[BIO 137] Chapter 1: The Human Body: An Orientation
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
overview of chapter 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Form
Anatomy
Function
Physiology
In what way does physiology depend on anatomy?
Function relies on form. The operation or function of a structure is promoted or prevented by its anatomy.
Levels of structural organization
Atom/element, molecules, organelles, cells, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes.
Essential life processes
Boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, growth, pathway
Boundaries
Essential for maintaining a distinct separation between internal and external environments. Ex: Integumentary system
Movement
The act of changing physical location or position, which is necessary for various life processes, including locomotion and the movement of substances within the body. Ex: Muscular system
Responsiveness
The ability of an organism to sense and respond to changes in its environment, crucial for survival. Ex: Nervous system.
Digestion
The process by which the body breaks down food into absorbable nutrients, essential for energy and growth. Ex: Digestive system.
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical reactions occurring within the body, enabling growth, reproduction, and energy production. Ex: Endocrine system
Excretion
The process of removing waste products from the body. Ex: Urinary system
Reproduction
Allows for the creation of offspring. Ex: Reproductive system
Growth
Allows for an organism to grow to its full potential and change.
Pathway
Allows for clear and easy movement of nutrients.
Integumentary system
The body’s main boundary from outside elements. Organs: Skin, hair, nails
Skeletal system
Provides support and structure for the body. Organs: Bones, joints
Muscular system
Allows manipulation, locomotion of the body and produces heat. Organs: Skeletal muscles
Nervous system
Main “control system” of the body, transmits sensory information to body using electricity. Organs: Brain, spinal cord, nerves
Endocrine system
Secretes hormones and chemicals to regulate and support metabolism and growth. Organs: Pineal gland, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, thymus, adrenal gland, pancreas, testis, ovary
Cardiovascular system
Supplies oxygen and nutrients for the body. Organs: Heart, blood vessels
Lymphatic/immune system
Attacks foreign substances in the body and drains fluids. Organs: Red bone marrow, thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic ducts, spleen, lymph nodes
Respiratory system
Supplies body with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. Organs: Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, lung, bronchus
Digestive system
Breaks down food into nutrients to be absorbed by the body, also excretes waste. Organs: Oral cavity, esophagus, liver, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus
Urinary system
Removes nitrogenous waste and regulates water content in the body. Organs: Kidney, ureter, bladder, urethra
Reproductive system
Allows the body to produce offspring. Male organs: Prostate, penis, testis, scrotum, dectus deferens. Female organs: Mammary glands, ovary, uterine tube, uterus, vagina
Law of mass balance
The amount of a substance that the body takes in must be the same as the amount of that substance the body loses.
Homeostatic control system
1.) Receptor: detects stimulus
2.) Control center: determines set point in which the variable is to be changed
3.) Effector: Carries out control centers response to stimulus
Negative feedback mechanism
Cause the variable to change in a direction opposite to that of the initial change, returning it to its “ideal” value (the set point). Ex: Shivering in response to feeling cold.
Positive feedback mechanism
The initial response enhances the original stimulus so that further responses are even greater. Ex: Blood clotting
Feedforward (anticipatory) response
Maintains homeostasis by taking action in anticipation of a change to the internal environment. Ex: Salivating after smelling food
Superior
Above/toward head
Inferior
Below/toward feet
Anterior
Front of the body/toward chest
Posterior
Back of the body/toward glutes
Medial
Middle of the body/towards “midline”
Lateral
Away from middle of the body/away from “midline”
Intermediate
Between medial and lateral
Proximal
Point on limb closer to trunk
Distal
Point on limb farther from trunk
Superficial
Towards body’s surface
Deep
Towards body’s insides
Axial
“Axis” of body: Head, neck, trunk
Appendicular
Appendages, limbs
Saggital plane
Divides body into left/right sections
Midsaggital = Midline
Frontal/Coronal plane
Divides body into anterior/posterior sections
Traverse plane
Divides body into superior/inferior sections
Dorsal body cavity
Protects fragile nervous system organs. Subdivisions: Vertebral, cranial
Ventral body cavity
Protects viscera/organs. Subdivisions: Thoracic, abdominal, pelvic
Vertebral cavity
Part of the dorsal cavity. Protects spinal cord.
Cranial cavity
Part of the dorsal cavity. Protects brain.
Thoracic cavity
Part of the ventral cavity. Protects heart and lungs. Split into three sections: Superior mediastinum, pleural, pericardial
Abdominal cavity
Part of the ventral cavity. Protects digestive organs.
Pelvic cavity
Part of the ventral cavity. Protects urinary and reproductive system.
Serosa/serous membrane
Double-layered membrane that protects and lines the walls of the ventral cavity and outer surfaces of organs.
Parietal serosa
Layer of the serous membrane lining the cavity walls.
Visceral serosa
Layer of the serous membrane directly lining the organs.
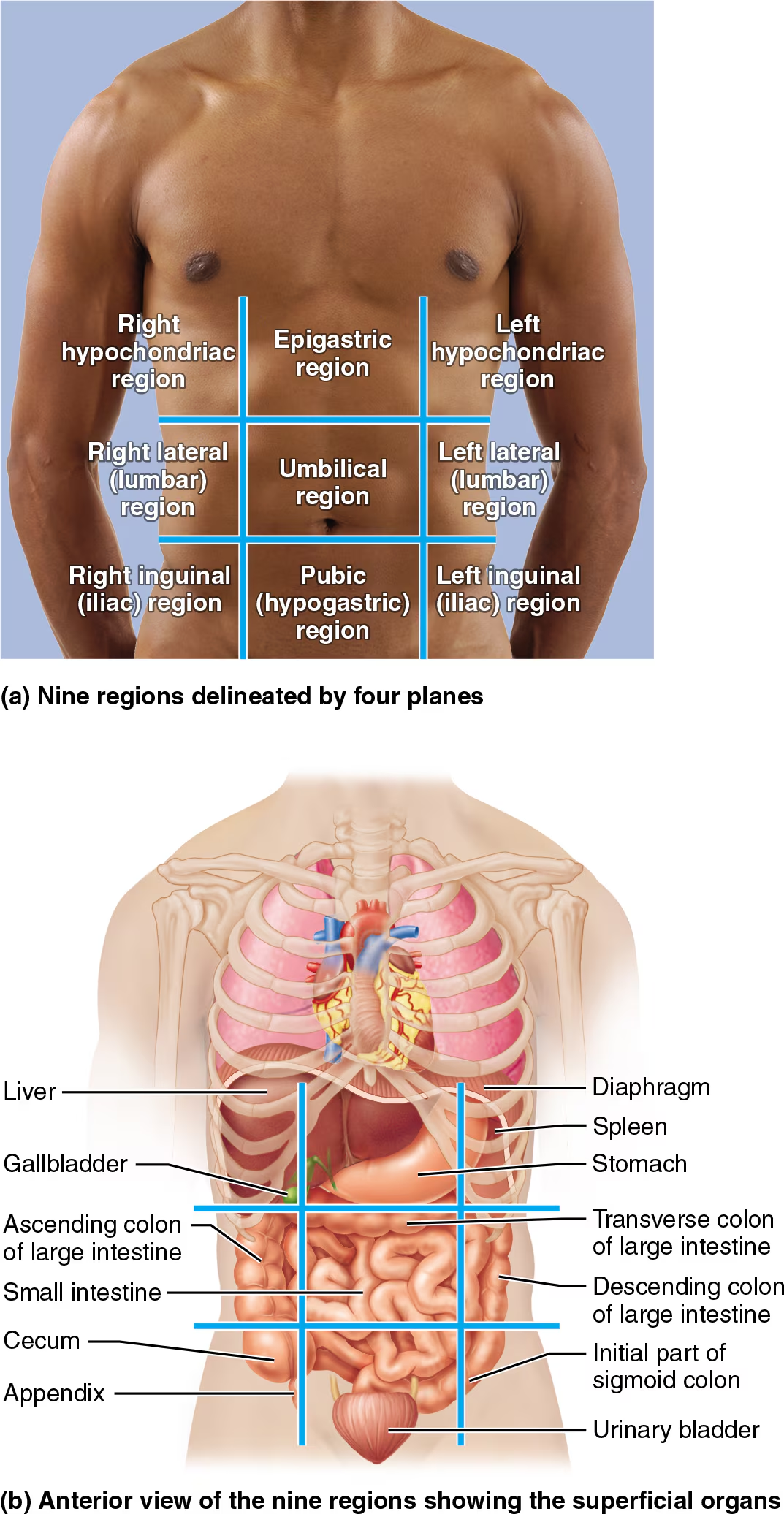
Nine abdominopelvic regions
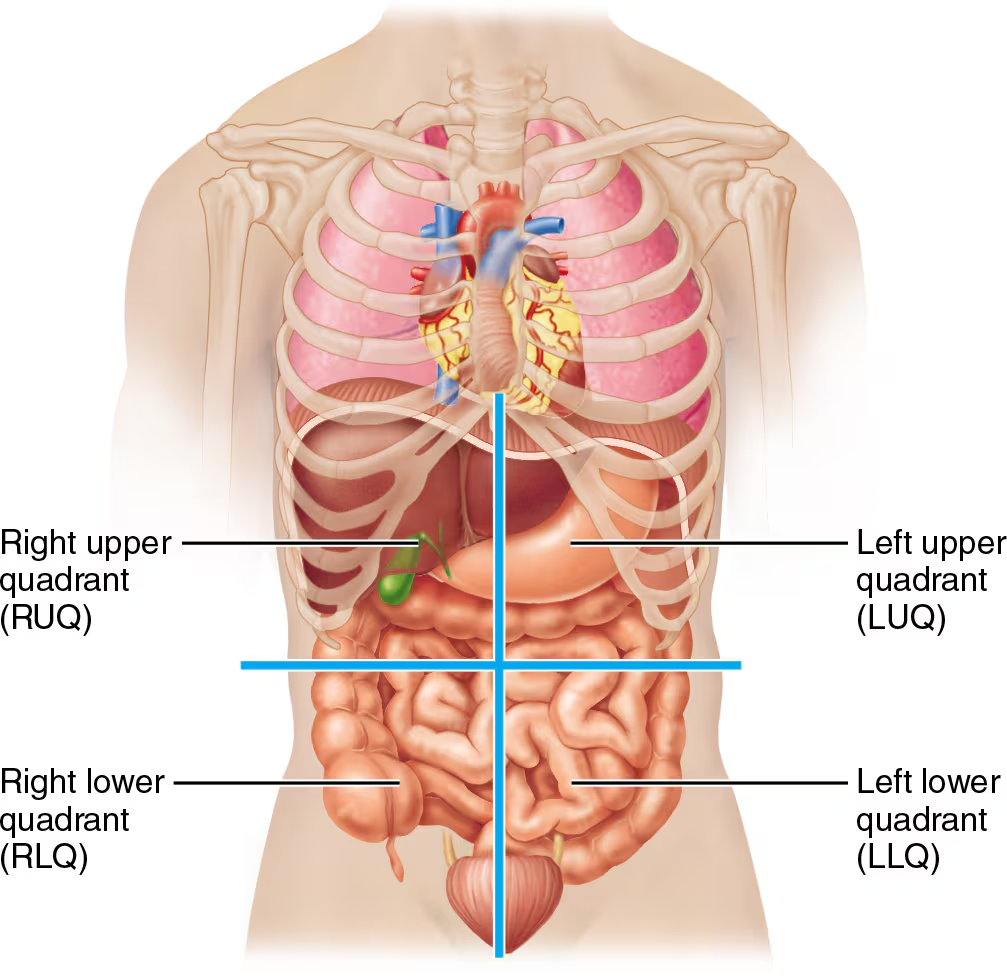
Four abdominopelvic quadrants
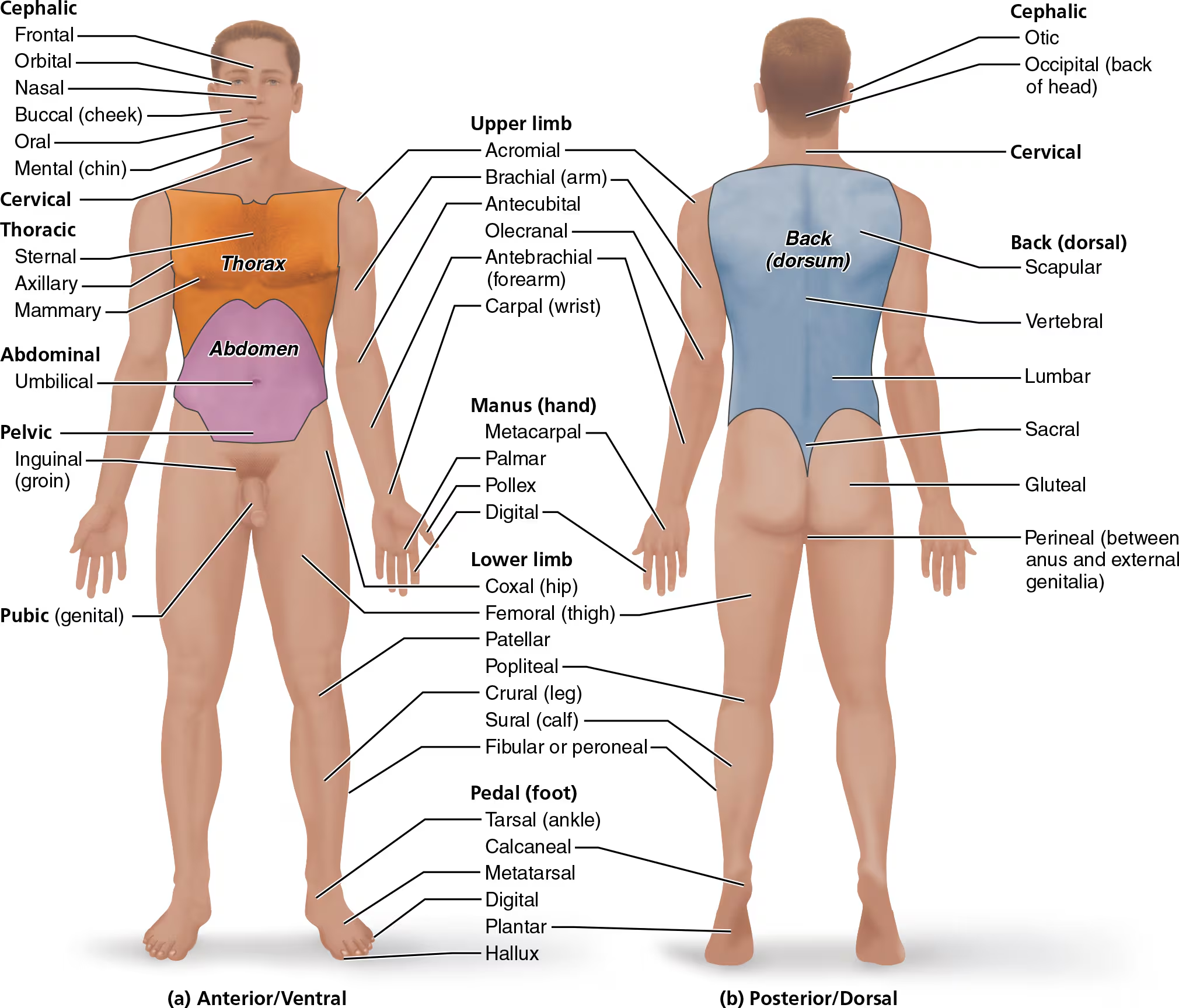
Surface body regions