biology final study guide
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
why is information about the carbon atom critical to understanding organic molecules?
it is a versatile element that is able to form 4 covalent bonds with other elements or itself
organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing…
carbon and hydrogen
which of the following is NOT true of carbon?
it is the main element in inorganic compounds
monomers are bonded together by which of the following processes?
dehydration synthesis
which of the following is NOT an organic molecule found in living organisms?
sodium chloride
carbohydrates are excellent energy storage molecules. what is the main reason for this?
carbohydrates contain many carbon-hydrogen bonds
starch has several advantages as a polymer of glucose molecules. for example, it can coil itself into a compact shape, and it is insoluble in water. these factors help it perform its principal function. what is that function?
energy storage in plants
oils and waxes are formed from which of the following macromolecules?
lipids
which of the following molecules is NOT a polymer?
glucose
which of the following molecules have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components, causing them to form into a double layer membrane?
phospholipids
which of the following is the most diverse group of macromolecules in both function and chemical structure?
proteins
which of the following best describes the differencebetween the functions of carbohydrates and nucleic acids?
carbohydrates store energy efficiently, while nucleic acids store and pass on a cell’s genetic information
when comparing proteins and carbohydrates, the following similarities can be identified:
both consists of linked monomers via the process of dehydration synthesis
three types of polysaccharides are particularly important to libing organisms. they each perform functions vital to cells. which of the following correctly identifies two of these types of polysaccharides and their primary functions?
starch = storage; glucose = energy
there are five types of nitrogenous bases, four of which are found within DNA molecules. these are…
adenine
thymine
cytosine
guanine
we can identify whether a lipid is saturated or unsaturated by its physical state. unsaturated fats are ____ and saturated fats are ____ at room temperature.
liquid; solid
protein, carbohydrate, and nucleic acid molecules are the results of smaller molecules bonded together. the process that occurs to attatch these smaller molecules to one another is…
dehydration synthesis
RNA and DNA differ in that they utilize different _____ within their nucleotides. RNA utilizes ____ and DNA utilizes _____.
sugars; ribose; deoxyribose
proteins are polymers formed from…
amino acids
which of the following molecules is made up of a glycerol and fatty acids?
lipids
in which process is water used to break apart polymers into individual monomers?
hydrolysis
which substance is a byproduct of dehydration synthesis?
water
the study of chemical compounds that contain bonds with carbon atoms
organic chemistry
a chain of many monomers chemically bonded together is called a…
polymer
polymers are assembled from smaller units called…
monomers
which molecules stores energy in the cells of an animal’s liver and muscles?
glycogen
which of the following is a polysaccharide?
chitin
which molecules is used in the cells walls of fungi and makes up exoskeletons of insects, arthropods, and crustaceans?
chitin
which molecule is the best source of short-term energy?
glucose
which molecules builds cell walls in plants, givesplants strength and flexibility, and is the most abundant organic compound on earth?
cellulose
steroids and triglycerides are examples of…
lipids
which molecule contains a polar hydrophilic headand two non-polar hydrophobic tails, and make up the cell membrane?
phospholipid
which of the following elements is NOT typically found in lipids?
nitrogen
which of the following elements is NOT typically found in carbohydrates?
phosphorous
which of the following elements is found in nucleic acids, but NOT in lipids, carbohydrates, or proteins?
phosphorous
about how many amino acids exist in nature?
20
which of the following is NOT a function of proteins?
long and short-term energy storage
what determines the unique properties of an amino acid?
R-group
what is the monomer of nucleic acids?
nucleotide
which type of macromolecule stores, transmits, and expresses genetic information?
nucleic acid
which of the following is NOT a function of lipids?
short-term energy storage
enzymes control the rate of chemical reactions in the body. what type of macromolecule are enzymes?
protein
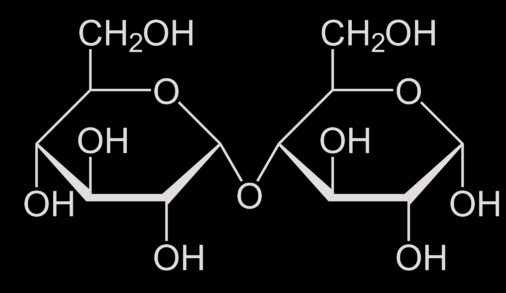
which type of molecule is shown?
disaccharide

which type of molecule is shown?
lipid
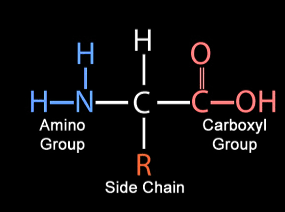
what molecule is shown?
amino acid
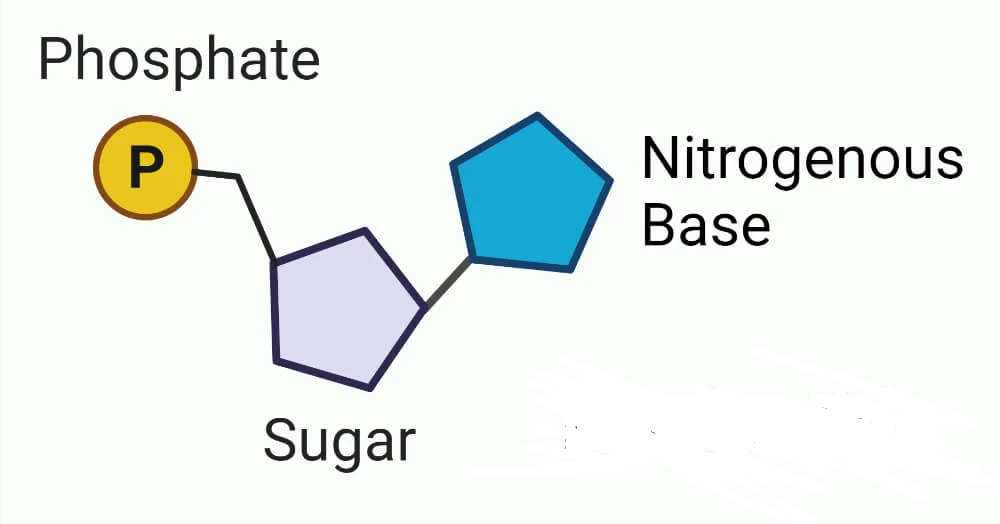
what molecule is shown?
nucleotide

what structure of protein is this?
quaternary structure
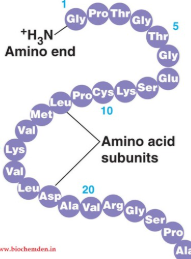
what structure of protein is this?
primary structure

what structure of protein is this?
tertiary structure

what structure of protein folding is this?
secondary structure