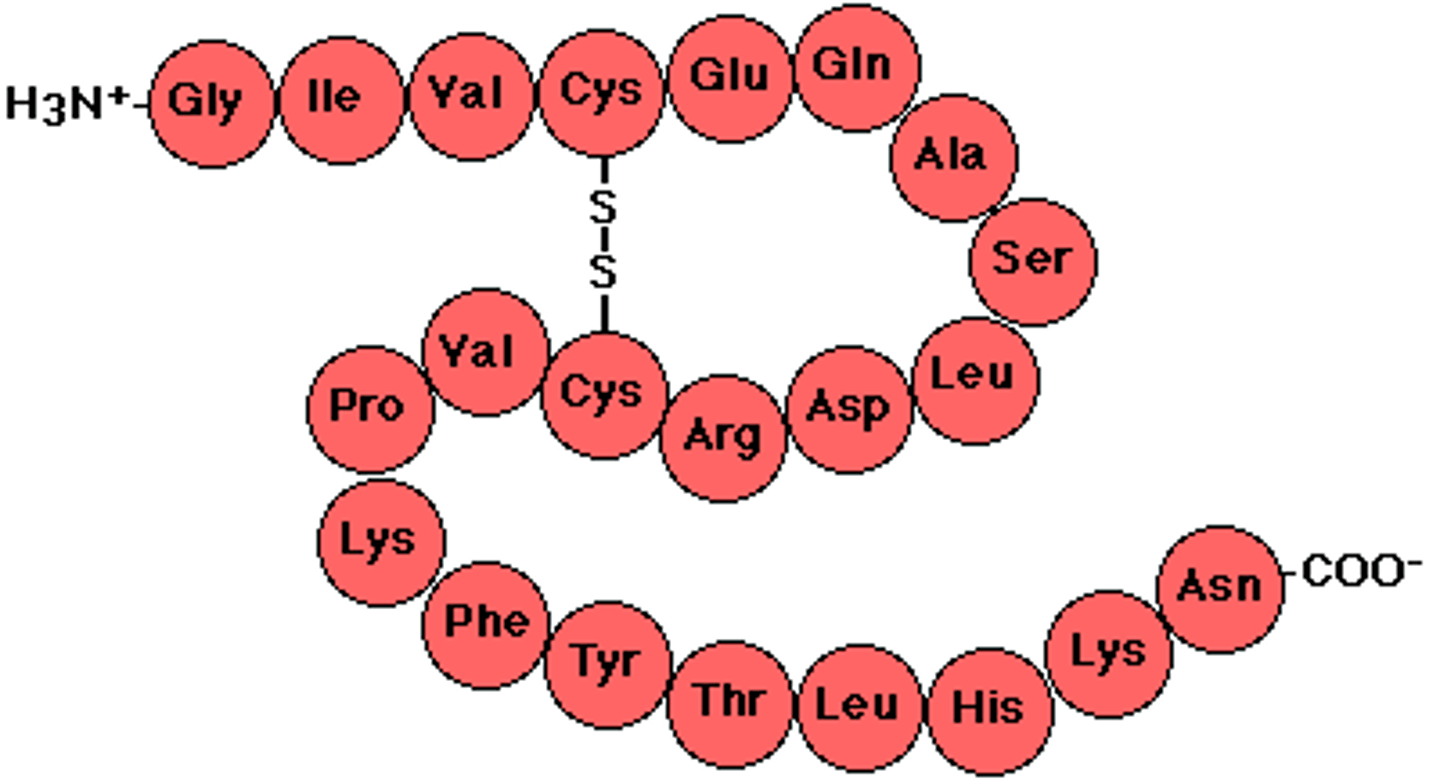
Unit 1 : Chemistry Of Life
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Hypothesis
A testable prediction based on observations
Theory
Summarizes a group of hypotheses
Experimental Group
A group in an experiment that receives the treatment of the variable being tested
Scientific Law
A statement of fact (mathematical formula)
Control Group
A group in an experiment that does not receive any of the treatment
Deductive Reasoning
Specific results are derived from general premises
Inductive Reasoning
Derive generalizations based on a large number of specific observations
Constants
Things that do not change throughout the experiment, they stay constant
Alternative Hypothesis
A hypothesis that may be supported or proven by data
Null Hypothesis
A hypothesis which the researcher tries to disprove, reject, or nullify a question
Independent Variable
The one factor that is changed by the person doing the experiment
Dependent Variable
The factor which is measured in the experiment
Central Tendencies
The center of the distribution can be described by the mean, median, or mode
Mean
The average of the data set
Median
The middle number in a range of data points
Mode
The value that appears most often in a data set
Variability
the measure of how far a data set diverges from the central tendency
Range
The difference between the largest and smallest values
Standard Deviation
A measure of how spread out the data is from the mean
Standard Error of the Mean
Used to determine the precision of and confidence in the mean value
Standard Error of the Mean formula
See image
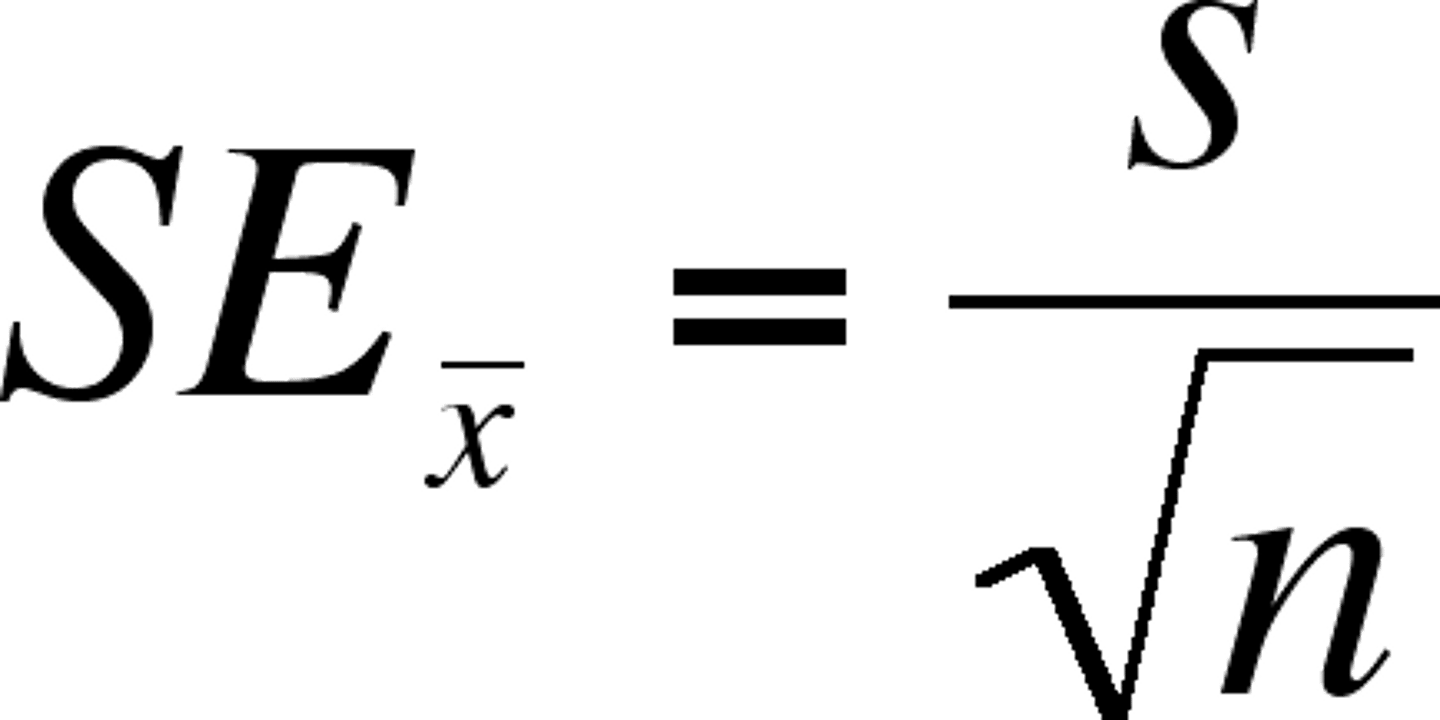
Data
recorded observations
Qualitative
observations with senses (think qualities)
Quantitative
measured using instruments (think numerical)
Positive Control Group
Group is not exposed to the experimental treatment or independent variable, but IS exposed to a treatment that is known to produce the expected result
Negative Control Group
Group is not exposed to any treatment or exposed to a treatment that is known to have NO effect
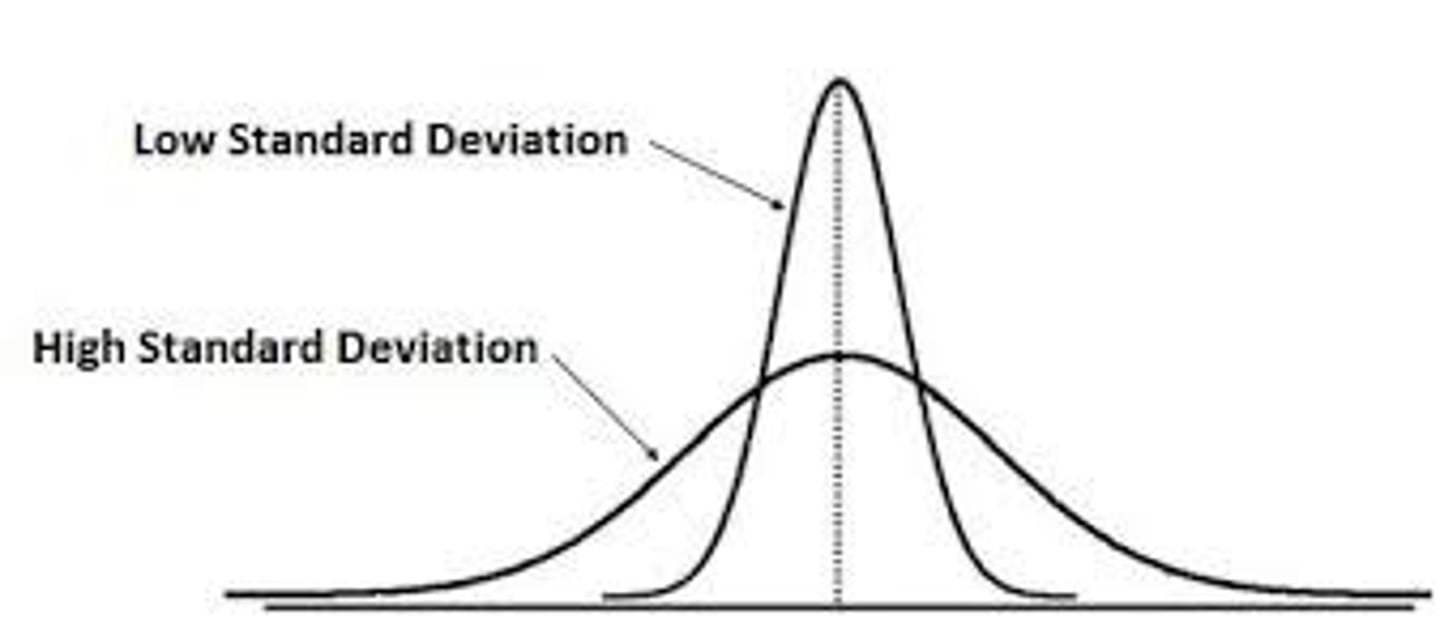
Low standard deviation
Means the data is closer to the mean ; independent variable is likely causing changes
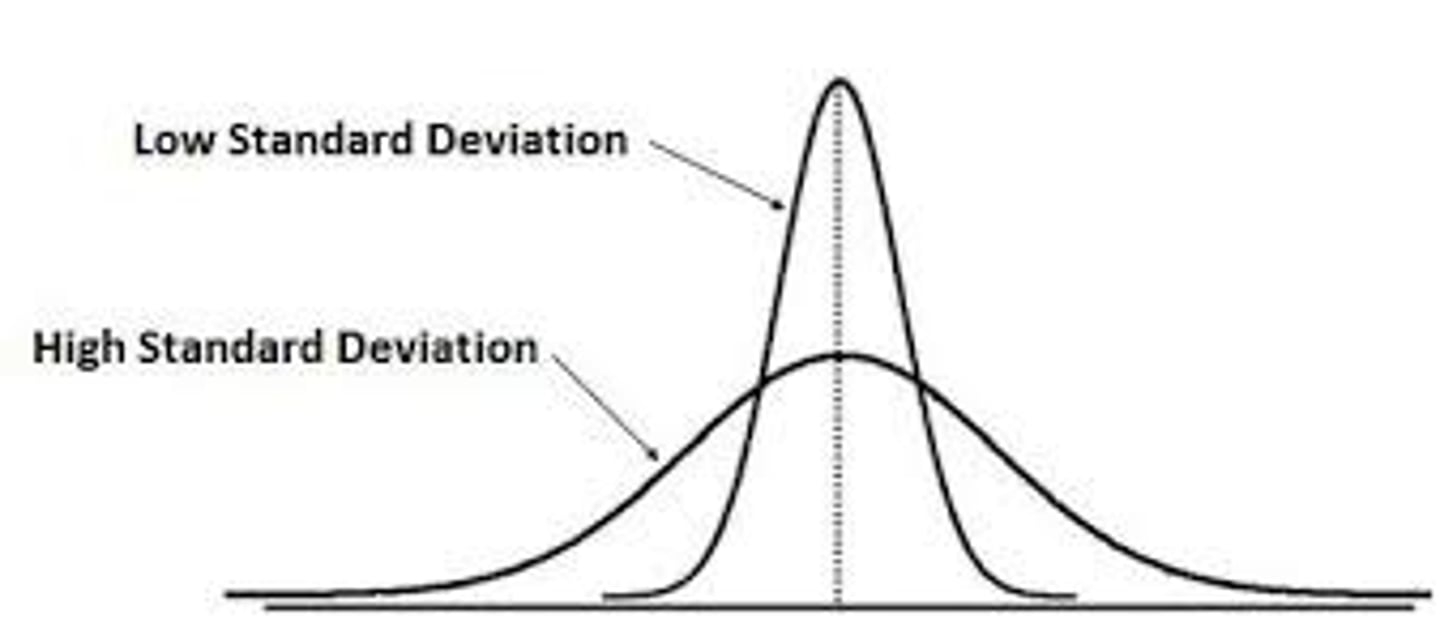
High standard deviation
Means the data is farther from the mean (more spread out) ; factors other than the independent variable are likely causing changes
Standard deviation formula
See image

If the error bars overlap
the difference is not significant
If the error bars do not overlap
the difference may be significant
Essential Elements
of the 92 naturally occurring elements 20-25% are essential to survive and reproduce (CHOPN) make up 96% of all living matter
CHOPN
carbon, hydrogen, phosphorus, and nitrogen
Trace Elements
of the 92 naturally occurring elements, these are required by an organism in very small quantities
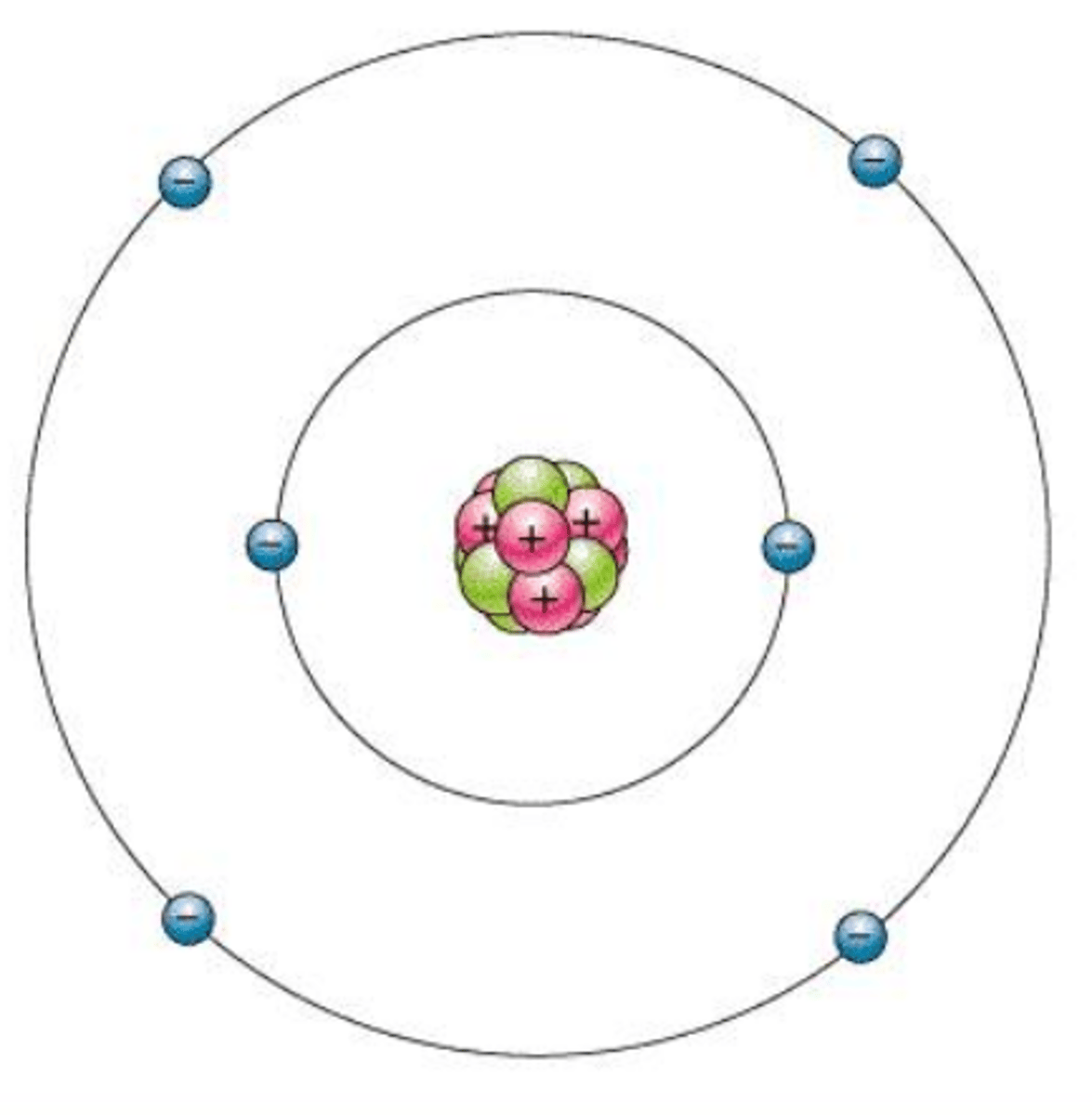
Bohr Model
shows electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom
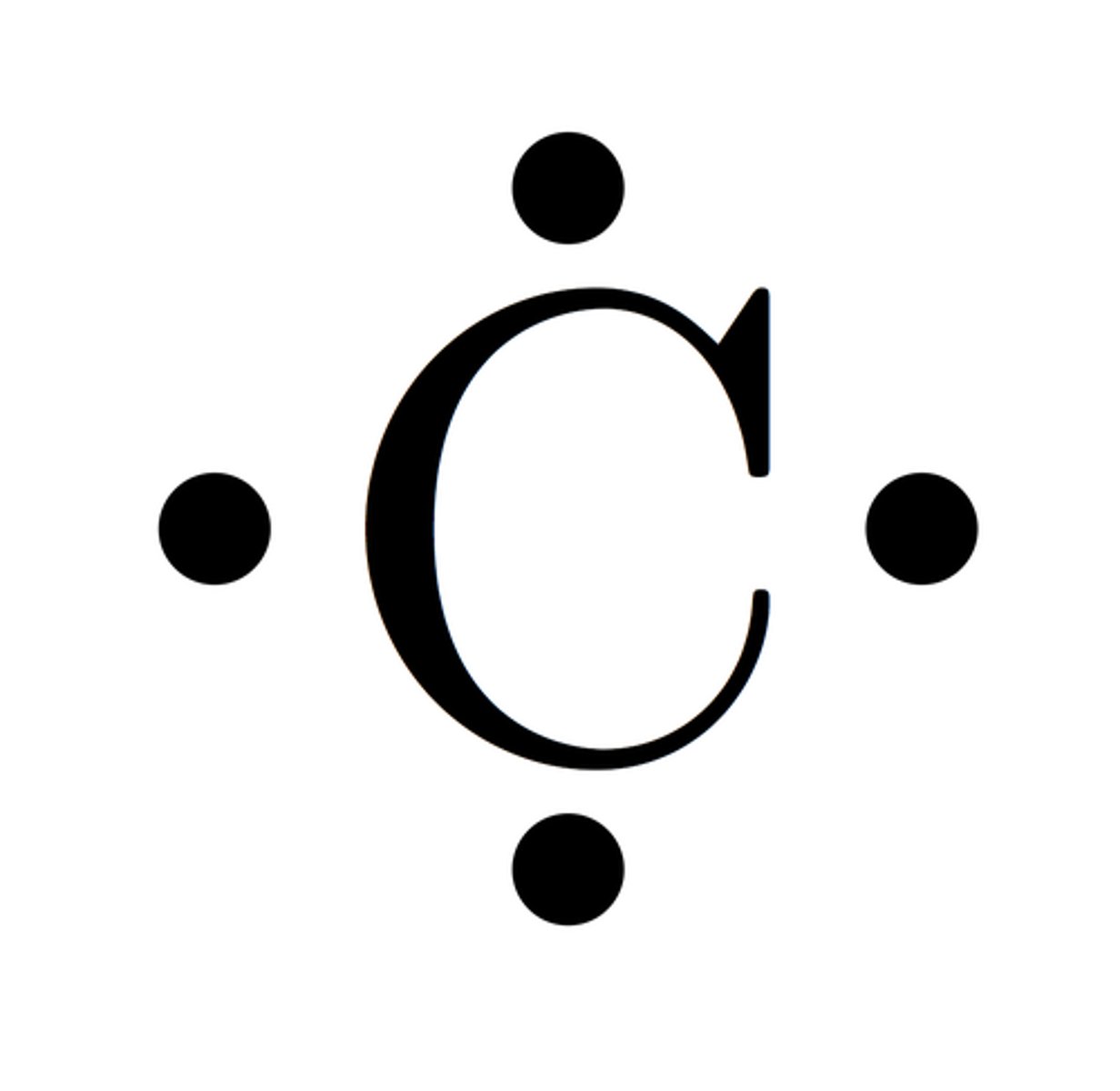
Lewis Dot Model
simplified bohr diagrams
Cation
positively charged ion
Anion
negatively charged ion
Polarity
unequal sharing of electrons makes a polar molecule
High specific heat
H2O resists changes in temperature
Evaporative Cooling
water has a high heat of vaporization
Water's Special Property of Density
as water solidifies it expands and becomes less dense
Matter
Anything that takes up space and has mass
Element
A substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions
Compound
A substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ratio
Octet Rule
Elements will gain, lose, or share electrons to complete their valence shell and become stable
Capillary Action
The upward movement of water due the the forces of cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension
Chemical Bonds
An attraction between two atoms, resulting from the sharing or transferring of valence electrons
Hydrogen Bonds
The partially positive hydrogen atom in one polar covalent molecule will be attracted to an electronegative atom in another polar covalent molecule
Covalent Bonds
When two or more atoms share electrons (usually between 2 nonmetals)
Ionic Bonds
The attraction between oppositely charged atoms ; there is a transfer of electrons
Cohesion
attraction of molecules for other molecules of the same kind
Electronegativity
The measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons
Adhesion
The clinging of one molecule to a different molecule
Atomic Mass
The number of protons plus neutrons averaged over all isotopes of an element
Solute
Substance that is dissolved
Solution
Homogenous mix of two or more substances
Solvent
Dissolving agent in a solution
Valence Electrons
The electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction
Functional Groups
Chemical groups attached to the carbon skeleton that participate in chemical reactions
Organic Chemistry
The study of compounds with covalently bonded carbon
Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen
Hydrocarbons
Organic molecules consisting only of carbon and hydrogen
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate is an organic compound that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cells
Macromolecule
A very large molecule (proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acid, and lipids) built up from smaller chemical structures
Dehydration Reaction
Bonds two monomers with the loss of H2O
Hydrolysis Reaction
Breaks down the bonds in a polymer by adding H2O
Monomers
The repeating units that make up polymers
Polymers
Chain like macromolecules of similar or identical repeating units that are covalently bonded together
Storage Polysaccharide
Stores glucose ; starch and glycogen
Structural Polysaccharides
Cellulose and chitin
Chitin
forms exoskeleton of arthropods
Carbohydrate
A macromolecule that include sugars and polymers of sugars
What does a carbohydrate contain
a carbonyl group and many hydroxyl groups
What is a carbohydrate comprised of
carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
Monosaccharide
Simple sugars ; monomers of carbohydrates
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides joined together by covalent bonds
Polysaccharide
Polymer with many sugars (monosaccharides) joined via dehydration reactions
Glycosidic linkage
A covalent bond that links two monosaccharides together
Starch
How plants store glucose ; a polymer of glucose monomers
Cellulose
A tough substance that forms plant cell walls ; a structural polysaccharide
Glycogen
How animals store glucose ; a polymer of glucose
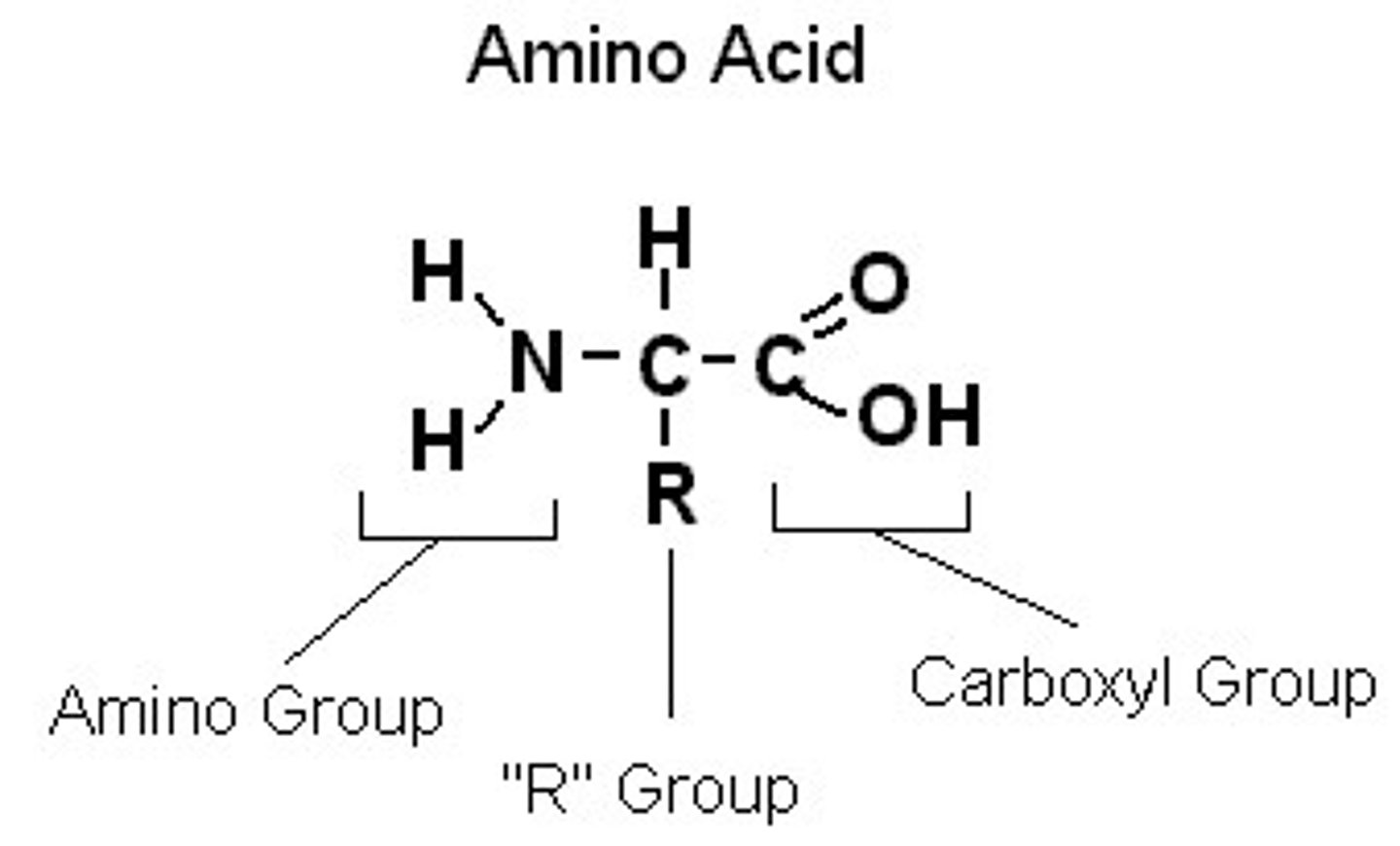
Amino Acids
Molecules that have an amino group and a carboxyl group ; a macromolecule
Polypeptide
Many amino acids linked by peptide bonds
Hydrophobic
Attract away from water
Hydrophilic
Attract towards water
Monomer of Carbohydrates
monosaccharides
Polymers of Carbohydrates
disaccharides and polysaccharides
Nonpolar side chain
hydrophobic
Polar side chain
hydrophilic
Charged/ionic side chain
hydrophilic/acidic/basic
Formation of Peptide Bonds
the carboxyl group of one amino acid must be positioned next to the amino group of another amino acid
Function of the Protein - Antibody
help protect the body from disease
Function of the Protein - Enzyme
carry out chemical reactions or assist in creating new molecules
Function of the Protein - Messenger
transmit signals (hormones)
Function of the Protein - Structural
provide structure and support
Function of the Protein - Transport/Storage
bind to and carry small atoms and molecules through the body
Protein
Molecule consisting of polypeptides (polymers of amino acids) folded into a 3D shape ; comprised of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur ; a macromolecule
Primary Structure
Linear chain of amino acids ; determined via genes ; dictates secondary and tertiary forms