immunopathologies
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
types of immune system diseases / disorders
immunodeficiency diseases
hypersensitivity disorders
autoimmune diseases
multisystem diseases
isoimmune diseases
immunodeficiency diseases
cannot mount an immune response to take care of an issue
general categories
-primary immunodeficiency
-secondary immunodeficiency
ex: hiv / aids
hypersensitivity disorders
too much of a response
-allergy
-asthma
autoimmune diseases
body starts to attack itself, MHC not functioning properly
-systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
-fibromyalgia
-rheumatoid arthritis
multisystem diseases
components of each type
ex: myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
isoimmune diseases
ex: organ transplants, bone marrow transplants
iatrogenic immunodeficiency
hospital / care provider induced
(secondary immunodeficiency)
-immunosuppressive drugs, radiation therapy, splenectomy, cytotoxic drugs
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
primary immunodeficiency
potential progressive loss of immune function
increased host susceptibility
******HIV DOES NOT = AIDS******
incidence and prevalance of HIV
1.2 million people living with HIV in the US end of 2021
new infections in US 36,136 in 2021 (7% decrease since 2017)
MSM: 24,107 new infections per year
etiology of HIV
retrovirus
HIV type 1 and type 2
retrovirus
virus gets into cell DNA and uses the DNA to replicate itself
transmission of HIV
exchange of bodily fluids (blood and semen)
direct contact
NOT casual or social contact (not transmitted by sneezing / a surface)
what is the average time between exposure and diagnosis of AIDS
8-10 years
which cells in the immune system should function to kill the HIV virus
T cells
risk factors for HIV
unprotected oral and anal sex
vaginal sex with infected partner
having 6 or more sexual partners in past year
exchanging sex for money or drugs
injecting drugs
pathogenesis of HIV
retrovirus that predominantly infects human T4 lymphocytes (CD4)
3 primary impacts of HIV on immune system
immunodeficiency with opportunistic infections and unusual malignancies
autoimmunity
neurologic dysfunction
****not seen until viral load is very high
CD4 count during asymptomatic stage of HIV
500 cells / mm3
no restriction on activities because no symptoms
CD4 count during early symptomatic to advance disease stages of HIV
200-500 cells / mm3
increasingly more compromised
restriction on activity based on symptoms, still benefit from exercise to boost immune system
CD4 count during advanced stage of HIV
200 cells / mm3 or less
neurologic symptoms and increasing opportunistic infections
what is treatment focused on in the advanced stage of HIV
pain management
what opportunistic infections are possible in the advanced stage of HIV
cytomegalovirus (retinitis / blindess)
pneumocystis pneumonia (fungal infection of lung)
kaposi sarcoma
malignant cancer of blood vessels
red and puffy
not contagious
*****often associated with CD4 counts
central and peripheral nervous system signs associated with CD4 counts
cognition, memory, weakness
burning, tingling, sensory loss, weakness
ability to perform ADLs decreases
medical management of HIV
PREVENTION
-pre exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
-post exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
TREATMENT
-Treatment as prevention (TasP)
-antiviral therapy (ART): regular use of condoms, use of antiviral meds for rest of their life to reduce viral loads
pre exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
given to someone with high risk factors
has to be used everyday
expensive
have to visit physician often
post exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
most effective if taken within 72 hours
take for 28 days
diagnosis of AIDS
blood tests
-quick screen: looks for virus
-definitive testing: looks for antibodies and CD4 cell counts
prognosis of HIV
mortality rate has been decreased by 80%
mortality
death rate
morbidity
impact on person
does not necessarily kill person
newer campaign of medical management for HIV
U= undetectable = untransmissable (as long as ART is continued, do not need condoms)
implications for PT for HIV
protect person with HIV
-patient : need to know CD4 count to know risk
prevent spread of infection
-standard precautions (unless coming in contact with blood)
-consider transmission
exercise and activity
-consider limitations based on stage
etiology of allergy
allergen/antigen causes immune response
type I: common form CAN RESULT IN ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK
type II: autoimmune component
type III: immune complex reaction
type IV: mediated by T cells
pathogenesis of allergy
overactive immune system
*anaphylaxis definition
systemic release of histamine
-systemic vasodilation (may appear red)
-bronchospasm
-increased mucus secretion
-edema (local or systemic)
*initial symptoms of anaphylaxis
itching, edema, sneezing
*progressive symptoms of anaphylaxis
wheezing
dyspnea: difficulty breathing
cyanosis: turning blue
circulatory shock
****which symptoms raise your level of worry to anaphylaxis
dyspnea (all of a sudden)
cyanosis
****other progression symptoms
initial symptoms starting suddenly
known contact with allergen
type I allergy
immediate
-wheezing
-hypotension
-swelling
-anaphylaxis possible
type II allergy (autoimmune)
multiple body systems
malaise
weakness
cardiovascular
upper/lower respiratory
GI
CNS
type III (immune complex)
headache/backache/chest pain
nausea & vomiting
tachycardia / hypotension
hematuria
urticaria
type IV (t cell mediated)
fever
arthralgias
lymphadenopathy
urticaria (rash)
anemia
allergy prevention
avoid stimulus
carry epi-pen
suppress immune system prophylactically (steroids)
allergy treatment
suppress immune system response
emergency management with anaphylaxis
allergy implications for the PT
****know signs of anaphylaxis
potential for reaction to products used in PT
may not see a reaction on first exposure
asthma
chronic disease involving inflammation of the bronchioles
triggered by allergen or other stimulus
what are the several types of asthma
exercised induced bronchoconstriction
allergic asthma response to allergen
occupational allergen
childhood asthma
2 kinds of medical management for asthma
relievers
preventors
relievers (asthma)
quick relief
taken after onset
before exercise
rescue medications often bronchodilators
inhaler or nebulizer
preventors (asthma)
long term controllers
taken daily
inhaled corticosteroids common
what are some important questions to ask a patient with a comorbidity of asthma
ask if they take a reliever or a preventer
ask if it is taken daily
long term management of asthma
avoid triggers
medications
knowing when to use meds and when to seek help
asthma implications for PT
know patient’s ability to manage it
encourage preventative reliever prior to exercise
single organ autoimmune disorders
thyroiditis
addison’s disease
graves disease
chronic active hepatitis
pernicious anemia
ulcerative colitis
insulin-dependent diabetes
systemic autoimmune disorders
fibromyalgia
rheumatoid arthritis
SLE
treatments of autoimmune disorders
“healthy” suppression of immune response
corticosteroids
salicylates
systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (Lupus)
systemic autoimmune disorder
can change over time
incidence of systemic lupus erythmatosus
most common in young women but can occur infancy to old age
etiology of systemic lupus erythmatosus
combo of immunologic, environmental, hormonal and genetic factors
risk factors of systemic lupus erythmatosus
appears to be a hereditary predisposition
physical or mental stress
streptococcal or viral infection
exposure to UV / sunlight
immunization
pregnancy
pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythmatosus
immune disregulation
early symptoms of SLE
fever, malaise, weight loss, fatigue
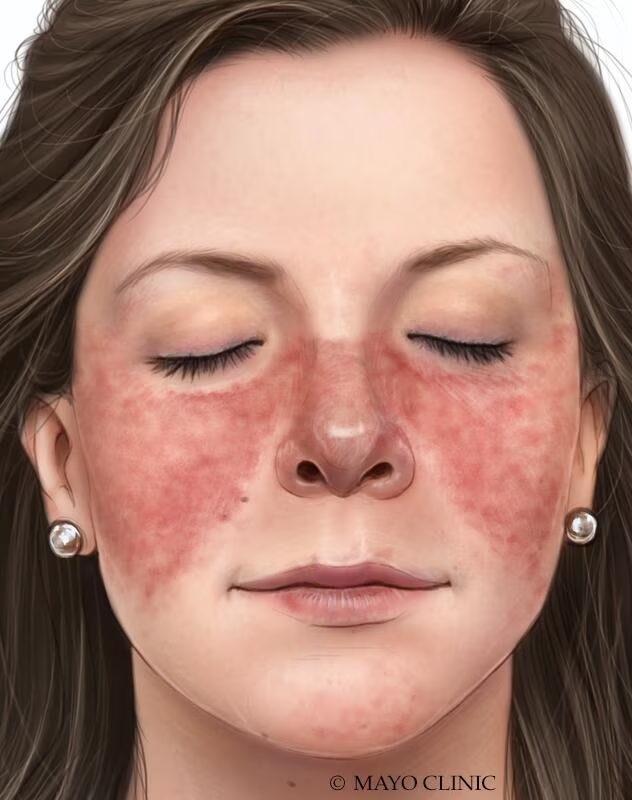
****hallmark: butterfly rash (only in about 50% of cases)
what is hallmark of systemic lupus erythmatosus
butterfly rash
medical management of SLE
clinical signs: synovitis or tenderness in at least 2 joints
30 minutes of morning stiffness
antinuclear antibody presence
antinuclear antibody presence in SLE
most people who have lupus have positive ANA test
*BUT you can have a positive ANA test without having lupus
test is sensitive but not specific
treatment of SLE
reverse autoimmune and inflammatory process
prevent exacerbations and complications
non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): relieve muscle and joint pain and inflammation
prognosis for SLE
better with early detection
poor when associated with cardiovascular, renal, neuro, or severe bacterial infections
SLE implications for PT
may treat arthritis symptoms, fatigue, generalized deconditioning
red flags related to SLE
pain in one joint (septic arthritis)
sudden onset pain with weight bearing (avascular necrosis)
constant pain
signs of renal failure
fibromyalgia
possible systemic autoimmune disorder
“migraine of the muscles”
diffuse pain, multiple tender points
no known cause or cure
incidence of fibromyalgia
more common in females
ages 20-55 years
etiology of fibromyalgia
possible genetic link
risk factors for fibromyalgia
prolonged anxiety and emotional stress or trauma
rapid steroid withdrawal
hyperthyroidism
viral and non viral infections
pathogenesis / hallmarks of fibromyalgia
increased activity (exercise level responses) of skeletal muscles, heart, stomach, intestines, blood vessels, and sweat glands during daily activities
increased substance P
decreased pain inhibiting neurotransmitters
diagnosis of fibromyalgia
*takes a long time
clinical manifestations
must rule out other medical causes
increased substance P
clinical manifestations of fibromyalgia
migraine of muscles, tender but not inflamed
diffuse pain / multiple tender points (11/18 tender points with 4kg of pressure bilaterally)
sleep disturbances with exhaustion, fatigue not relieved by rest
visual disturbances, morning stiffness >30min, anxiety/depression, headache, IBS, TMJ pain, swelling in feet
treatment for fibromyalgia
stress management
cognitive behavioral therapy
nutrition
support (support groups, etc)
meds for symptom management
prognosis for fibromyalgia
life long symptoms
mild: may manage without intervention
moderate or severe: early treatment improves outcomes
fibromyalgia implications for the PT
lessen pain and fatigue
exercise when tolerated
aquatic therapy
aerobic fitness
education and support
stress management
work simplification
psychotherapy
myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
multisystem condition
immunodeficiency
incidence of myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
75% women, middle class, white
onset 40-50 years old
etiology of myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
unsure exactly what causes it
viruses, bacteria, toxins, mold, genetics
may have increase epstein barr virus levels
immune system biomarkers of myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
low natural killer cell function
abnormal increase in pro inflammatory cytokines
nervous system biomarkers of myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
reduced white and gray matter in the brain (can cause headaches, mild memory impairment, sensitive to light)
reduced blood flow to brain
neuroinflammation
endocrine system biomarkers of myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
dysfunctional communication between endocrine glands (flight vs fight)
decreased cortisol and dysfunction of other hormones
low growth hormone (associated with sleep disturbance)
what disease is associated with mitochondrial impairment
myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
mitochondrial impairment (myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome)
leads to reliance on anaerobic metabolism for energy
abnormal fatigability
may be associated with viral infection
will impact cardiac function
will impact blood flow to brain
high lactate levels (causes pain in muscle)
five cardinal symptoms of myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
fatigue: profound energy loss, not relieved by rest (limits ADLs, may end up bedridden)
post-exertional malaise: onset 12-24 hrs after exertion, extended recovery, can be tested with 2 day consecutive cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET)
cognitive impairment: brain fog, impaired attention / decision making
pain: not always present, may include hypersensitivity to heat, cold, touch, etc
sleep disorder: hypersomnia, insomnia, etc
what is the hallmark for myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
sudden onset of symptoms is most common and a hallmark that distinguishes it from other diseases
****disabling fatigue and post-exertional malaise unrelieved by rest
diagnosis of myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
signs: BP often low, orthostatic
fluctuating temp throughout day
tachycardia
irritated throat
screening tests, exclusionary tests, confirmatory tests (2 day CPET, low NK cells)
treatment for myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
herbal remedies
pharmaceutical managements
nutritional supplements
massage, chiropractic, PT, biofeedback
cognitive behavior therapy
prognosis for myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome
varies from minimal impact to severely debilitated
8-63% show improvement
5-10% total remission
an individual with HIV is referred to PT for evaluation and treatment. what are some key questions you need / want to know
what differentiates myalgic encephalomyelitis / chronic fatigue syndrome from fibromyalgia? how do patients with these present similarly?