The American Constitution, Part I
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms

Magna Carta (1215)
- established that everyone must follow the law, even the King

Mayflower Compact (1620)
-established that the law comes from the people and that people must obey laws made by the group

Articles of the Confederation (1781-1789)
-the first government of the United States, in effect from 1781 to 1789
- unicameral in structure (one house)

Articles of the Confederation (Strengths)
- Treaty of Paris (1783) and the ability to make other treaties
- Northwest Ordinance (1787)
- open trade state to state
- make war and peace
- build a navy/army
- borrow money
- send ambassadors to other countries
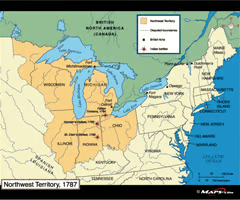
Northwest Ordinance (1787)
- It set up a government in the Northwest Territory guaranteeing basic rights to settlers.
- No slavery was allowed in the Northwest Territory.
- Once the territory had 60,000 free settlers, it could ask Congress to be admitted as a new state.
- considered a strength of the Confederate Constitution because it opened up a huge area to land expansion

Articles of the Confederation (Weaknesses)
- in debt and no way to pay
- can't impose taxes
- can't regulate interstate trade
- no executive branch
- no supreme court
- amendments require unanimous (all 13) vote
- new law required 9 of 13 votes
- really can't enforce any laws

Shay's Rebellion (1786-1787)
- an armed uprising by farmers in western Massachusetts in 1786-1787, protesting high taxes, debt collection, and the state's economic policies following the Revolutionary War
- illustrated the Articles of Confederation's

Constitutional Convention (1787)
- a meeting in Philadelphia to revise the Articles of Confederation, but delegates ended up creating the U.S. Constitution instead

The Virginia Plan
- presented at the Constitutional Convention as one proposal for the new constitution
- bicameral legislature (house and senate)
- favored the large states because representation would be based on state population

The New Jersey Plan
- presented at the Constitutional Convention as one proposal for the new constitution
- unicameral legislature (one house)
- favored the small states because representation would be equal regardless of state size
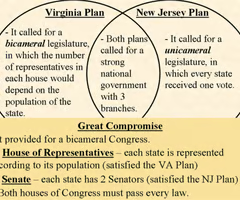
The Great Compromise
- an agreement during the 1787 Constitutional Convention that created a bicameral legislature
- Senate - each state will have 2 senators
- House of Representatives - representative number based on state population

3/5s Compromise
- enslaved people would be counted as three-fifths of a person for the purposes of both representation in the House of Representatives and taxation

Declaration of Independence (Grievance 1) - How was this grievance addressed in the new Constitution?
- "He (King George) has refused his Assent (agree) to Laws, the most wholesome and necessary for the public good."
--Very similar to Congress's ability to override a presidential veto when necessary.

Declaration of Independence (Grievance 2) - How was this grievance addressed in the new Constitution?
- "For suspending our own Legislatures, and declaring themselves invested with power to legislate for us in all cases whatsoever..."
--Sounds a lot like Article I, Section 1 of the Constitution: "All legislative powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States..."

Declaration of Independence (Grievance 3)
- "For imposing taxes on us without consent."
--Explains why colonists were unhappy about their lack of representation in the British parliament.

7 Principles of the new U.S. Constitution
- Popular Sovereignty
- Republicanism
- Federalism
- Separation of Powers
- Checks and Balances
- Limited Government
- Individual Rights

Popular Sovereignty
- the government gets its power from the people
- the people rule!
Ex. Amendment 19 gave women the right to vote (women, people, now have the power)
Republicanism
- people elect representatives to government to make decisions on behalf of the voters
Ex. Voters in Virginia elected the first African American governor to office in 1989
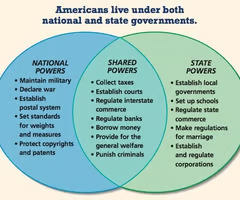
Federalism
- power is shared between the Federal Government and the state
Ex. states make marriage laws for their own state

Separation of Powers
- the Federal Government is divided up into 3 separate branches.
Ex. The President is commander-in-chief of the military
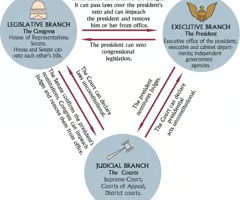
Checks and Balances
- 3 branches have the power to veto (check) the actions of the other branches
Ex. Congress approved President Reagan's appointment of Sandra Day O'Conner to the Supreme Court

Limited Government
- the government has only the power the Constitution gives to it
Ex. The President and all other government officials must obey the law like all American citizens

Individual Rights
- Protection of people's individual freedoms - found in the Bill of Rights
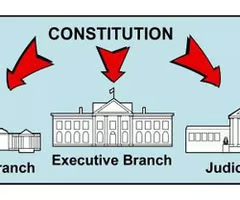
Three Branches of Government
Legislative
Executive
Judicial

Legislative Branch
Congress (Senate and House of Representatives)
- bicameral (two houses)
- make laws
- Article I of the Constitution

Executive Branch
President, Vice President, and Cabinet
- enforces/carries out laws
- Article II of the Constitution

Judicial Branch
Supreme Court and other federal courts
- interprets the laws
- Article III of the Constitution