Physical Geography Essentials: Module 1: The Science of Geography
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for key terms related to map projections, remote sensing, and GIS.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Map
Flat representation of Earth portraying spatial relationships in two-dimensions
Map Scale
Relationship between distance on the map and actual distance on the ground
Large-scale map
Map with a relatively large representative fraction, used to show a small portion of Earth’s surface with great detail
Small-scale map
Map with a small representative fraction, used to show a relatively large area with limited detail
Map projection
Earth’s curved surface transformed for display on flat surface
Equivalent map projection
Map projection where size ratio of areas are maintained but shapes are distorted
Conformal map projection
Map projection where proper angular relationships are maintained, distorting the size of an area
Compromise map projection
Map projection that is neither equivalent nor conformal, balancing reasonably accurate shapes with reasonably accurate areas
Loxodrome
Line on sphere crossing meridians at same angle
Interrupted projections
Minimize distortion of landmasses by “interrupting” oceanic regions
Isoline
Line joining points of equal value, separated at intervals
Contour line
Elevation contour line on topographic maps
Digital elevation models (DEMs)
Shaded-relief images resulting from database of precise elevations
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)
System of satellite technologies providing precise location data
Remote sensing
Any measurement by a device not in contact with Earth’s surface
Orthophoto maps
Multicolored, distortion-free photographic maps prepared from aerial photographs and/or digital images
Lidar
Uses reflected laser light to measure distances and three-dimensional information
GIS (Geographic Information Systems)
Computer systems that analyze and display spatial data
Overlay analysis
Involves two or more layers of data that are superimposed or integrated
What term describes a system that has no exchanges of energy or matter beyond the system itself?
Closed System
Which feature is part of the HYDROsphere?
LAKE Ontario
Which example is an open system?
A hurricane
What mechanism in a system allows the system to make minor and routine adjustments to maintain equilibrium?
Feedback loops
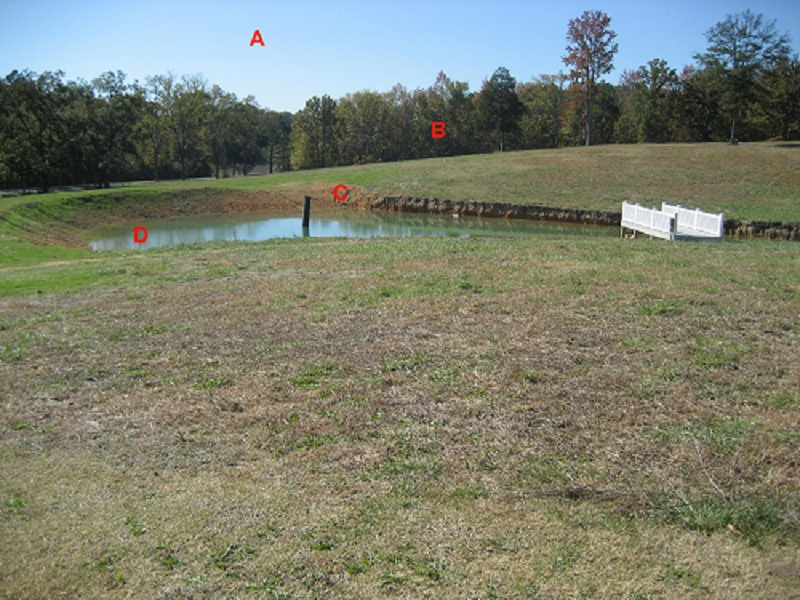

Which sphere is labeled B?
Biosphere
Which feature is part of the atmosphere?
Smog
Which feature is part of the lithosphere?
A deltais a landform created by the deposition of sediment at the mouth of a river.
What is the point at which input causes significant change to a system?
Threshold
What is an example of output in a glacial system?
Meltwater from glaciers
What is the term for an ordered collection of interconnected components?
System
What term describes a system that exchanges matter or energy beyond itself?
Open
Which is an example of a closed system?
A terrariumthat does not allow matter to enter or leave.
What is exemplified by water flowing out of an overflow pipe in a pond during a thunderstorm?
Negative feedback
What is an example of a model?
A globe
What is a simplified replica of something designed to facilitate study and understanding?
Model
Considering the narrow, material-based definition rather than the conservation-based definition, which feature is part of the biosphere?
Phytoplankton

Which sphere is labeled D?
Atmosphere
Which feature is part of the lithosphere?
A delta
What is the condition of a system when the inputs and outputs are balanced?
Equilibrium
What is the point at which input causes significant change to a system?
Threshold
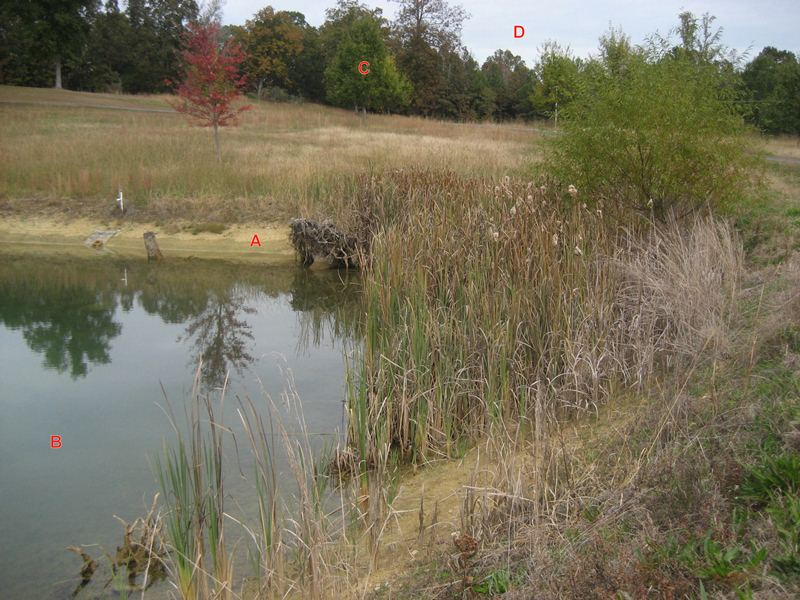

Which sphere is labeled A?
Lithosphere
What is a mechanism that helps a system maintain a steady state through time?
Feedback. Feedbacks occur after an action or change in the system requires adjustment for the system to return to the prior equilibrium.
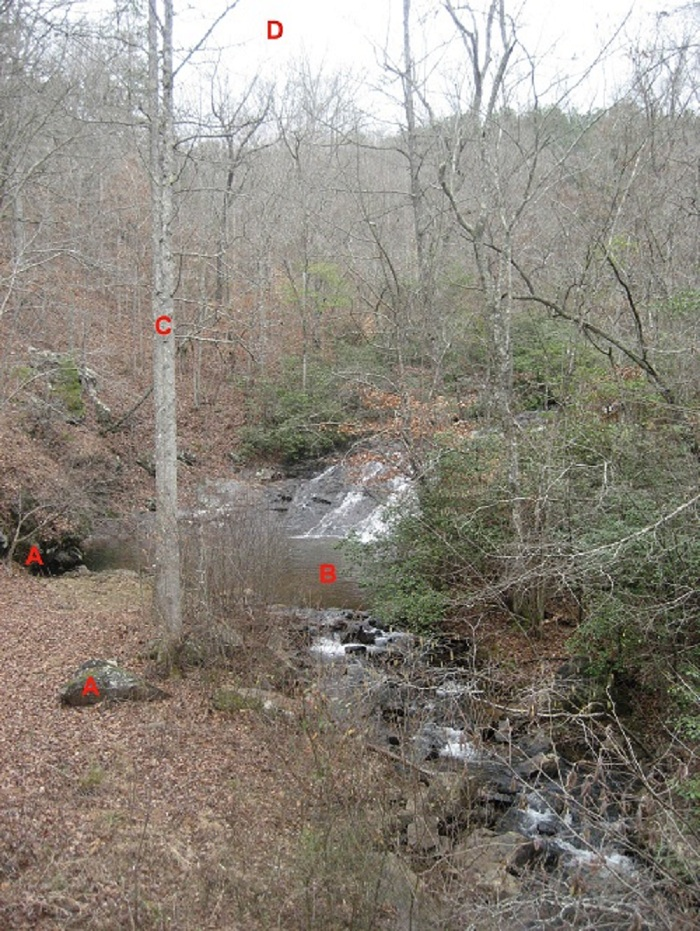

Which sphere is labeled B?
Hydrosphere
Why are feedback loops normally associated with negative feedback?
They act to bring a system back toward equilibrium.
What is the interdisciplinary study of collections of interacting objects as it applies in both natural and cultural applications?
Systems theory
What is the condition when a system responds in the opposite direction from the introduced input?
Negative feedback
What is the condition when a system responds in the direction of the introduced input?
Positive feedback
What is a mechanism that helps a system maintain a steady state through time?
Feedback
What lines are used to measure latitude?
Parallels
Who is noted for using observations at Syene and Alexandria and geometry to calculate the size of Earth?
Eratosthenes
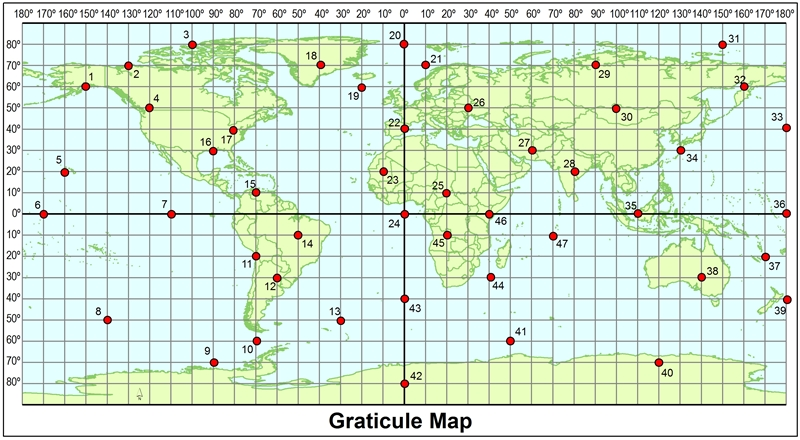
Using the map, what are the coordinates of point 39?
40 degrees south of the equator and 180 degrees
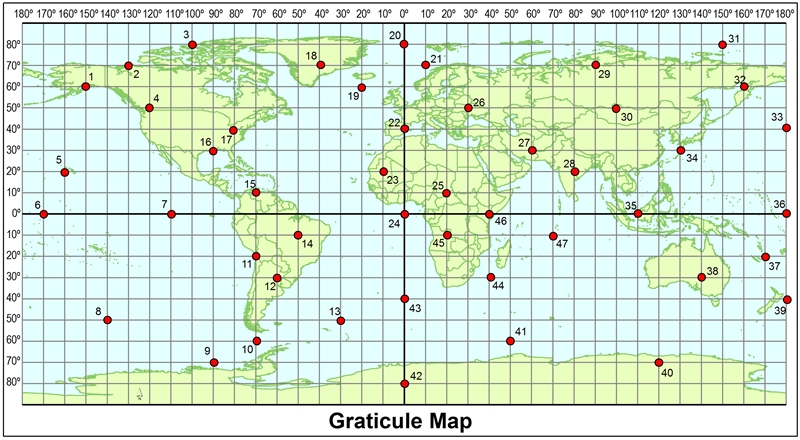
Using the map, what point is at 40°S, 0°?
43
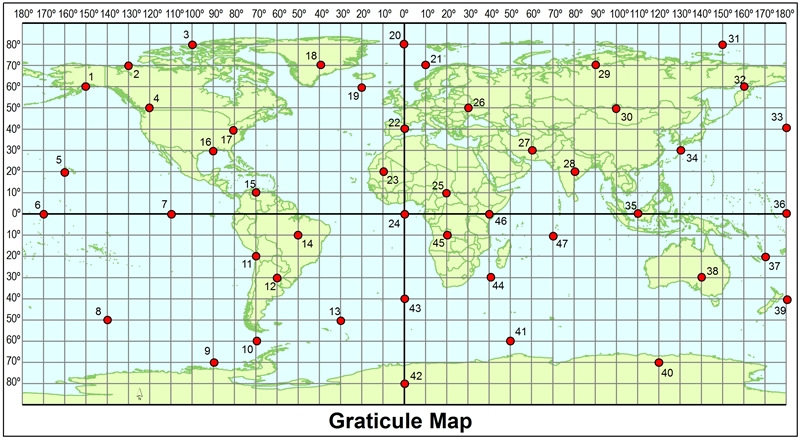
Using the map, what are the coordinates of point 26?
50°N, 30°E
Which latitude values are correct without a directional indicator?
Equator
What is the correct way to write 58.75°, -119.5° in DMS format?
58° 45'N, 119° 30'W
How does the circumference of Earth at the equator compare to the circumference that passes through the poles?
The circumference at the equator is about 42 miles longer.
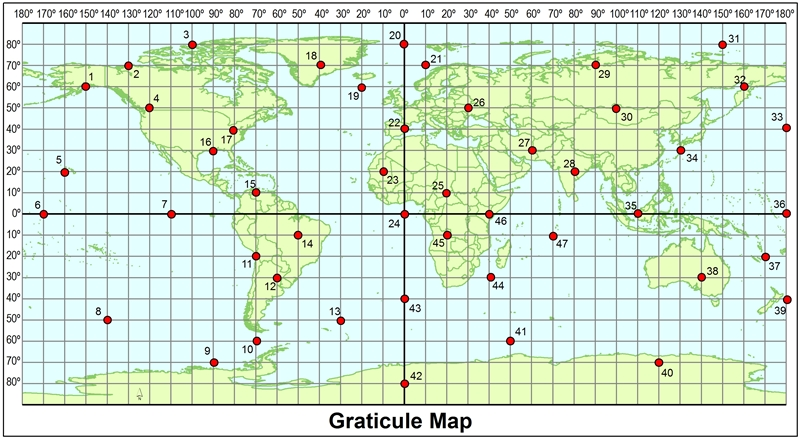
Using the map, what are the coordinates of point 14?
10°S, 50°W
What is the highest latitude possible?
90°
Which is another way of writing 45° 15'S, 30° 45'E?
-45.15, -30.45
About what distance is represented by one degree of longitude?
Anywhere from 0 to 69 miles
Why was longitude at sea especially difficult to discern before 1760?
No timepiece was sufficiently accurate, and solar observations needed to be compared with a control.
What is the significance of a great circle route?
This curved path is the shortest distance between two points on Earth.
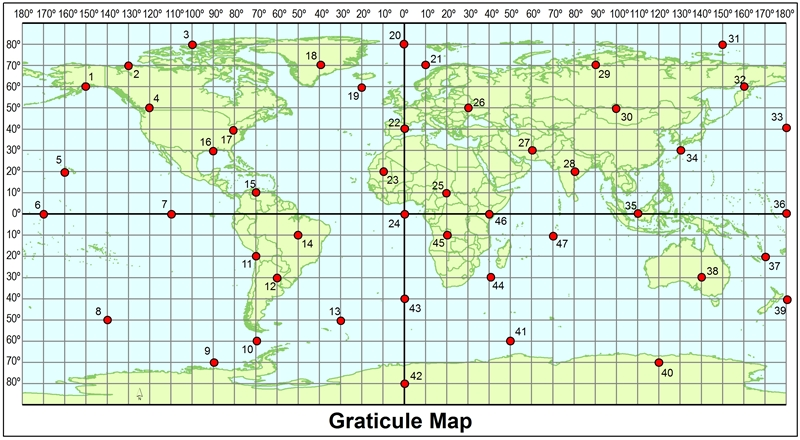
Using the map, which point would have a positive latitude and a negative longitude value?
17
What is the highest longitude possible?
180°
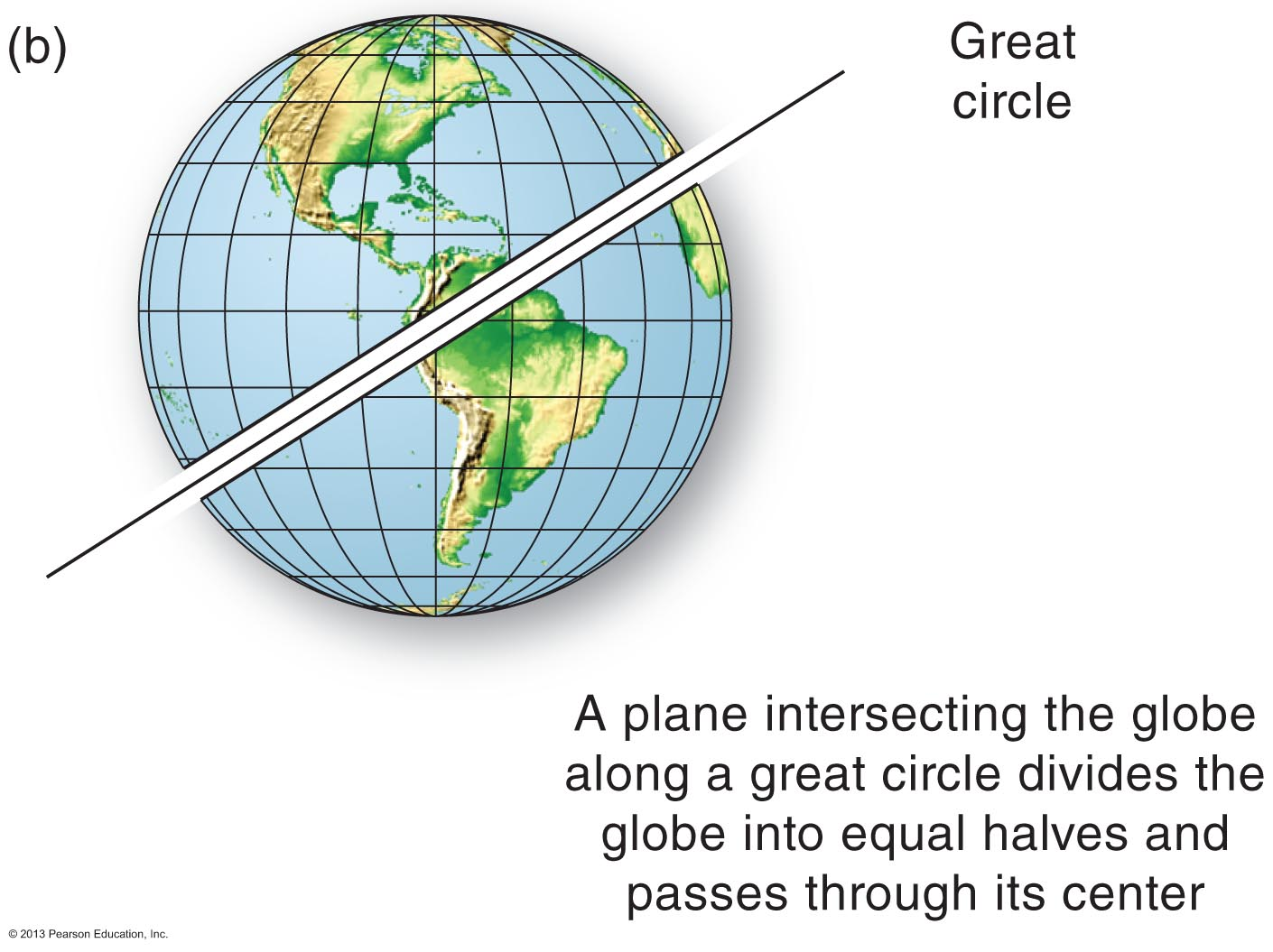
How do great circles differ from small circles?
All planes formed by great circles intersect Earth's center.
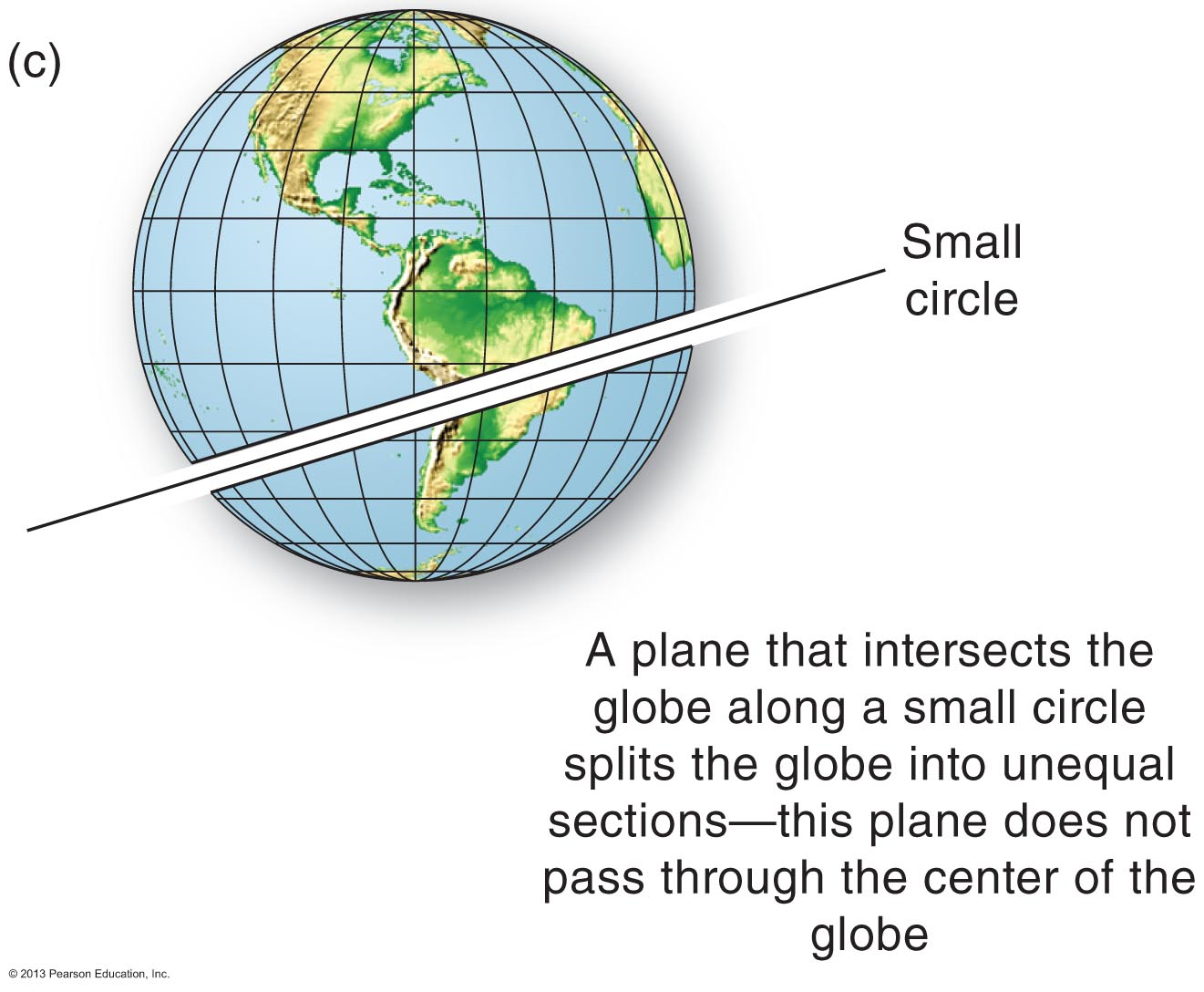
What is the significance of a great circle route?
This curved path is the shortest distance between two points on Earth.
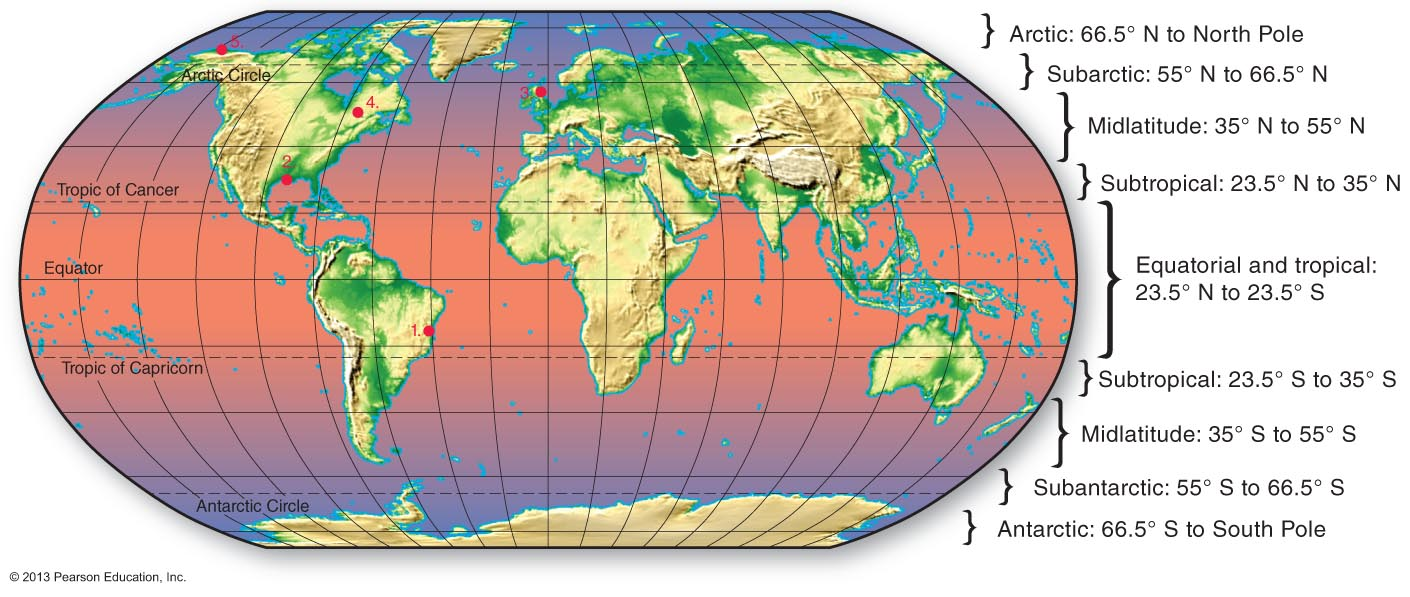
Within which latitude zone is 32°S?
Subtropical
About what distance is represented by one degree of latitude?
69 miles
Which coordinate is correctly written?
85° 0' 28"N, 173° 57' 51"E
About what distance is represented by one degree of longitude?
Anywhere from 0 to 69 miles
What is the correct way to write 58.75°, -119.5° in DMS format?
58° 45'N, 119° 30'W
Which is another way of writing 45° 15'S, 30° 45'E?
45.25°S, 30.75°E
What is the highest longitude possible?
180°
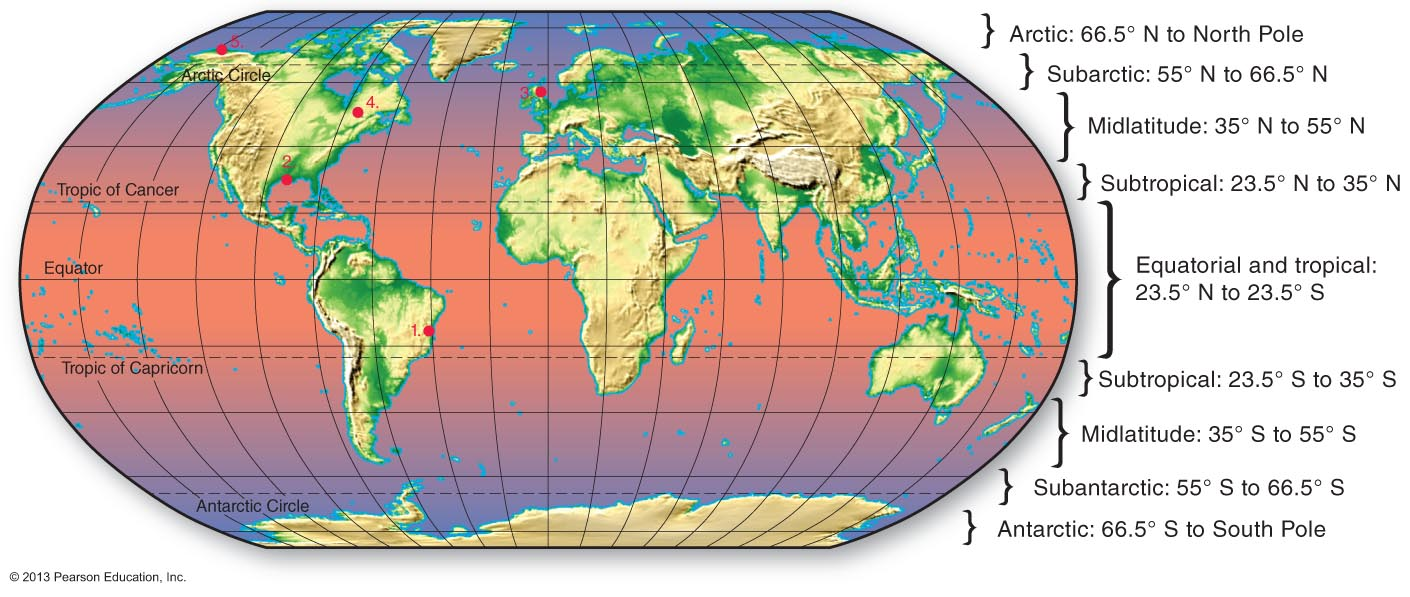
Within which latitude zone is 32°S?
Subtropical
What is the significance of a great circle route?
This curved path is the shortest distance between two points on Earth.
How does GPS work?
A GPS device times communications with a minimum of three satellites, and with its accurate clock, it computes its coordinates.
What is the correct way to write 58.75°, -119.5° in DMS format?
58° 45'N, 119° 30'W