Introduction to Memory
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Storage
The process of retaining information in the brain or a computer system for later retrieval and use
Explicit Memory
retention of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and “declare”

episodic memory
explicit memory of personally experienced events

Semantic memory
explicit memory of facts and general knowledge

Implicit memory
retention of learned skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection

Procedural memory
a type of long-term memory that stores information related to motor skills, habits, and actions

prospective memory
remembering to perform actions at a specific time or event in the future

long-term potentiation
an increase in a cell’s firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation
working memory
active processing of incoming auditory and visual information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory
working memory model
describes the human memory as a complex system comprising of multiple components, rather than a single unitary store.
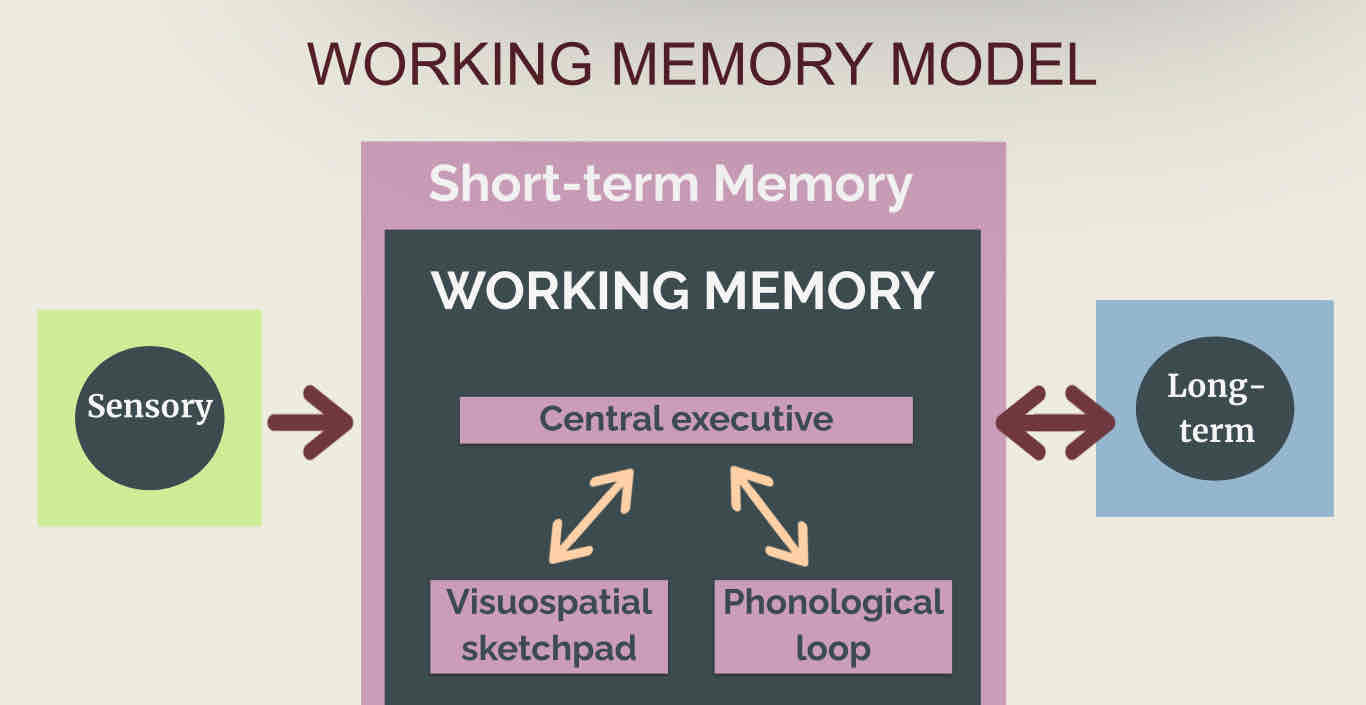
primary memory system
the short-term memory section of the working memory model
cental executive
controls the center of the working memory
phonological loop
deals with auditory information
visuospatial sketchpad
deals with visual information
long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system
multi-store model
describes memory as a linear process comprising three distinct stores: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory

Sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli

echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
automatic processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information and of well-learned information
effortful processing
encoding that required attention and conscious effort
levels of processing model
a cognitive framework that explains how information is processed and stored in memory

structural, phonemic, semantic
in the levels of processing model, there is shallow processing, short-term retention of information, and deep processing, more meaningful analysis of information leading to better recall