VT111 Lec. 8 Arthrology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
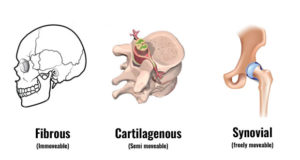
Types of Joints: Arthro-
Junctions between bones
3 types of joints:
Fibrous:
ex: sutures of skull
essentially immovable (synarthrotic joint)
Gomphosis: teeth in socket-not a true joint
Cartilaginous:
ex: symphysis of pubis; intervertebral joints, mandibular symphyis
very slightly movable (amphiarthrotic joint); “rocking joints”
Synovial:
ex: joints of limbs
freely movable, bones separated by joint cavity containing synovial fluid (diarthrotic joint)
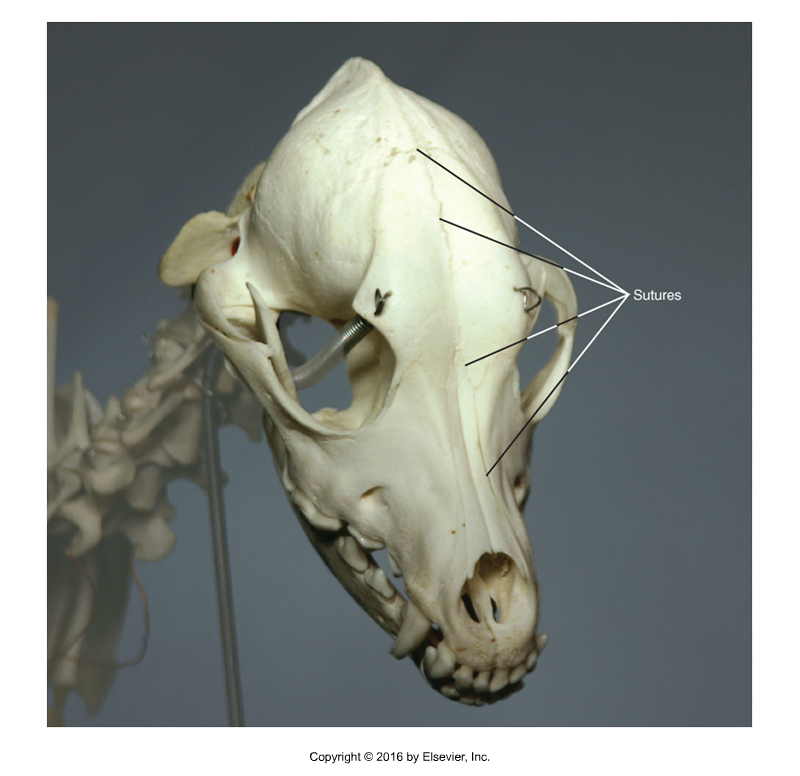
Type of Joint?
Fibrous joint
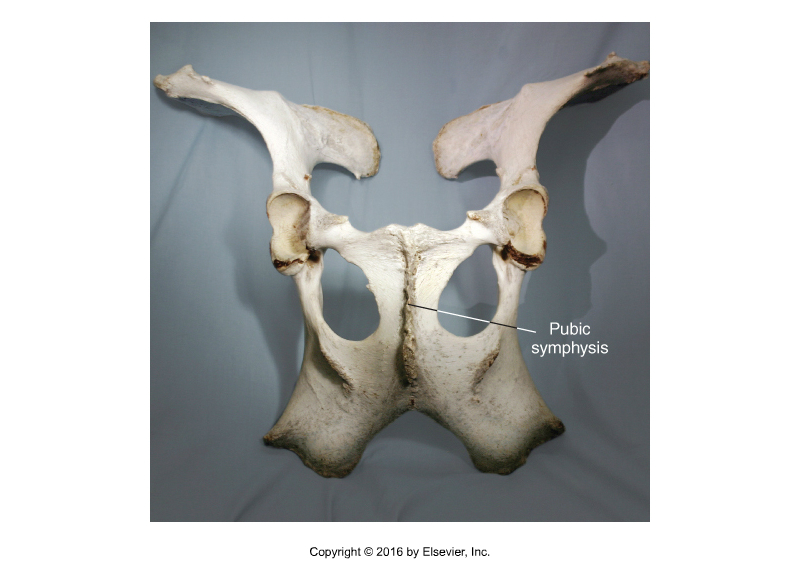
Type of Joint?
Cartilaginous joint
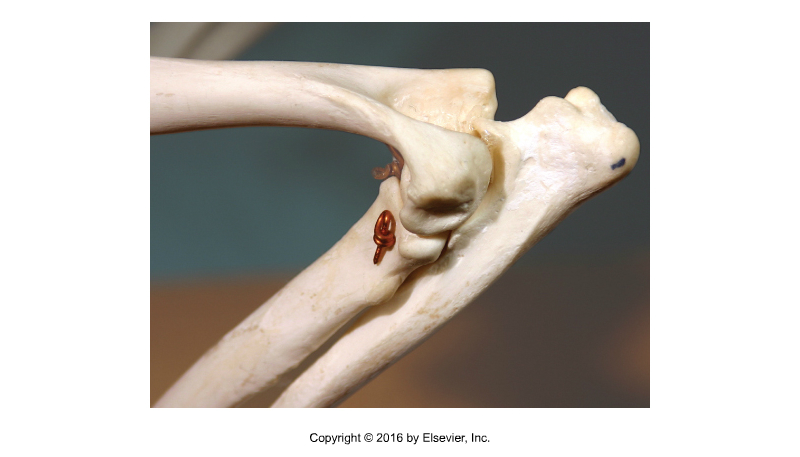
Type of Joint?
Synovial joint → Hinge joint
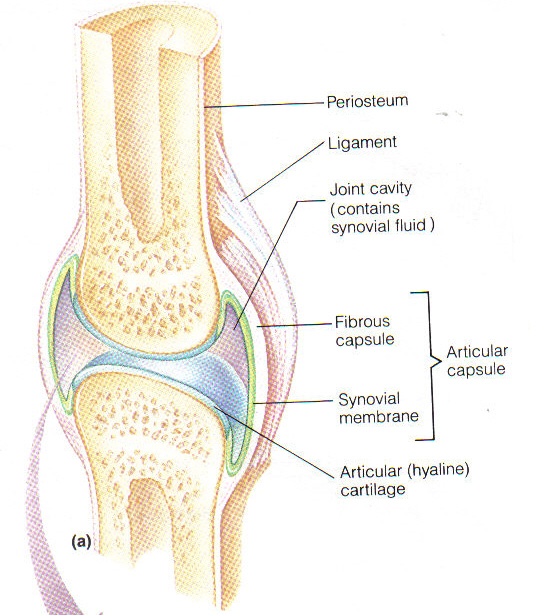
Structures of a Diarthrotic Joint
Articular cartilage covers articular surface of bone
Hyaline cartilage
Teflon-like coating to reduce friction
Joint space/cavity
Fluid filled
Surrounded by fibrous joint capsule
Capsule lined by vascular synovial membrane
Secretes joint fluid (synovial fluid)
“motor oil”; nutrient transport
+/- Reinforcing ligaments
Fibrous connective tissue
Dense regular
Stability to joint
Join bones to other bones
(tendons join muscle to bone)
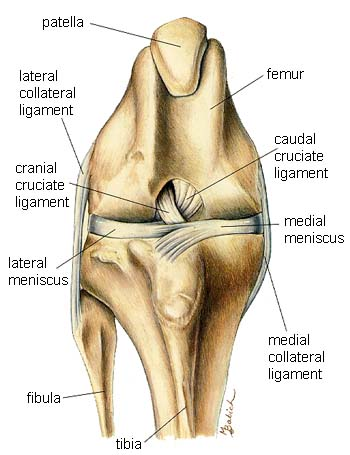
Synovial (Diarthrotic) Joint
What joint is this?
femorotibial joint = stifle joint
Ligaments to stabilize
Connect bone to bone
Area of possible injury
Meniscus
Made of hyaline cartilage
Padding
Classification of Synovial Joints
Number of articulating surfaces
Simple = 2
Compound = >2
Function of joint
Shape or form of the joint
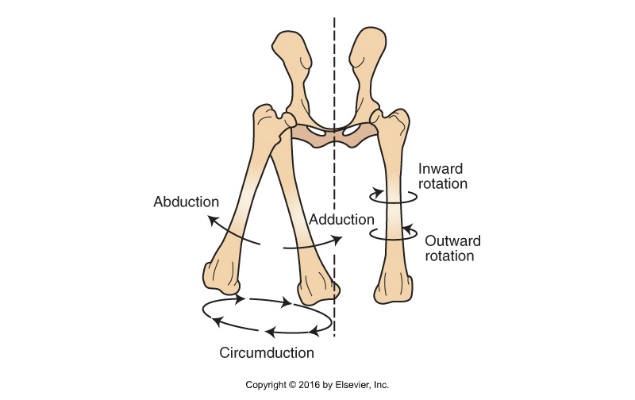
Types of Joint Movement
Flexion: decreases angle between two bones
Extension: increases angle between two bones
Adduction: movement of extremity toward medial plane
Abduction: movement away from median plane
Rotation: twisting on its own axis
Circumduction: distal end of extremity moves in a circle
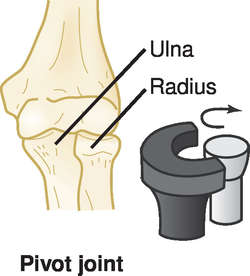
Types of synovial joints based on movement, shape and/or form
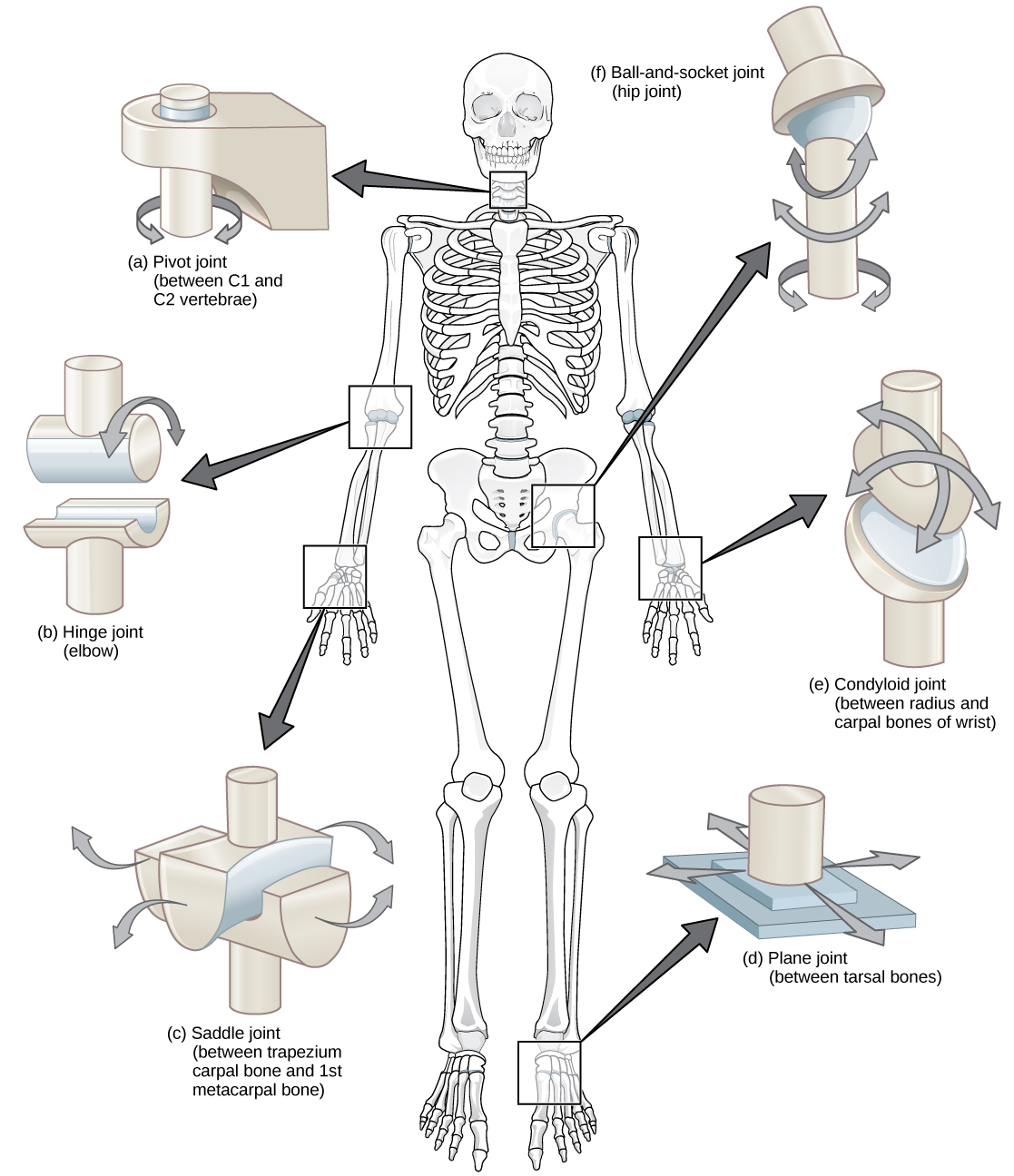
Hinge joint (ginglymus): movement in a single plane like a gate hinge (elbow). Only flexion and extension.
Gliding (plane) joint: joint surfaces are flat; movement between is a rocking motion of one bone on another, like carpal joints.
Pivot joint: rotational around a pivot point, like radio-ulnar joint or atlantoaxial joint
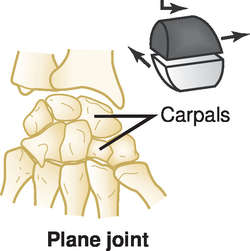
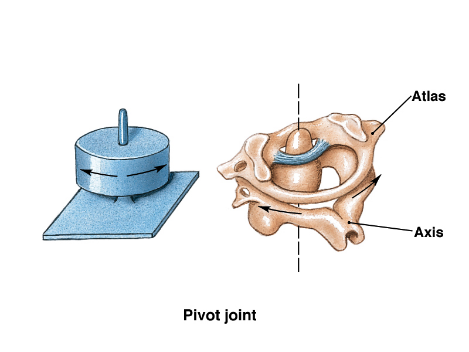
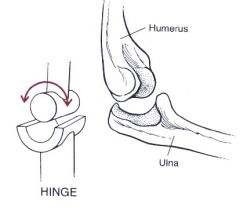
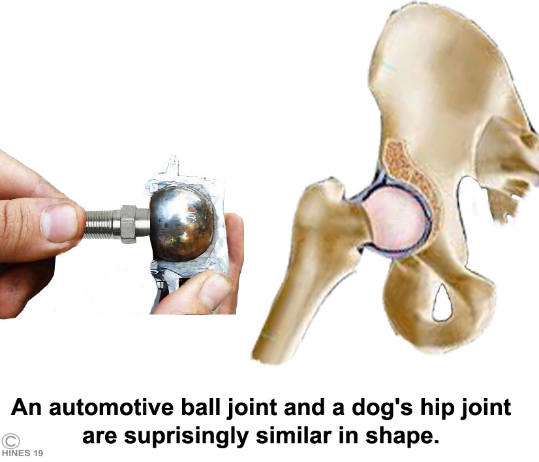
Types of synovial joints based on movement
Ball and socket (spheroidal): self explanatory, like coxofemoral (hip) joint. Allows for all types of movement: adduction, abduction, circumduction etc.
Condyloid joint (ellipsoidal): rounded projection (condyle; “knuckle-shaped”) of one bone fits depression of another bone similar to knuckle or femorotibial joints. Allows movement in two planes.
Saddle joint: where two bones fit together like sitting in a saddle (carpometacarpal joints)
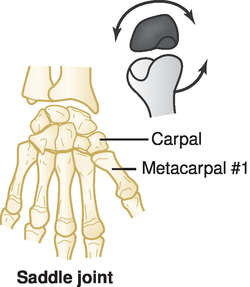
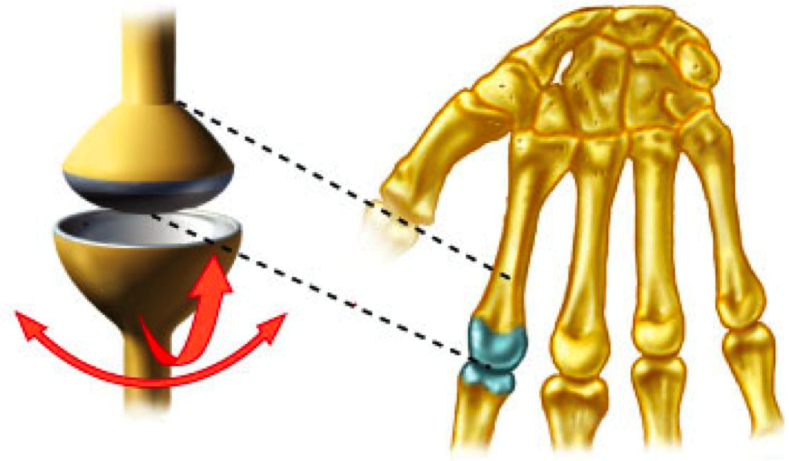
Diagram of Different Joints
What Type of Joint?
A. Atlas vertebrae → head = synovial joint = hinge joint = atlantooccipital joint = neck to head → “yes” joint
B. Atlas vertebrae → axis vertebrae = pivot joint = synovial joint = atlanto-axial joint = “no” joint
What Type of Joint?
synovial joint = Scapulohumeral = ball in socket = shoulder joint
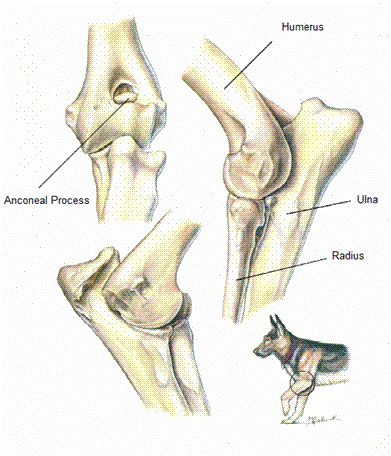
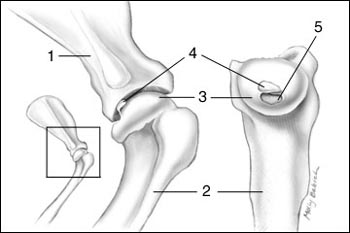
What Type of Joint?
synovial joint = Humeroradioulnar = elbow joint = hinge joint → flexes and extends
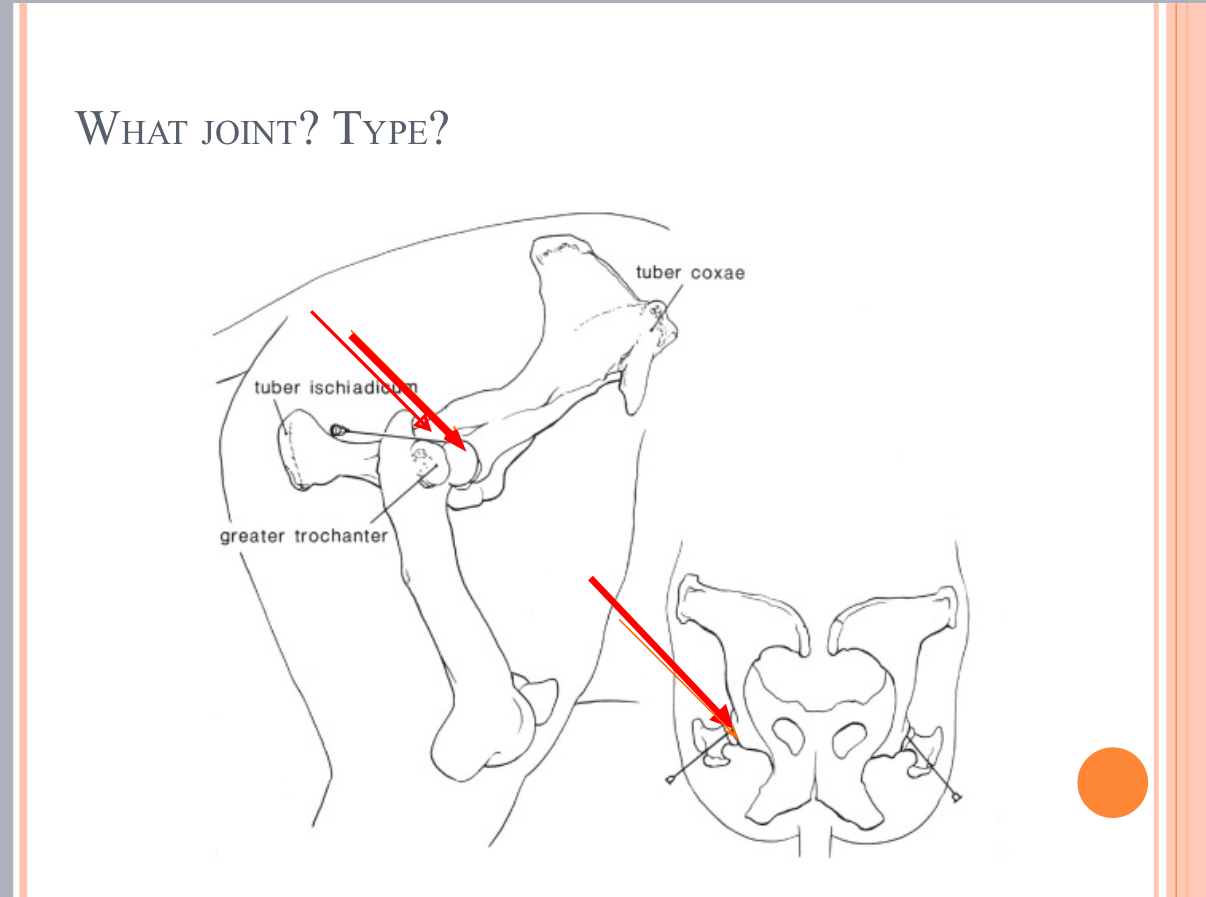
What Type of Joint?
Cartilaginous joint = sacroiliac joint = loin/croup joint → slightly moveable
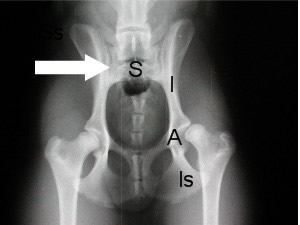
What Type of Joint?
Synovial joint = coxofemoral joint = ball in socket joint = hip joint
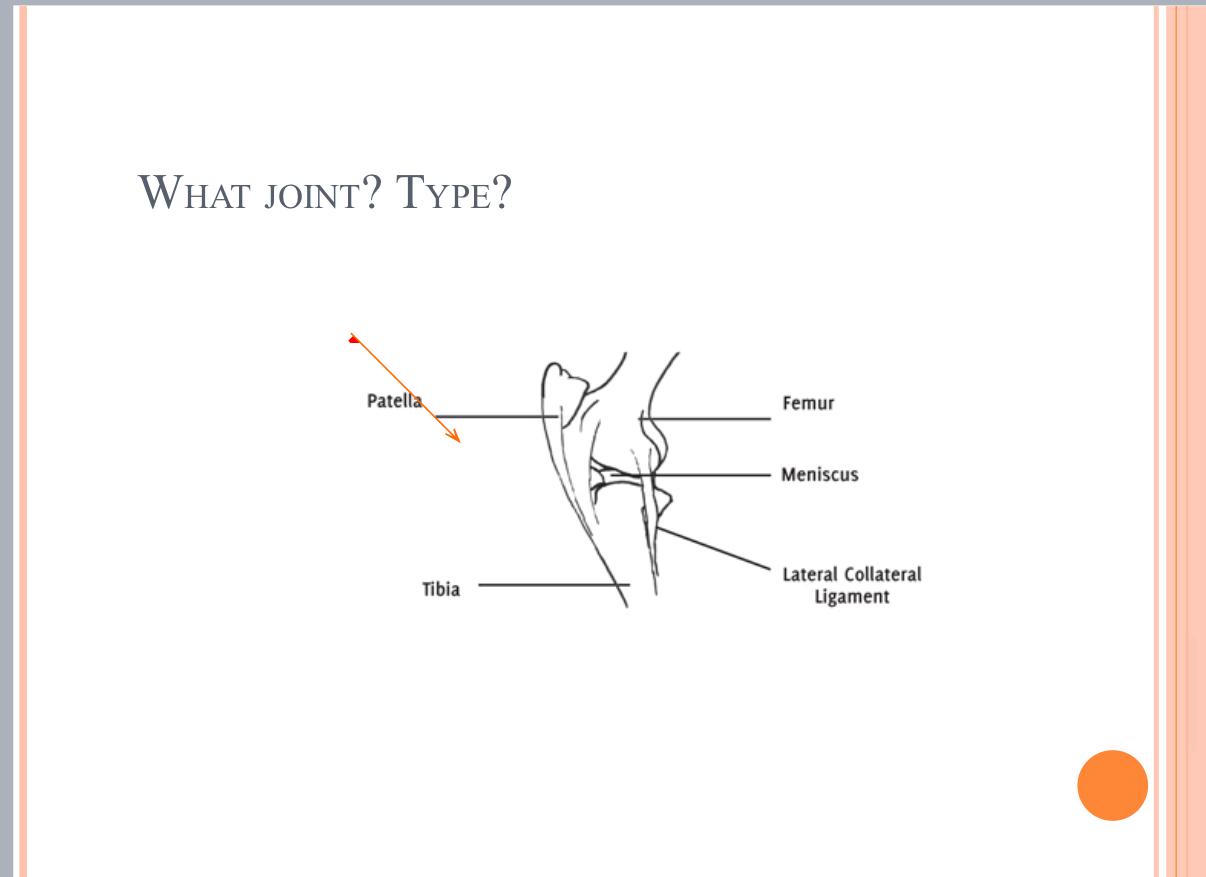
What Type of Joint?
synovial joint = femorotibial joint = condyloid (elipsoidal) joint = stifle joint
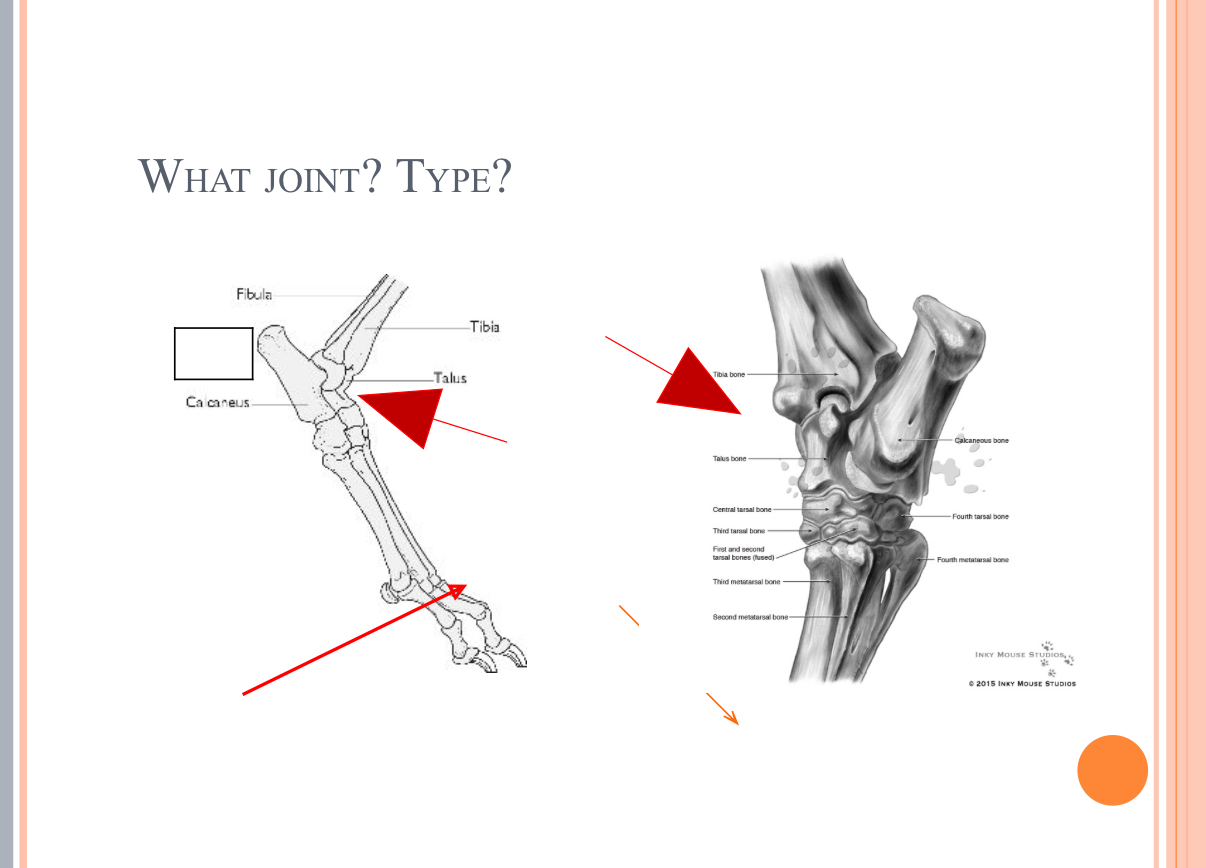
What Type of Joint?
synovial joint = tibiotarsal joint = hinge/gliding joint = hock joint
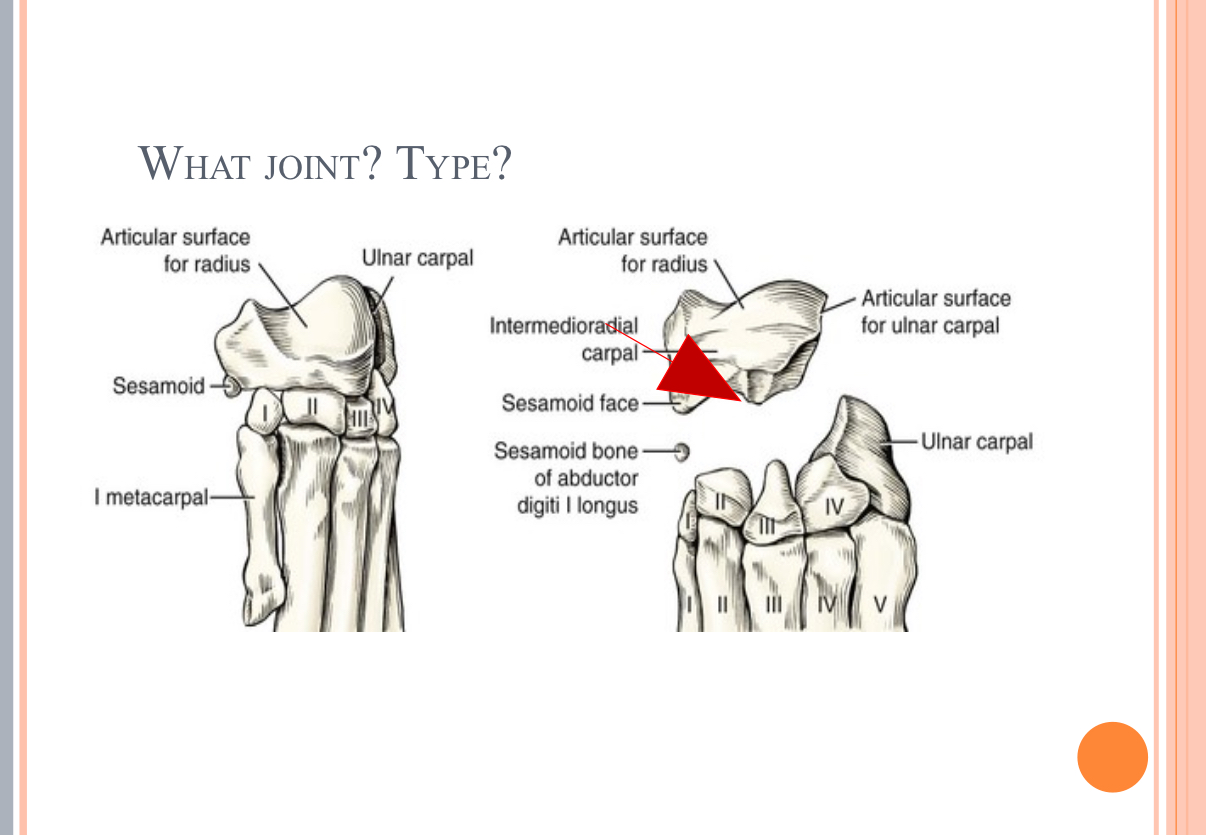
What Type of Joint?
synovial joint = Intercarpal joint = gliding joint = wrist (knee in horse) joint
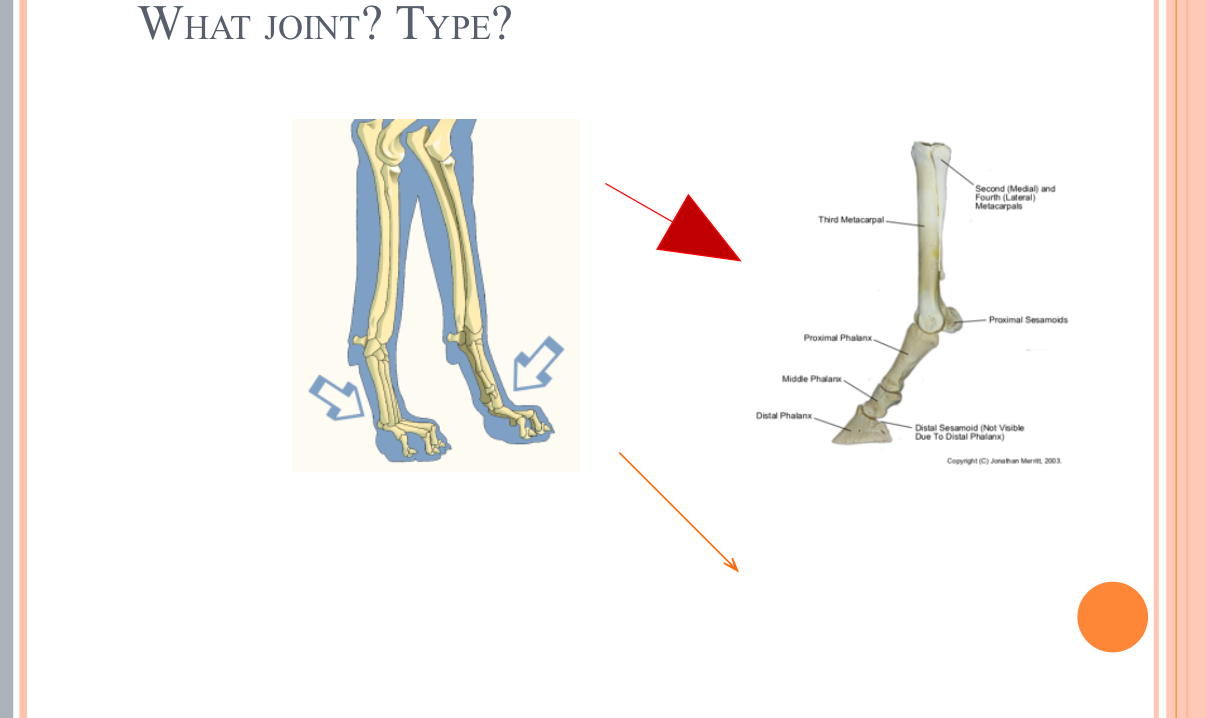
What Type of Joint?
Synovial joint = Proximal metacarpophalageal joint = hinge joint = fetlock joint (horse) flexion/extension; condyloid joint in a dog
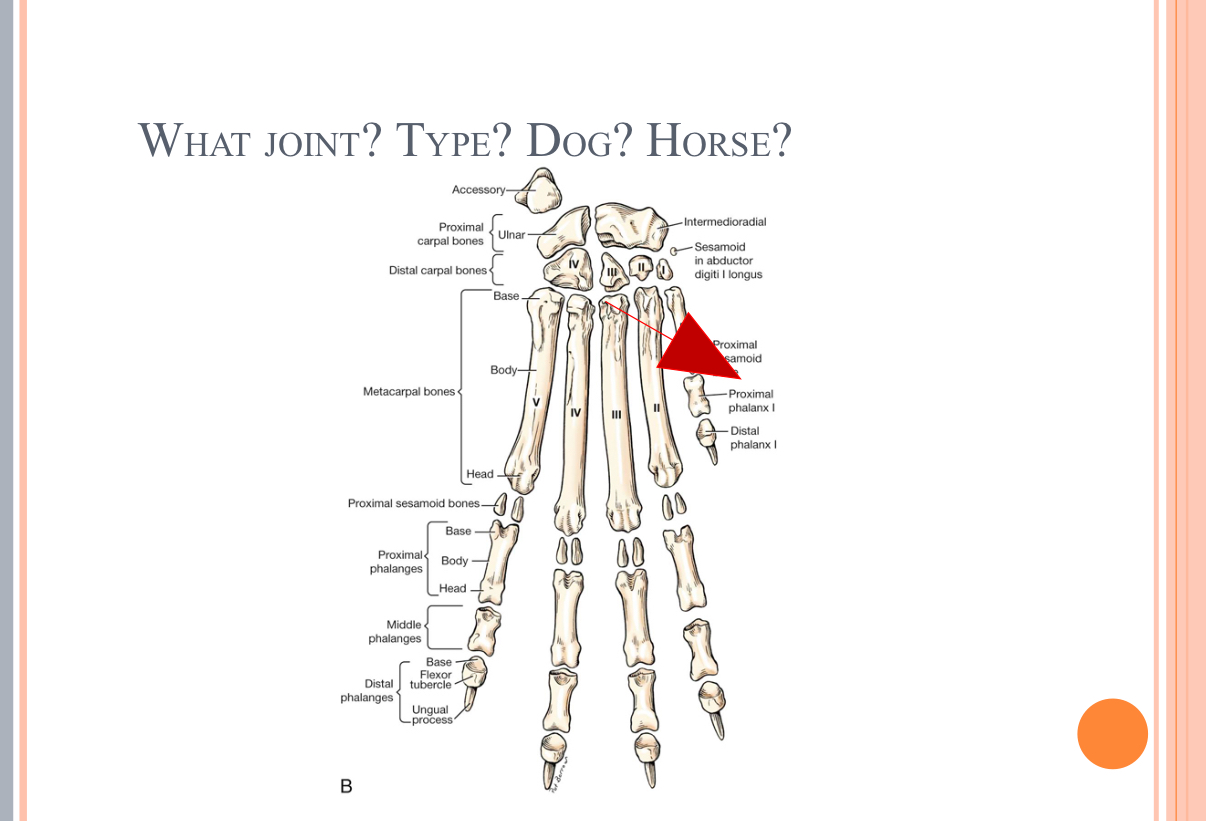
What Type of Joint?
Synovial joint = Saddle joint = Distal Interphalageal joint = coffin joint (horse)
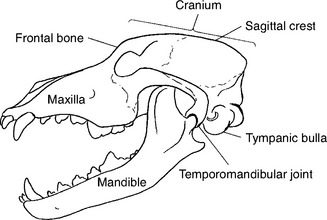
What Type of Joint?
synovial joint = tempromandibular joint = condyloid (elipsoidal) joint = jaw joint