y10 physics
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
speed
the rate of change of distance
formula for speed
speed = delta distance/delta time
is speed a scalar or vector quantity?
scalar
average speed
the average of instantaneous speeds over a period of time
formula for average speed
Sav = total distance/total time
instantaneous speed
how fast an object is moving at a single moment
instantaneous vs average speed
instantaneous speed is how fast an object is moving at a single moment, while the average speed is the average of instantaneous speeds over a period of time
what does the gradient in a distance/time graph tell you?
the speed
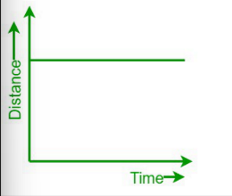
what can you say about the gradient and the speed of this distance-time graph?
the gradient is 0 therefore the speed is 0
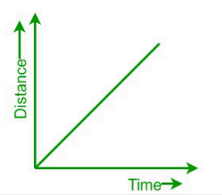
what can you say about the gradient and the speed of this distance-time graph?
the gradient is equal to distance/time and the speed is uniform
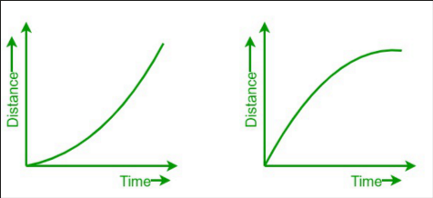
what can you say about the gradient and the speed of these distance-time graphs?
the gradient is equal to the instantaneous speed and the speed is non-uniform
what does the gradient tell you in a velocity/time graph?
the acceleration
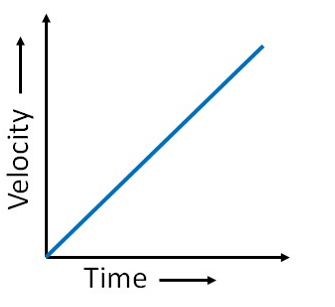
what can you say about the acceleration and the gradient of this velocity-time graph?
the acceleration is uniform and the gradient is equal to velocity/time
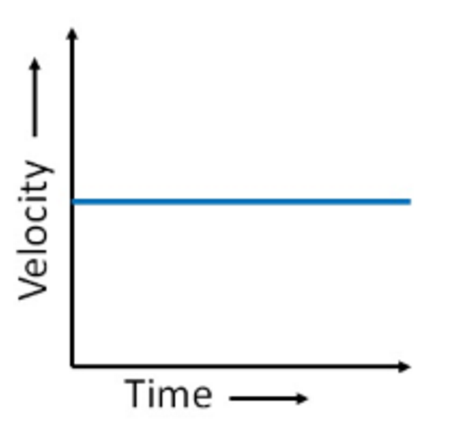
what can you say about the acceleration and the gradient of this velocity-time graph?
the acceleration is 0 and the gradient is 0 therefore the speed is constant
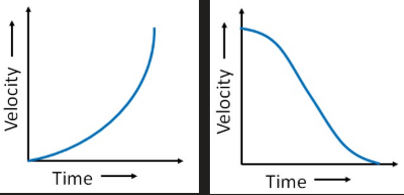
what can you say about the acceleration and the gradient of these velocity-time graphs?
the acceleration is non-uniform and the gradient is equal to the instantaneous acceleration
scalar vs vector quantity
scalar quantity has magntitude and no direction, vector quantity has both a magnitude and a direction
distance
how far an object has travelled
formula for distance
d = savt
is distance a scalar or vector quantity?
scalar
displacement
a change in position of an object
how is displacement measured?
a straight line from the object’s starting to ending point
is displacement a scalar or vector quantity?
vector
velocity
the rate of change of displacement
formula for velocity
delta displacement/delta time
is velocity a scalar or vector quantity?
vector
negative velocity
when the body travels in the exact opposite direction
acceleration
the rate of change of velocity
formula for acceleration
delta velocity/delta time
is acceleration a scalar or vector quantity?
vector
what does negative acceleration mean if negative directions have not been defined?
positive acceleration = body is getting faster
negative acceleration = body is slowing down
what does negative acceleration mean if negative directions have been defined?
for something moving in the positive direction, negative acceleration = slowing down
for something moving in the negative direction, negative acceleration = speeding up
inertia
the natural tendency of an object to maintain its velocity
what does the law of inertia say?
an object at rest tends to stay at rest
a moving object tends to keep moving with the same speed in the same direction
inertia is not a force
newton’s first law of motion
an object will keep moving with the same speed and direction unless acted on by a net force
newton’s third law of motion
every force has an equal and opposite reaction force
what must be the case between an action and a reaction force?
they must:
be equal in size
be opposite in direction
be of the same type
act on different objects
newton’s second law of motion
net force = mass x acceleration
newtons = kg x m/s2
what is the relationship between force and acceleration?
as force increases, acceleration increases
what is the relationship between mass and acceleration?
as mass increases, acceleration decreases
what is the relationship between force and mass?
as force increases, mass increases