Hormonal contraception
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is the combines oral contraceptive pill?
tablet containing oestrogen and progesterone
generally taken for 21 days with a 7 day break
99% effective with perfect use, 91% effective with typical use
licensed up to 5 years
What is the mechanism of action of the COCP?
suppresses ovulation
progesterone thickens cervical mucus
progesterone inhibits proliferation of the endometrium reducing chance of successful implantations
How does the COCP work?
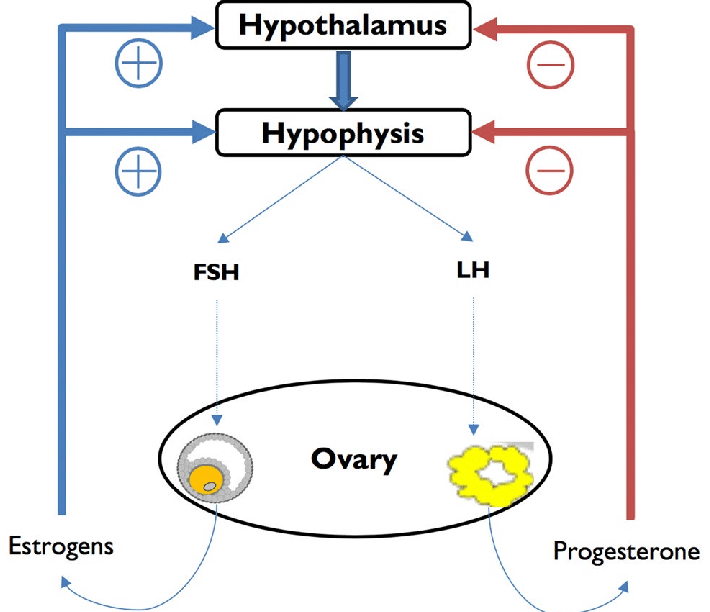
oestrogen and progesterone have a negative feedback effect on the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary suppressing release of gonadotrophic releasing hormone, luteinising hormone, and follicular stimulating hormone
this suppresses ovulation
What are pros of taking the COCP?
reliable
independent of sexual intercourse
helps to regulate bleeding and dysmenorrhoea
improve premenstrual symptoms
reduced risk of endometrial, ovarian, and colon cancer
reduced risk of benign ovarian cysts
What are cons of taking COCP?
risk of DVT, stroke, breast cancer
missed pills
failure rate 9% in first year with typical use
What regimes are there for COCP?
21 days on and 7 days off
63 days on (three packs) and 7 days off (“tricycling“)
Continuous use without a pill-free period
What are side effects of COCOP?
unscheduled bleeding
breast pain and tenderness
mood changes and depression
headaches
hypertension
venous thromboembolism
small increase in breast and cervical cancer returning to normal after stopping
small increase in MI and stroke
What are CI of COCP?
uncontrolled HTN
migraine with aura
breast cancer
history of VTE
ages >30 and smoking >15 cigarettes per day
vascular disease of stroke
IIHD, cardiomyopathy, AF
liver cirrhosis/tumours
SLE or antiphospholipid syndrome
BMI >35 is UKMEC 3
How is the COCP started?
start on day 1 of cycle offers instant protection
starting after day 5 requires contraception for 7 days
when switching from POP to COCP can swap at any time but needs 7 days protection
when swapping from desogestrel they can swap at any time with no additional contraception
What are missed pill rules for COCP?
1 missed pill (more than 24 hours late)- no extra precautions take pill as soon as remembered
2 or more missed pills (72 hours since last pill)- take last pills when remember, condoms used for 7 days
Is emergency contraception needed for missed pills on COCP?
If day 1 – 7 of the packet they need emergency contraception if they have had unprotected sex
If day 8 – 14 of the pack (and day 1 – 7 was fully compliant) then no emergency contraception is required
If day 15 – 21 of the pack (and day 1 – 14 was fully compliant) then no emergency contraception is needed. They should go back-to-back with their next pack of pills and skip the pill-free period.
Should COCP be stopped before surgery?
stops four weeks before major operation or any procedure that requires the lower limb to be immobilised
What is the progesterone only pill?
tablet containing progesterone that is taken continuously
>99% with perfect use but 91% effective with typical use
What are two types of POP?
traditional - 3 hours delay to take the pill
desogestrel- 12 hours late
What is the mechanism of action of traditional POP?
thickens cervical mucus
altering endometrium making it less accepting of implantation
reducing ciliary action in the fallopian tubes
What is the mechanism of action of desogestrel?
inhibits ovulation
Thickening the cervical mucus
Altering the endometrium
Reducing ciliary action in the fallopian tubes
How is POP started?
started on day 1-5 means protected immediately
start any other day requires contraception for extra 48 hours
What are SE of POP?
unscheduled bleeding
breast tenderness
headaches
acne
increased risk of ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancy with traditional POPs, minimal increased risk of breast cancer that returns to normal 10 years after stopping
What are missed pill rules for POP?
use extra contraception for 48 hours
What is a CI for POP?
active breast cancer
What is the progesterone injection?
IM or SC injection of progesterone given every 12-14 weeks (depot medroxyprogesterone acetate)
99% effective with perfect use 94% effective with typical use
What are absolute CI for progesterone injection?
active breast cancer
What are probable CI for progesterone injection?
ischaemic heart disease and stroke
unexplained vaginal bleeding
severe liver cirrhosis
liver cancer
can cause osteoporosis so be mindful for patients on steroids or in older women
What is the mechanism of action of the progesterone injection?
inhibit ovulation by inhibiting FSH secretion by the pituitary gland preventing development of follicles in the ovaries
thickens cervical mucus
alters endometrium
What are cons of progesterone injection?
takes up to 12 months for fertility to return
osteoporosis risk
can cause weight gain
When is the progesterone injections started?
start day 1-5 immediate protection
start after day 5 requires 7 days of contraception before it becomes effective
What are SE of progesterone injection?
irregular bleeding
weight gain
acne
reduced libido
mood changes
flushes
hair loss
skin reactions
reduced mineral bone density
small increased risk of breast and cervical cancer
What can be used to settle bleeding with the progesterone injection?
COCP for three months in addition to the injection to settle bleeding
What are pros of the progesterone injection?
very reliable
improves painful periods and endometriosis
reduces risk of ovarian and endometrial cancer
reduced severity of sickle cell crisis in patients with sickle cell anaemia
What is the progesterone implant?
small 4cm plastic rod inserted in the upper arm beneath the skin above the SC fat that slowly releases progesterone
lasts for 3 years
99% effective
What implant is used in the UK?
Nexplanon- contains 68mg of etonogestrel
licensed between ages 18-40
What is the mechanism of action of progesterone implant?
inhibits ovulation
thickens cervical mucus
alters endometrium
How is the implant inserted?
inserted 1-5 immediate protection
after day 5 requires 7 days contraception
uses lidocaine to insert and remove
What are pros of the implant?
very reliable
not user dependent
no delay in return to fertility
can improve painful periods, make periods lighter
doesn’t cause weight gain
no effect on bone mineral density
no thrombosis risk
no restriction for use in obese patients
What are cons of the implant?
irregular bleeding
requires minor procedure for inserting
can lead to acne
can become impalpable and move occasionally into vessels and migrating around the body
How can Nexplanon be identified on scans?
has barium sulphate manufactured into it to make it radio-opaque so can be seen on X-rays