Pharm Antipsychotics, Bipolar, Stimulants + Practice Questions
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
positive
These are all __________ symptoms of schizophrenia:
•Paranoid Delusions
•Auditory Hallucinations
•Enhanced Sensory Awareness
•Disorganized Behavior
negative
These are all __________ symptoms of schizophrenia:
•Diminished Sociability
•Restricted Affect
•Impoverished Speech
•Poor Self Care
> 2, > 6
Schizophrenia is diagnosed by ______ schizophrenia symptoms for ______ month
hallucinations
false sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
delusions
fixed, false beliefs despite evidence to the contrary
flat Affect
Anhedonia
Avolition
Alogia
Apathy/Asociality
List the negative symptoms of schizophrenia:
Hint "AAAAA"
catatonia
a state of unresponsiveness to one's outside environment, usually including muscle rigidity, staring, and inability to communicate
block receptors for dopamine
MOA of first gen antipsychotics for schizophrenia?
positive
First-gen antipsychotics are used especially for ________ symptoms in schizophrenia.
false - positive only
T/F: first gen antipsychotics are used for BOTH positie and negative sx in schizophrenia.
1-2 days
2-4 weeks
several months
How long does it take for first-gen antipsychotics to have initial effects?
how long for substantial improvement?
how long for FULL effects?
haloperidol
What is the high-potency first-gen antipsychotic drug used in schizophrenia?
true
T/F: despite the higher risk of having EPS, Haloperidol is the preferred FGA for initial therapy in schizophrenia because it causes LESS sedation, orthostatic hypotension and anticholinergic effects.
acute
Haloperidol is used for acute or chronic psychosis?
chlorpromazine, thioridazine
List the low potency first gen antipsychotics for schizophrenia?
less, more
When compared to high potency FGA, the low potency FGAs have ________ EPS sx and _________ sedation, hypotension, and anticholinergic effects.
acute dystonia (reversible, hours-days)
akathisia (reversible, days-weeks)
pseudoparkinsonism (reverisble, weeks-moths)
list the timeline for Drug-induced movement disorder (EPS).
extrapyramidal sx
What are the ADE of FGA?
acute dystonia
spasm of the muscles of tongue, face, neck, back
usually starts within hours/days of starting/increasing dose
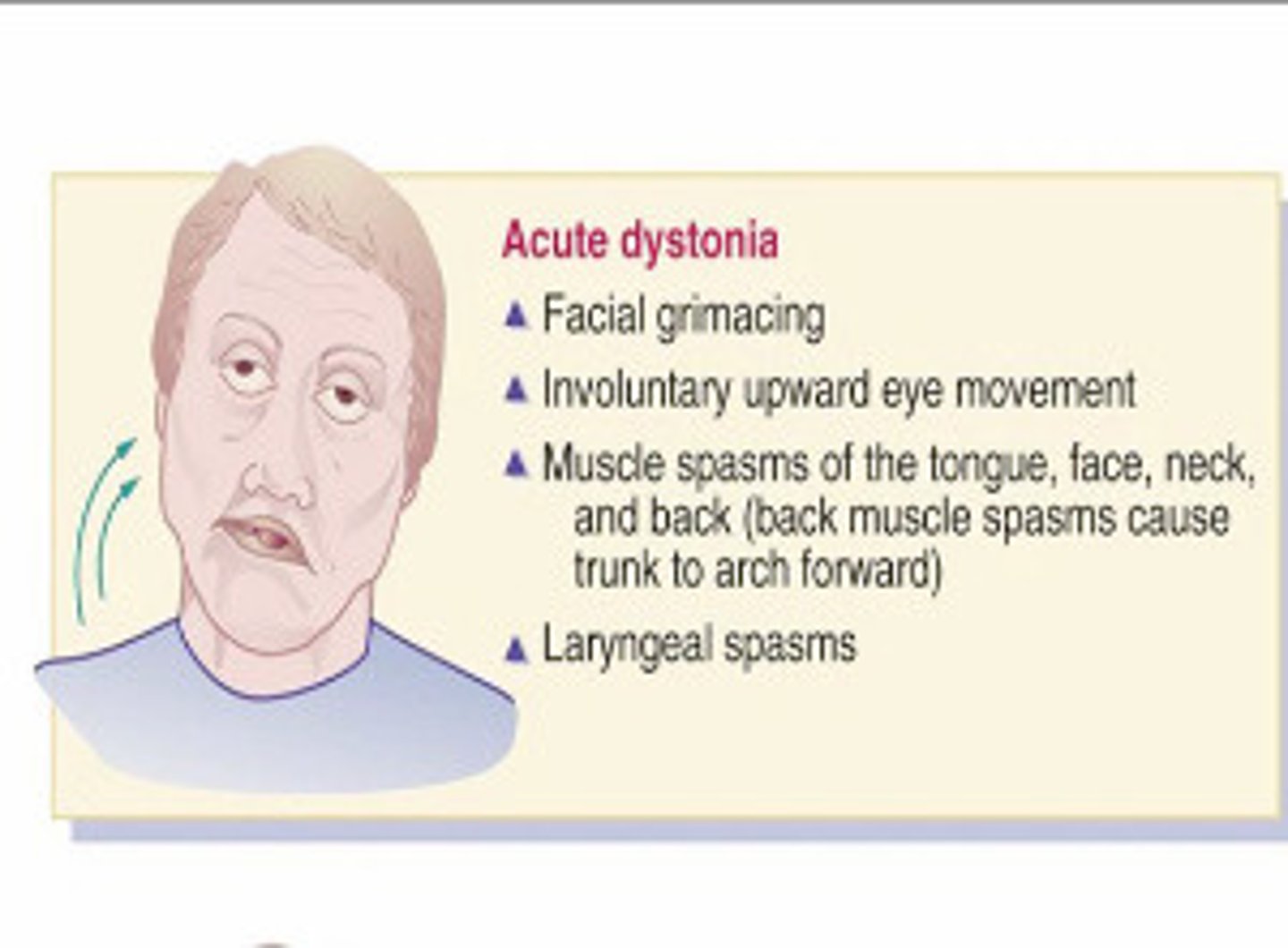
diphenhydramine
benztropine
How do you tx acute dystonia?
parkinsonism
bradykinesia, mask-like facies, tremor, rigidity, shuffling gait, drooling, cogwheeling, stooped posture, resting tremors (pill-rolling)
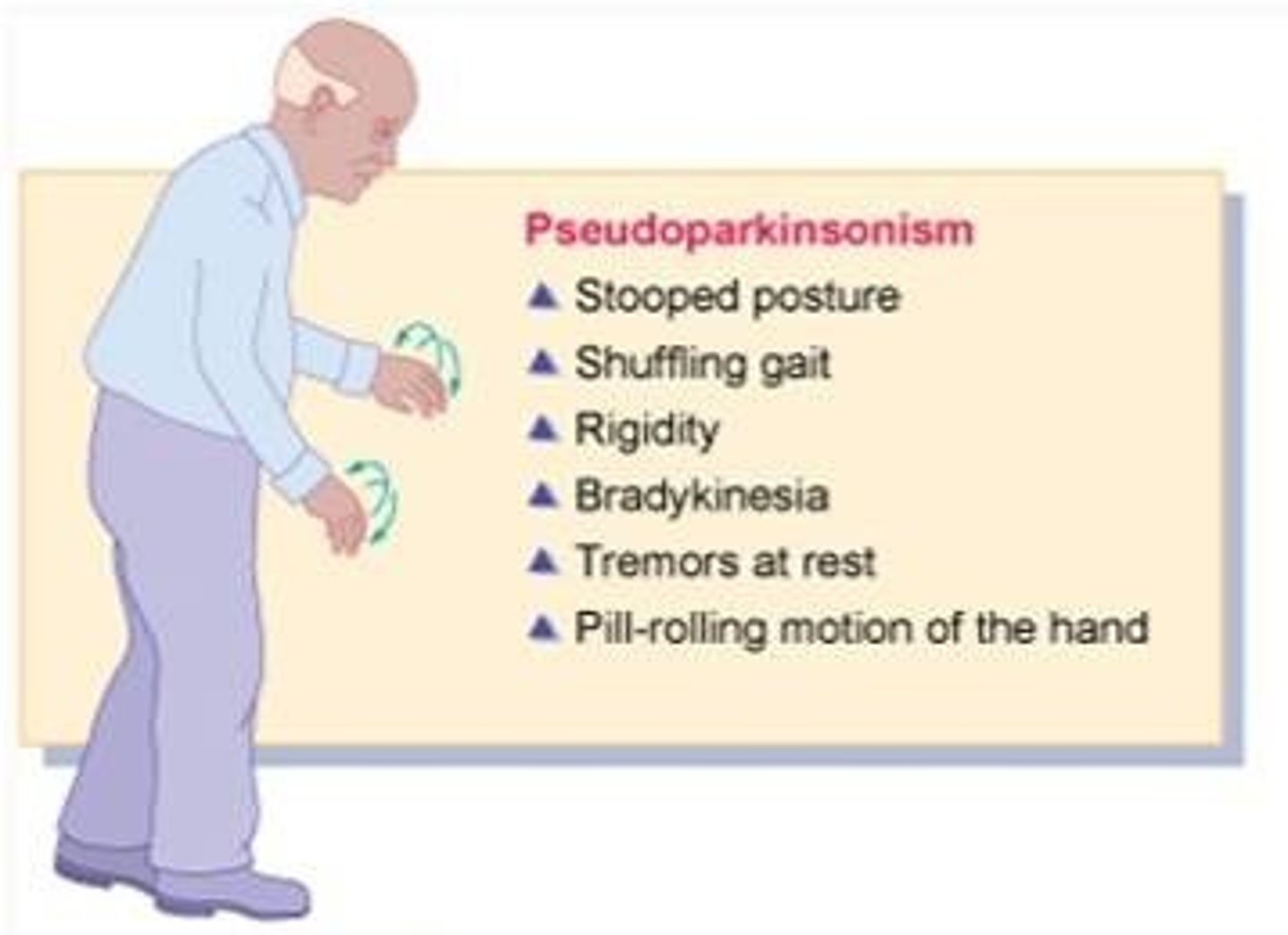
benztropine
amantadine
anticholinergics
How do you treat parkinsonism?
akathisia
MC EPS symptom.
"inner restlessness"
compulsive, restless movements, anxiety, agitation, inability to sit still
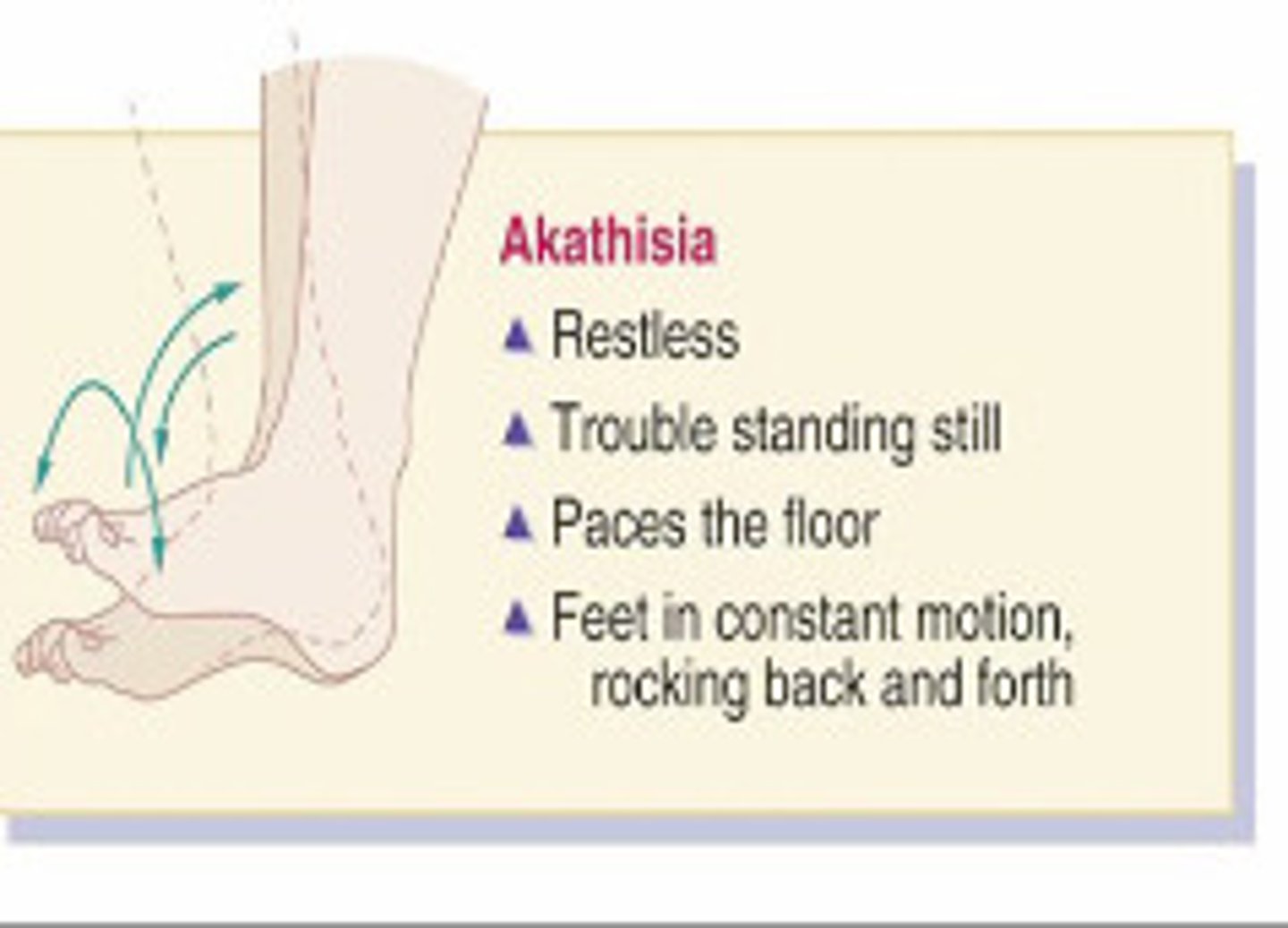
reduce dosage or switch meds
benzotropine
propanolol
What is the tx for akathisia?
tardive dyskinesia
What adverse effect from taking FGA occurs later on and has less reliable treatment?
d/c offending agent
switch to SGA (slozapine)
What is the tx for tardive dyskinesia?
VMAT2 inhib
Benzodiazepine
What is symptom management for tardive dyskinesia?
Valbenazine (Ingrezza)
Deutetrabenazine (Austedo®)
Tetrabenazine (Xenazine®)
List the VMAT2 inhibitors.
hint "Benazine"
inhibit VMAT2 which decreases reuptake of dopamine into vesicles
What is the MOA of VMAT2 inhibitors?
worsened depression
emergent suicidality
Patients on VMAT2 inhibitors should be monitored for which side effect?
neuropletic malignant syndrome
This adverse side effect of Schizophrenia meds is rare (4% mortality risk) and is more likely to present with high potency FGAs.
"Lead pipe rigidity, sudden high fever, sweating, autonomic instability, dysrhythmias, BP fluctuations"
d/c antipyschotic, antipyretics, hudration, benzos
dantrolene (skeletal muscle relaxant)
bromocriptine (dopamine agonist)
What is the tx of neuropletic malignant syndrome>?
2 weeks
After treating neuropletic malignant syndrome, wait _____ weeks before initiation of antipsychotic, and consider SGA.
Anticholinergic effects
orthostatic hypotension
PROLONGED qt
sedation
neuroendocrine effects
seizures
sexual dysfunction
aganulocytosis
List all of the other adverse effects of first gen antipsychotics.
T/F: ALL FGA have a BBW for increase risk of mortality when used to treat dementia-related psychosis in older adult patients.
Aripiprazole
Risperidone
Clozapine
Olanzapine
Quetiapine
List the second gen antispcyhotics.
block receptors for dopamine and serotonin (5-HT)
What is the MOA of second gen antipyschs?
less blockade of dopamine D2 receptors
Why do SGAs cause less EPS than FGAs?
true
T/F: SGAs are preferred over FGAs due to less EPS sx including tardive dyskinesia.
false - help with both pos and neg
T/F: SGAs only help with positive symptoms.
psychosis and bipolar mania
What are SGAs used for?
clozapine, olanzapine
Which SGAs have serious metabolic effects including weight gain, diabetes, and dyslipidemia --> lead to cardiovascular event and premature death.
clozapine
Which SGA is more effects than other agents and is reserved for pts who have not responded to other antipsychotics + has significant side effects and medical risks
REMS program
What is required before prescribing clozapine?
monitoring WBC and ANC
check for agranulocytosis
must be WNL prior to starting
What is included in the REMS program before prescribing clozapine?
weekly for 6 months
2 weeks for additional 6 months
How often do you check WBC and ANC before starting clozapine?
WBC < 3000
WBC < 2000
When should you STOP taking clozapine?
when should you permanently stop?
myocarditis
stop med and never use again!
What is the rate but fatal BBW specific to clozapine?
if occurs, what should you do?
anticholinergic effects
orthostatic hypotension
sedation
neuroendocrine effects
seizures
prolonged QT
What are the ADEs of SGAs?
agranulocytosis
Which ADE of SGAs causes marked leukcytopenia (esp neutrophils), high fever, weakness, necrotizing oral lesions, hypotension and increased infection risk?
measure weight, blood sugar, lipids prior to starting + monitor throughout treatment
How should you monitor the metabolic effects of SGAs?
oral
What is the preferred route of administration of antipsych meds?
intramuscular
Which route of admin is reserved for pts with severe, acute schizophrenia and for long term maintenance?
whichever one worked well in the past
When picking a medication for schizoprenia, which should you choose first?
2
patient must be on manufacturer recommended dose for ____ weeks minimum before declaring failure
clozapine
Which med should be considered in patients with suicidal ideation?
clozapine
If a patient has failed two appropriately dosed antipsychotic meds which med should you try next?
retry monotherapy with med not used before
combo therapy (little evidence)
augment w/ non antipsychotic meds
If clozapine has failed, what should you do next?
haloperiodol
diphenhydramine or benztropine
What is the medication of choice for a patient with severe agitation?
If given IM, what should you also give to reduce EPS risks?
olanzapine
Your patient presents to the ED with severe agitation. They agreed to take an oral medication. What med should you give them?
quetiapine
Which medication should be used for patients with insomnia + schizo because its more sedating?
FGA or aripiprazole
Which med should you give to patients with schizo + at risk for metabolic syndrome?
lowest
Patients > 70 years old with schizo should be given _______ dose
Ziprasidone
Quetiapine
Chlorpromazine
IV haloperidol
A patient with long QT risk should avoid which meds?
weekly (adjust pharm and psychosocial tx)
When should you follow up after an acute episode of schizo?
monthly (if continues in remission)
After 3 months, when should you follow up with your schizo patient after an acute episode?
med benefits
side effects
adherence
What needs to be discussed at every follow up appointment?
relapse
After control of an acute episode, antipsychotic therapy should continue indefinitely because a withdrawal of medication can cause _________.
long acting depot injection
Which med is good for patients with relapse due to nonadherence?
q 2-4 weeks
How often are depot injections given for maintenance?
maintenance
All schizophrenic patients should have __________ therapy to reduce relapse risk.
A newly diagnosed patient with schizophrenia is seen and needing to start treatment. Which of the following antipsychotic agents may have the best chance to improve his apathy and blunted affect?
Olanzapine
1 multiple choice option
A patient is treated with haloperidol for schizophrenia. His psychosis is well managed with haloperidol; however, he is reporting restlessness and the inability to sit still at the dinner table. He also states that his family notices that he frequently paces the hallway. Which of the following is the best describes these symptoms?
Akathisia
3 multiple choice options
A patient with a history of treatment-resistant schizophrenia presents for routine monitoring of absolute neutrophil count, as the medication he was prescribed can cause severe neutropenia or agranulocytosis. Which medication is the patient most likely taking?
Clozapine
3 multiple choice options
A patient with schizophrenia is experiencing the extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) of dystonic reactions in his arms and shoulders from perphenazine. He is now being considered for a switch to an antipsychotic with a lower risk of EPS. Which of the following agents is the most appropriate choice for this patient?
Quetiapine
3 multiple choice options
bipolar disorder
Recurrent fluctuations in mood:
Abnormally elevated
Abnormally depressed
Periods of normalcy
Pure manic episode (euphoric mania)
Hypomanic episode (hypomania)
Major depressive episode (depression)
Mixed episode
What are the 4 types of mood episodes in bipolar disorder?
bipolar I disorder
manic episode +/- major depressive +/- hypomanic episode
bipolar II disorder
hypomanic episode + major depressive episode
mood stabs
antipsychotics
antidepressants
What 3 medication types are used in bipolar disorder?
lithium
divalproex sodium
carbamazepine
List the 3 mood stabilizers used in bipolar disorder.
SGA (olanzapine, risperidone)
list the antipsychotics used in bipolar disorder.
Bupropion
Venlafaxine
Fluoxetine
Sertaline
List the antidepressants used in bipolar disorder.
lithium
What is the drug of choice for patients with acute mania in bipolar disorder?
5-7 days
2-3 weeks
How long does lithium take for the antimanic effect onset?
How long does it take to reach full benefit?
use care with renal impairment
Lithium is excreted by the kidneys unchanged therefore you should do what?
increases lithium levels
use caution with diuretics
diarrhea/dehydration
If a patient has hyponatremia, how does this effect lithium levels?
How should you avoid this?
what can increase lithium levels to toxicity?
GI sx
tremor
polyuria
renal toxicity
goiter and hypothyroid
teratongenic
What are the adverse effects of lithium at therapeutic levels that are early and subside?
reduce with BB
How can you reduce the adverse effect of tremors in a patient on lithium?
drink 8-12 glasses if fluids daily
reduce with amiloride
How can you reduce the polyuria adverse effect of lithium?
thyroid panel
What do you need to obtain before prescribing a patient lithium because one of the ADE is hypothyroidism?
Hepatotoxicity
Pancreatitis
Teratogenic
What is the BBW for lithium?
narrow
2-3 days
3-6 months
}
Lithium has a ________ therapeutic index. Therefore plasma drug levels must be measured routinely.
Beginning of tx: every ________ days.
Maintenance: every ___________ months.
underlying renal insuff
effective volume depletion
older adult pts
When is the risk of lithium toxicity increased?
hemodialysis
What is the tx for lithium if its elevated > 2.5?
increase, increase
Diuretics _______ risk for lithium toxicity
NSAIDS ______ lithium levels by up to 60%
true
T/F: you can not use NSAIDS with lithium, however you CAN use aspirin
divalproex sodium (valproate)
valproate sodium (depacon)
valproic acid (depakene)
List the antiepileptic drugs that are first line BPD treatment options.
Used for sx control in acute manic episodes and prevention of relapse into mania.
pancreatitis
liver fail
teratogenic
What are the BBW adverse effects of divalproex sodium (valproate)?
CBC w/ diff
drug lvl
fasting BG
lipid panel
LFTs
weight
What do you need to monitor in a bipolar patient on divalproex sodium (valproate)?