PSYC 425 Chapter 4
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
psychopharmacology
the study of the effects of drugs on the nervous system and behavior
drug effects
the changes a drug produces in an animal's physiological processes and behavior
sites of action
location at which molecules of drugs interact with molecules located on or in cells of the body, thus affecting some biochemical processes of these cells
5 routes of administration
ingestion, injection, inhalation, absorption, intracerebral administration
ingestion
oral route
pros of ingestion
easy and relatively safe
cons of ingestion
absorption via digestive tract is unpredictable
types of injection
intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, and intraperitonal,
subcutaneous
SC
intramuscular
IM
Intravenous
IV
Intraperitonal
IP
subcutaneous
under the skin
intramuscular
into large muscle
intravaneous
into veins, drug delivered directly to brain
intraperitonal
to abdominal cavity
inhalation
Absorbed through capillaries in lungs
pros of inhalataion
very rapid effects
absorption through mucous membranes
nose mouth rectum, topical administration
intracerebral administration
directly into brain
intracerebral administration use
some drugs cannot get through the blood brain barrier so drug Injected into brain or CSF
Intracerbral Administration
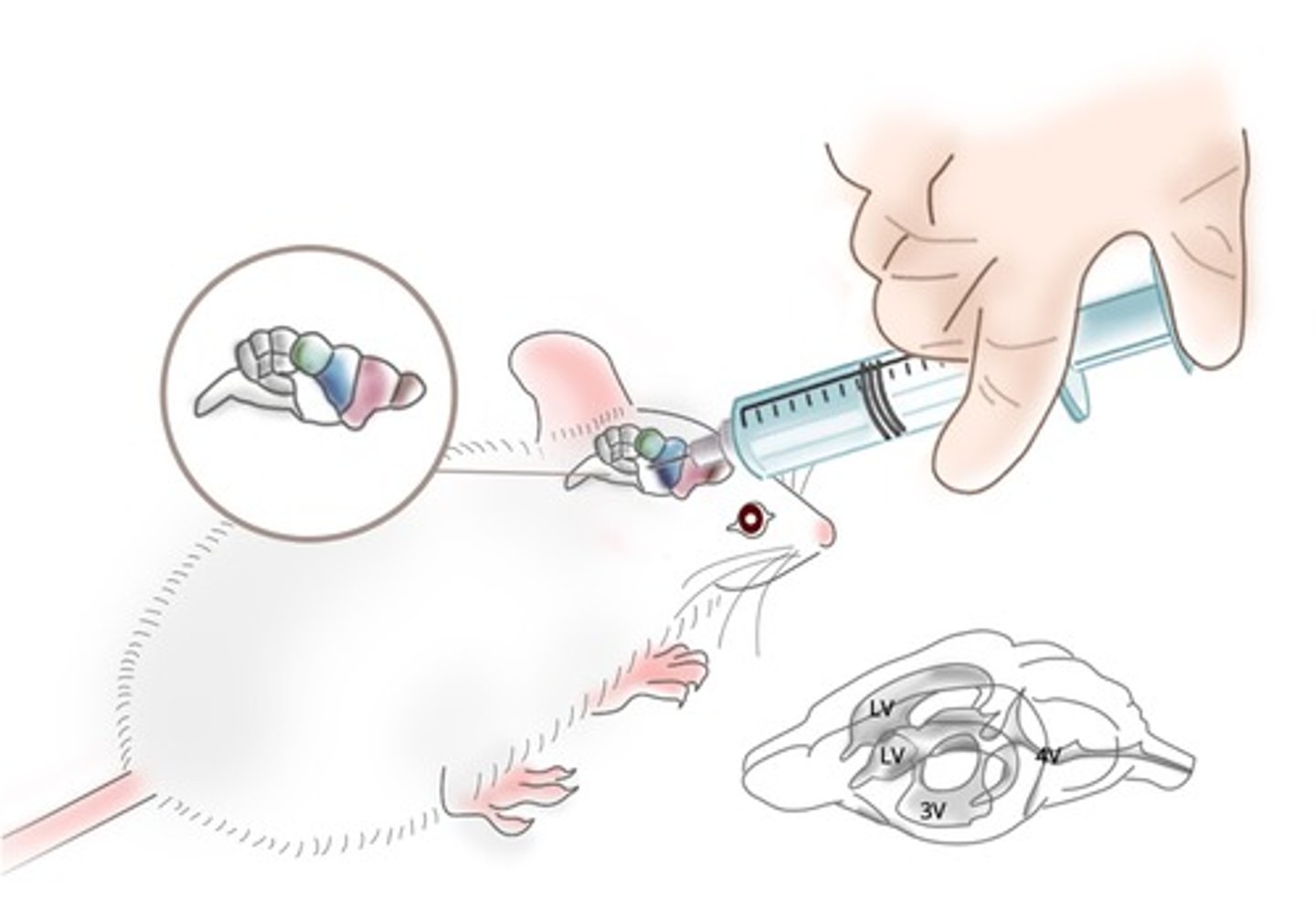
solubility of blood brain barrier
fat soluble molecules
why heroin more effective than morphine
heroin more fat soluble so it acts more quickly on the brain
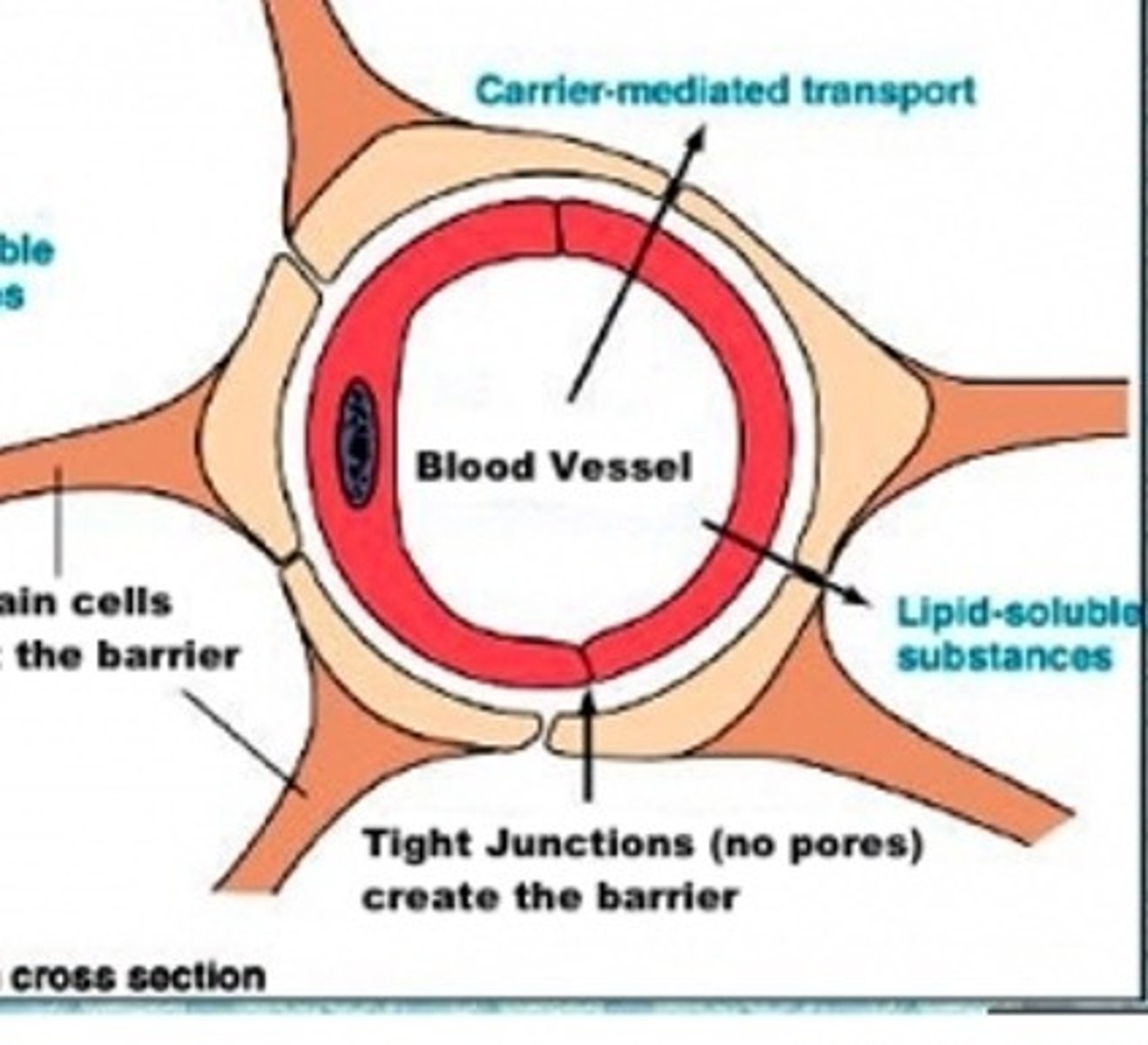
normal blood vessel
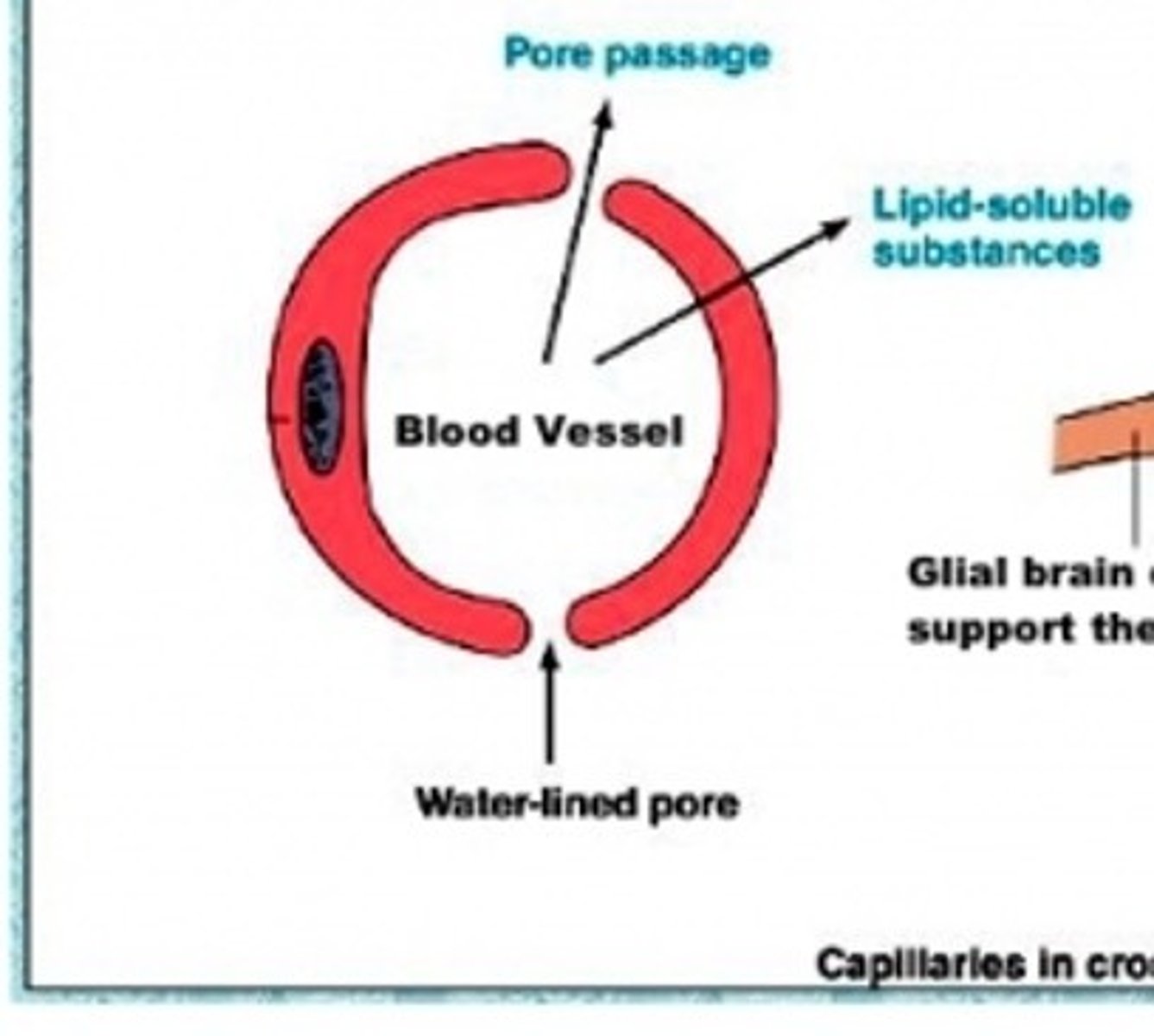
brain blood vessel
dose response curve
dose response curve
A graph of the magnitude of an effect of a drug as a function of the amount of the drug administered
best way to measure drug effectiveness
does response curve
how dose response curve is measured
subjects given various doses of a drugs based on mg per kg of body weight; effect are plotted
analgesia
inability to feel pain
margin of safety (therapeutic index)
Dose that produces desired effect 50%, dose that produces toxic effect 50%
margin of safety
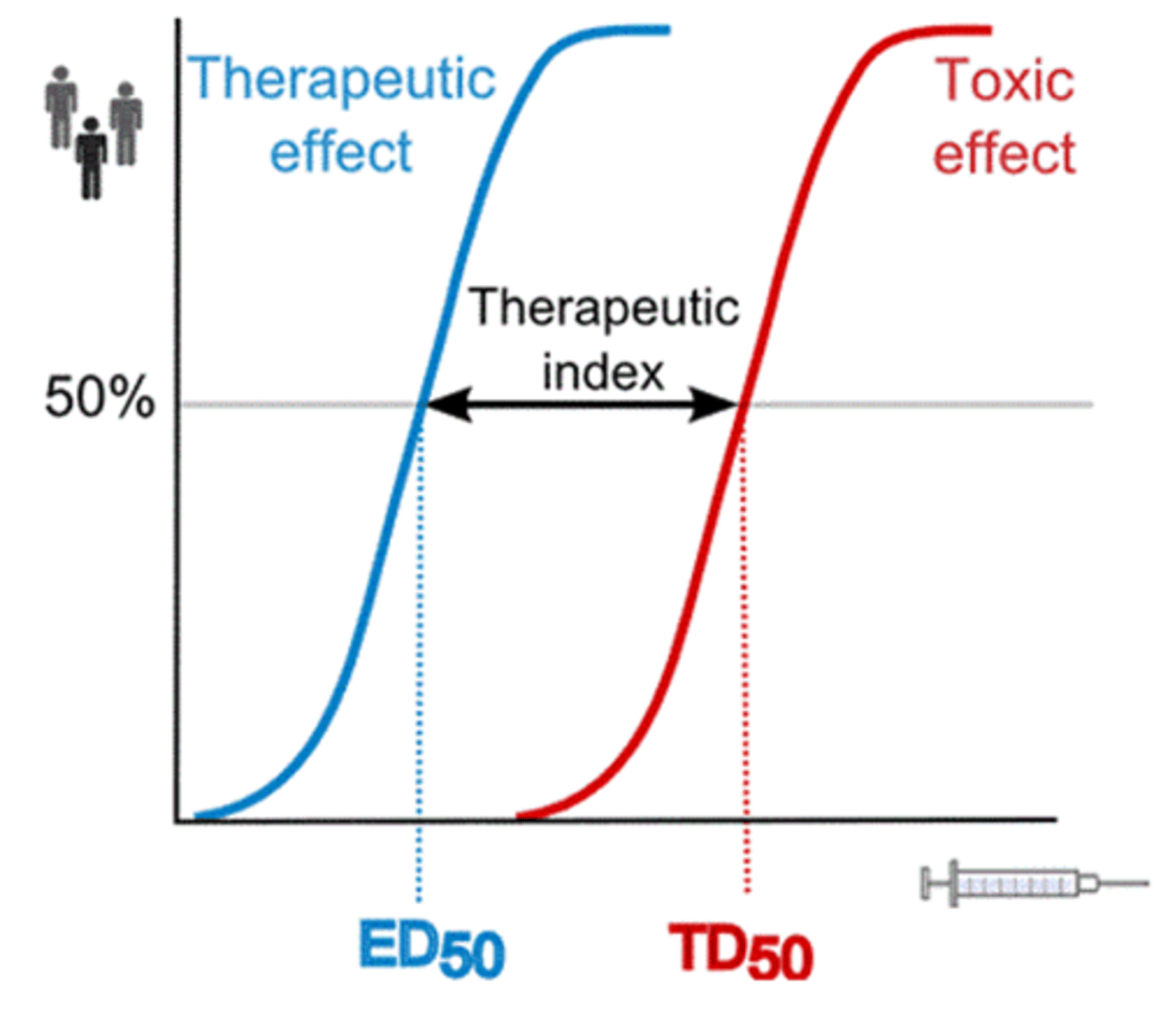
low index
more risk for adverse reactions and toxic effects
low affinity
more drug needed
high affinity
less drug needed
affinity
the readiness with which two molecules join together (binding sites)
tolerance
decrease in the effectiveness of a drug that is repeatedly administered
sensitization
increase in the effectiveness of a drug that is administered repeatedly
high tolerance
need more drug to get the effects
low tolerance
need less drug to get the effects
withdrawal symptoms
Appearance of symptoms opposite to those produced by the drug
why tolerance occurs
Result of the body's attempt to compensate for the effects of the drug
compensatory mechanisms
body's attempt to compensate for loss or alteration, fight back, make up for the change
upregulation
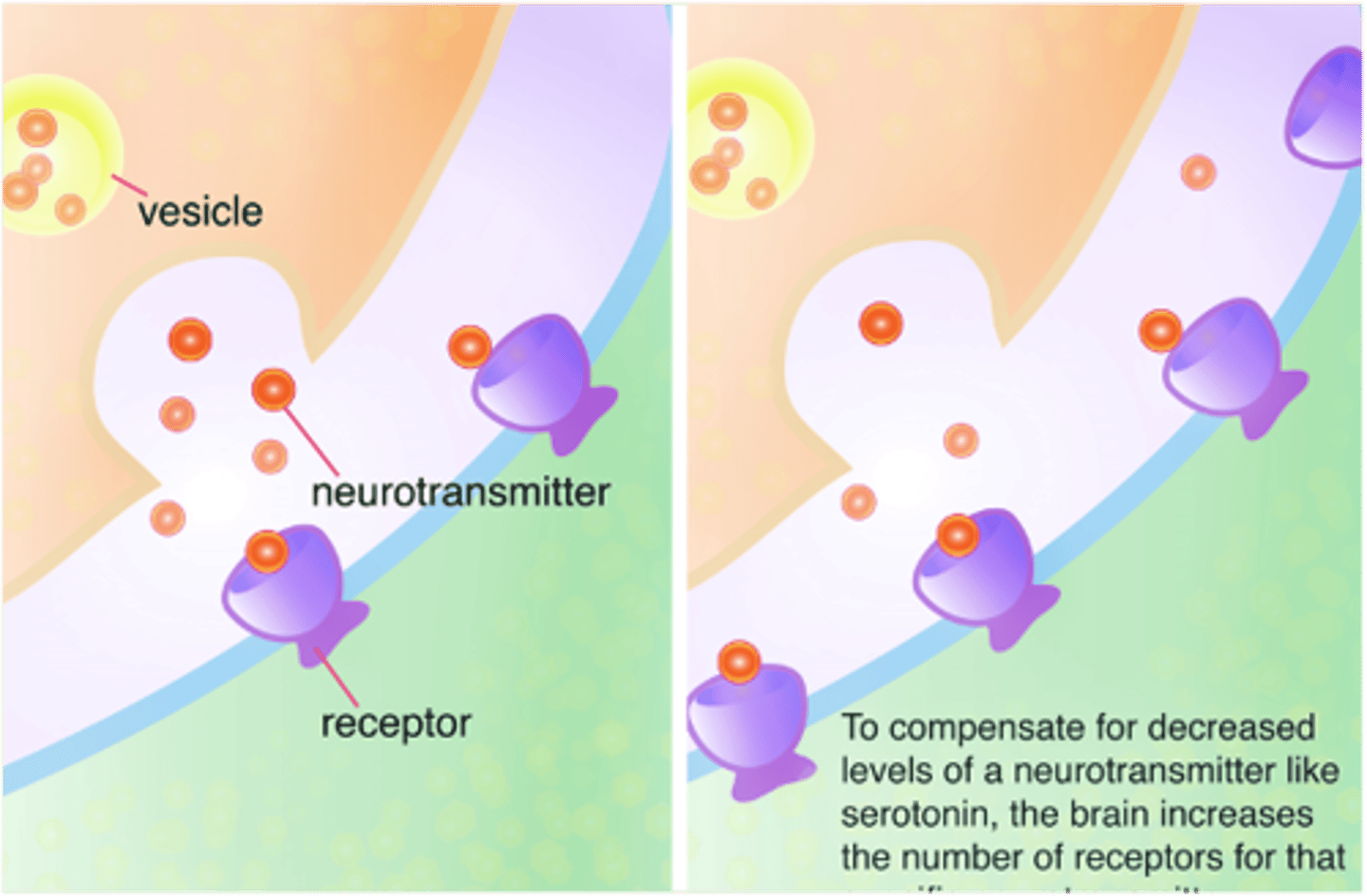
prolonged expose to drug
the coupling (ion channels/ second messengers) does not work
sensitization example
cocaine will more likely develop movement disorders, convulsions, and psychosis
sensitization likelihood
less common than tolerance because of compensatory mechanisms
antagonist drugs
a drug that inhibits the effects of a particular NT on the postsynaptic cell
agonist drugs
drug that facilitates the effects of a particular NT on the postsynaptic cell
synthesis of NTs
controlled by NT-specific enzymes
metopirone
blocks cortisol synthesis by inhibiting 11ß-hydroxylase
metopirone treatment
Cushing's disease
transporter molecules
help move NTs into the vesicle
transporter molecules location
in the membrane of synaptic vesicles and the terminal
antagonist drug effects
prevent release of NTs into synapse; deactivate proteins that cause the vesicle's fusion to the membrane
presynaptic and postsynaptic receptors
most common and most complex sites of action
direct agonist
Molecules of drug attach to the binding site that the NTs normally connect with
direct agonist image
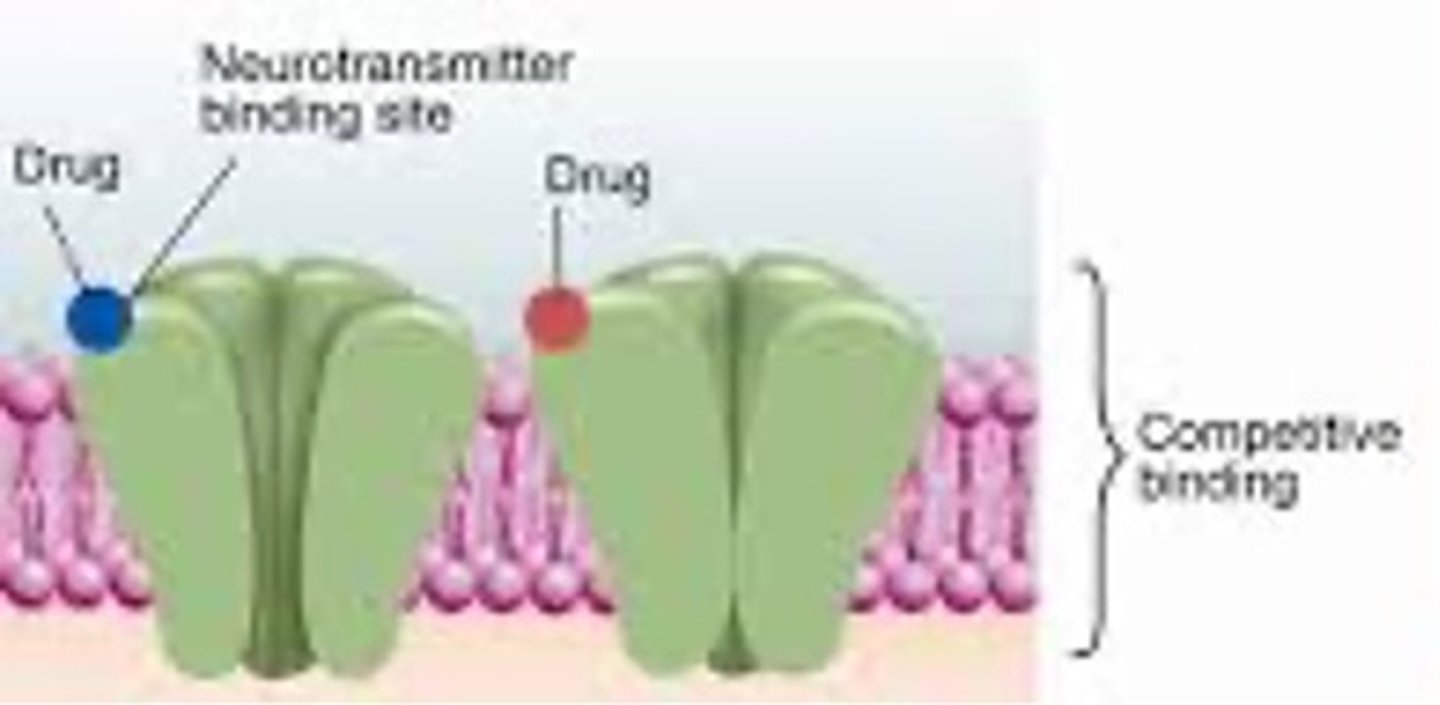
effect of direct agonist
causes ion channels controlled by the receptor to open
action fo direct agonist
MIMICS the effects of the NT
indirect agonist image
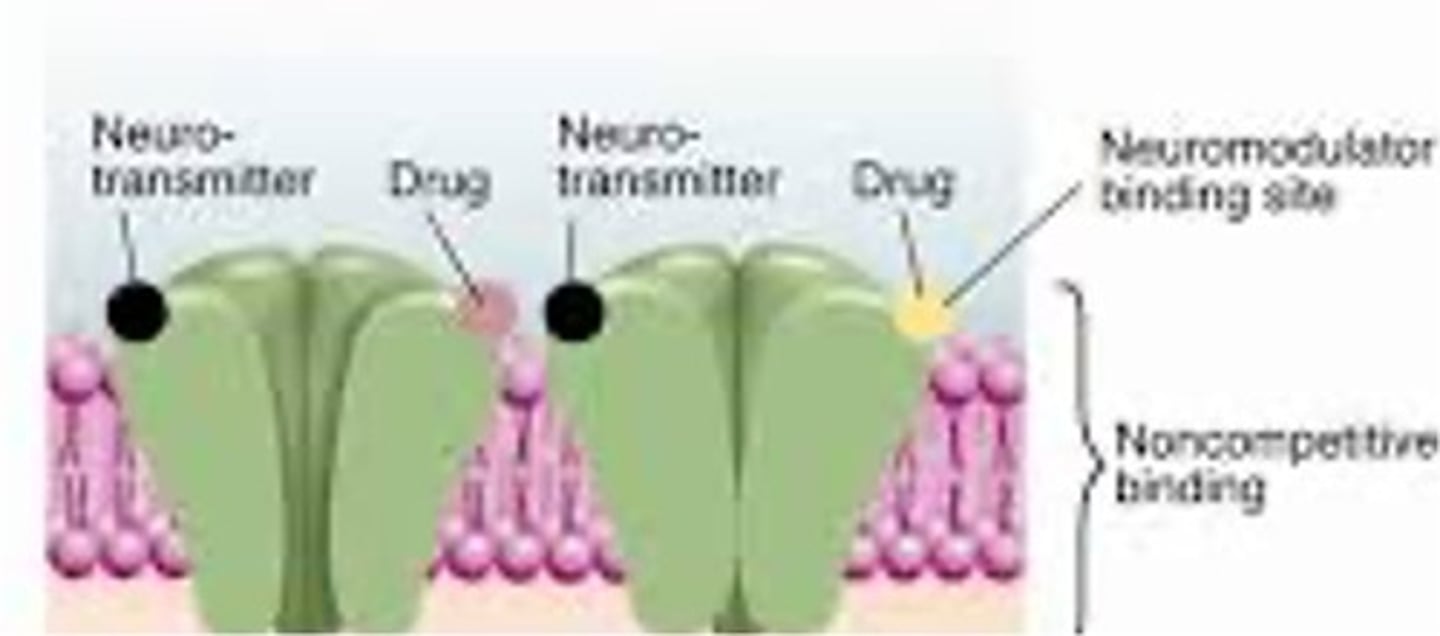
indirect agonist
a drug that attaches to a binding site on a receptor and facilitates the action of the receptor; does not interfere with the binding site for the principal ligand
effects of indirect agonist
Facilitates the opening of the ion channel
direct antagonists
receptor blockers; block binding by NTs
indirect antagonist
noncompetitive binding; prevents ion channel from opening
Trucyclics
Drug molecules attach to transporter molecules and deactivate them; Stop reuptake.
exmaple of trycyclics
Elavil, SERT andNET
drugs that target acetylcholinesterase
Drug molecules bind to enzymes and deactivate them; Stops enzymatic degradation.
example of drug that targets acetylcholinesterase
donepezil
acetylcholine NT type
excitatory
Acetylcholine location
CNS and PNS
Acetylcholine action
muscle action (PNS), learning (basal forebrain), memory (medial septum), & REM sleep (pons)
Increase in ACh effeects
muscle spasm
increase in ACh example
black widow venom
decrease in ACh
reduced muscle activity
decrease in ACh example
botulinum toxin; botox; alzheimer's
acetylcholine abreviation
ACh
ACh synthesis enzyme
Acetyl-CoA (coenzyme A)
mechanism of production of ACh and CoA
When in the presence of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), acetate ion is transferred from acetyl CoA to the choline molecule
Nicotic receptors
Ionotropic receptor site stimulated by nicotine and blocked by curare
curare
blocks nicotinic receptors located near muscles. Causes paralysis; found in plants- poison darts
muscarnic receptors
metabotropic receptor site stimulated by muscarine and blocked by atropine
muscarine example
poisonous mushrooms
atropine example
found in belladonna
monoamines
catacholamines and indolamines
example of catecholamines
dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine
synthesis of catecholamines (precursor)
tyrosine
indolamine example
serotonin
synthesis of indolamines (precursor)
tryptophan
dopamine NT type
excitatory and inhibitory
dopamine controls
¡oluntary movement, attention, learning, and the ability to recognize opportunities for rewarding experiences.
origin of dopamine in the brain
mostly originate in the midbrain
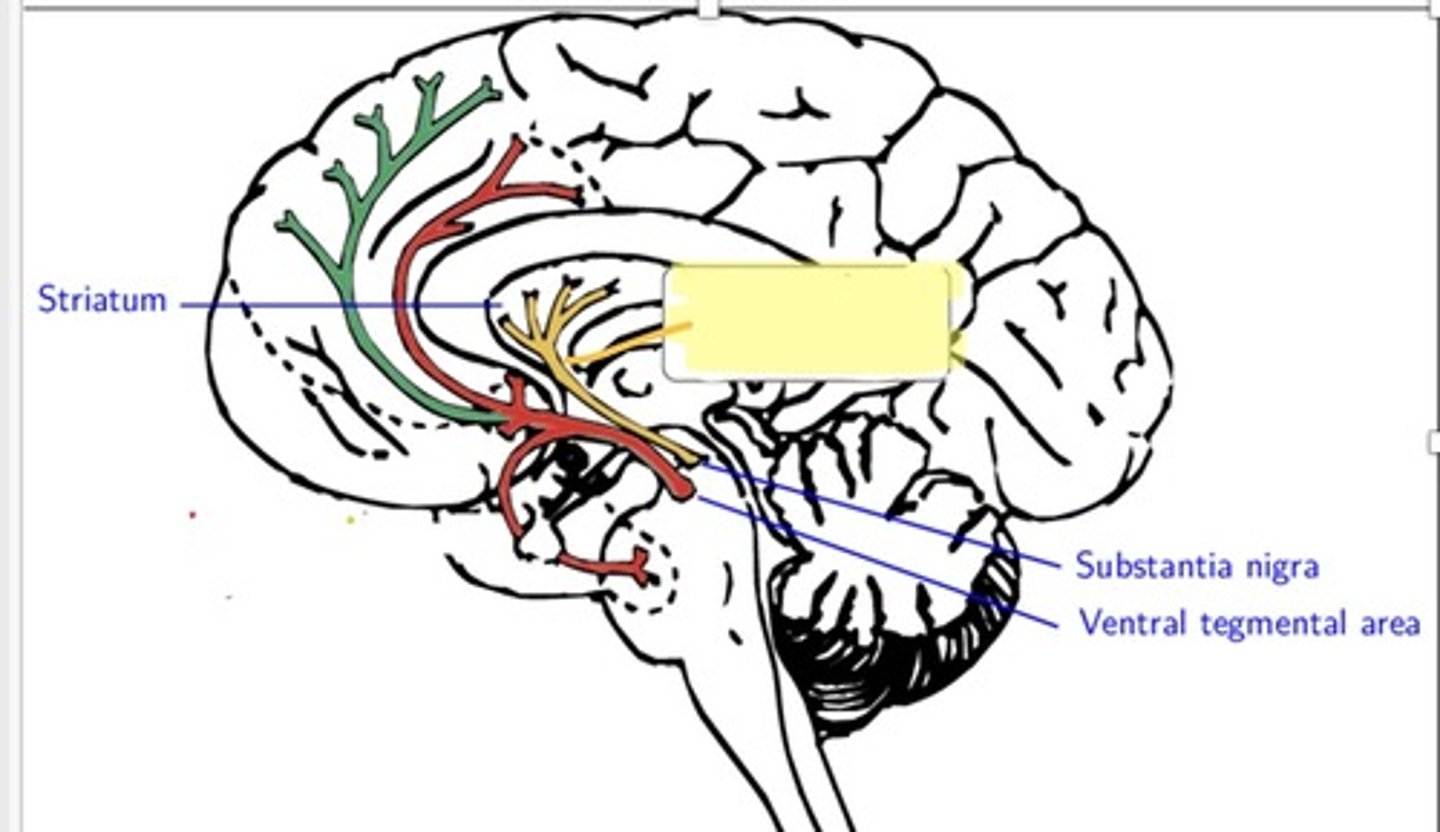
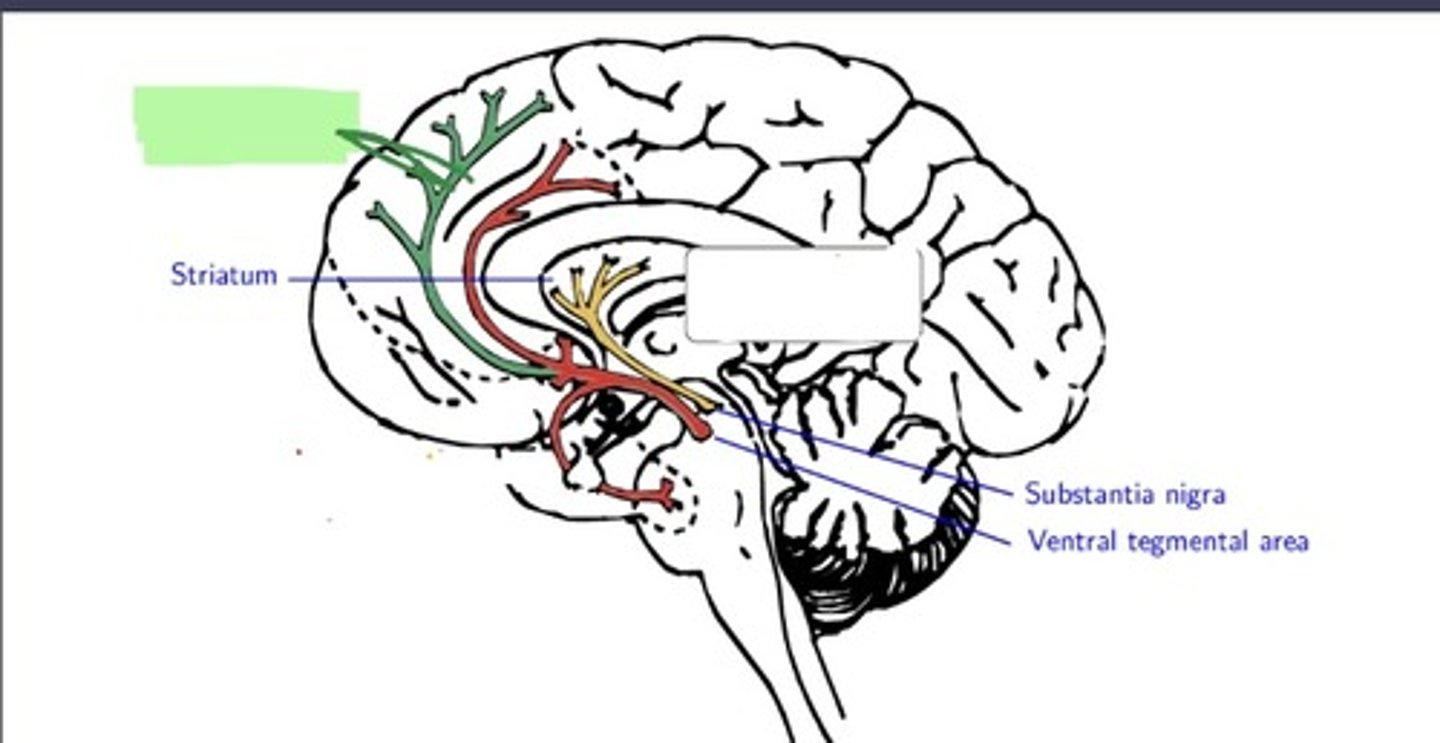
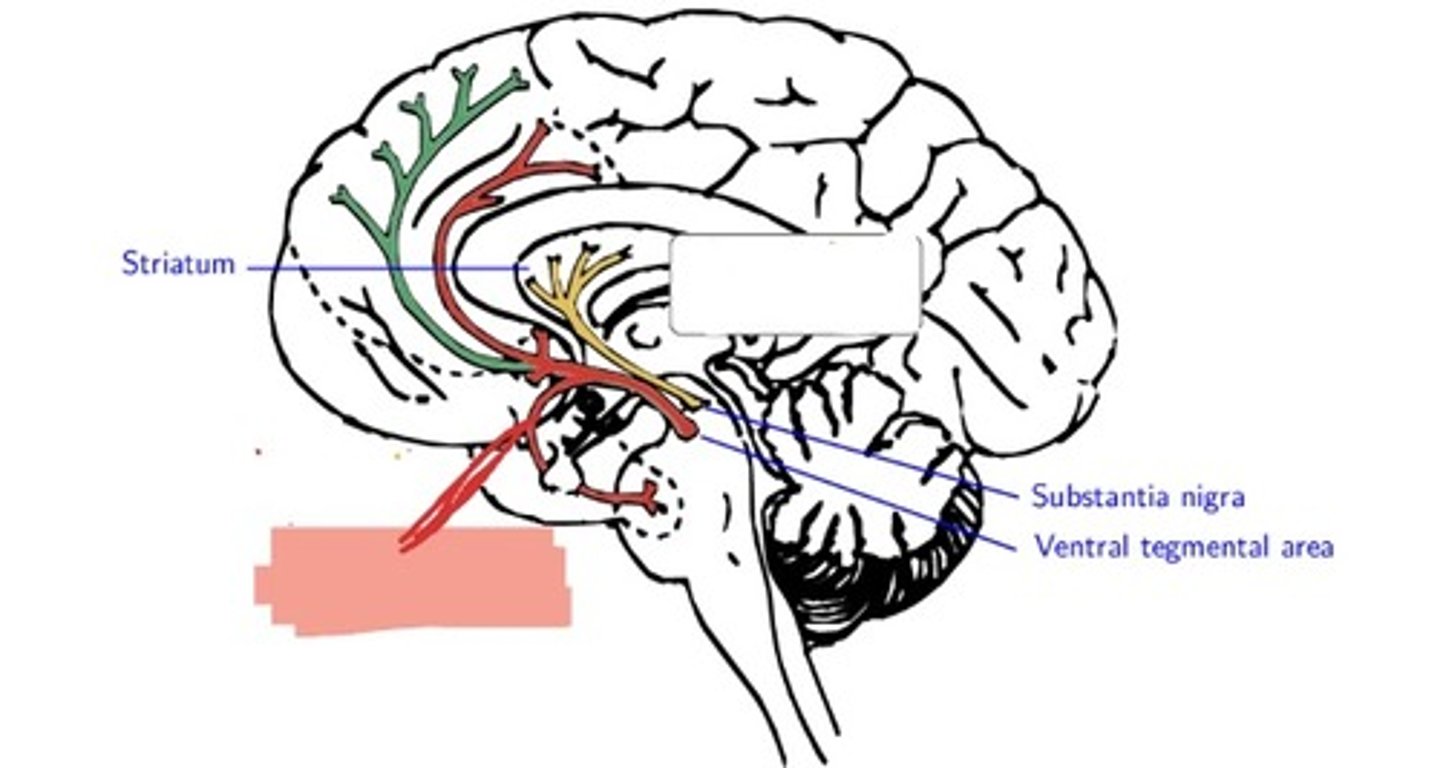
Nigrostriatal Pathway of dopamine
Substantia nigra to the neostriatum (basal ganglia) ---> movement
Mesolimbic Pathway of dopamine
Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) to the nucleus accumbens (NA) and other parts of the limbic system---> reinforcing behavior
mesocortical pathway of dopamine
¡VTA to the prefrontal cortex---> short term memory, planning, problem solving
mesostrial pathway
mesocortical pathway
mesolimbic pathway
parkinsons treatment
L-DOPA