Phonetics 1: Articulation
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards based on the lecture notes about phonetics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Phonetics
The study of speech sounds.
Three A's of phonetics
Articulatory
Acoustic
Auditory
Articulatory Phonetics
the production of speech sounds.
Acoustic Phonetics
how we hear speech sounds
Auditory Phonetics
the perception of speech sounds.
Phases of Speech Production
Initiation
Phonation
Articulation
Initiation
The lungs produce an air pressure by inhaling, which is then expelled through throat and mouth or nose. (Pulmonic egressive air stream)
Phonation
The air stream passes through the larynx and sets the vocal folds/cords in motion. This vibration produces the actual voice. (voiced vs. voiceless sounds)
Articulation
The oscillating air stream passes through pharynx, the mouth or nose and is then modified by articulating speech organs (articulators: e.g. tongue, palate, teeth, lips)
Pulmonic egressive airstream(initiation)
Airflow produced by exhaling, used in speech production.
Glottis
The opening between the vocal folds.
Homorganic
Sounds that share a place of articulation.
passive articulator
Palate
Alveolar ridge
teeth
Active Articulator
Term describing the tongue and lips.
Manner of Articulation
The different ways of obstructing the airstream.
Three Major Articulatory Configurations
Sustained contact (complete closure) ≈ closed door
Close approximation ≈ hedge
Open approximation ≈ open door
Representation of Plosives
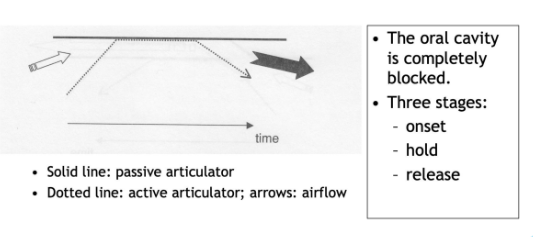
Major Articulatory Configurations
Sustained contact (complete closure): plosives (nasals if there is no velic
closure)
Close approximation: fricatives
Open approximation: median and lateral approximants
Trill/Tap
A sound produced by momentary contact between active and passive articulators.