astronomy
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
black hole
a region of space having a gravitational field so intense that no matter or radiation can escape.
event horizon
a theoretical boundary around a black hole beyond which no light or other radiation can escape.
accretion disk
a flat, rotating disk of gas and dust surrounding a condensed mass, such as a young stellar object, a forming planet, or a collapsed star in a binary pair
singularity
A point in which matter is infinitely dense, as in the center of a black hole or the universe at the very beginning.
big bang theory
the theory that all matter was originally compacter with infinite density and heat, called a singularity. it began expanding slowly and cooled off into the world that we know it.
cosmic background radiation
also known as microwaves. the leftover radiation from the big bang, observed by the COBE, WMPA and Plank satellites
significance of cosmic background radiation
-it has travelled very far
-we are seeing it as it was years ago
-allows us ot learn about the conditions of the universe at a large scale
Galaxies (us and the nearest)
Us: Milky way galaxy
Nearest: Andromeda galaxy
Light year
the distance light travels in one Earth year (365 days)
Theory of Relativity
-all matter is equal to light
-energy and matter are equal because they are different forms of the same thing
-energy moves at the speed of light
*Einstein's theory
how does gravity work
-gravity is a distortion of space caused by the presence of matter or energy (gravitational fields are generated by warping the geometry of the space around the object)
Edward Hubble
-discovered the universe was expanding
-1929
-discovered light moved towards the rid of light spectrum
-universe is expanding --> galaxies moving apart --> increase in volume = decrese in density
Hubble telescope
-size of a school bus
-uses energy from solar panels
-pictures of locations 13.4 billion light years away
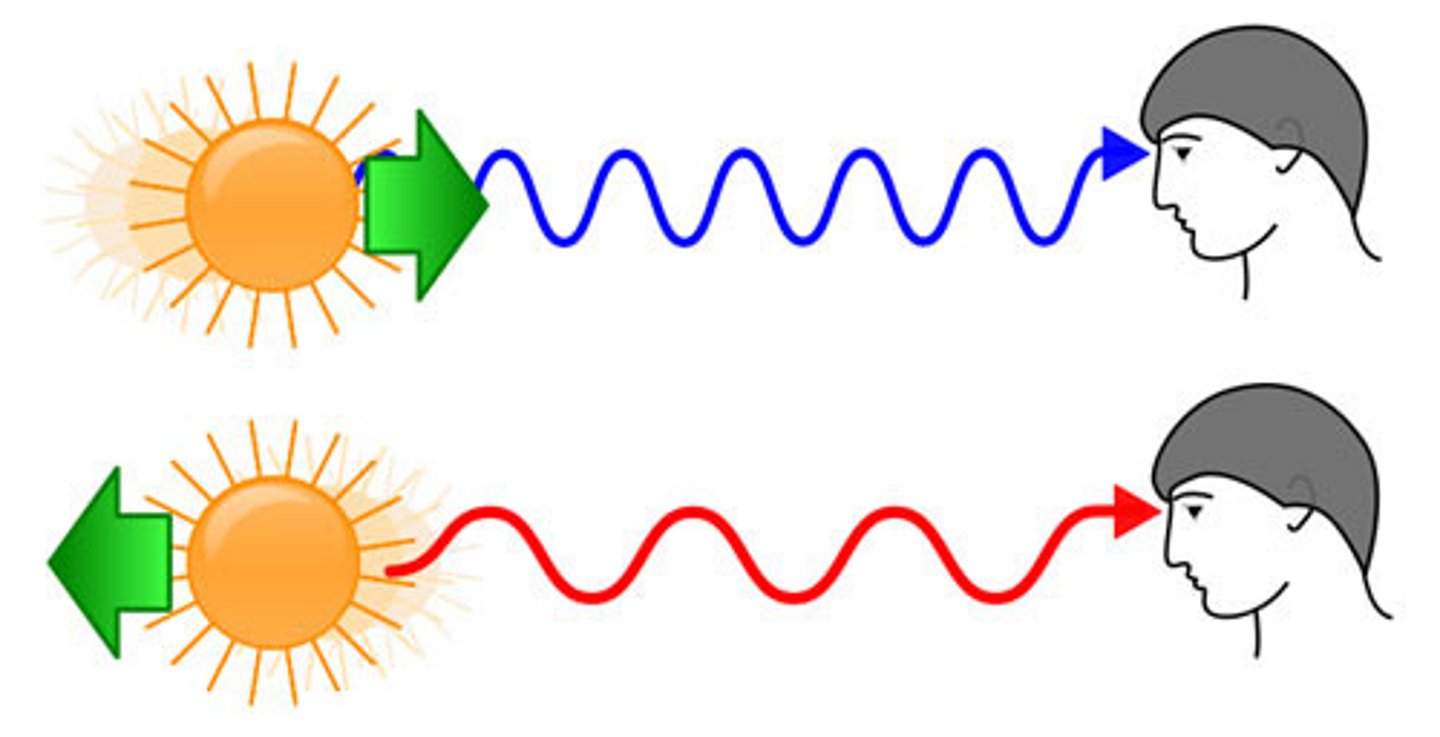
Doppler effect
Red and Blue Doppler shift
-describes the changes in frequency of a light wave
-Doppler effect is waves will be bigger if slow/low energy and smaller if higher energy
-when an object moves away the light is known as a red shift
-when it moves towards us the light is a blueshift
-used to estimate the object's distance from the earth
-the wavelength of light is stretched, and therefore "shifted" toward the red or blue part of the spectrum
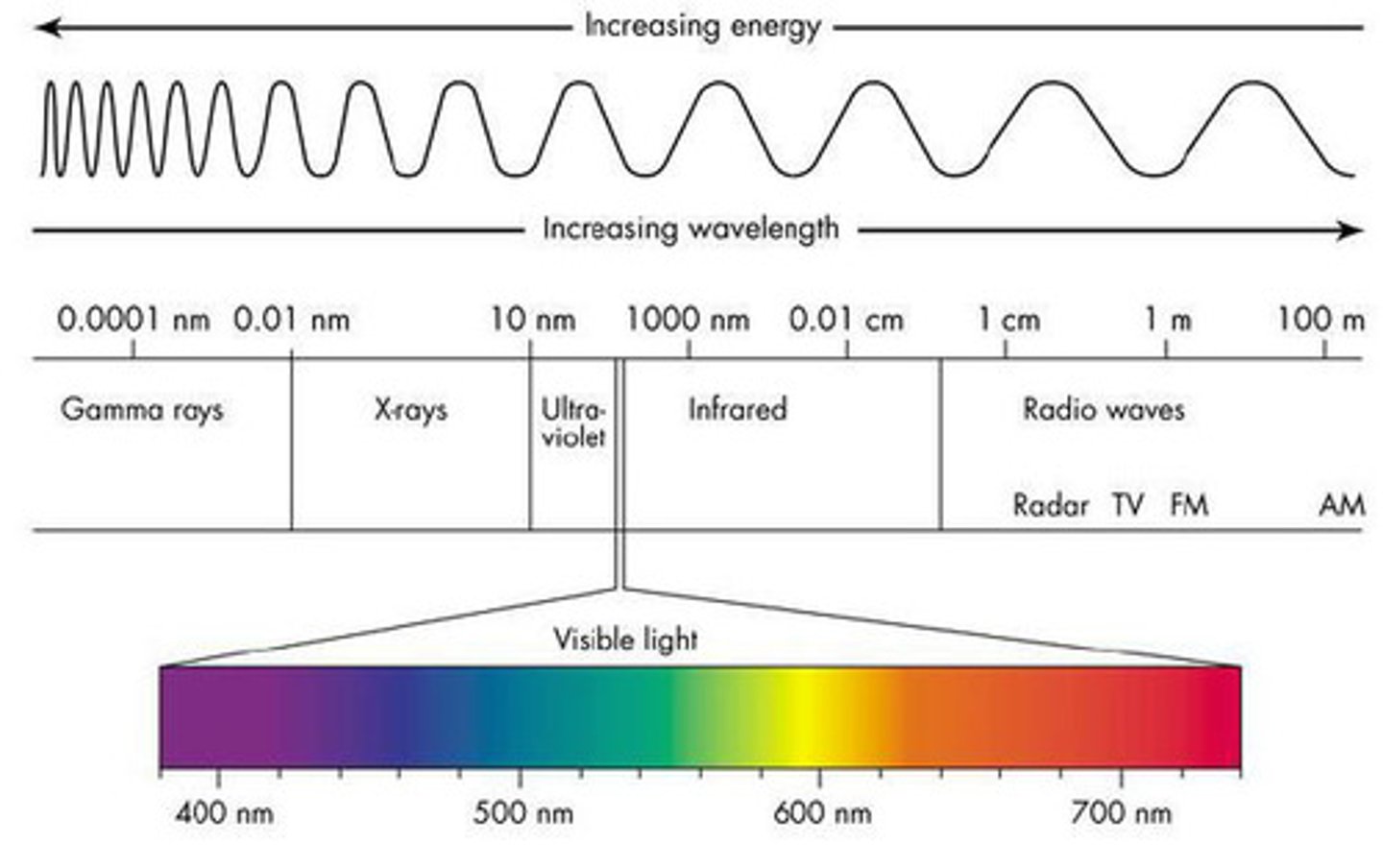
increasing wavelength and increasing energy
-theory of the doppler effect
-towards Blue = increasing energy
-towards Red = increasing wavelength
Zodiac Constellations
-the 12 constellations along the ecliptic
-also known as star signs
-the sun appears to "pass through" them as it seems to move across the sky (known as the ecliptic)
-it takes about 1 month to pass in front of each of the 12 zodiac constellations
ecliptic
the apparent path of the sun
precession
-stars precess or move, so over thousands of years constellations change
-meaning, what we see now is different from what people saw thousands of years ago
constellations
-groups of stars that seem (to us) to make shapes
-thes patterns are artificial, earth-based concepts
-they would look different from other points of the universe
how many constellations are there
-88
-some visible to the northern and southern hemispheres
-some are visible to only one
southern: 32
northern: 56
astrology
the study of the movements and relative positions of celestial bodies interpreted as having an influence on human affairs and the natural world.
created by the Babylonians, against Christian beliefs
what is a planet
a celestial body that moves around the sun that has:
-a sufficient enough mass to establish hydrostatic equilibrium (ie. is round)
-has a large enough mass to clear objects out of its orbit
-orbits the sun
(round, orbits sun, large, clears objects, has gravity)
-there are 8 in our solar system, plus a dwarf planet)
planets and their distance to sun
closest to farthest:
1. mercury
2. venus
3. earth
4. mars
5. jupiter
6. saturn
7. uranus
8. neptune
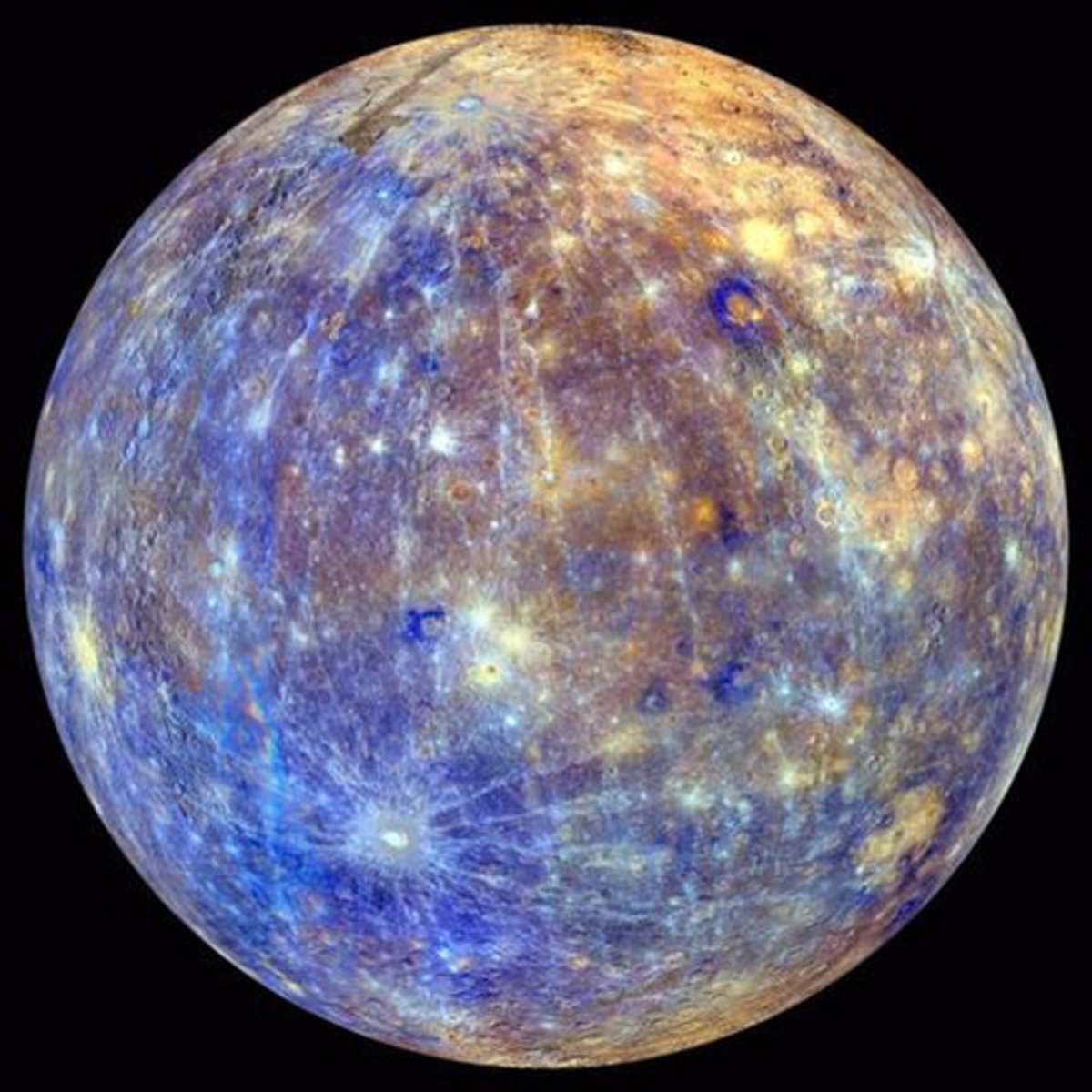
mercury
-closest to sun
-rocky crust with craters
-cold on half
-hot on half facing the sun
-gray in colour

venus
-second from sun
-nicknamed "the evening star"
-poisonus fog
-hottest planet
-orange in colour
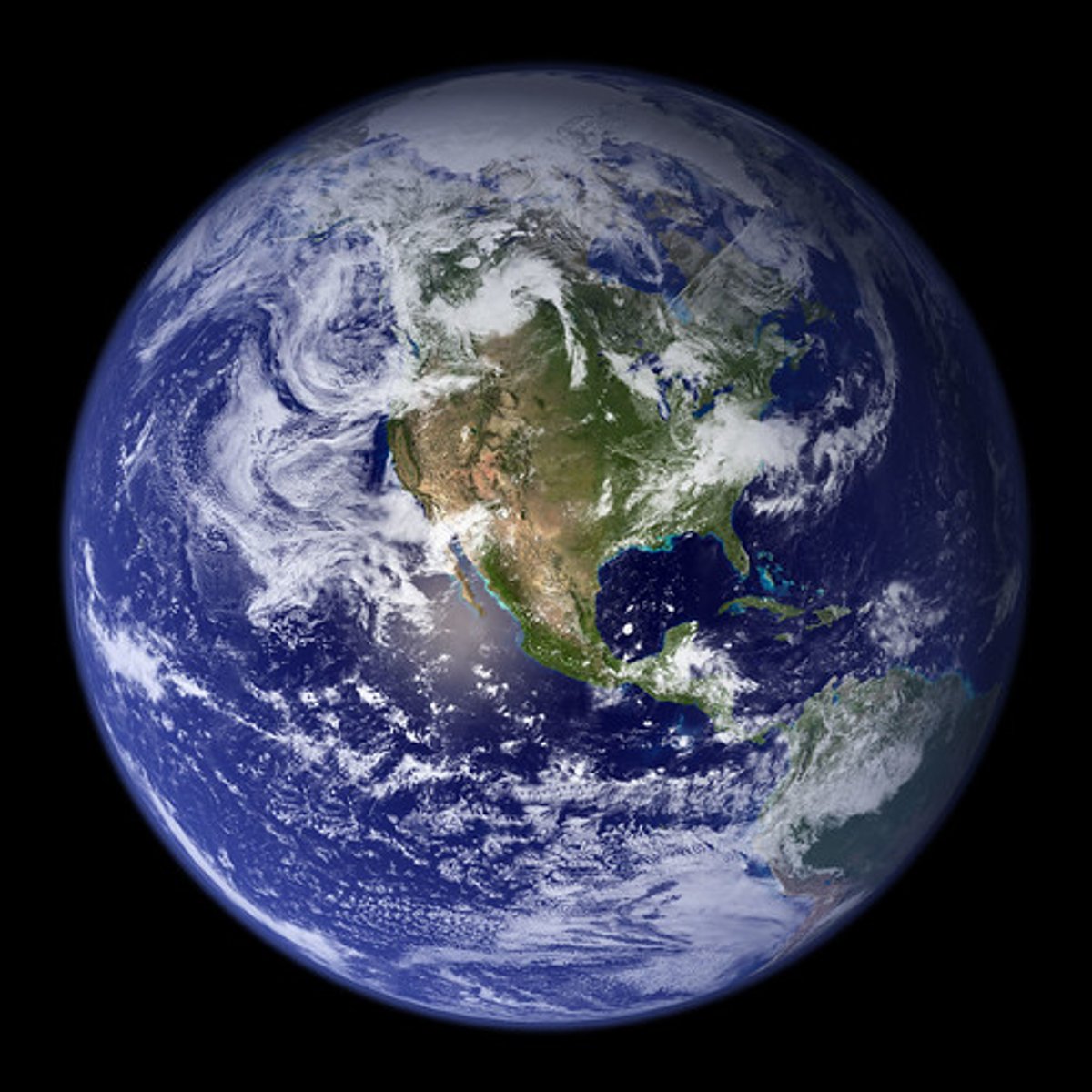
earth
-where we live
-third from sun
-only planet with large amounts of water
-only planet with living things
-has white clouds

mars
-fourth from sun
-the RED planet
-has 2 moons
-volcanoes and canyons
-rocks and sand
-thin and poisonus atmophere
-pink-gold in colour

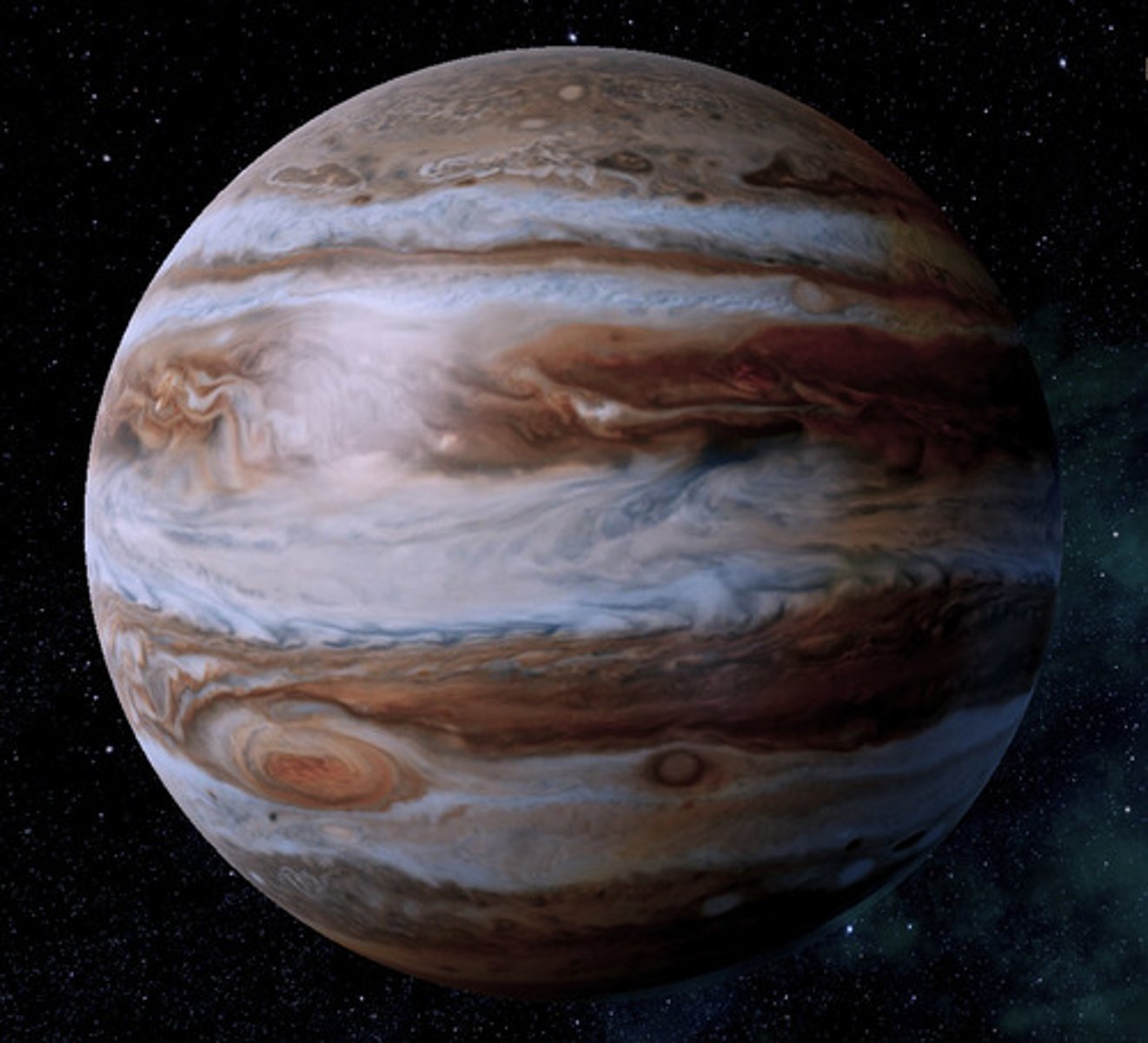
jupiter
-fifth from sun
-largest planet
-giant ball of swirling gas
-has 16 moons
-has 2 very thin rings
-has a large red spot which is a giant storm

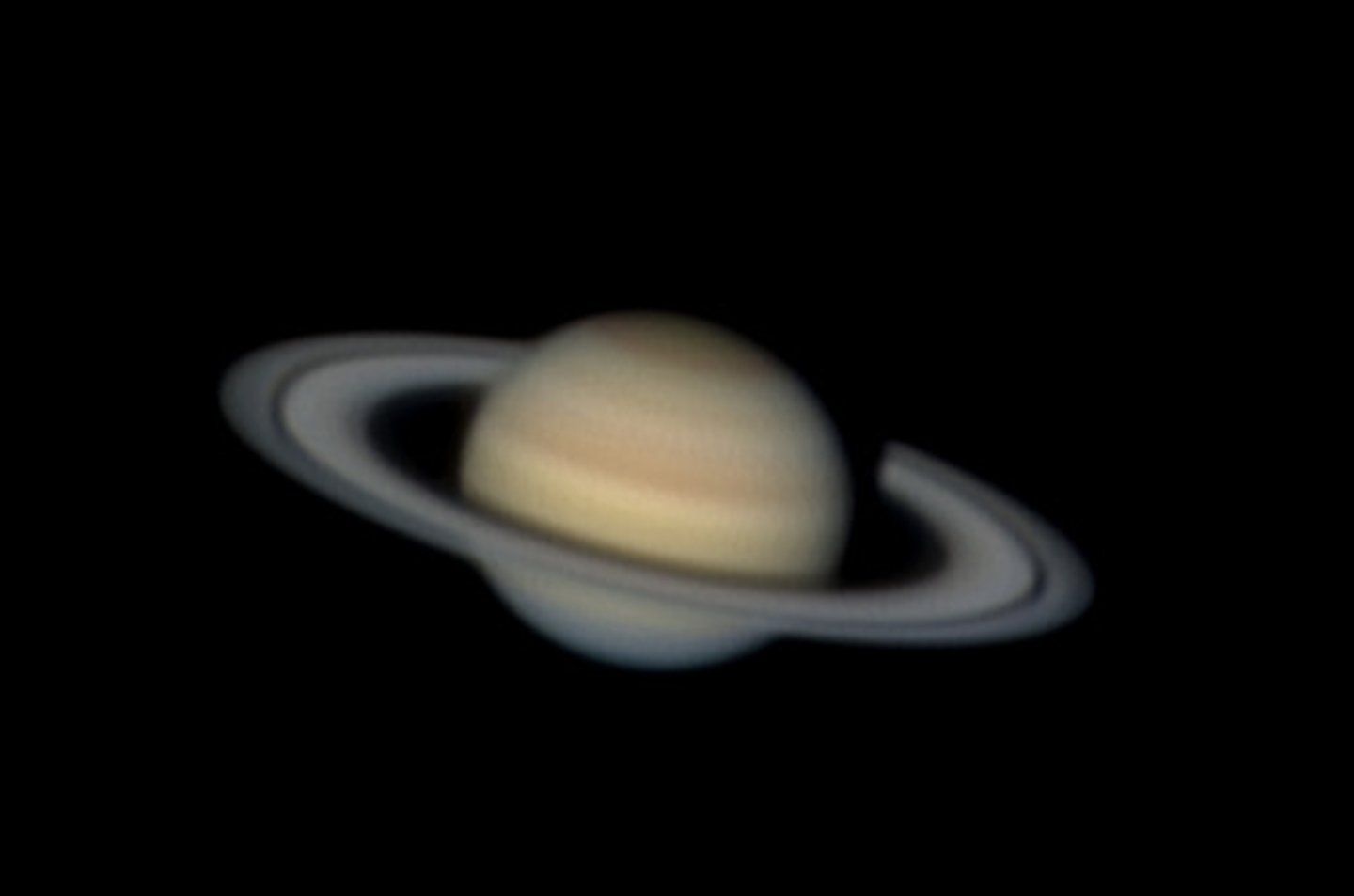
saturn
-sixth from sun
-second-largest planet
-has 3 rings made up of frozen ice, gas, and rock
-has 18 moons
-yellow in colour

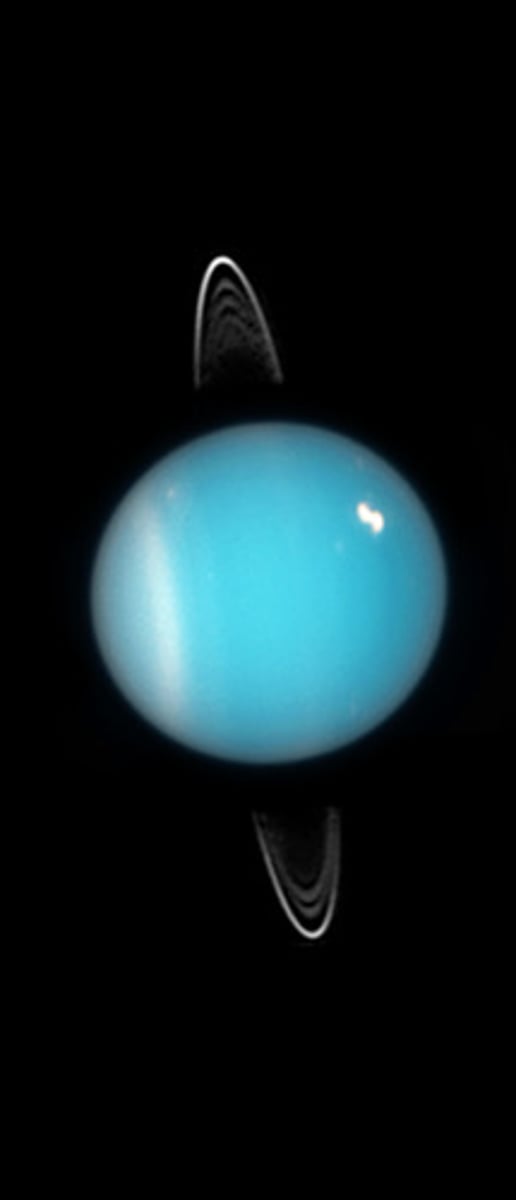
uranus
-seventh from sun
-third-largest planet
-looks like its on its side
-has around 21 moons
-has some rings
-blue-green in colour

neptune
-eigth from sun
-fourth-largest planet
-seven thin rings
-has 8 moons
-2 dark spots
-blue in colour
pluto
DWARF PLANET
-used to be considered a planet
-one of neptune's moons
-gray in colour
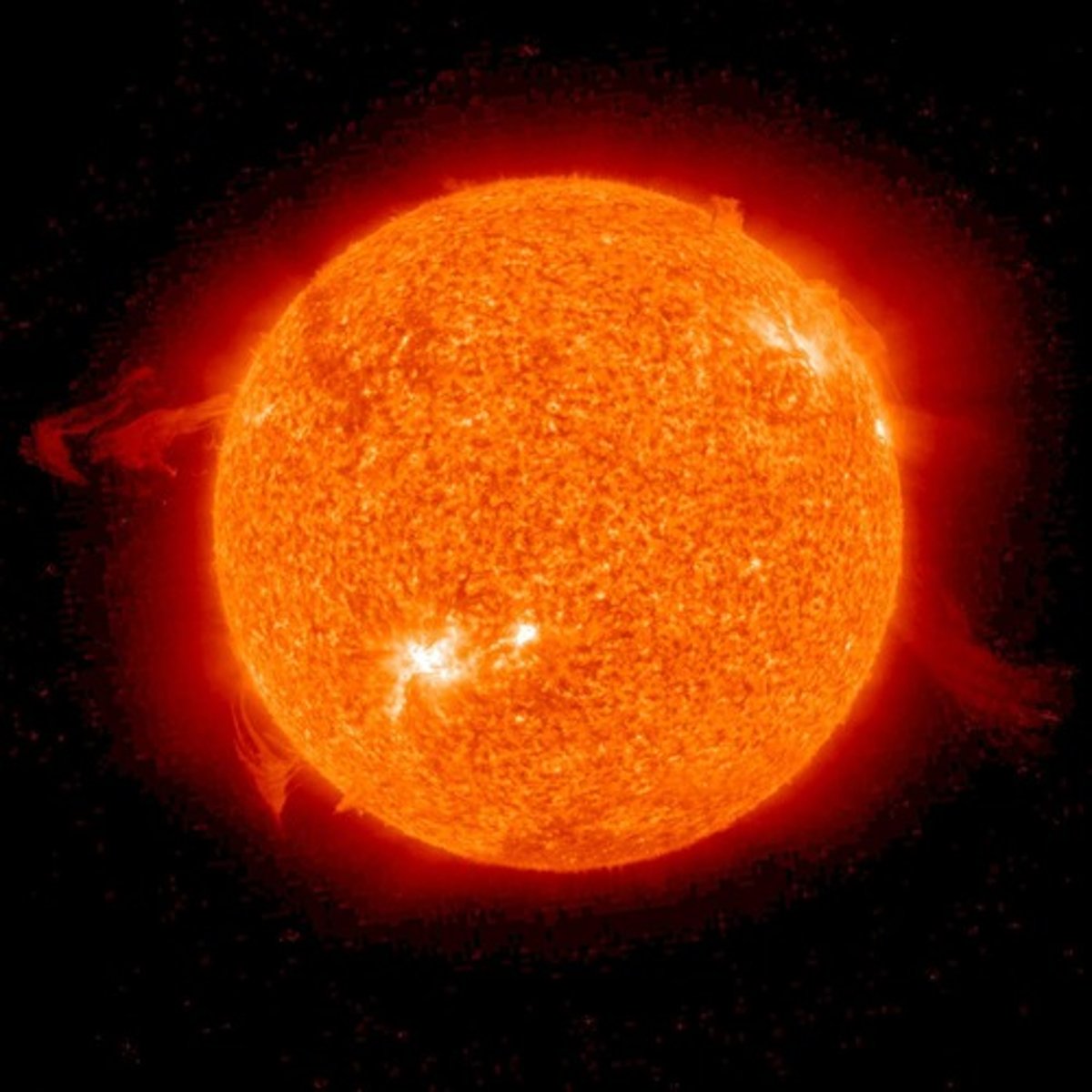
the sun
-a star
-brings light and warmth
-center of our solar system
-giant ball of gas
-makes lots of energy
international space station
An orbiting space satellite, construction of which began in 2001 with the cooperation of 16 nations; used for scientific and space research.
-brings together flight crews, lanuch vehicles, scientific research community, etc.
star
A ball of hot gas, primarily hydrogen and helium, that undergoes nuclear fusion.
nuclear fusion
a nuclear reaction in which atomic nuclei of low atomic number fuse to form a heavier nucleus with the release of energy.
hydrostatic equillibrium
a state of equilibrium in which the inward pull of gravity (from outer layers) in a star is just balanced by the outward forces of gas and radiation pressure
-pressure from the KE of particles
-pushing out = GPE of the star pushing in
-all forces are balanced
E1 = KE of gas pressure
E2 = GPE
and:
KE = GPE
Prostar
-an object in temporary hydrostatic equilibrium that is still collecting mass
-first stage of a star's life cycle
Star's life cycle
1. stellar nebula
2. main sequence
3. giant phase
4. final phase
5. remnants
Stellar nebula
a large mass of collapsing gas and dust located in the universe that forms stars and planets
Main sequence
High mass star vs. low mass star
-Nuclear reactions at a star's centre (or core) provide the energy that make sit shine brightly
-Main-sequence stars are fusing hydrogen into helium
-Stars in hydrostatic equilibrium
-Larger stars use up their fuel faster
Giant phase
-Low mass: red giant
-High mass: red supergiant
Final phase
-Low mass: planetary nebula
-High mass: supernova
Remnants
-Low mass: white dwarf, then black dwarf
-High mass: neutron star, black hole
red giant
A star that expands and cools once it runs out of hydrogen fuel
-When the hydrogen in the centre of a star runs out, the star begins to use hydrogen further out from its core.
-This causes it to start to grow. Its radius can reach up to 400 times its original size.
-As the star expands it also cools. The change in temperature causes the star to glow redder.
red supergiant
The stage in the life cycle of a massive star during which the star increases in size and becomes very bright.
-they have the largest radius of all known stars.
-use up the hydrogen and helium in their cores within a few million years.
-They then start to burn carbon, and the stars expands and cools.
-they have low surface temperatures
planetary nebula
A huge cloud of gas that is created when the outer layers of a red giant star drift out into space
-During this phase, the star sheds its outer layers. This creates an expanding, glowing shell of very hot gas.
-At that point, the star becomes highly unstable and starts to pulsate producing strong stellar winds, which throw off the outer layers of the star.
supernova
A gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses and throws its outer layers into space
-the layers each fuse a different element until fuel is ran out
-iron core is left and stable
-gravity is stronger and collapses the star
-all the levels fall into and then bounce off of the iron core, causing an explosion
-releases heavy black nuclei into space
white dwarf
the blue-white hot core of a star that is left behind after its outer layers have expanded and drifted out into space
black dwarf
Star that results when a white dwarf stops giving off energy
neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive star. It is what is left of the star, after a supernova explosion.
-when the outer layers of a star collapse inward (in a supernova explosion) it squashes the star's core to the point where the atoms are smashed to pieces, leaving only neutrons.
-The only object denser than a neutron star is a black hole.
high mass star
-more than the minimum amount of mass needed to trigger nuclear fusion
-core is denser and hotter
----more mass = more inward force, and therefore much hotter
-gases are not convective, and the heat stays in the core
-uses fuel (gases) faster than a low mass star)
-lifespan: approx. 12 billion years
-shorter lifespan
-can fuse heavier elements (carbon, oxygen, silicone, iron)
low mass star
-less than 1/4 of the mass of the sun
-go through main sequence as low mass star, red giant, white dwarf, and black dwarf
-gases are convective (use entire mass as fuel through movement and circulation)
-lower mass = longer life
Spectroscopy
the study of the absorption and emission of light and other radiation by matter
A spectroscope breaks the light from a single material into its component colors the way a prism splits white light into a rainbow. It records this spectrum, which allows scientists to analyze the light and discover properties of the material interacting with it.
4 theories of creationism
1. young earth creationism
2. old earth creationism
3. evolutionary creationism
4. naturalistic evolution
how do stars die
-it dies when it is entirely dependant on the mass of the original main sequence star
-they can be classified as two main categories low large mass stars
-they eventually stop working, and the layers all fall into the core and bounce off creating a supernova
components of a black hole
Event horizon, accretion disk, singularity
impact of spectroscopy
understand:
-how objects produce light
-how fast light moves
-how colours are absorbed
-determine pressures of gas
-measure distance to galaxies
-learn about active galaxies, neutron stars, and black holes
-how much light there is at each wavelength
young earth creationism
-God is the creator
-NO evolution
-NO macroscopic evolution
old earth creationism
-God is the creator
-there is evolution
-NO macroscopic evolution
evolutionary creationism
-God is the creator
-there is evolution
-there is macroscopic evolution
naturalistic evolution
-God is NOT the creator
-there is evolution
-there is macroscopic evolution