Myoglobin and Hemoglobin
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Protein Ligand Interactions
reversible, transient process of chemical equilibrium (A+B ←→ AB)
binding molecule (ligand) binds at the binding site via non-covalent forces
equilibrium composition is characterized by Ka = [PL] / [P][L] where large Ka means tight binding; Kd for reverse process
Binding
the fraction of occupied binding sites is theta
[L] is free ligand concentration
![<p>the fraction of occupied binding sites is theta</p><p>[L] is free ligand concentration</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7fba265c-6ffd-4277-9f6e-984dd3b48724.png)
Binding Curves
fraction of bound sites depends on the free ligand concentration and Kd (ligand concentration at half saturation when half the binding sites are taken up)
typically ligand concentration is known independent variable
Kd can be found graphically or through least-squares regression
Thermodynamic Connections
interaction strength can be expressed as:
association constant Ka
dissociation constant Kd, 1/Ka
interaction free energy dGnought
strong binding is when Kd < 10 nM

O2 Binding Subunits
each subunit binds one iron containing heme group
alpha subunit has 7 helices; beta has 8
in each subunit the heme group is bound in a hydrophobic pocket between the C, F, and E helices
no covalent attachment between heme and protein
MYOGLOBIN = MONOMER (1 peptide chain)
HEMOGLOBIN = tetramer
Myoglobin
monomeric protein in muscle tissue made of 153 amino acids in a single polypeptide
O2 storage and transport within muscle tissue → increases solubility of O2 in the cells and the diffusion rate within the tissue
binding curve is hyperbolic - at high pO2 it binds oxygen well, at low pO2 it will not release it (bad for transport protein)
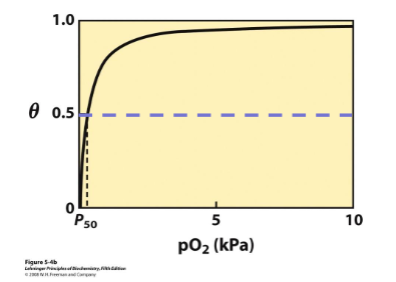
Hemoglobin
tetrameric protein (a2b2) tetrameric protein in red blood cells
alpha subunit is 141 amino acids and beta subunit is 143 amino acids
transports O2 to tissues from lungs and CO2 from lungs to tissues
binding curve is sigmoidal
How to Measure O2 Binding
heme group is a strong chromophore that absorbs both in UV and visible range
changes in electronic state of Fe causes changes in absorbance
binding of oxygen can be monitored by UV-Vis spectrophotometry
Why partial pressure of O2?
Mb is used for movement of oxygen within the muscle
Hb is used for moving oxygen from lungs to tissues
pO2 measures amount of O2 dissolved in aqueous solution inside the cell or blood
Myoglobin Function
increase solubility of oxygen
MbO2 diffuses well in water
oxygen storage especially for deep living mammals
bad transport protein
needs tight binding of oxygen in lungs and low binding at tissues - must have multiple binding sites that are able to interact with each other → cooperativity
Positive Cooperativity
first binding event increases affinity at the other binding sites
Hemoglobin Binding Curve
sigmoidal shape because of positive cooperativity from low affinity T state to high affinity R state
Hb has high affinity and low affinity states
at high pO2 it has high affinity for oxygen
at low pO2 it has low affinity for oxygen
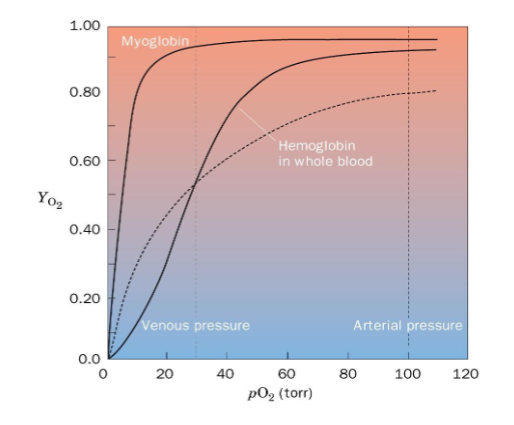
T and R States
T (tense) state: Hb conformation in DEOXY-state; low affinity at all 4 binding sites
R (relaxed) state: Hb conformation in the OXY-state; high affinity and binds well at all 4 binding sites - central pocket of molecule is smaller than T state
Hb binds O2 in lungs where pO2 is high and releases in body where pO2 is low - this is why alternation between high and low affinity matters
Effectors of O2 Binding
effector: molecule or ion that binds to a protein or enzyme and changes its activity
+ effectors increase affinity or activity - activator
- effectors decrease affinity or activity - inhibitor
homotropic effector binds to same site as substrate (like O2)
heterotropic effectors bind at a site other than the active site
H+ and CO2 stabilize the T state → decrease O2 affinity by binding to N terminus
BPG stabilizes T state → decrease O2 affinity
The Bohr Effect
increasing acidity (decreasing pH) shifts the Hb binding curve to the right from decreased affinity to O2 → increased O2 delivery to tissues
carbamate formation increases the acidity of the blood → more O2 released stabilizes the T state
2 Bohr protons bind at the C termini of the beta chains and the n termini of the alpha chains in the T state
Haldane Effect
CO2 binding decreases affinity for O2
The BPG Effect
purified Hb behaves differently than Hb in the blood
carbamate formation at the N termini of the change
H+ affects
BPG binding
BPG
bis-phophoglycerate
small triose sugar found in the blood
has 5 negative charges!
1 BPG per tetramer binds to Hb in the central region between the subunits in the T state (pocket too small in the R state) that has 6+ residues → decreases O2 affinity
mutation in BPG binding pocket decreases O2 affinity, e.g. fetal Hb
BPG O2 Binding Curve
decreased affinity and increased p50 with increased [BPG]
has consequences in high altitude and fetal Hb
![<p>decreased affinity and increased p50 with increased [BPG]</p><p>has consequences in high altitude and fetal Hb</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3da9e6f5-eb1a-417d-a37c-1e56150494aa.png)
Effect of BPG at High Altitude
less oxygen available to breathe in from environment at high altitudes
more O2 is dropped off in the body than normal → increased O2 transport than at low [BPG]
p50 is raised as [BPG] increases so it can deliver more oxygen to tissue
![<p>less oxygen available to breathe in from environment at high altitudes</p><p>more O2 is dropped off in the body than normal → increased O2 transport than at low [BPG]</p><p>p50 is raised as [BPG] increases so it can deliver more oxygen to tissue</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/28a69c59-2b72-41c5-bb7c-6b98f6240207.png)
Effect of BPG on Fetal Hb
need to get O2 from mom’s blood to fetus
fetal Hb is a mutation that has a stronger affinity for O2 than adult Hb so fetus can get proper oxygen
fetal red blood cells picks up oxygen from the mother’s blood
will gradually be replaced by adult Hb after birth
p50 is lowered as opposed to raised in high altitudes - pulls curve left
Myoglobin
O2 carrying protein in the muscle that primarily facilitates diffusion of O2 in rapidly respiring muscle tissues
protein is 80% alpha-helical with helices A to H having 153 amino acids
structure has 8 alpha helices and 1 heme
heme binding between E and F helicesHE stabilized tertiary structure
hydrophobic interactions, ionic interactions (salt bridges), LDFs stabilize the structure
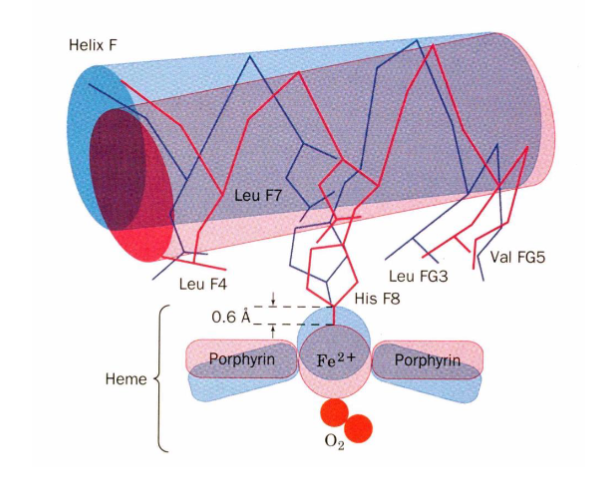
Heme Binding in Myoglobin
HisF8 coordinates the iron binding, HisE7 restricts the size of the binding site and orientation of oxygen when it binds
H bond prevents superoxide from leaving the heme
Val68 and Phe 43 prevent Fe2+ from being oxidized to Fe3+ so that O2 can bind reversibly
Structural Properties of Hb
4 subunits, 2 alpha with 7 alpha helices and 2 beta with 8 alpha helices
dimer of dimers
lots of a1b1 contacts (35)
a1b2 contacts are very important (19)
not so much b1b2 and a1a2 contact since the protein communicates oxygen binding - needs to talk between subunits
similar structures between Hb and Mb but only 12% sequence identity
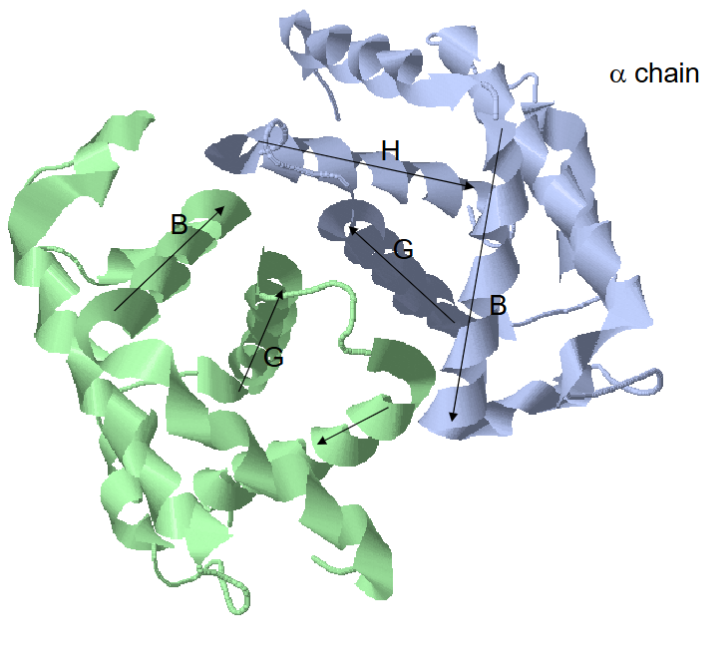
Structural Changes When O2 Binding Hb
changes in heme: Fe2+ gets smaller since e- are being pulled away and moves about 0.6 angstroms into the heme plane
F-helix moves about 1 angstrom (iron pulls on His F8)
changes at a1b2 interface: Asp G1b H bond with Tyr C7a ←→ Asn G4b H bond with Asp G1a
at C termini of alpha and beta chains: O2 stabilizes R state and H bonds stabilizes T conformation
What holds hemoglobin together?
hydrophobic interactions between subunits
interactions between subunits which is important in R to T transition
H bonds and LDFs
Hb Variants
gamma Hb is derived from beta Hb
Fetal Hemoglobin
tetramer with a2y2 composition where gamma subunit is like the beta subunit in adult Hb
lacks His143 b → important for BPG binding (does not bind as tightly as adult form)
has ser instead which decreases BPG binding since T state stabilizer is gone (removes positive charge so (-) on BPG has less interactions)
higher affinity for O2 at all pO2 values means fetal Hb traps O2 that comes from mother’s Hb
decreased BPG binding biases fetal Hb to R state
Sickle Cell Hb (HbS)
single amino acid change in beta chain (Glu6 changed to Val) makes long fibers in the deoxy T state because pO2 increases
Val6b binds to hydrophobic pocket in a beta chain of another Hb tetramer ONLY in T state
fiber formation makes sickle cell shape in the capillaries so they clog
Hb Hammersmith
PheCD1 (42) b → ser
disrupts hydrophobic heme pocket
Hb Bristol
Val E 11(67) b → Asp
disrupts hydrophobic pocket that holds heme
Hb Svannah
Gly B6(24) b → val
B and E helix interface gets disrupted
Hb Philly
Tyr (35) Phe disrupts H bond at a1b1 interface → destabilizes
HbM
Fe2+ oxidized to Fe3+ so can’t bind O2
aka methemoglobin
Hb Iwate
His F8 (87) a → tyr
disrupts O2 binding site and iron gets oxidized
Hb Milwaukee
Val E11 (67) b → glu
glu side chain stabilizes Fe3+
Hb Boston
His E7 (58) a → tyr
Yakima Mutaiton
Asp99 → His
disrupts H bond that stabilizes T state (now is destabilized)
Kansas Mutation
Asn 102B → Thr
disrupts H bond that stabilizes R state (now is destabilized)
Mutation
in switch region can stabilize T or R state, depends on specific mutation
b1b2 interface will affect BPG binding mostly
mutation near heme binding site will mostly affect O2 binding
mutations that increase O2 affinity decrease cooperativity
mutations that disrupt BPG binding increase O2 affinity