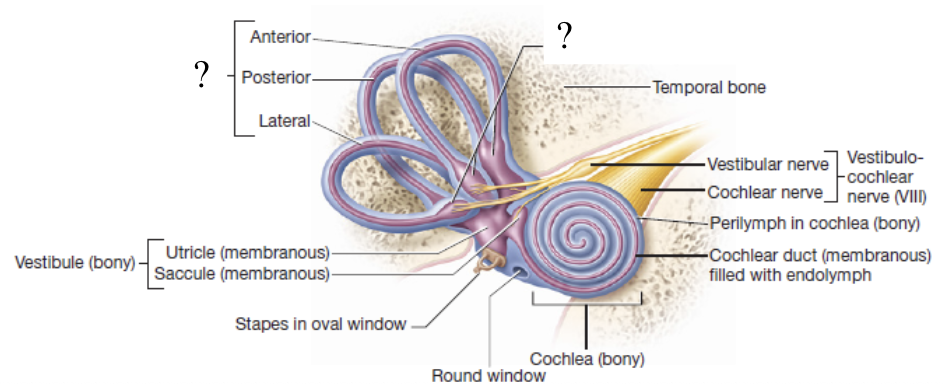
rotational/dynamic equilibrium
ability to maintain balance when the body or head is moving
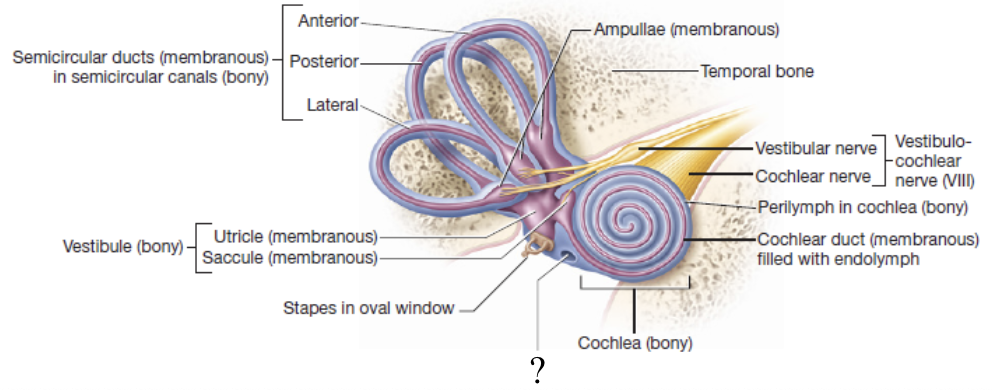
cochlea
spiral bony canal that contains the cochlear duct
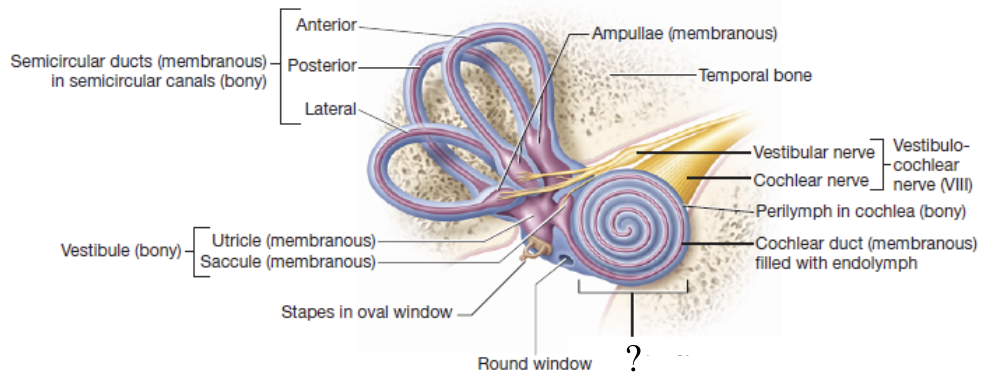
spiral organ/organ of corti
structure whose specialized hair cells depolarize and transmit sound impulses to the cochlear nerve in response to sound wave vibrations
round window
hole in the lateral wall of the cochlea which plays a role in allowing perilymph in the cochlea to vibrate
palpebrae
covers the eye and meet medially and laterally at the medial and lateral canti
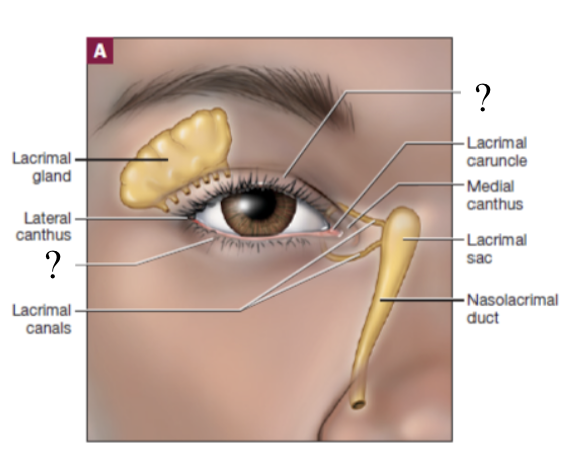
lacrimal caruncle
gland at the medial canthus that lubricates the palpebrae and anterior surface of the eyeball
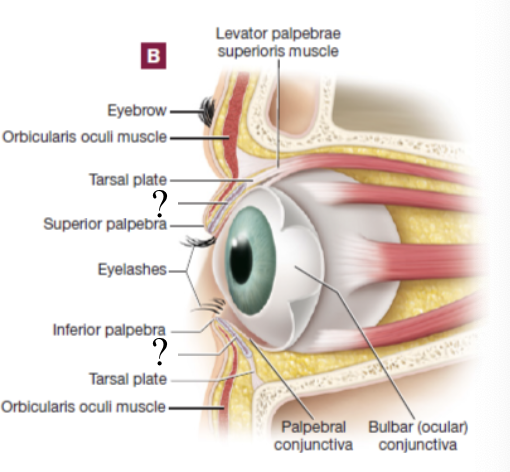
tarsal plate
dense connective tissue at each palpebea
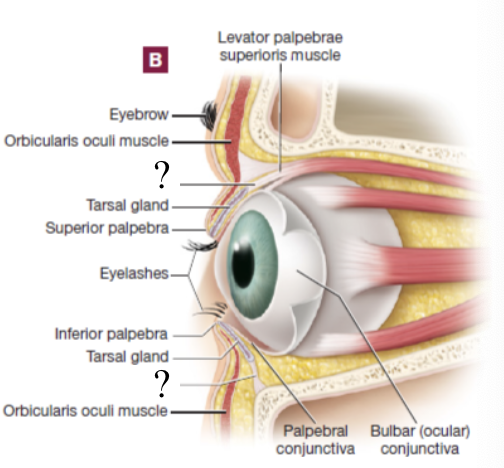
tarsal gland
sebaceous gland associated with each tarsal plate
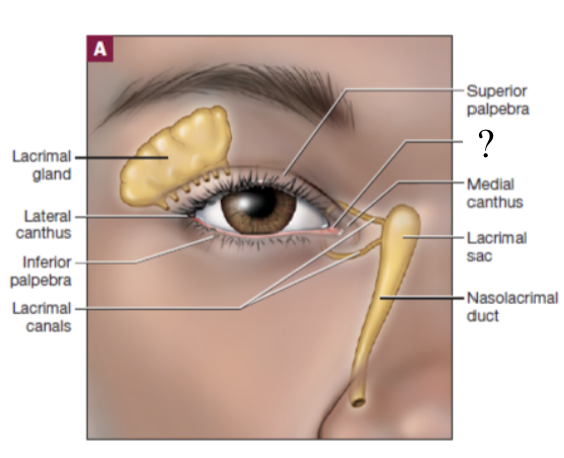
lacrimal apparatus
one of the most prominent external structures of the eye which functions to produce and drain tears
starts at the lacrimal gland → to the lacrimal ducts that drain tears → tears accumulated from the eye drain into lacrimal canals near medial canthus → drain into the lacrimal sac → tears travel through nasolacrimal duct → empty into the nasal cavity
pathway of tears
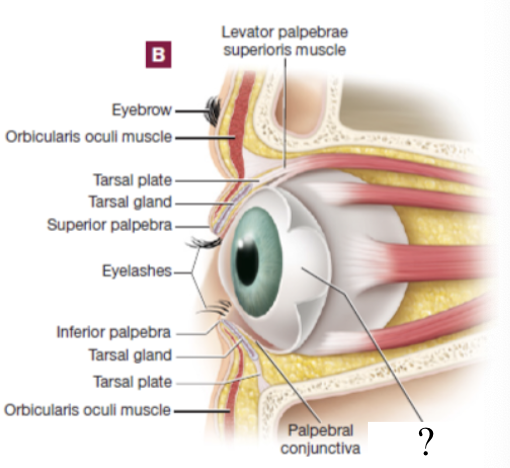
palpebral conjunctiva
thin mucous membrane that lines the internal surfaces of the palpebrae
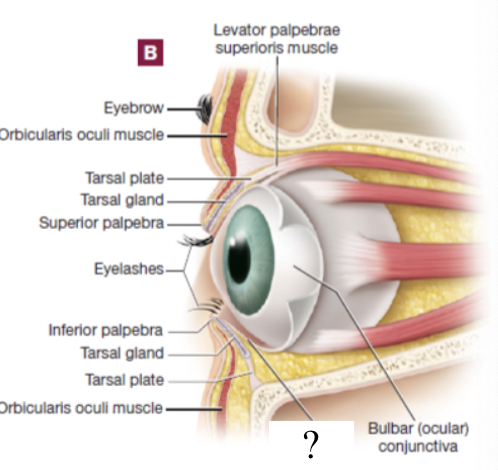
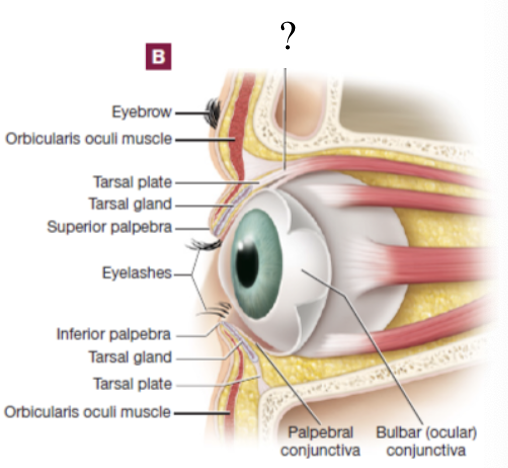
bulbar conjunctiva
the palpebral conjunctive curls around to become this which functions to line much of the eyeball’s superficial surface
conjunctivities
pink eye or inflammation or swelling of the tiny blood vessels found in the mucous membrane
caused by viral or bacterial infection or an allergic reaction
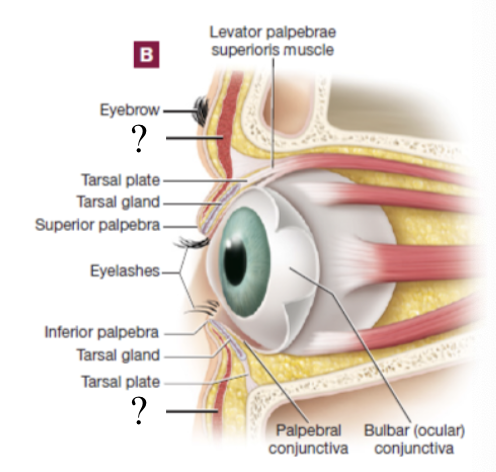
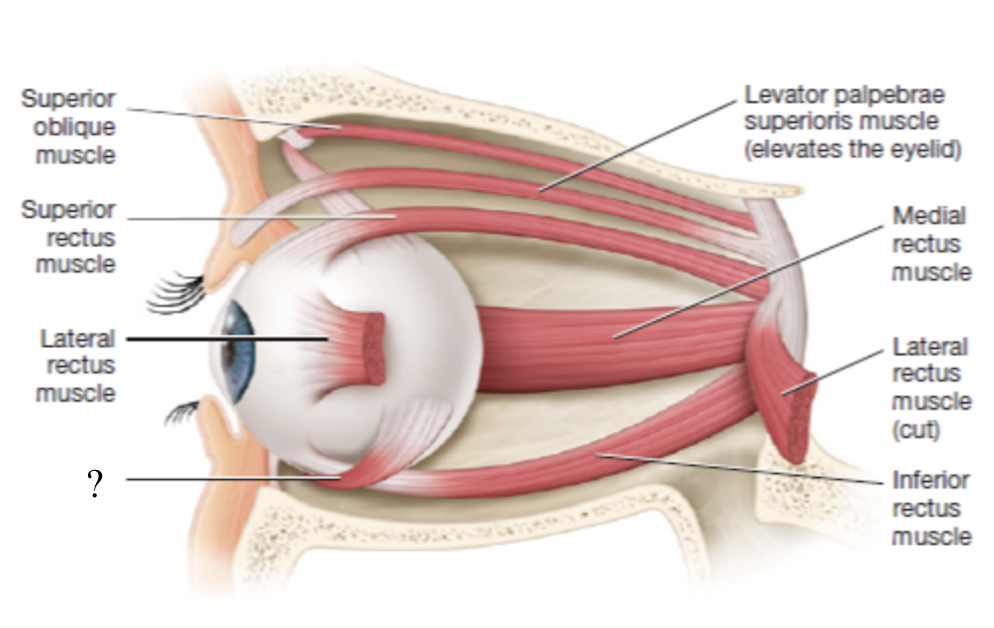
levator palpebrae superioris muscle
elevates the upper eyelid to open it
orbicularis oculi muscle
closes the eyelid
lateral rectus muscle
moves the eyeball laterally (abduction)
innervated by CN VI abducens nerve
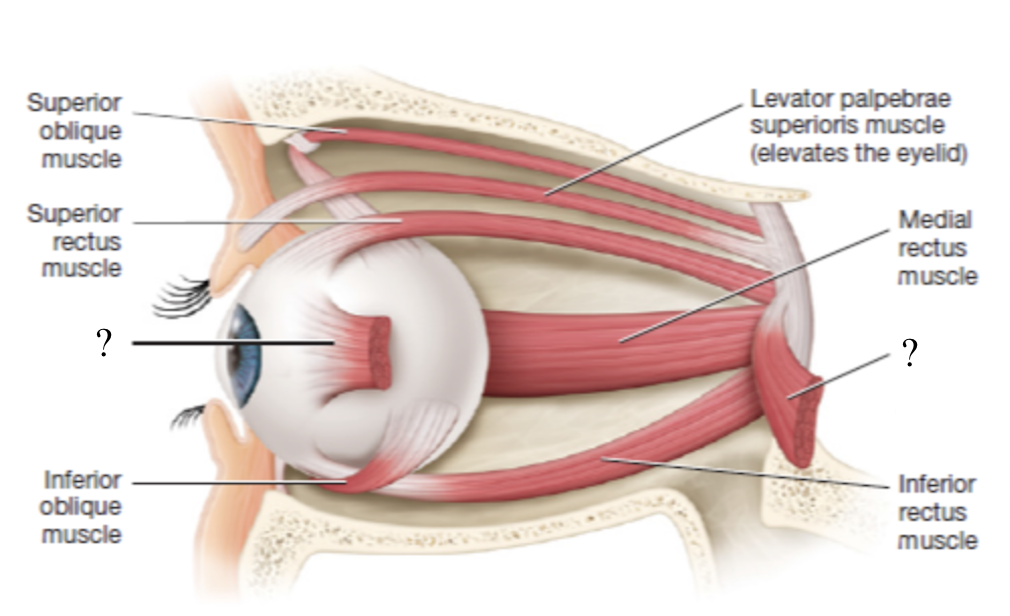
medial rectus muscle
moves the eyeball medially (adduction)
innervated by CN III oculomotor nerve
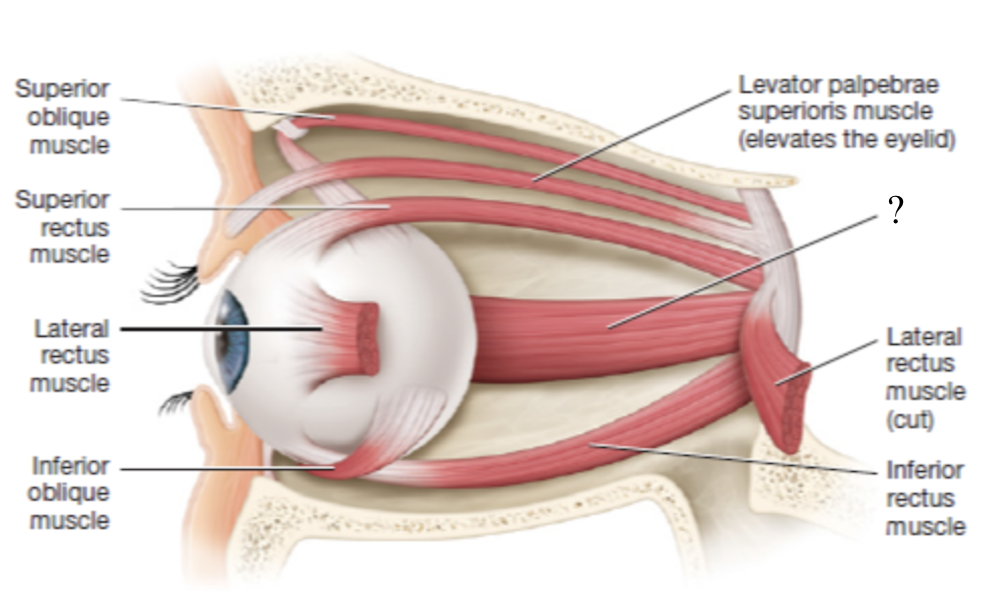
superior rectus muscle
moves the eyeball superiorly
innervated by CN III oculomotor nerve
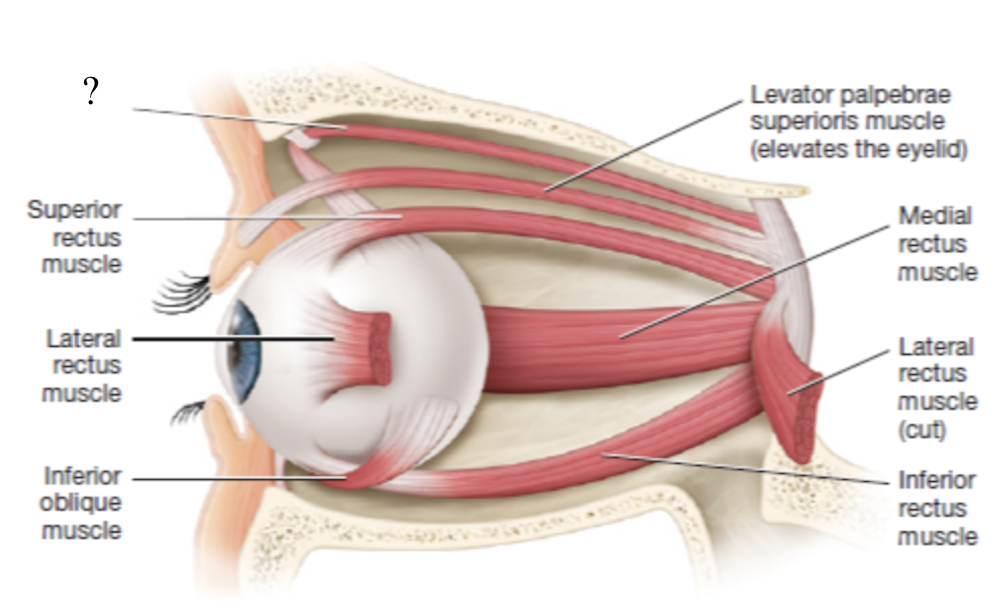
inferior rectus muscle
moves the eye inferiorly
innervated by CN III oculomotor nerve
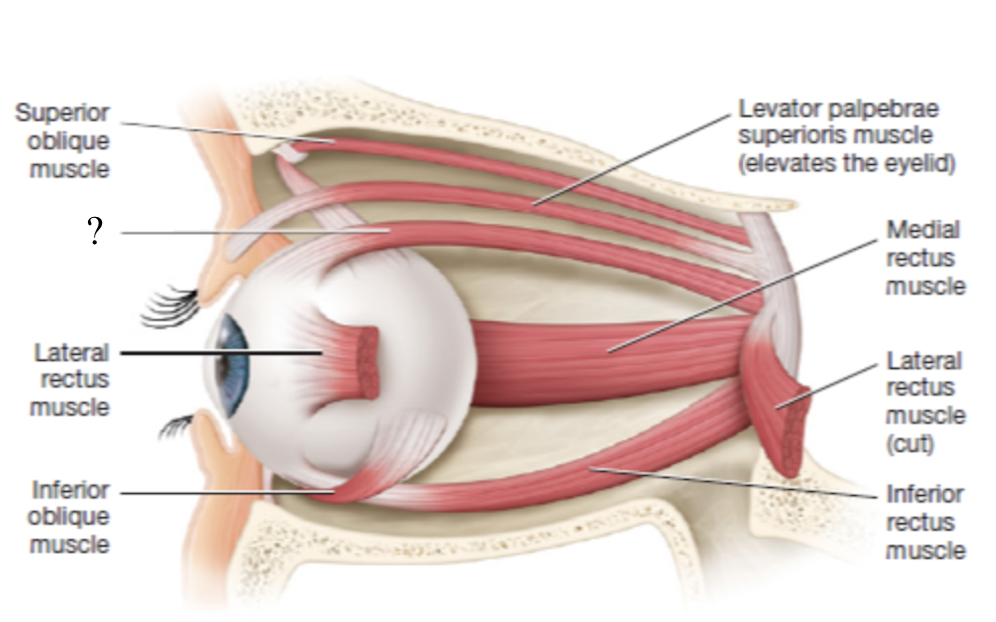
superior oblique muscle
rotates the eyeball inferiorly and slightly lateral
innervated by CN IV trochlear nerve
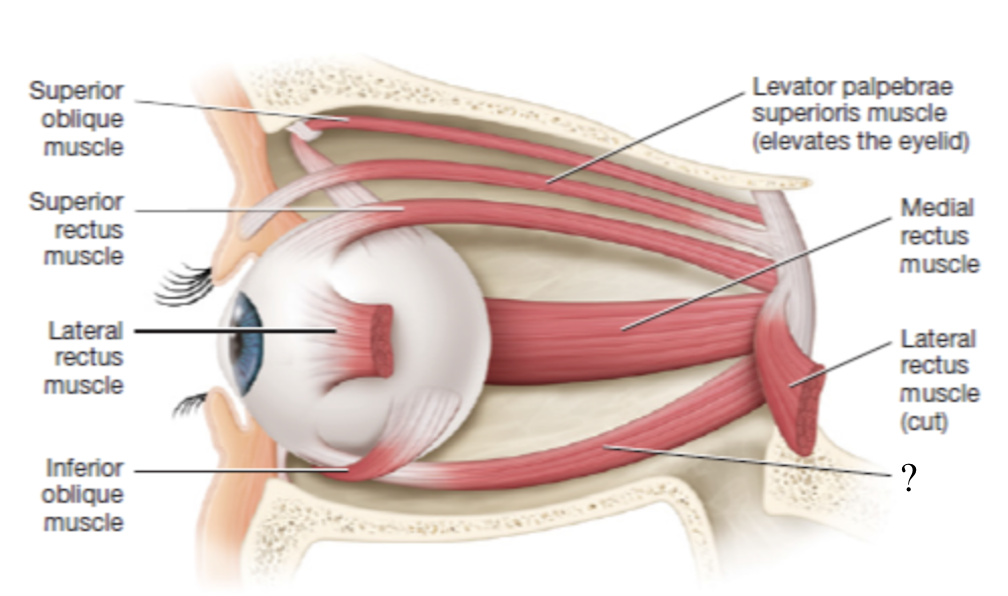
inferior oblique muscle
rotates the eyeball superiorly and laterally
innervated CN III oculomotor nerve
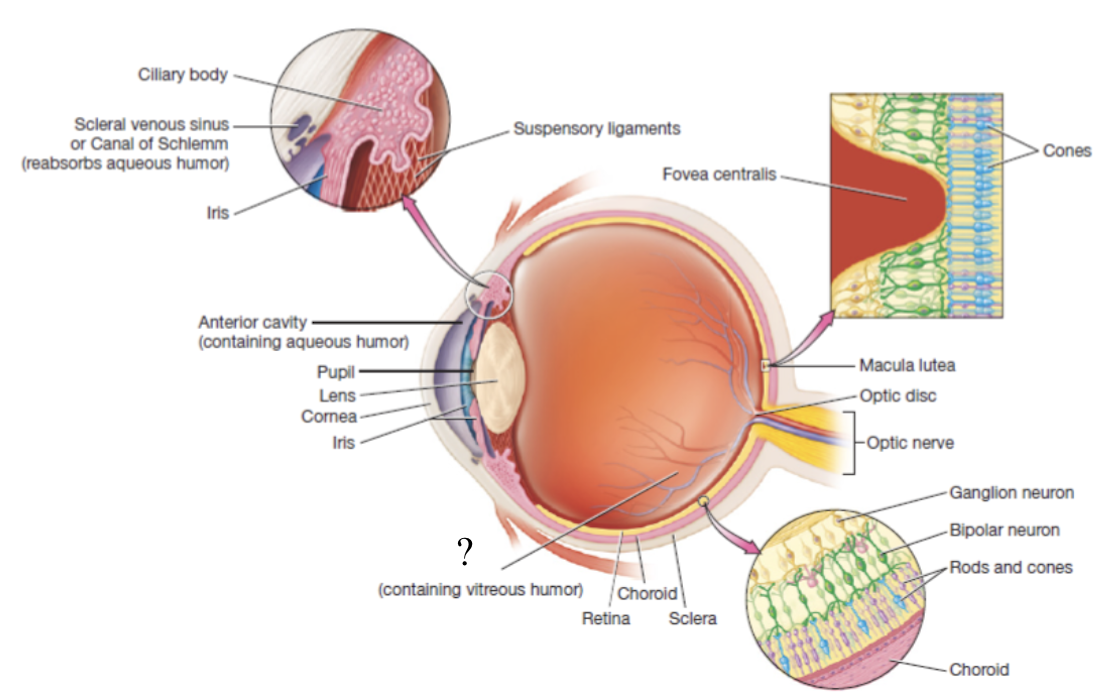
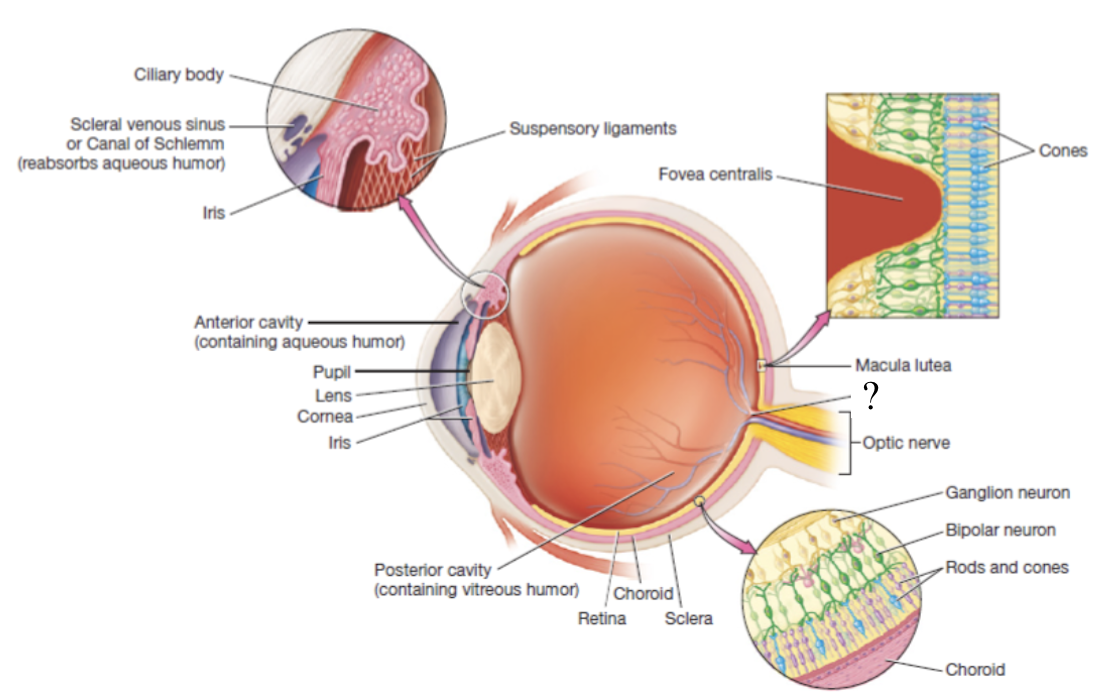
eyeball
hollow organ that is divided into two main portions of the anterior and posterior cavity
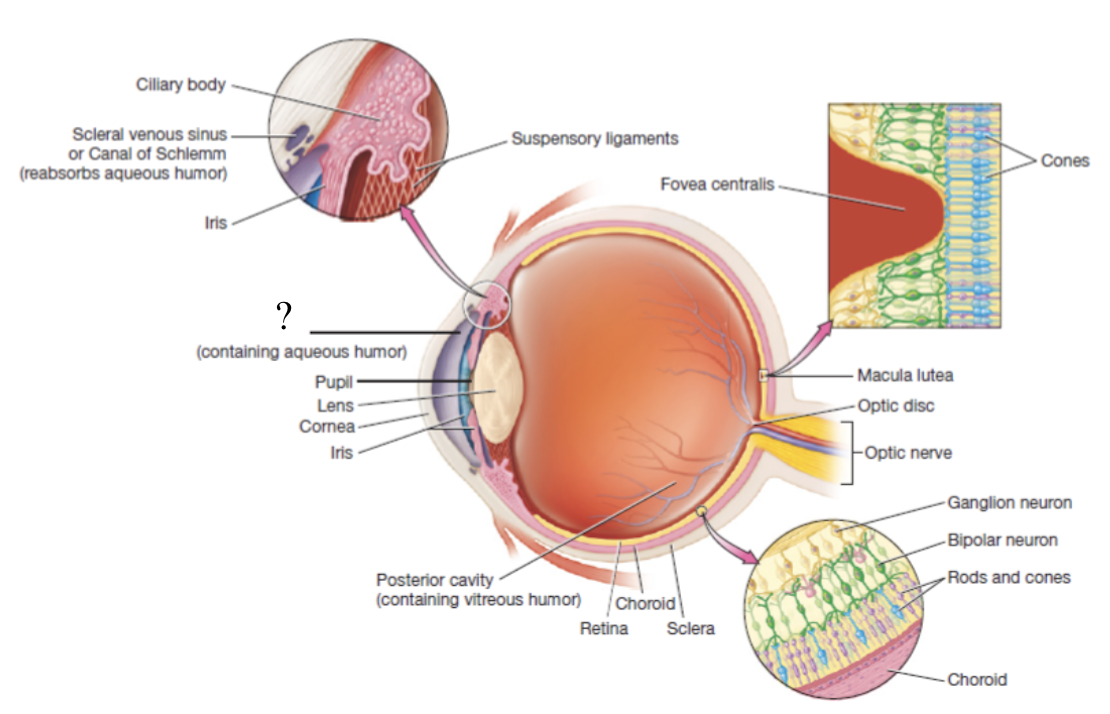
lens
crystalline structure that is the boundary of the anterior and posterior cavities in the eye which refracts light coming into the eye to focus it
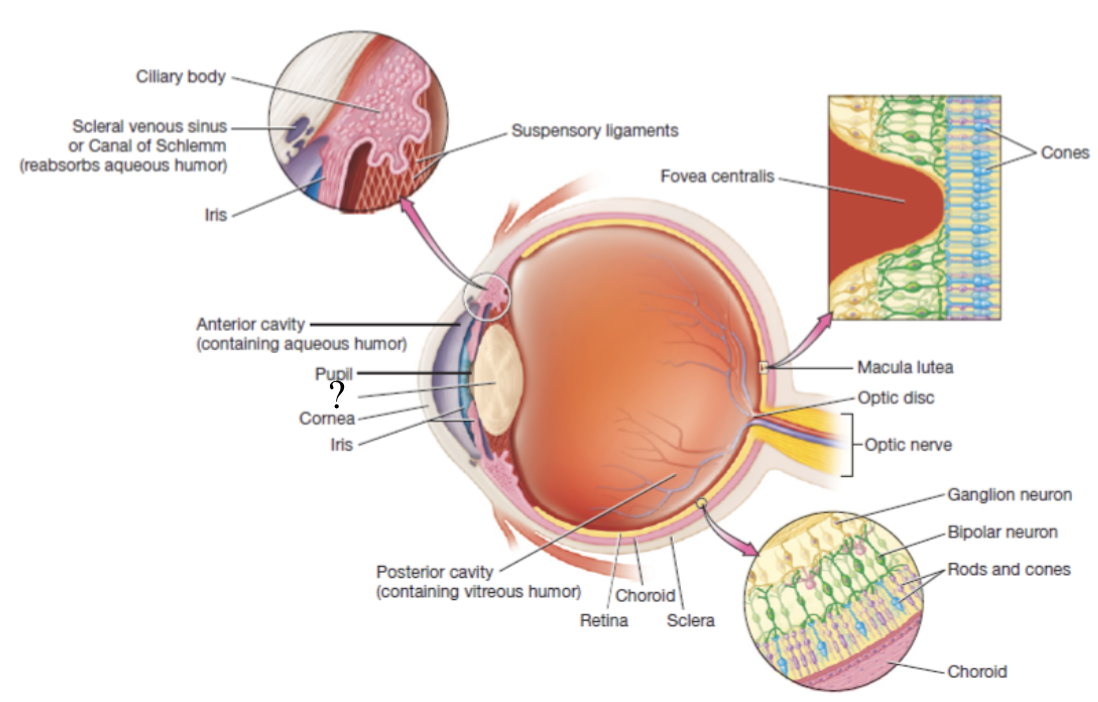
anterior cavity
anterior to the lens and filled with a watery fluid called aqueous humor
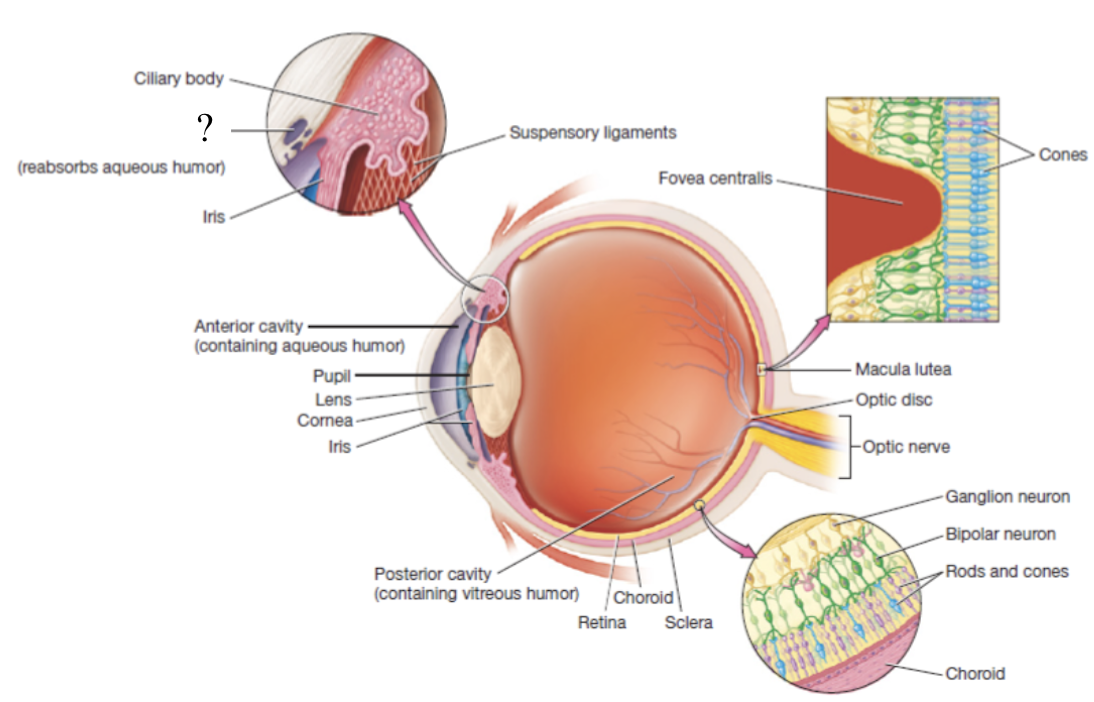
scleral venous sinus
structure contained in the sclera that functions to drain aqueous humor
posterior cavity
posterior to the lens and contains thick fluid called vitreous humor which is present at birth and remains unchanged throughout life
fibrous tunic
outermost layer of the eyeball made mostly of dense irregular collagenous connective tissue, avascular, and consists of the sclera and cornea
sclera
white part of the eyeball that makes up 5/6 of the fibrous tunic and has numerous collagen fibers
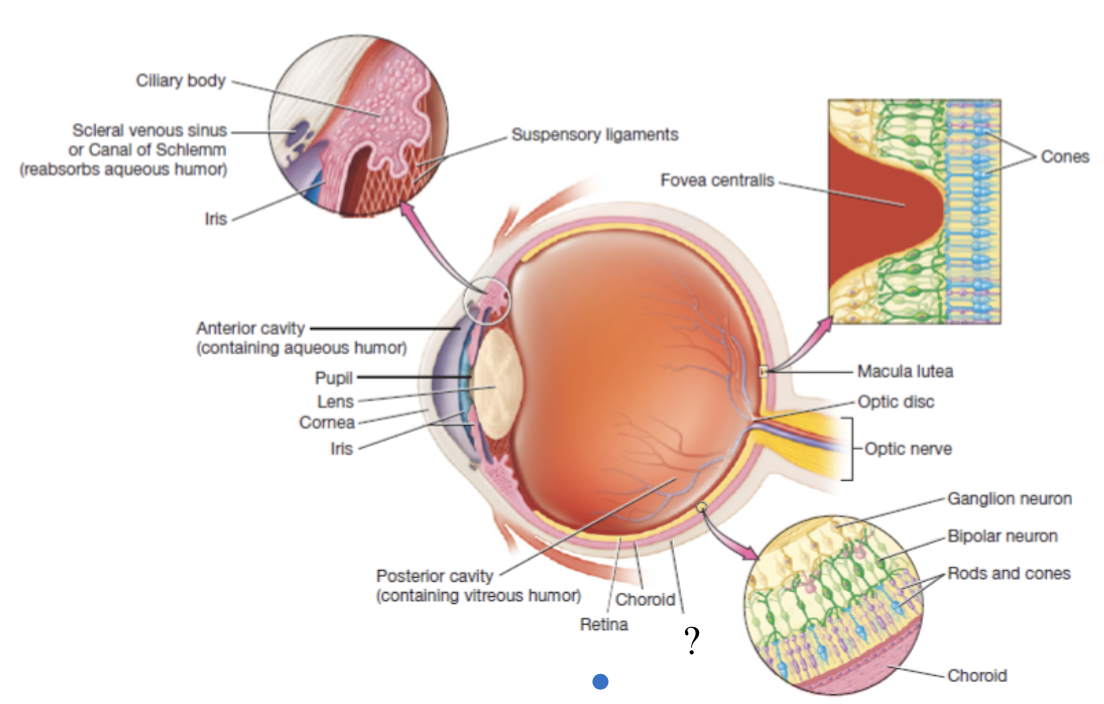
cornea
clear structure that makes up 1/6 of the fibrous tunic and is deep/posterior to the conjunctiva
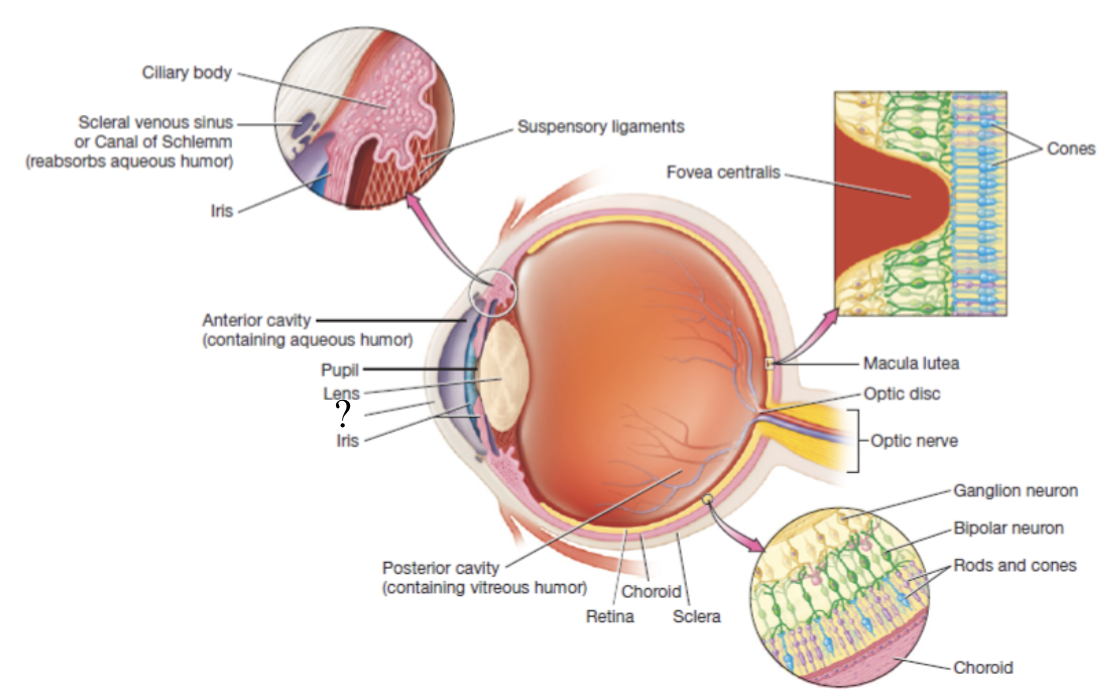
vascular tunic
also called the uvea, functions to carry most of the blood supply to the tissues of the eye, and consists of the choroid, ciliary body, and iris
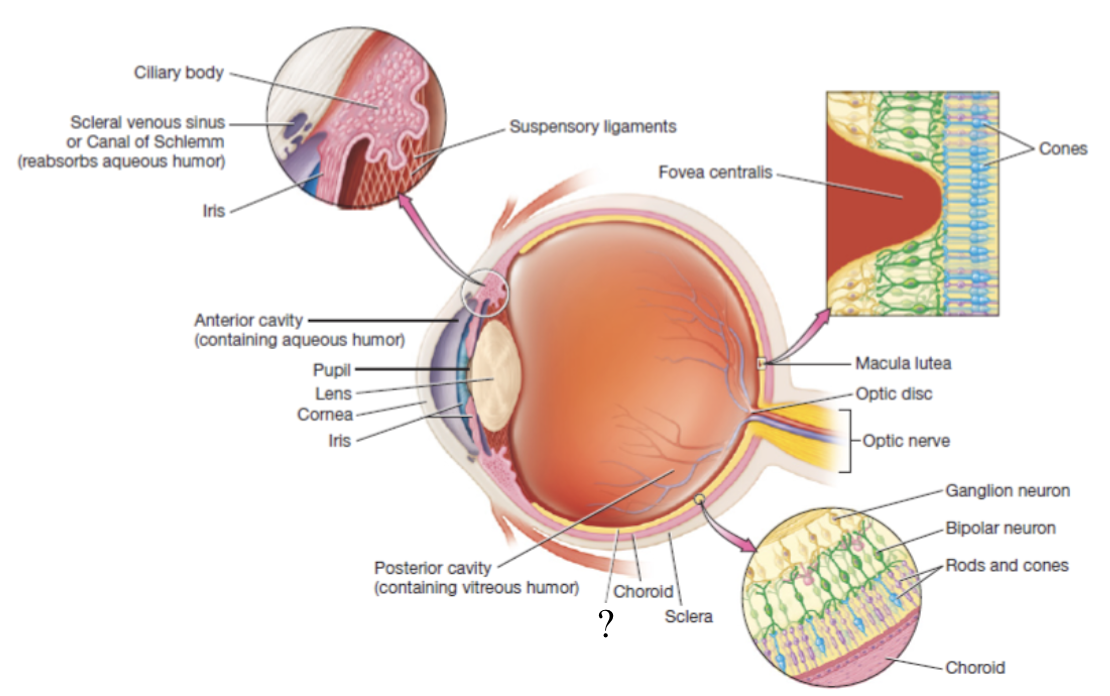
choroid
highly vascular and makes up posterior part of the vascular tunic
brown/black in color to prevent light scattering in the eye and provides oxygenation, nourishment, and waste removal to retina
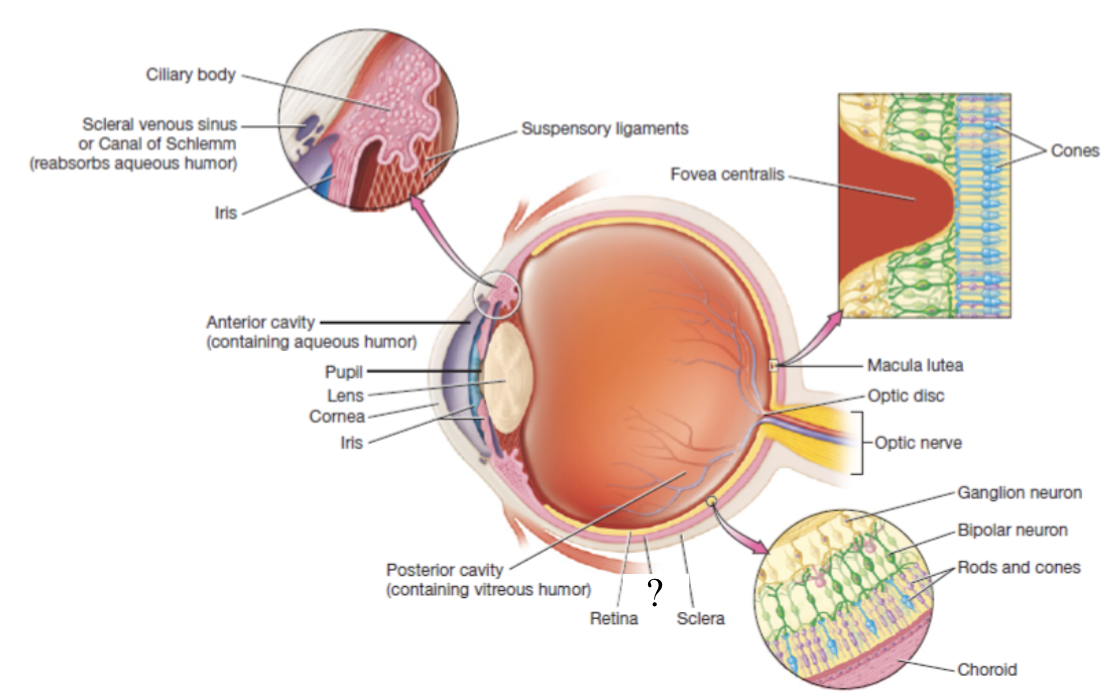
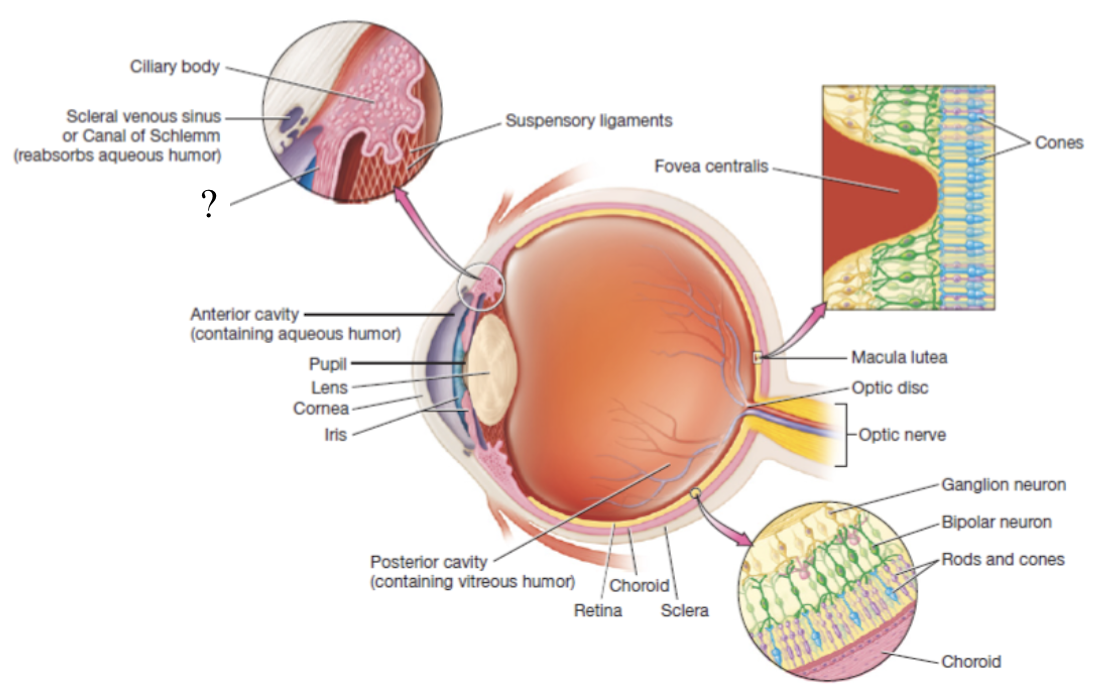
ciliary body
thickened extension of the choroid at the anterior aspect of the vascular tunic that produces aqueous humor
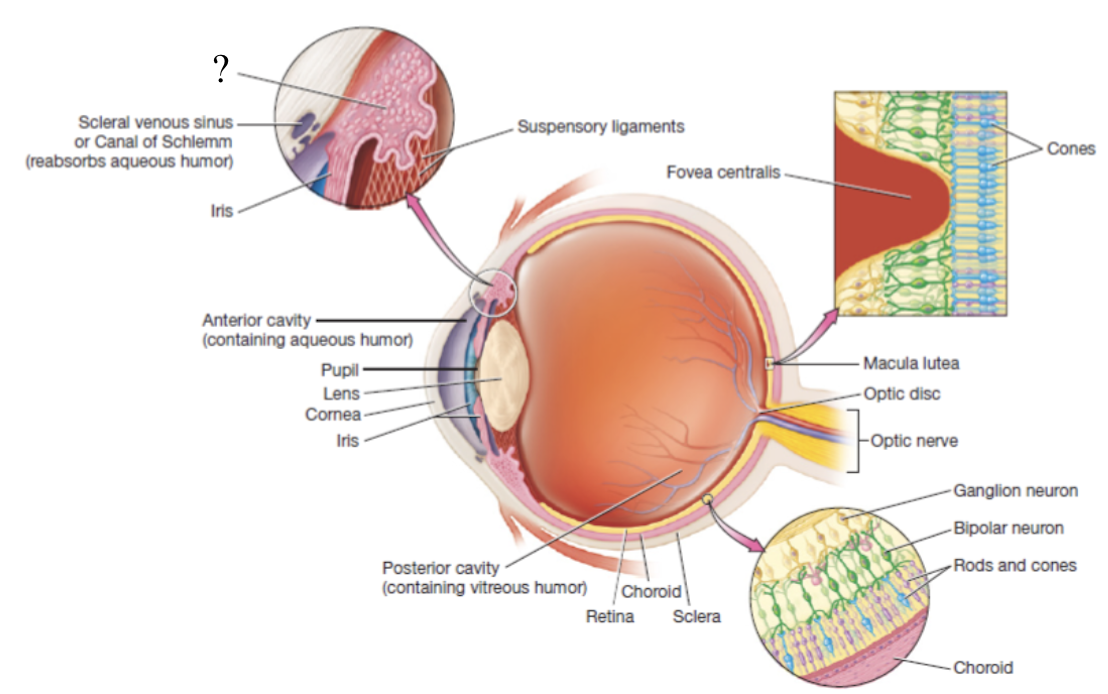
ciliary muscle
smooth muscle that controls the shape of the lens via its fingerlike projections called ciliary processes which attach to the lena via suspensory ligaments
iris
pigmented and adjustable structure at the most anterior portion of the vascular tunic
iris sphincter muscles
make up the iris and are arranged around the pupil
contract to perform pupillary constriction or pupillary dilation
anterior and posterior segments
the iris divided the anterior cavity into two smaller subdivisions where aqueous humor travels to called …
sensory/nervous tunic
deep layer that consists of the retina and the optic nerve
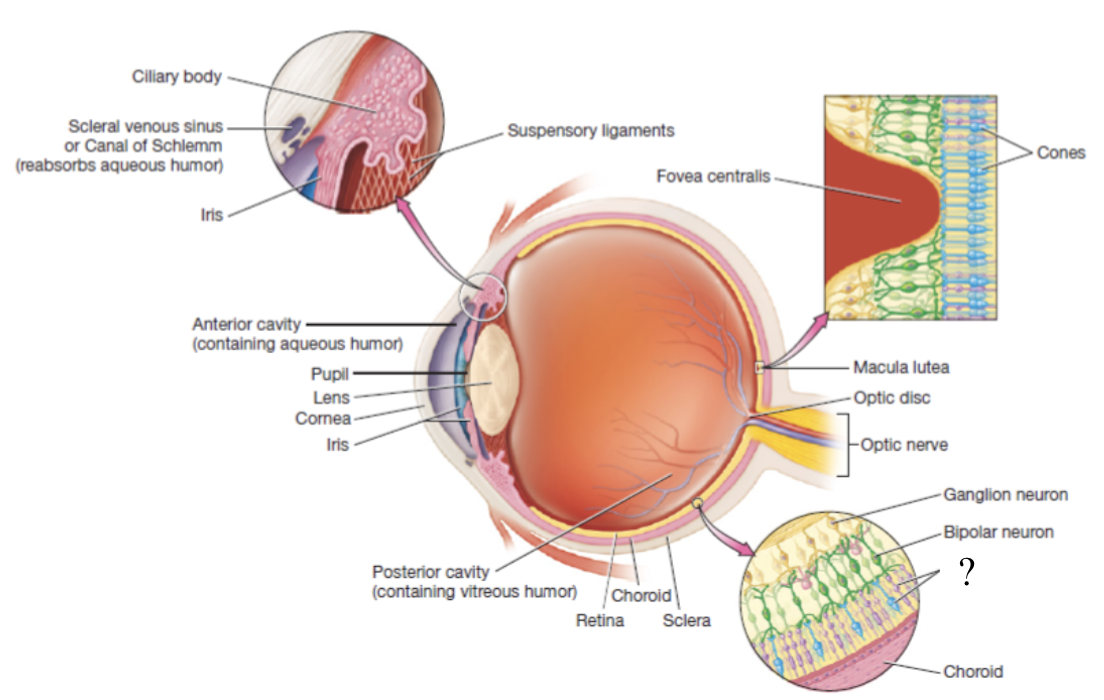
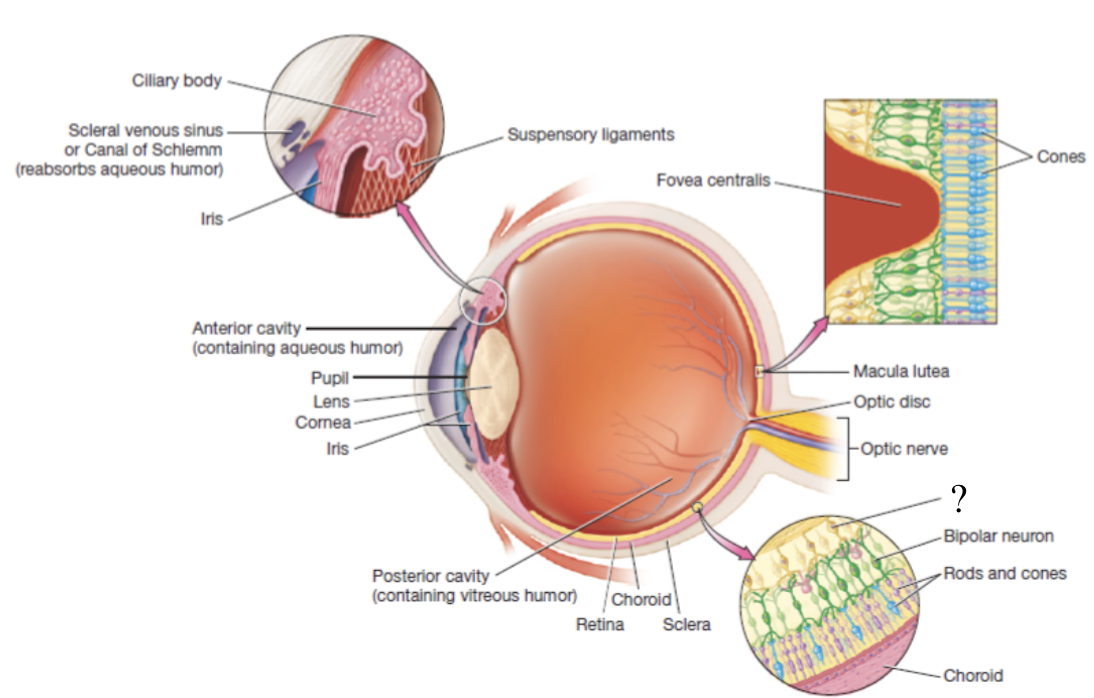
retina
thin, delicate structure that contains three layers of neurons
photoreceptors, bipolar neurons, and ganglion cells
photoreceptors
detect light
rods: responsible for vision in dim light, peripheral vision, and black and white vision
cones: responsible for color and high-acuity vision in bright light
macula lutea
area with high numbers of cones
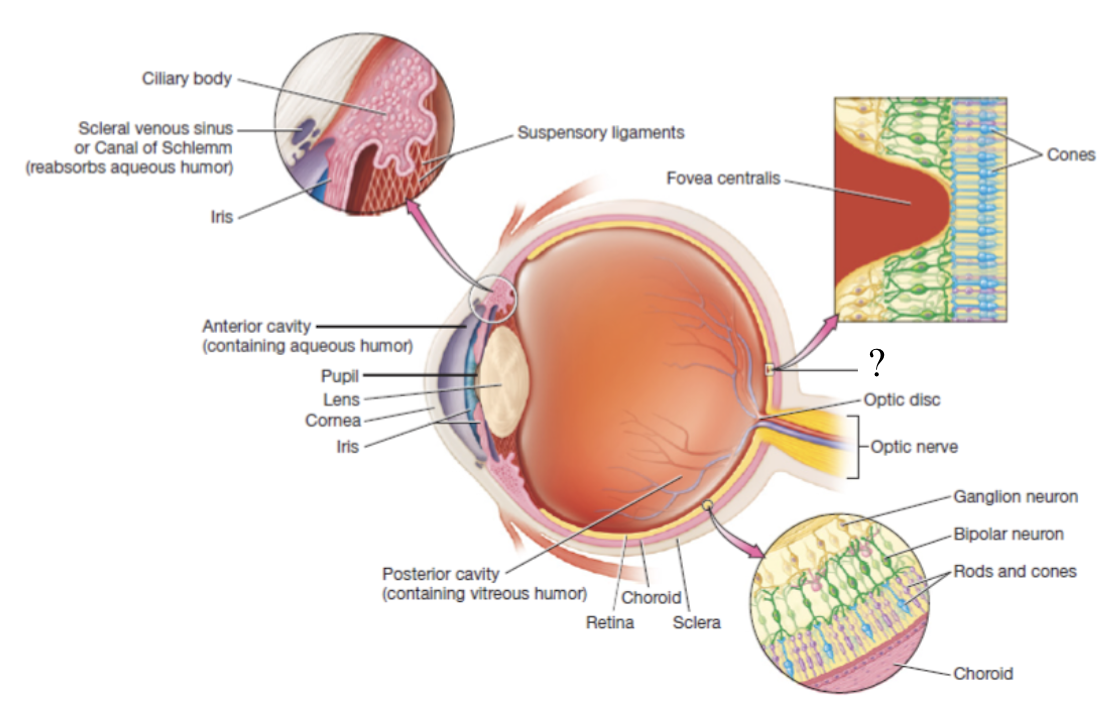
fovea centralis
center of the macula lutea that only contains cones
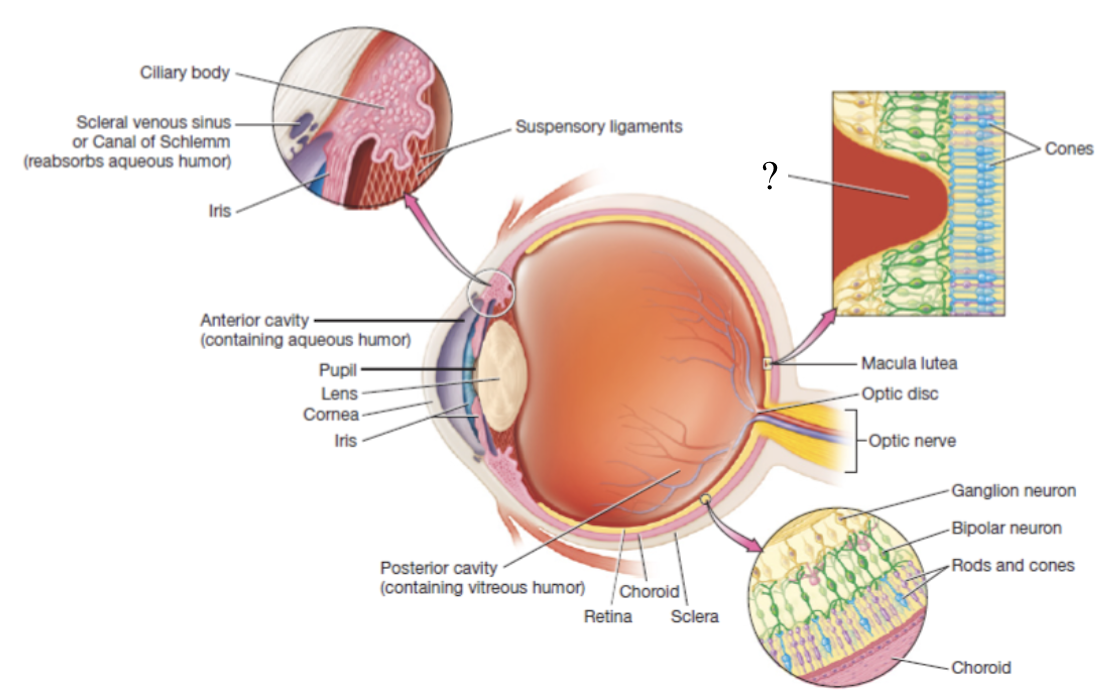
bipolar neurons
receives input from photoreceptors
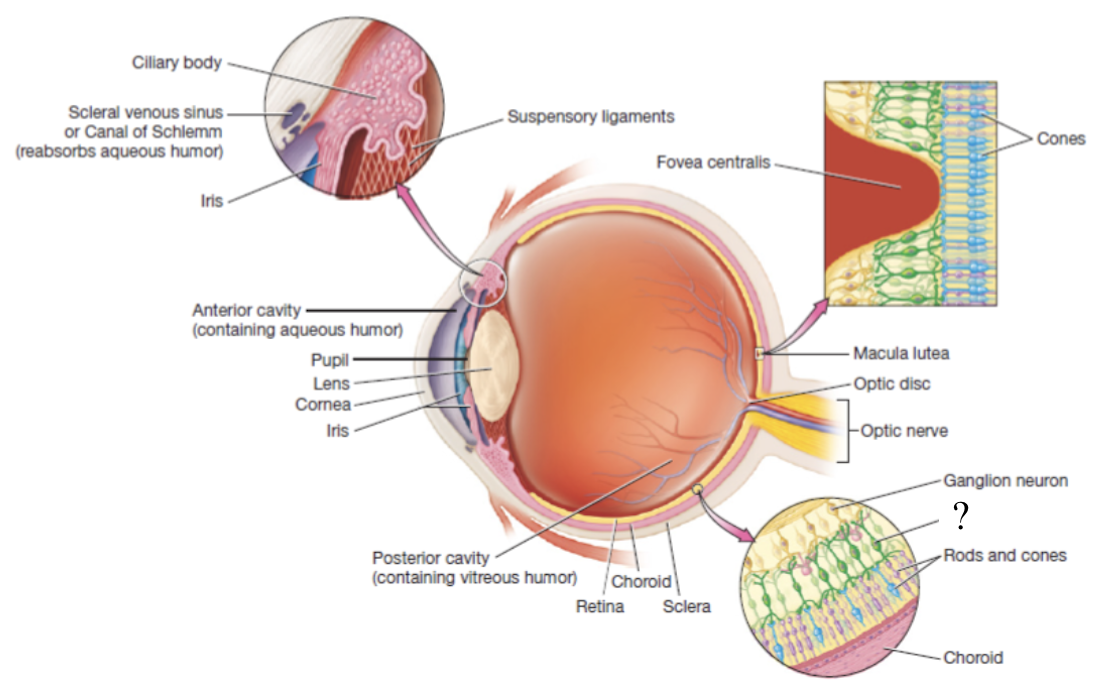
ganglion cells
its axons converge to form the CN II optic nerve
optic chiasma
optic nerves exchange axons at this X-shaped before diverging into the two optic tracts
blind spot
also known as the optic disc, area with no rods or cones at the posterior most aspect of the eyeball where the optic nerve leaves the eyeball
first light hits the cornea → through the aqueous humor → through the lens → through the vitreous humor
light has to pass through this 4 refractive media before it hits the retina
cornea and lens
which refractive media have the greatest refractive power?
2/3
the cornea itself accounts for about __ of the eye’s refractive power
accommodation
adjustment in which the lens become rounder for additional “fine-tuning” when viewing nearer objects
autonomic nervous system
largely involuntary branch of the peripheral nervous system charged with maintaining homeostasis of different physiological variables
two branches: sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
its cell bodies are located in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord
“fight-or-flight” so its activated by any excitation, emotion, or exercise
axons release epinephrine, norepinephrine, and ACh
parasympathetic nervous system
cell bodies are location in cranial nerve nuclei and sacral portion of spinal cord
“rest and digest” so it promotes functions associated with digestion, defecation, and diuresis
axons release ACh