Cell Theory, Cells - Cell Theory, Animal Cell Biology, Body Systems Glossary
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
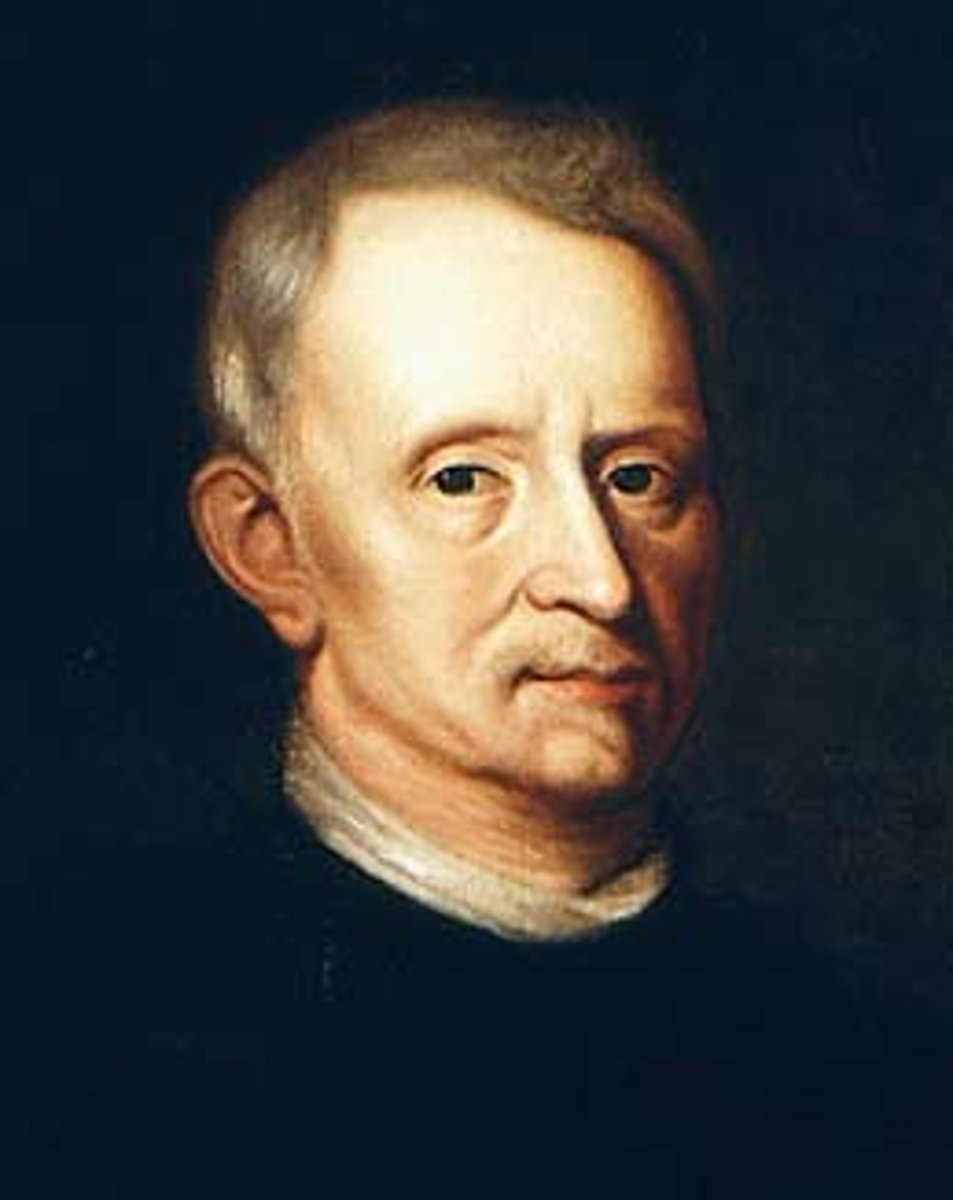
Robert Hooke
He gave us the word "cell" for use with living things. He discovered cells looking at cork.

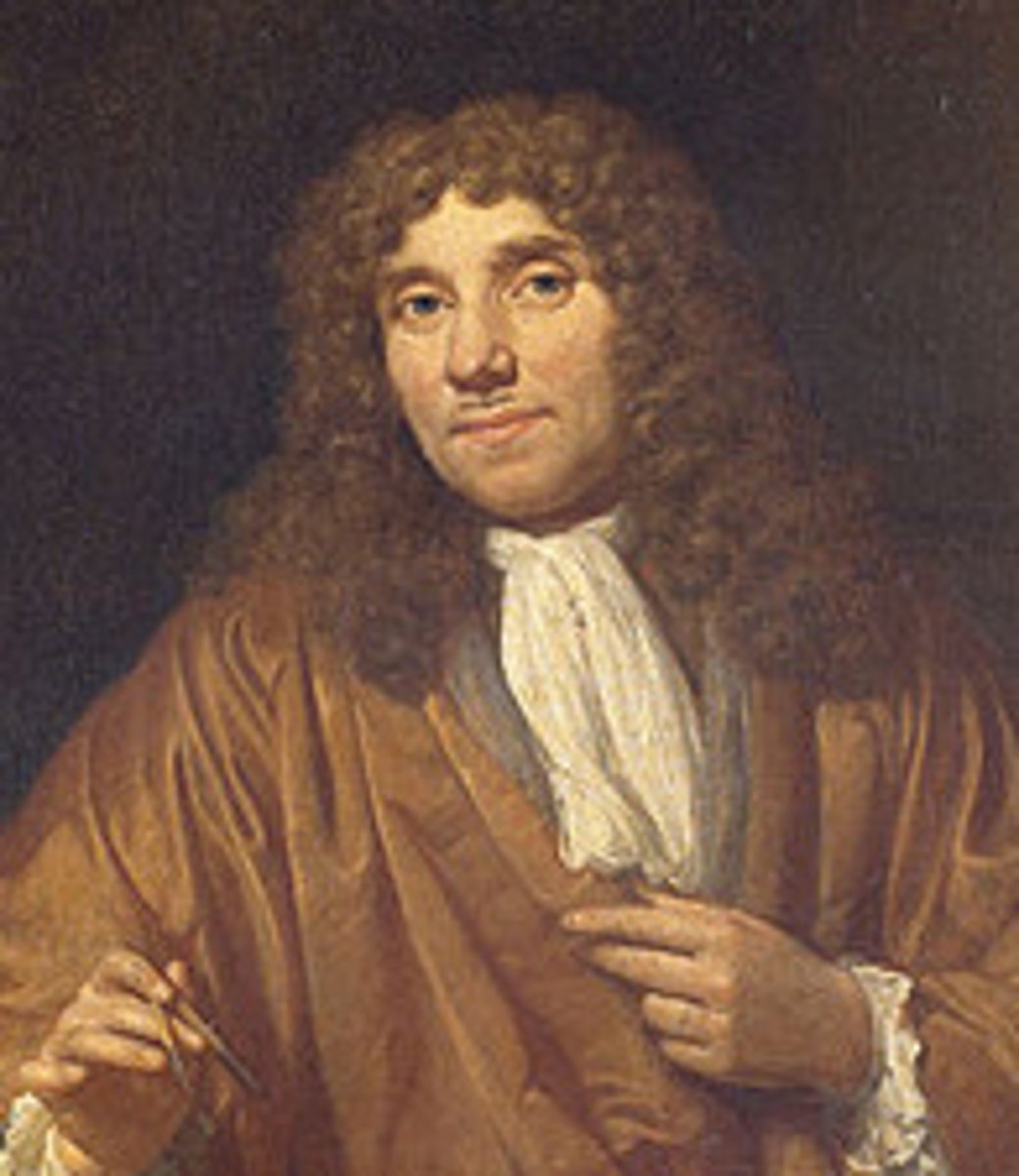
Anton von Leeuwenhoek
He saw the first living microorganisms.

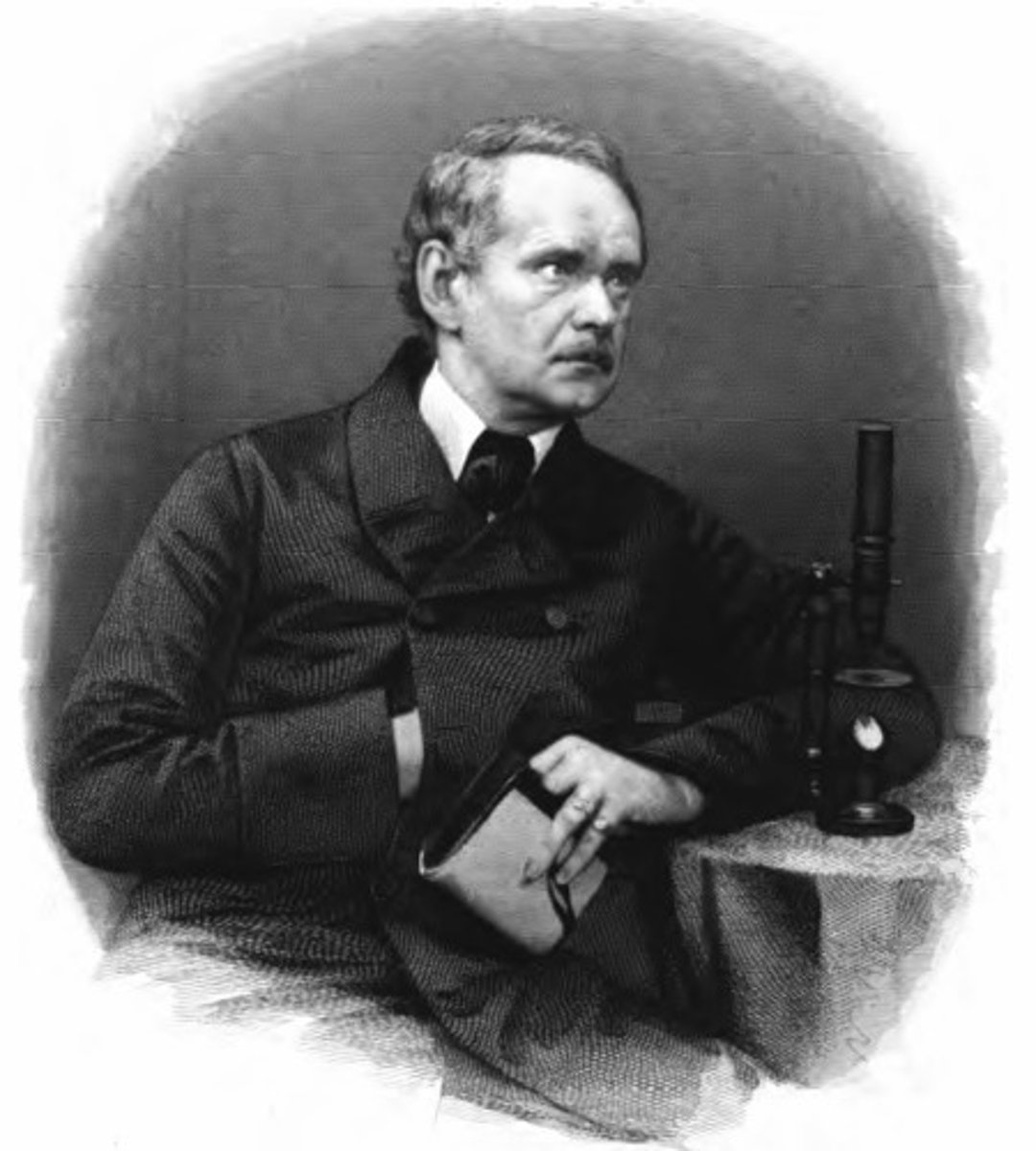
Matthias Schleiden
He studied plants. He looked at lots of plants under the microscope; their leaves, flowers, roots and stems. He decided that "All plants are made of cells".

Theodor Schwann
He studied animals. He looked at animal tissues under the microscope and saw cells. He came to the conclusion, "All animals are made of cells".

Rudolph Virchow
He was a doctor. He studied human illness and looked at diseased body tissue. He observed living cells dividing into two parts. He came to the conclusion that living cells reproduced and made new living cells.

Microscope
A tool used by biologists to study microscopic (TINY) details of living things.

All living things are made of cells.
The first part of The Cell Theory based on the work of Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann.
Cells only come from living cells.
The third statement of The Cell Theory. This is based on Rudolf Virchow's observation of living cells reproducing.
Cells
What are the tiny boxes Robert Hooke saw in this drawing?

cell theory
*All living things are composed of cells
*Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things
*New cells are produced from existing cells
cell
The basic unit of life
cell membrane
The thin flexible barrier that surrounds a cell
nucleus
The large membrane-enclosed structure that contains genetic information in the form of DNA and controls many of the cell's acitivities
eukaryotes
Cells that enclose their DNA in nuclei; animal and plant cells
prokaryotes
Cells that do not enclose their DNA in nuclei; bacteria
cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the plant cell
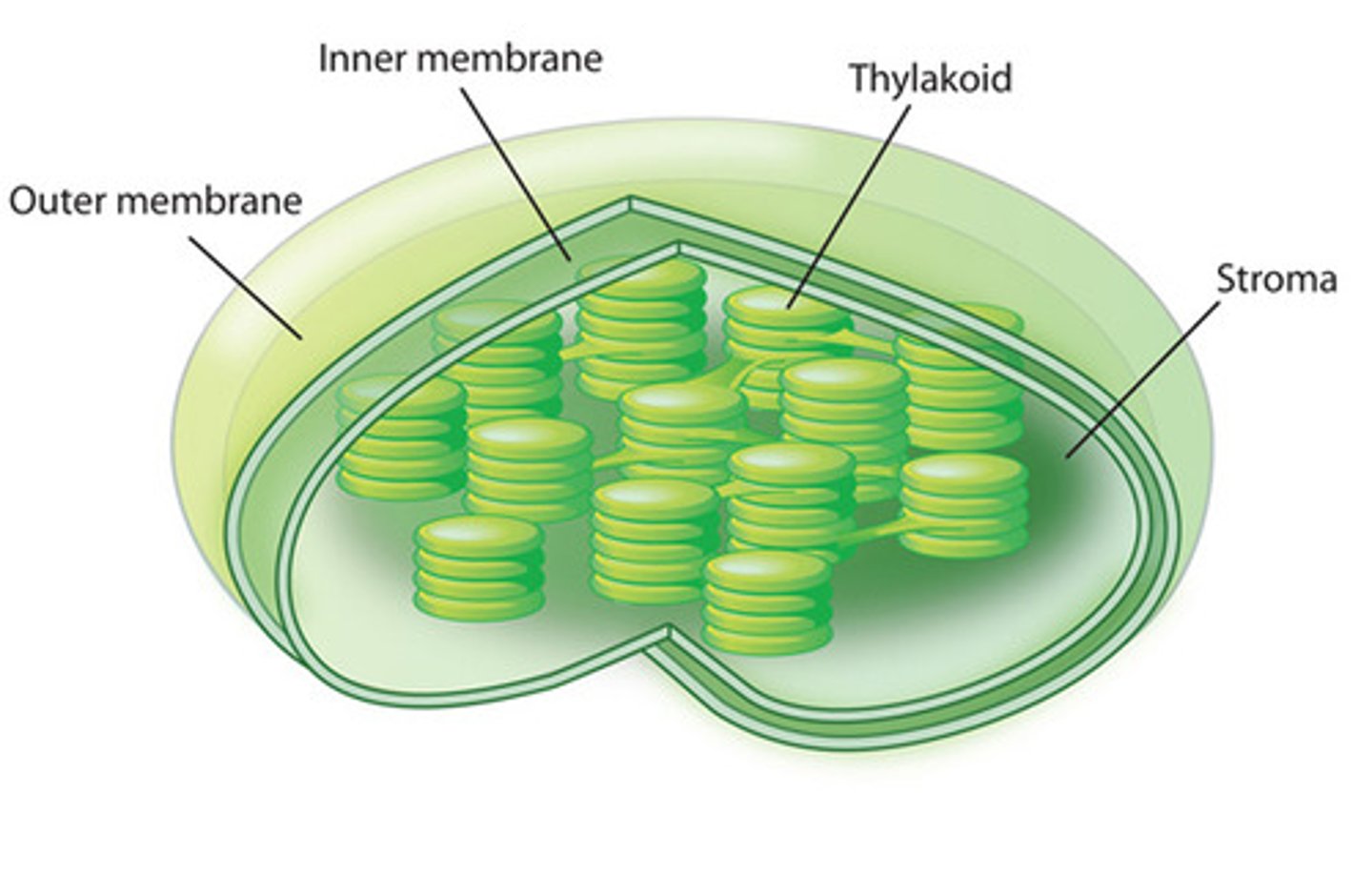
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
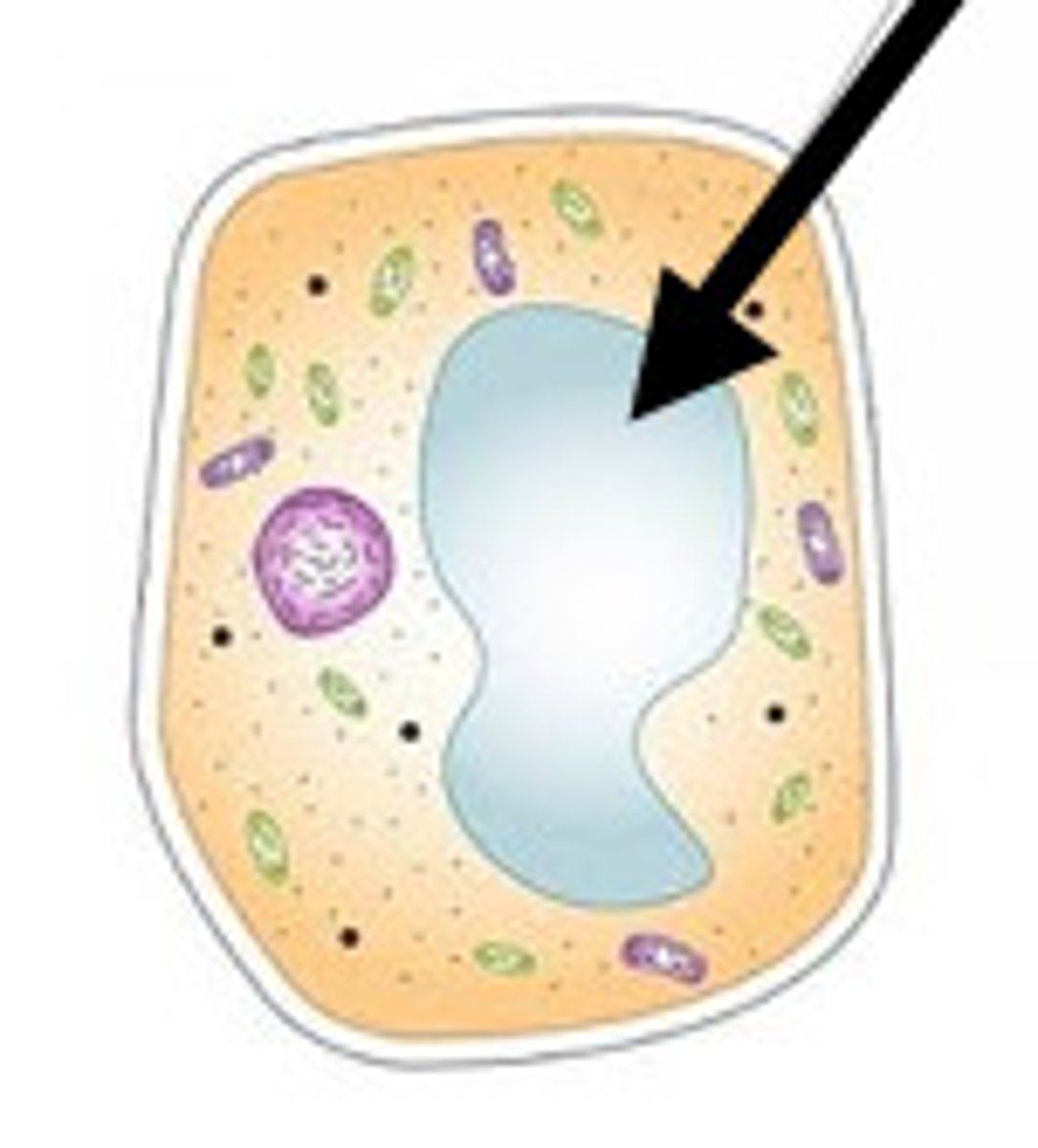
animal cell
The basic unit of animal tissues and organs
cell
The smallest unit of life. All living things are made of cells. Most cells are too small to see with the naked eye.
cell division
The splitting of a cell to form new cells. All cells come from pre-existing cells. Cell division allows organisms to grow and reproduce.
cell membrane
A thin layer that forms the boundary of a cell. The cell membrane holds the cell contents in and controls which substances pass in and out.
cell wall
A rigid structure that protects and strengthens some cells. Plant cells have cell walls around their cell membranes. Animal cells do not have cell walls.
chloroplast
An organelle that absorbs sunlight energy and stores it in sugars. Chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis in some plant cells. They are not found in animal cells.
cytosol
A jelly-like fluid that fills the space inside a cell. Small structures called organelles float in the cytosol.
mitochondrion
An organelle that breaks down sugars to supply energy. Mitochondria are a cell's 'power plants'.
multicellular organism
A living thing made up of two or more cells. Humans, insects, mushrooms and trees are examples of multicellular organisms.
neuron
A branched cell that sends signals in the brain or through nerves. Neurons have branching structures that help them send and receive signals.
nucleus
An organelle that controls a cell's activities. The nucleus stores DNA, which instructs how the cell grows and functions.
organ
A body part that performs a specific function. Organs are made up of tissues. Examples of organs include the brain, heart, lungs and stomach.
organelle
A structure in a cell that performs a particular function. Organelles, or 'little organs', carry out the processes needed to keep cells alive.
plant cell
The basic unit of plant tissues and organs. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have cell walls, large vacuoles and often chloroplasts.
red blood cell
A small, round cell that carries oxygen around the body. Red blood cells have disc shapes and contain haemoglobin to help them carry oxygen.
specialised cell
A cell with unique structures to perform certain functions in the body. The size, shape and features of a specialised cell are adapted to help it do its job.
tissue
A group of similar cells that work together. A group of tissues form an organ. Examples of tissues include muscle, bone, blood and skin.
unicellular organism
A living thing made up of a single cell. Bacteria and yeast are examples of unicellular organisms.
vacuole
An organelle that stores fluids, nutrients and wastes. A plant cell has a large vacuole to store water. Animal cells have many small vacuoles.
chemical digestion
The breakdown of food by saliva, stomach acid and other digestive juices.
digestion
The breakdown of food into simple nutrients the body can absorb.
digestive system
The group of organs that break food down into simple nutrients the body can absorb.
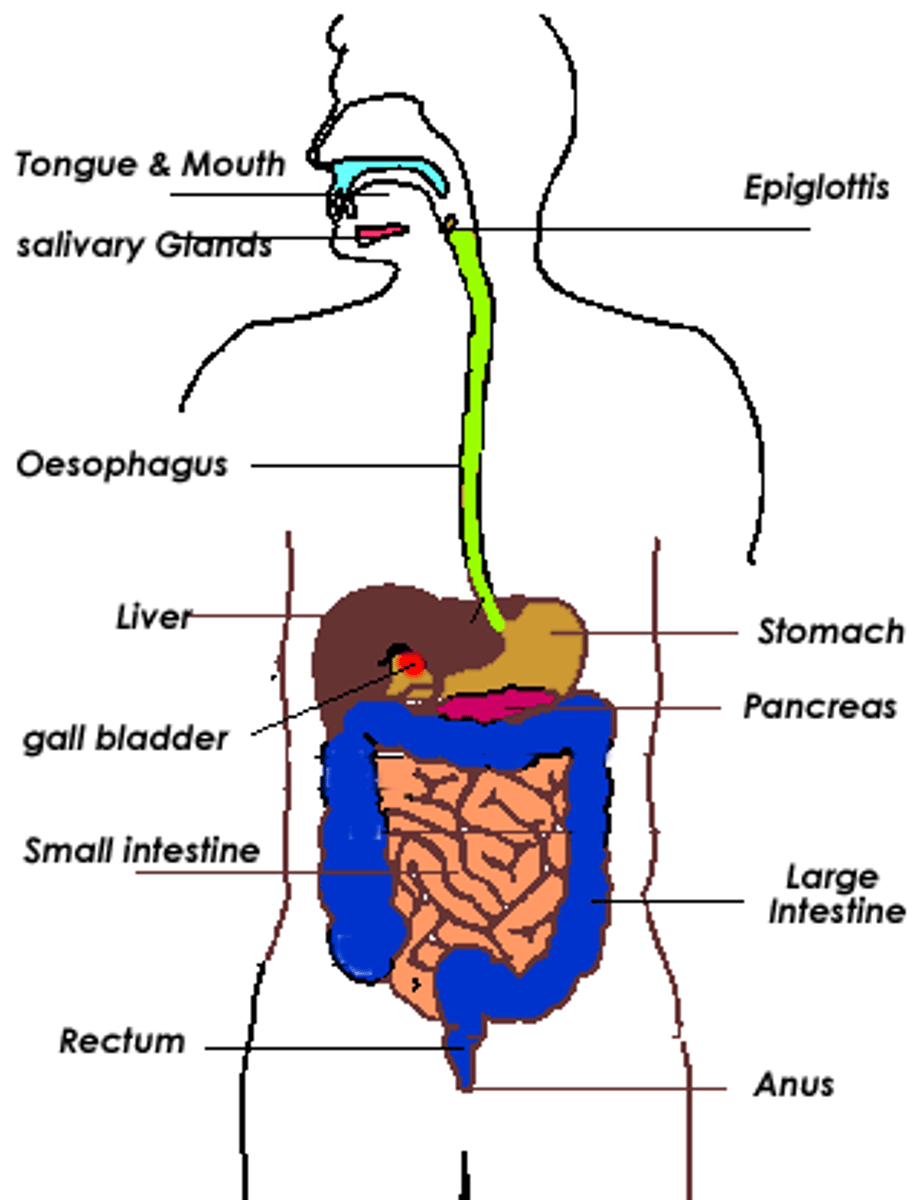
digestive tract
The connected organs that food passes through as it is broken down.
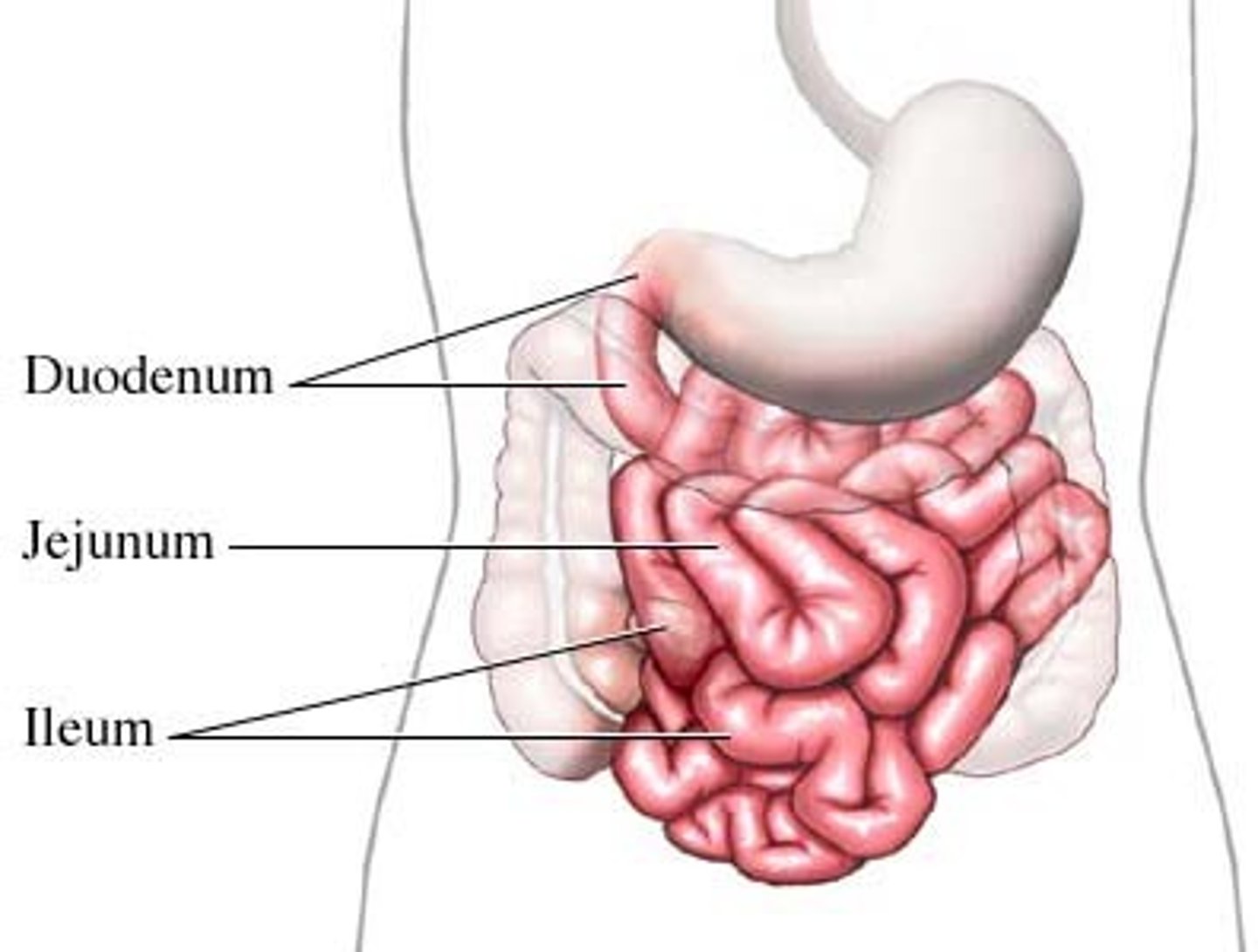
large intestine
A wide tube where water is absorbed and most good bacteria live.
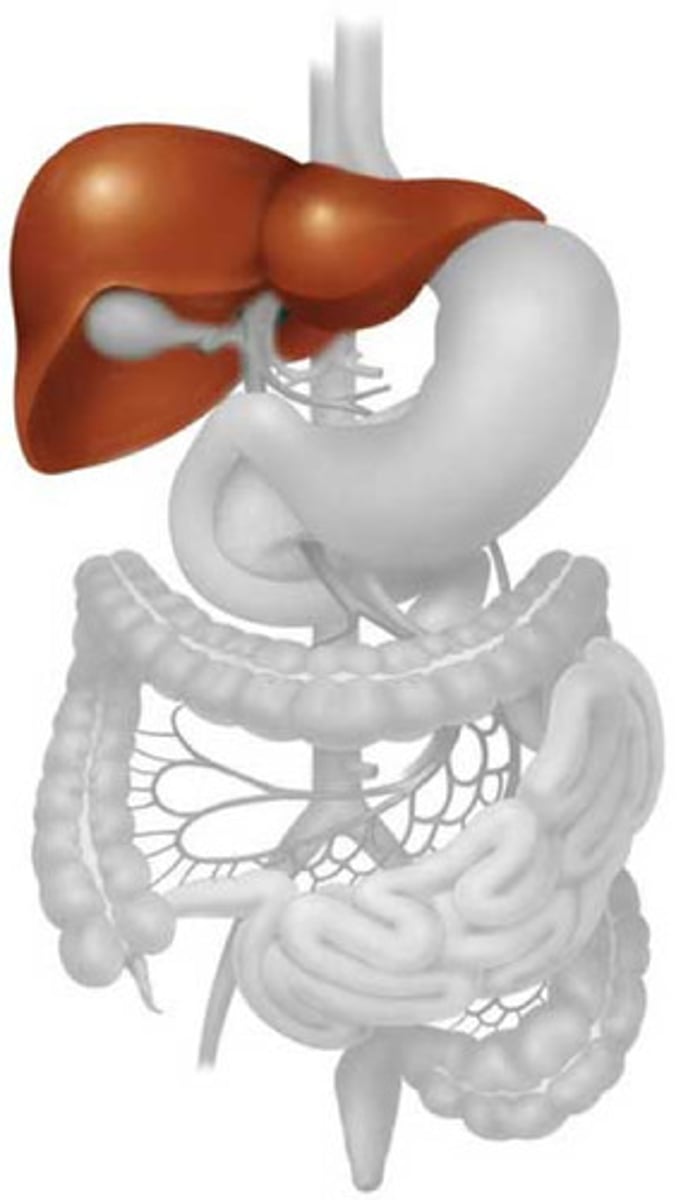
liver
A large organ that produces bile to help digest fats.
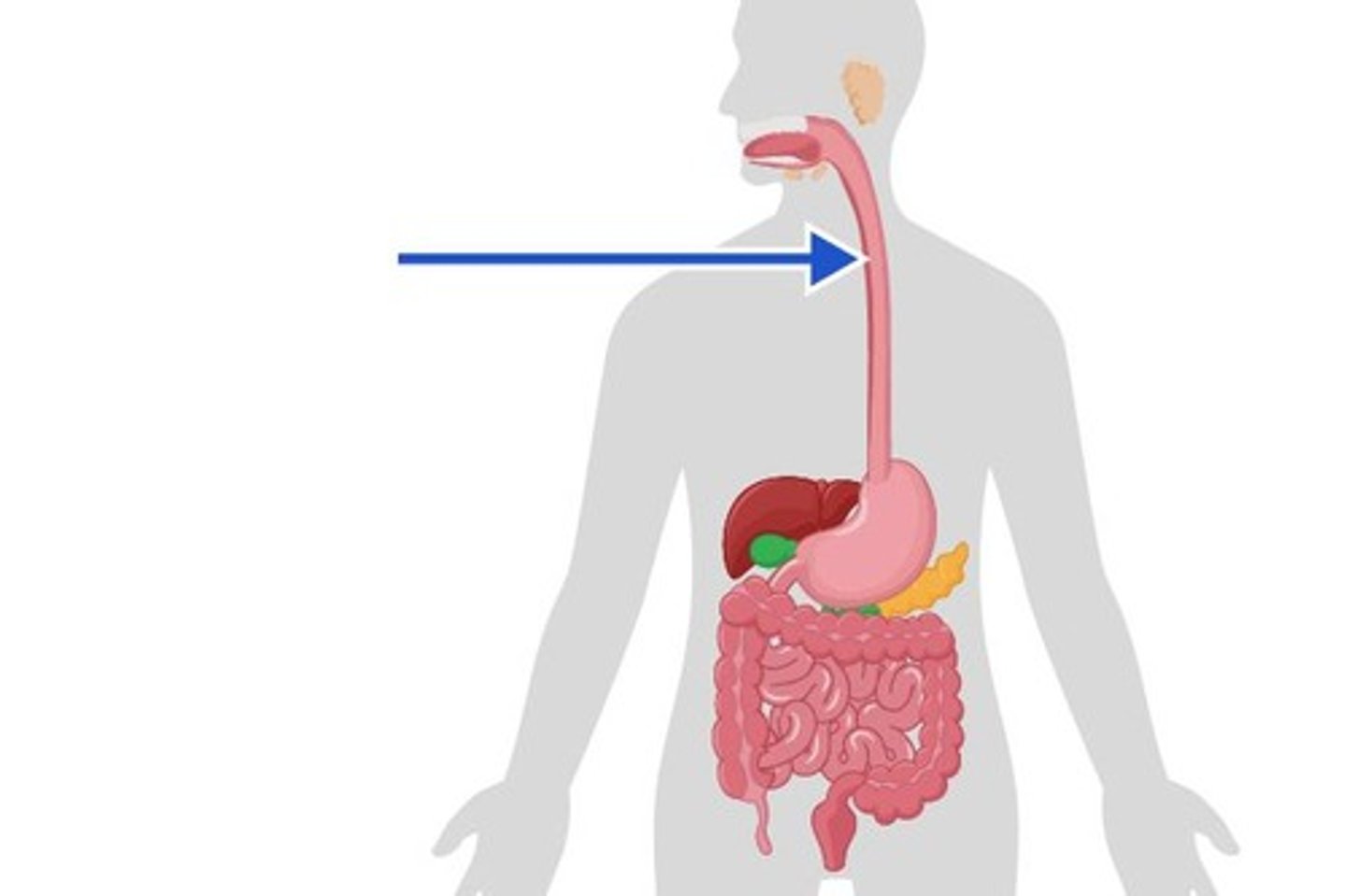
oesophagus
The tube that connects the throat to the stomach.
peristalsis
Involuntary muscle contractions that push food through tubes.
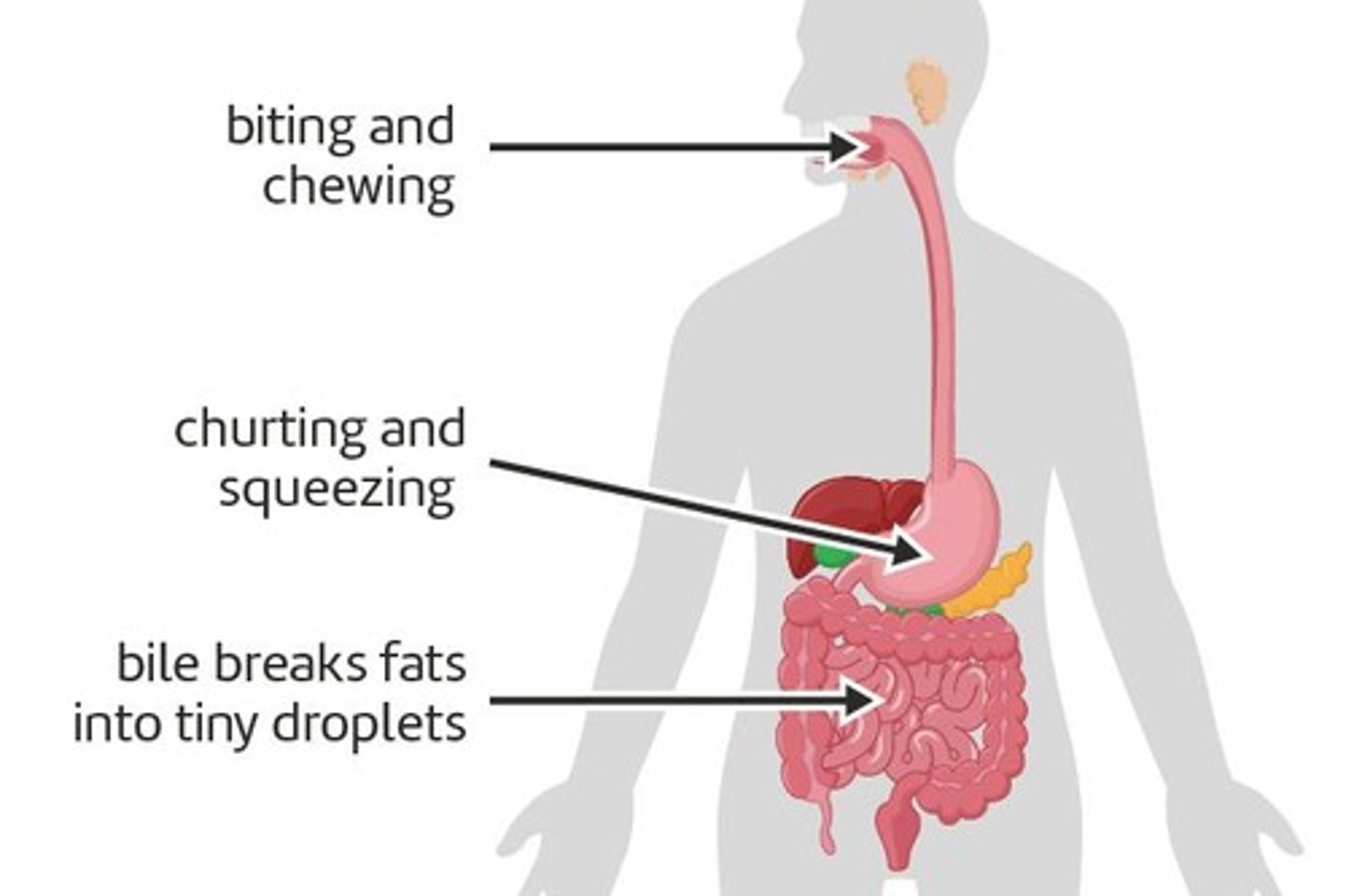
physical digestion
The breakdown of food by mashing, grinding, churning or mixing.
small intestine
A long, narrow tube where most nutrients are absorbed by the body.
stomach
A muscular pouch that churns and squeezes food into liquid.
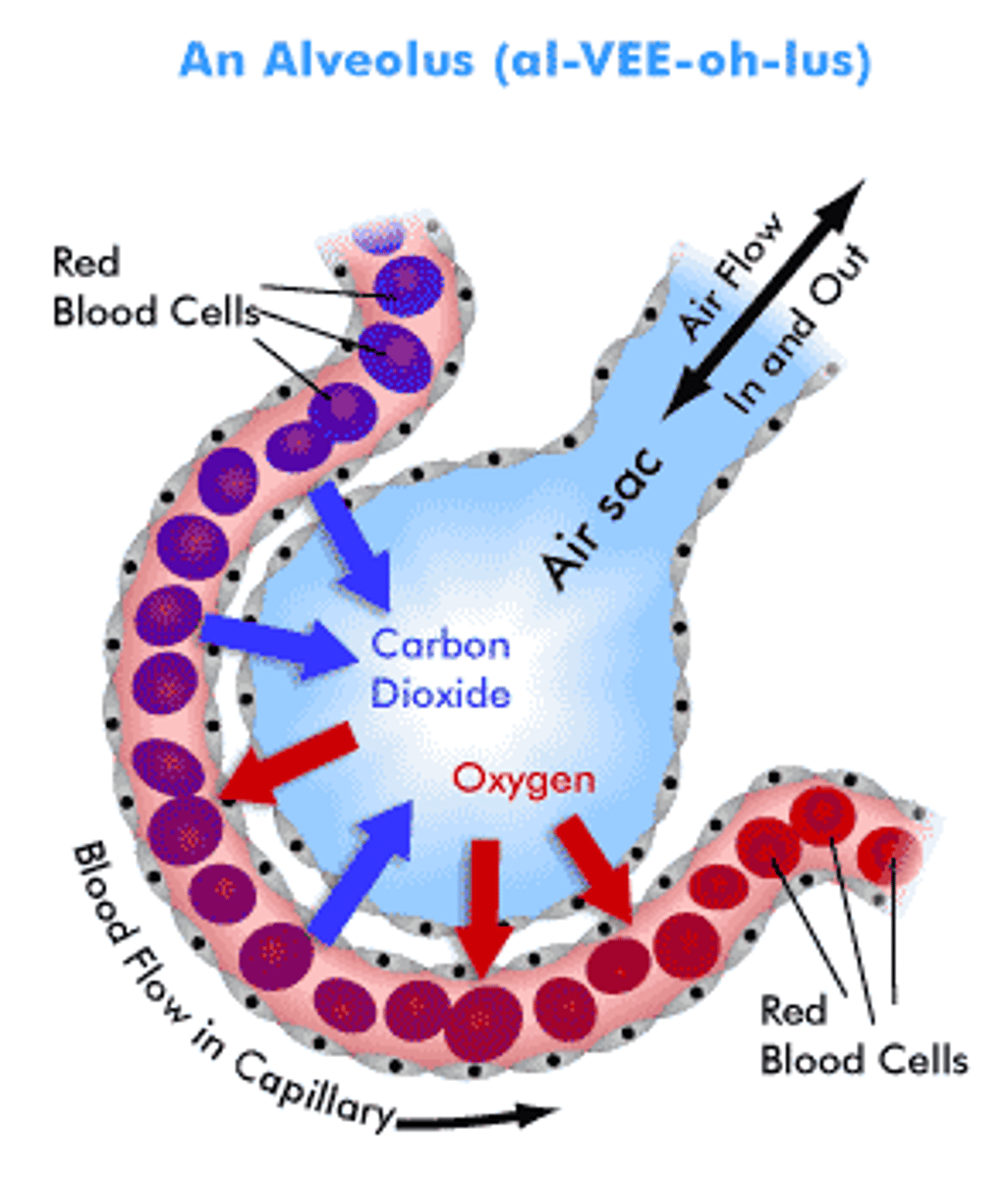
alveolus
A tiny air sac in a lung where gas exchange occurs.
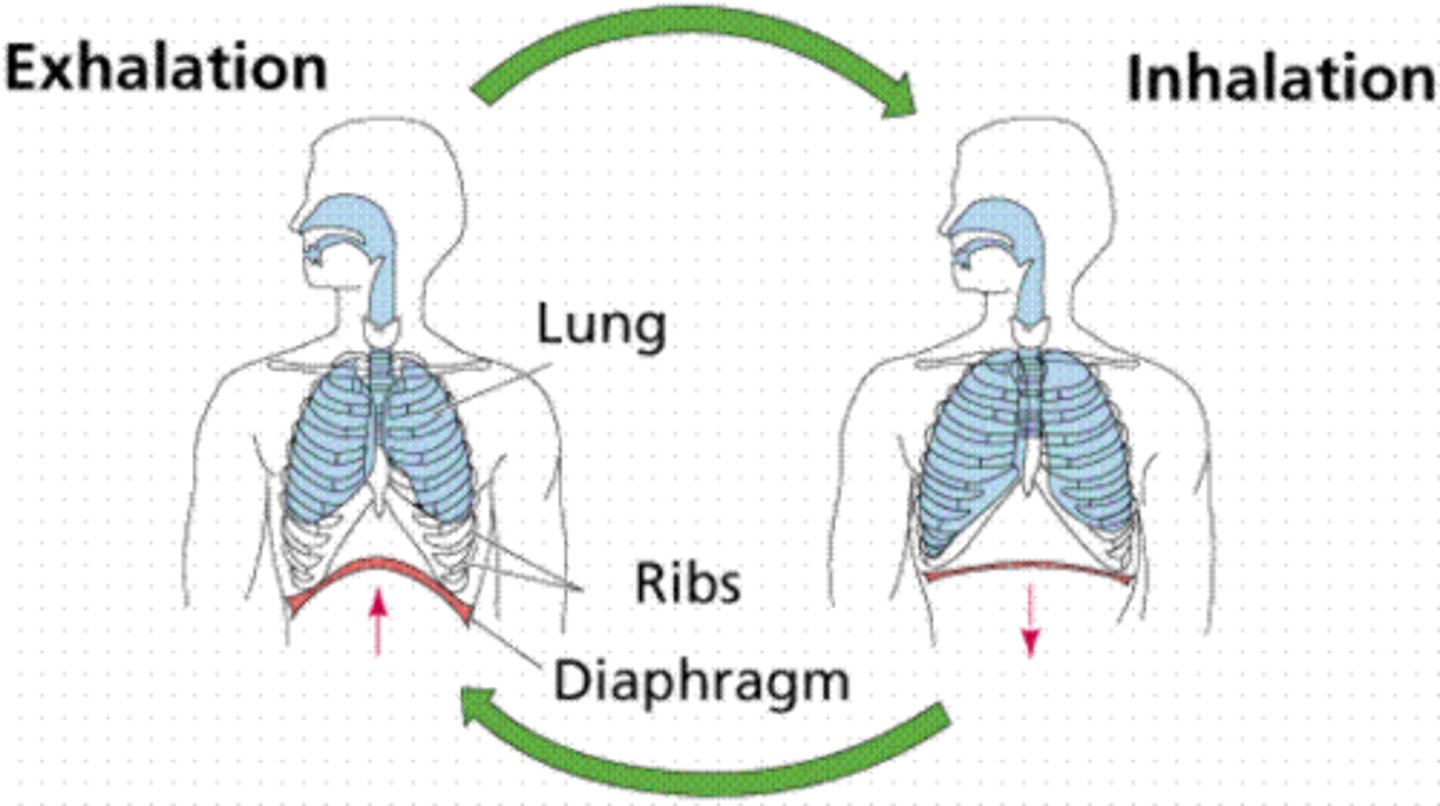
breathing
The process used by animals to exchange gases with the atmosphere.
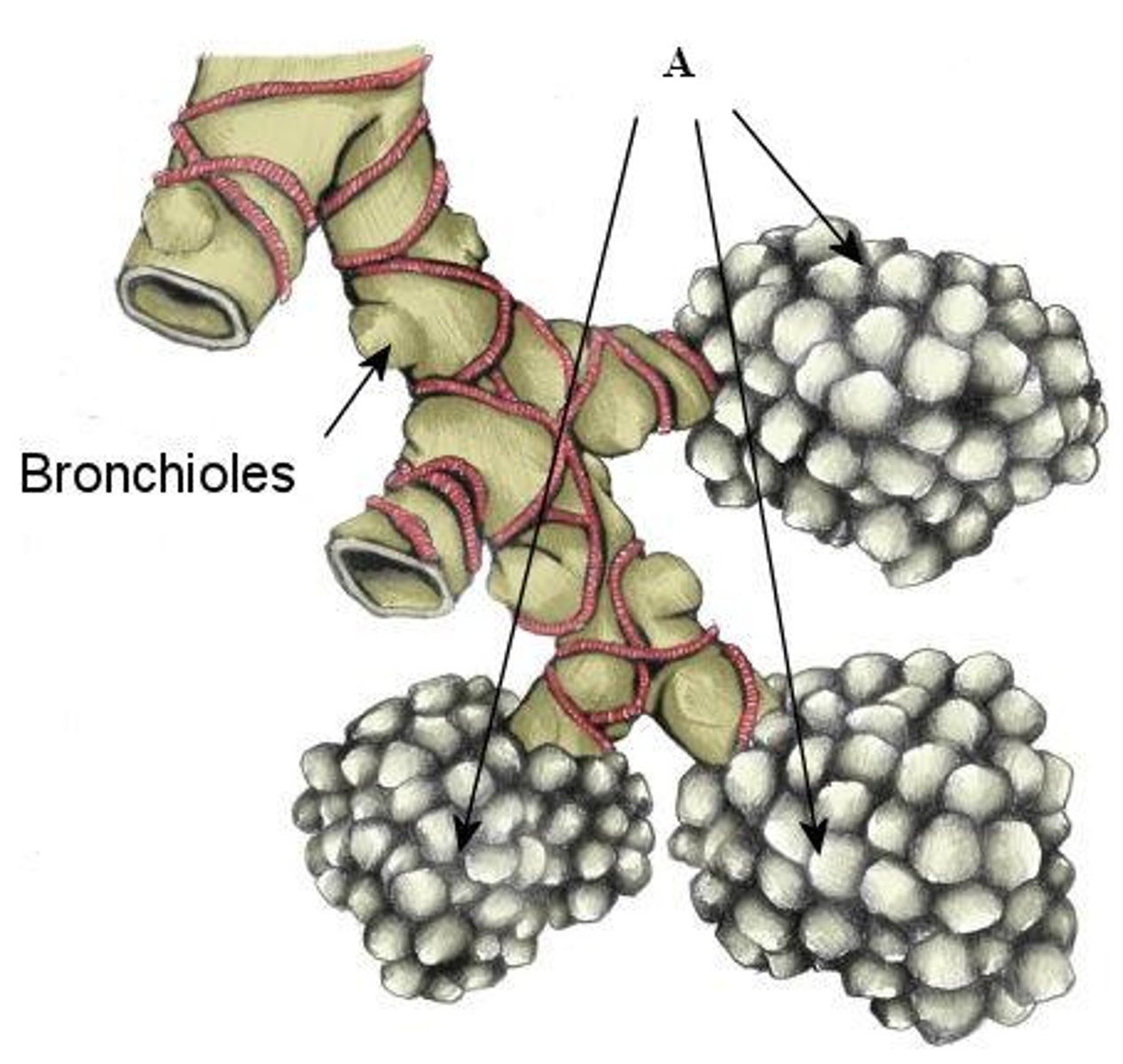
bronchiole
A tube that carries air through a lung.
cellular respiration
The process used by all living cells to release energy.

diaphragm
A large sheet of muscle that contracts to draw gas into the lungs.
diffusion
The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration.
gas exchange
The movement of oxygen into the blood and carbon dioxide out of it.
lung
An organ where gas exchange occurs between air and blood
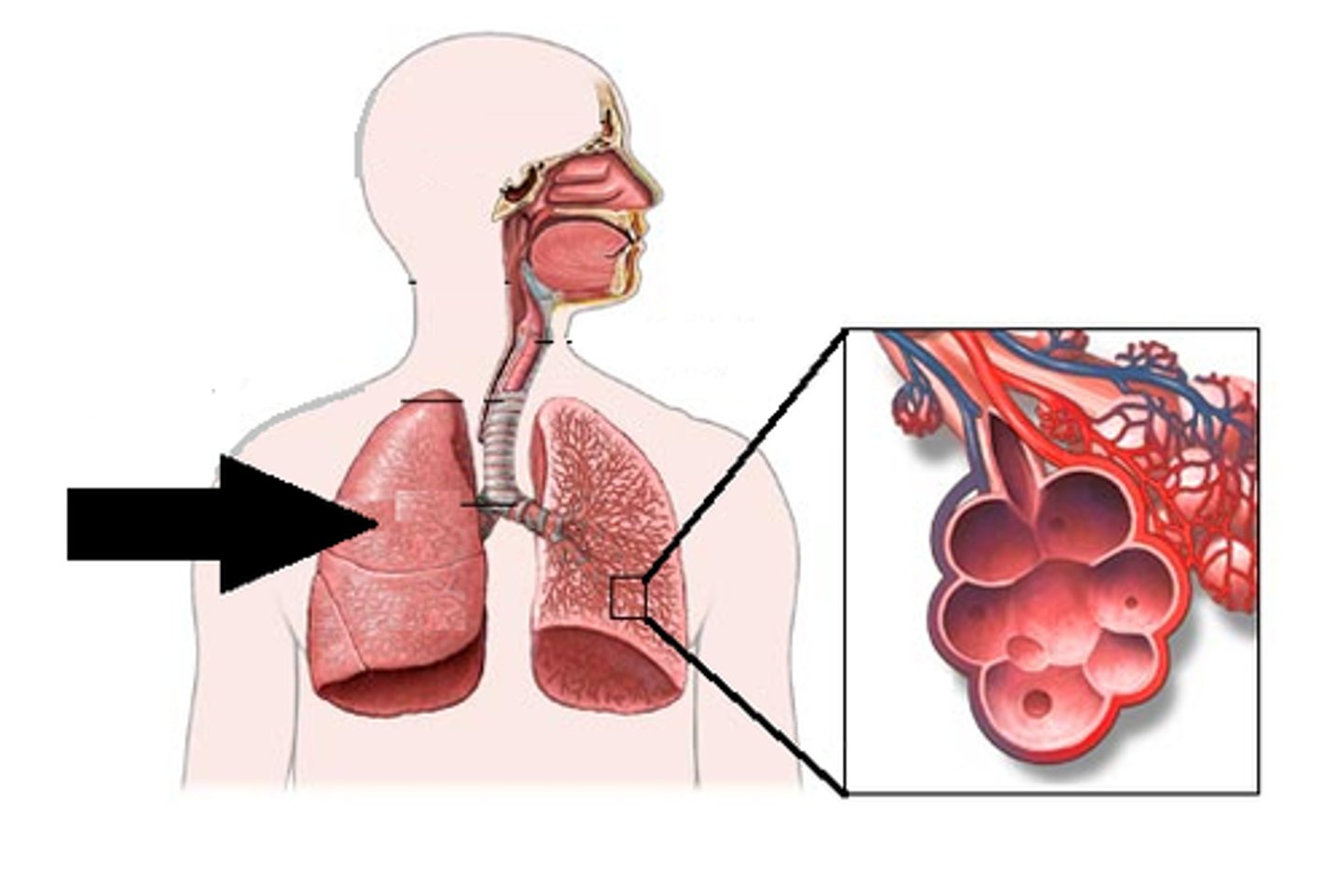
respiratory system
A group of organs that allows an animal to exchange gases with its environment
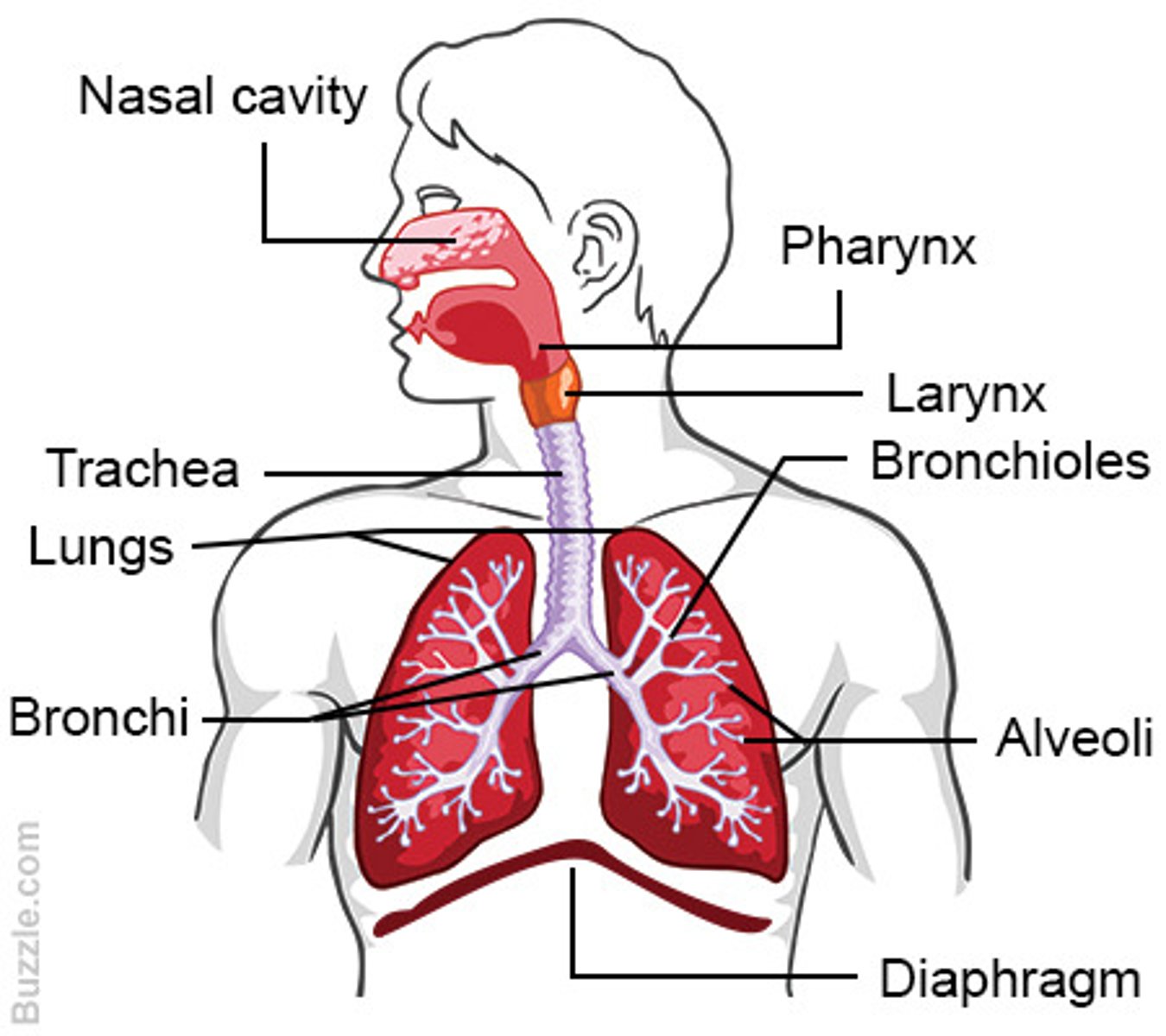
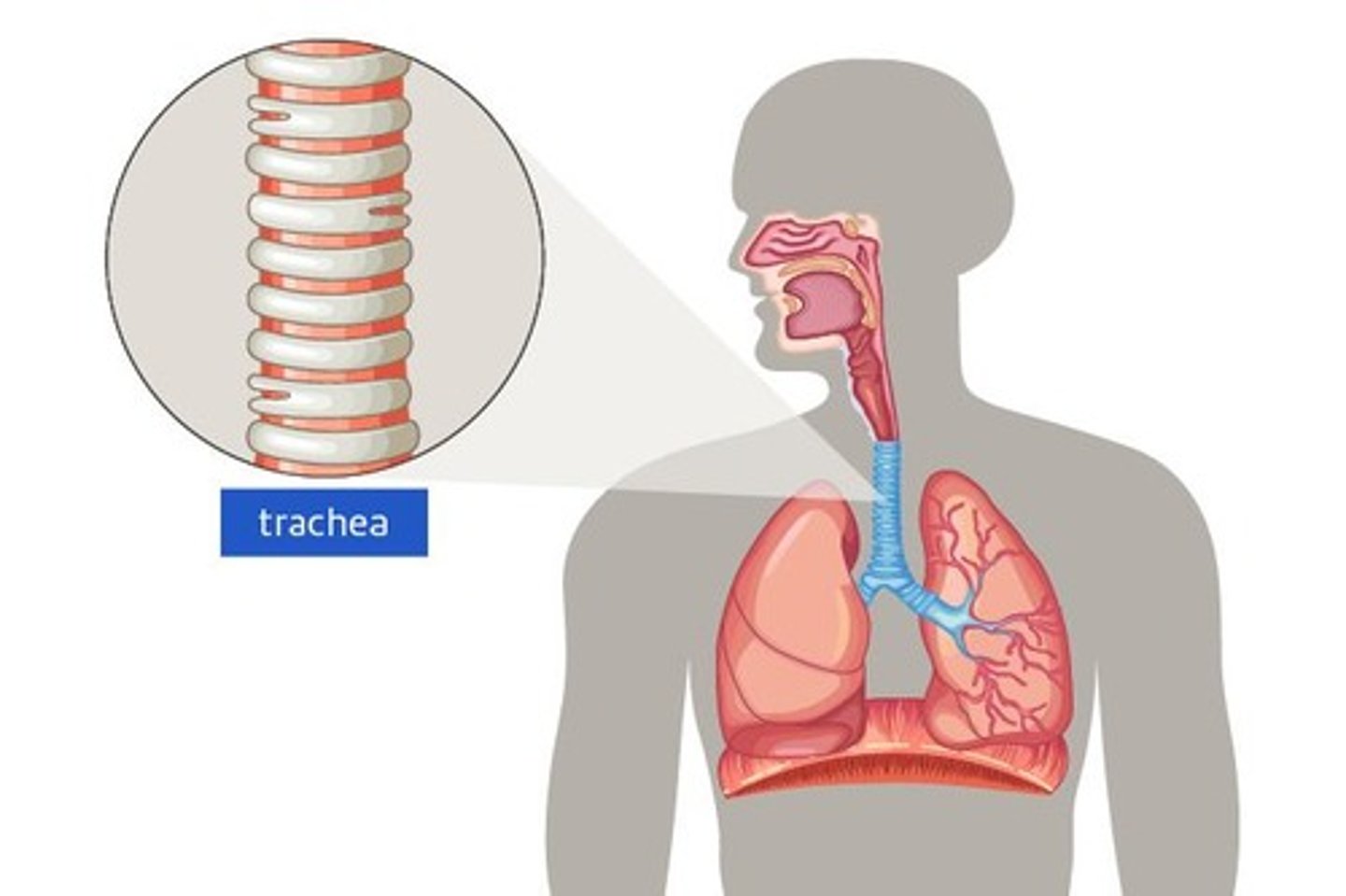
trachea
The main airway between the throat and the lungs
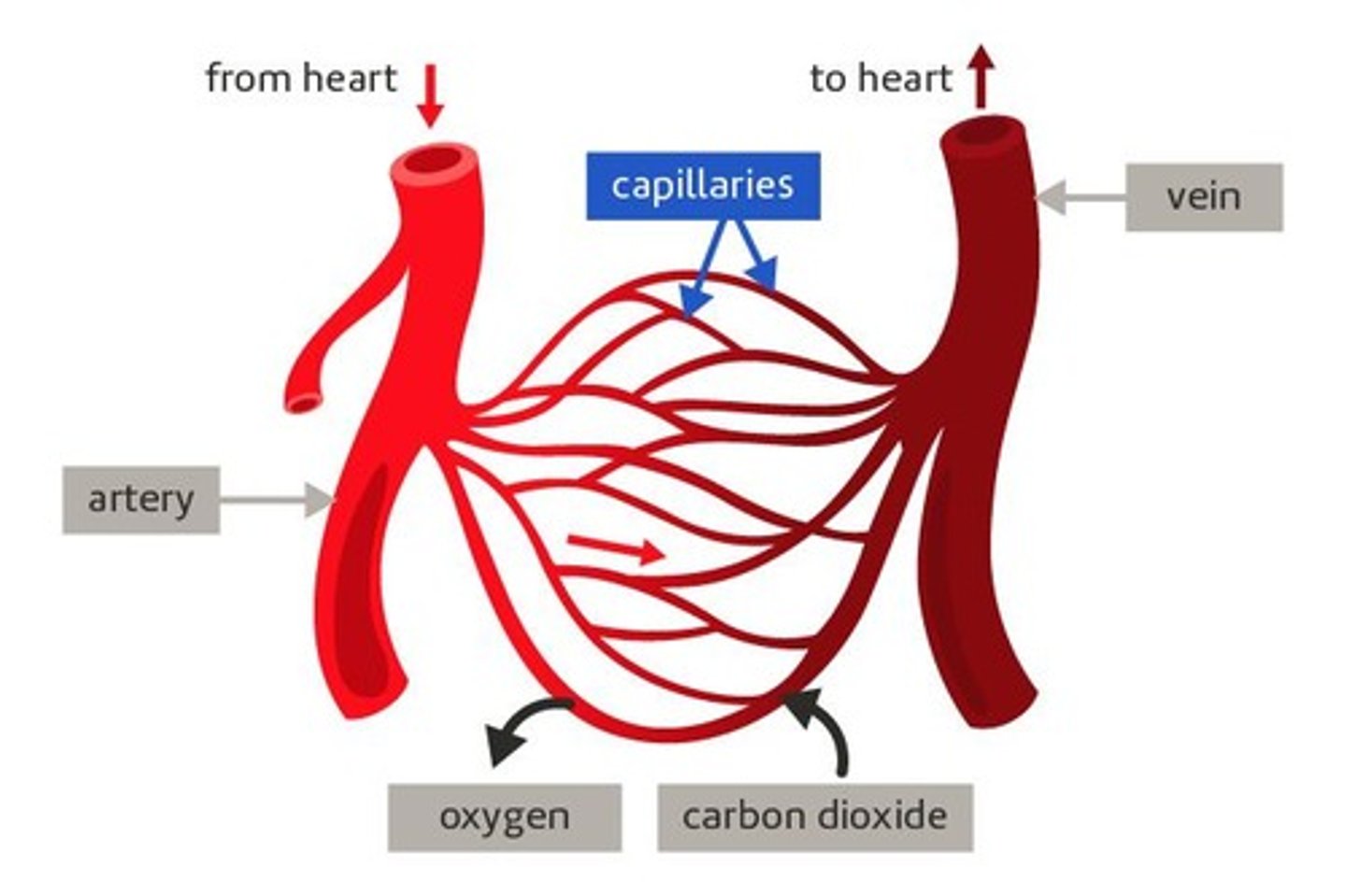
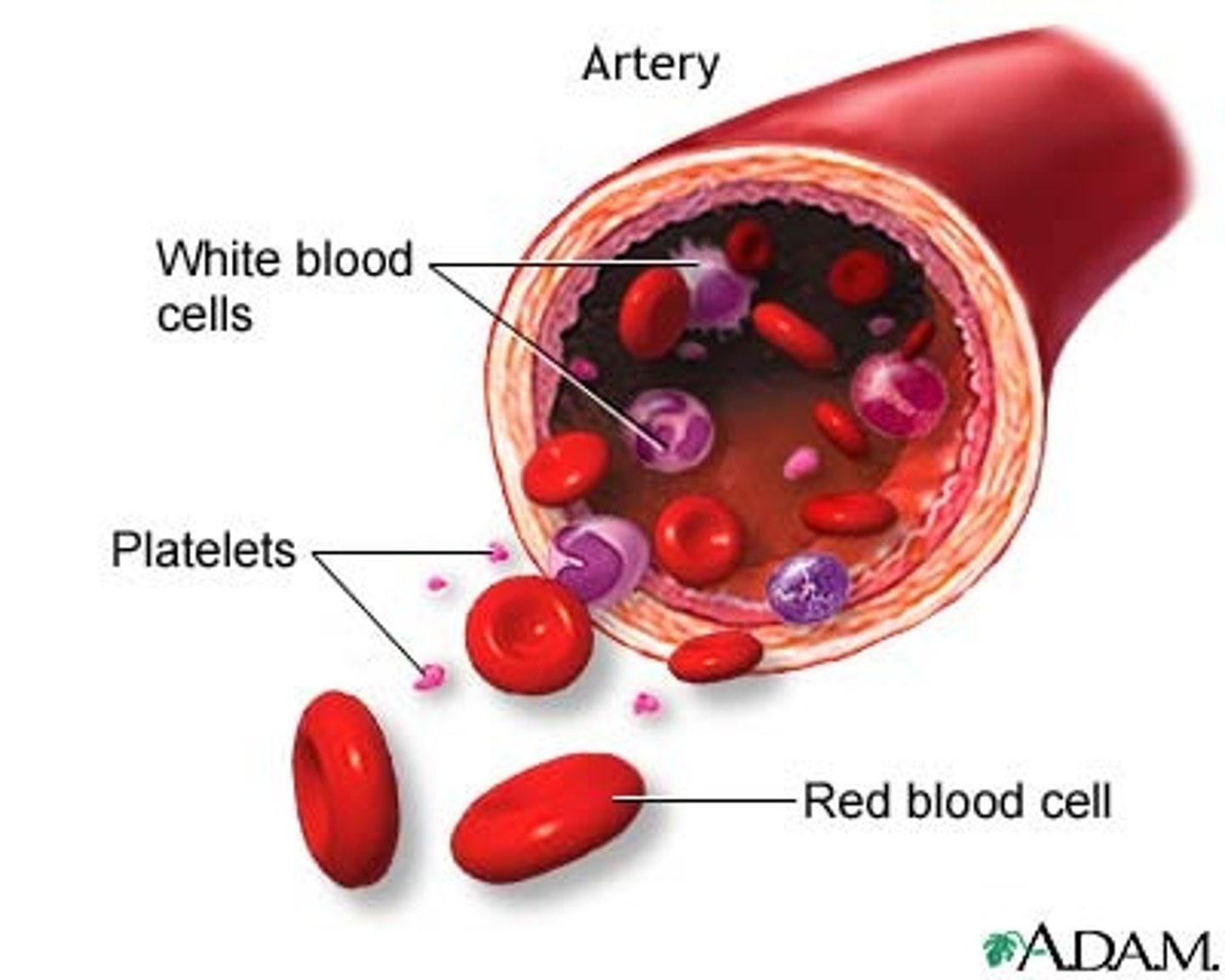
artery
A tube that carries blood away from the heart
blood
The fluid pumped by the heart around the circulatory system
blood vessel
Any tube that blood flows through
capillary
A tiny blood vessel where substances pass to and from the blood
circulatory system
The body system that moves blood throughout the body
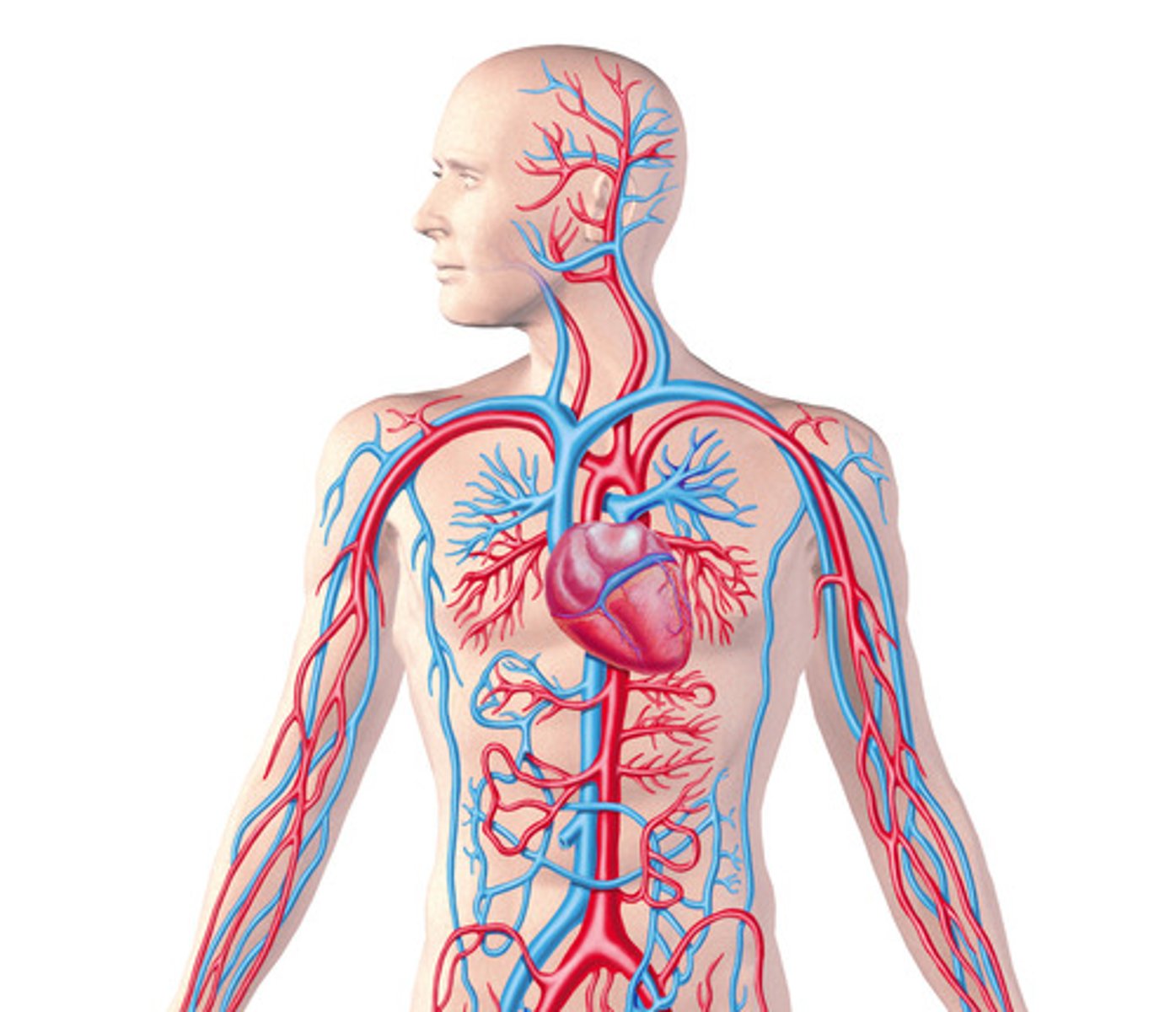
heart
A muscular organ that pumps blood around the body
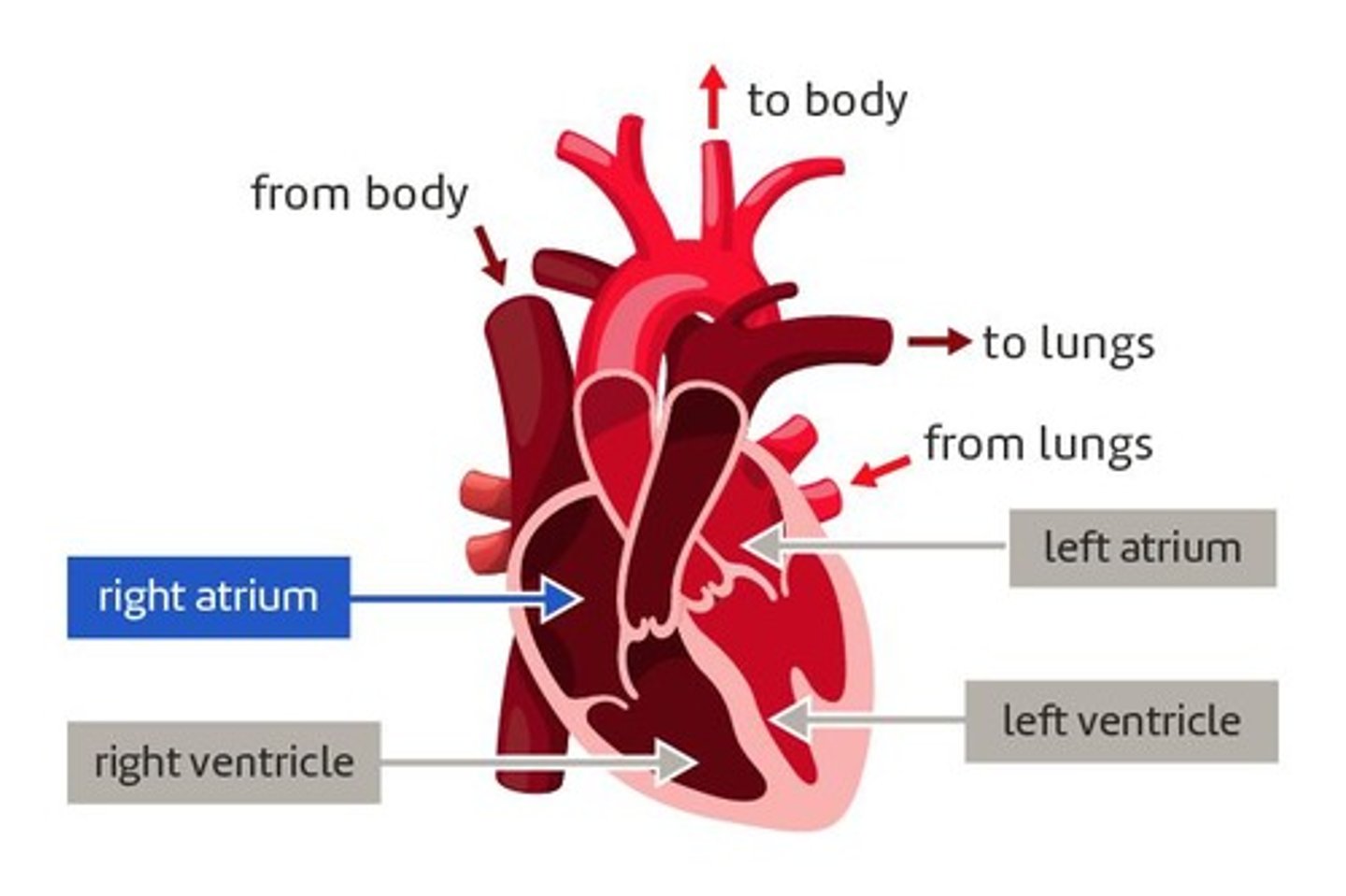
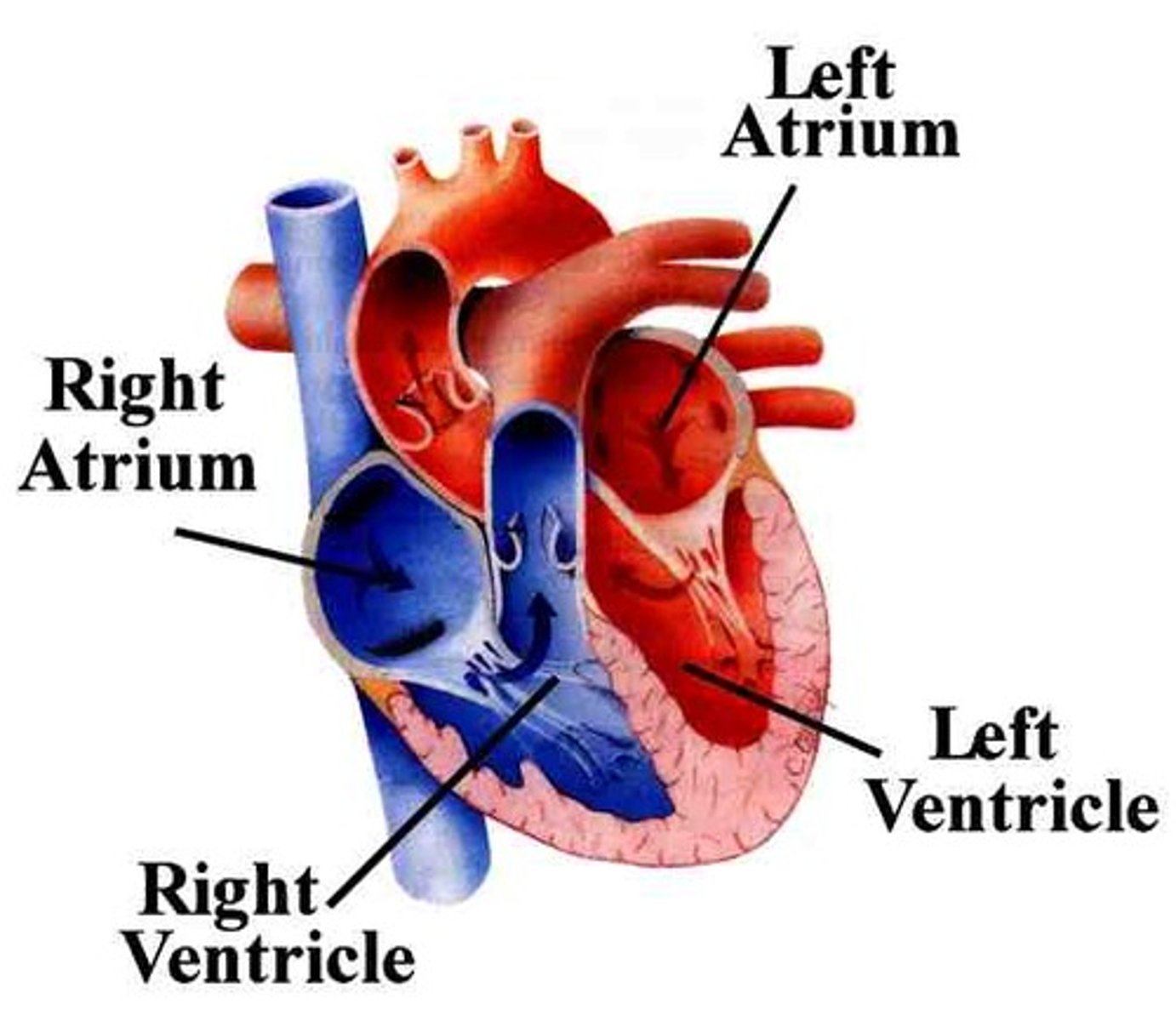
left atrium
A heart chamber that receives blood from the lungs
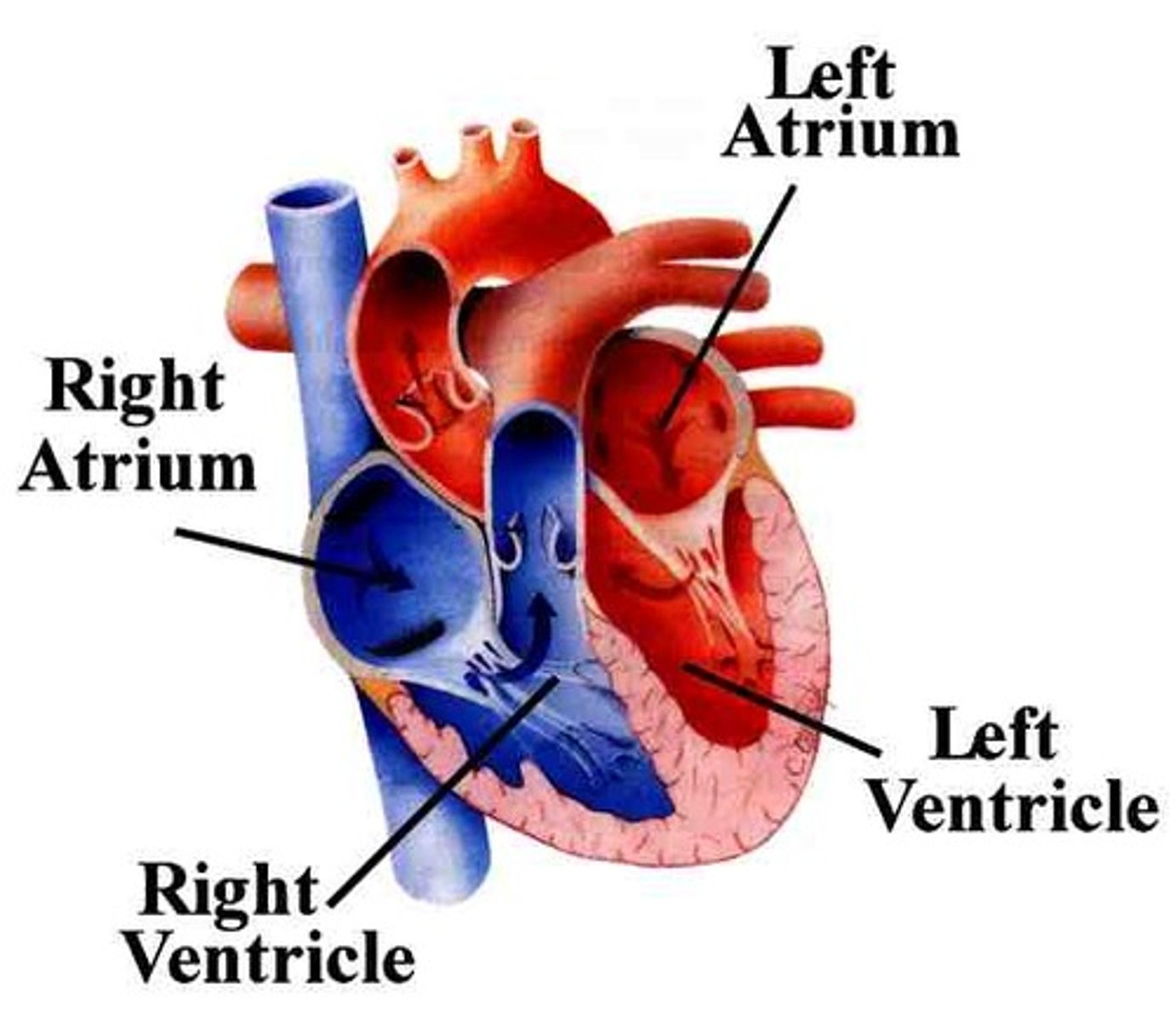
left ventricle
A heart chamber with thick walls that pumps blood to the body
red blood cell
A blood component that transports oxygen
right atrium
A heart chamber that receives blood from the body
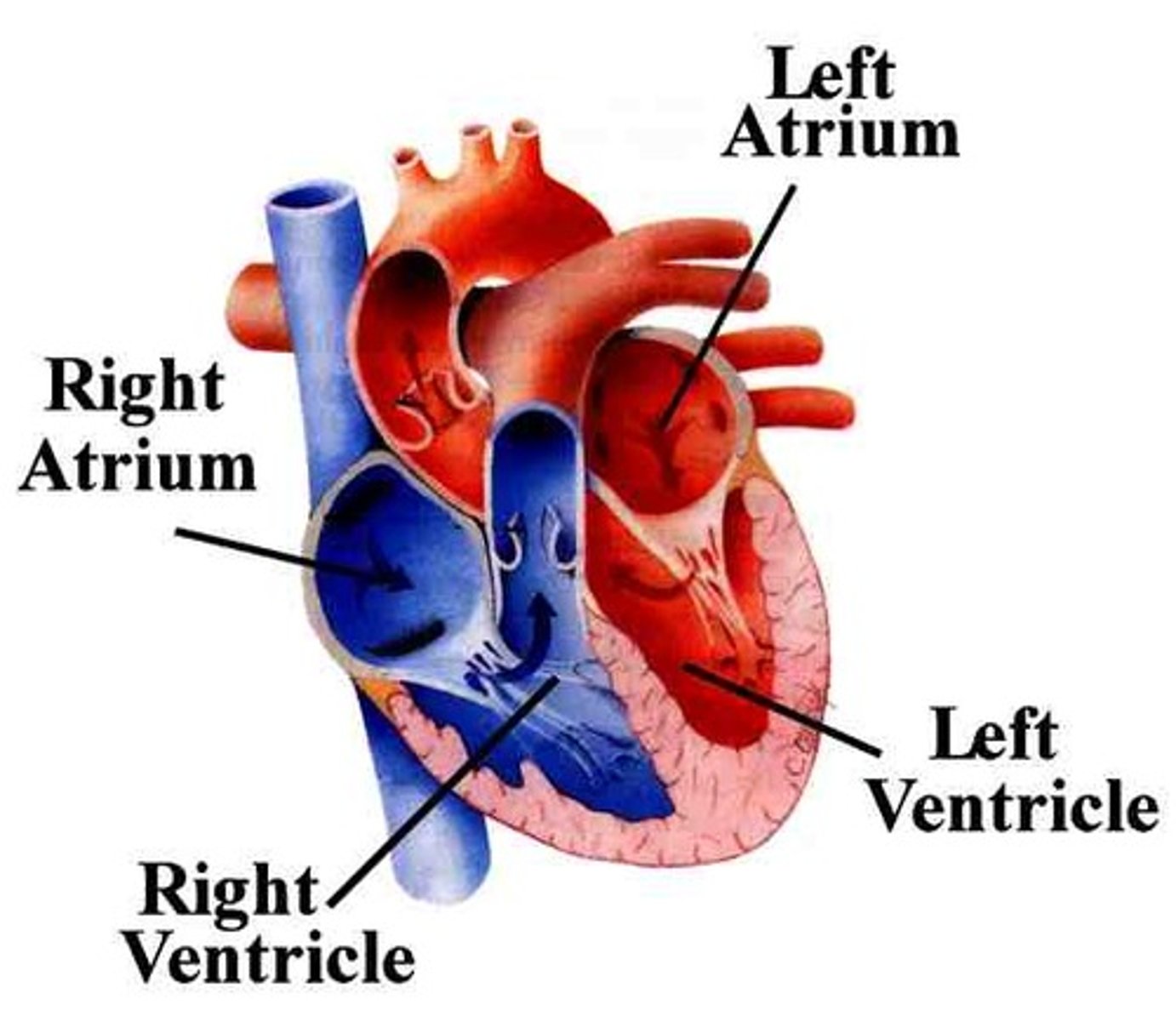
right ventricle
A heart chamber with thick walls that pumps blood to the lungs
vein
A tube that carries blood back to the heart
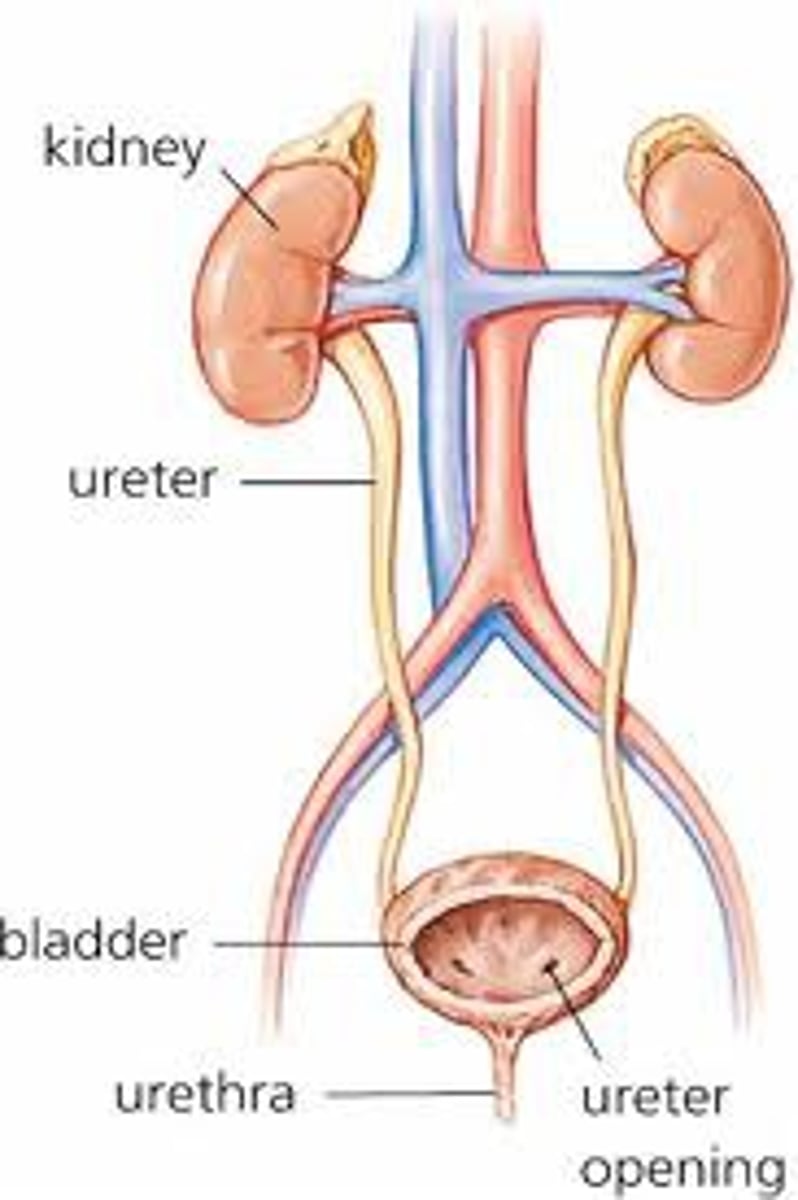
bladder
A muscular pouch that receives and stores urine
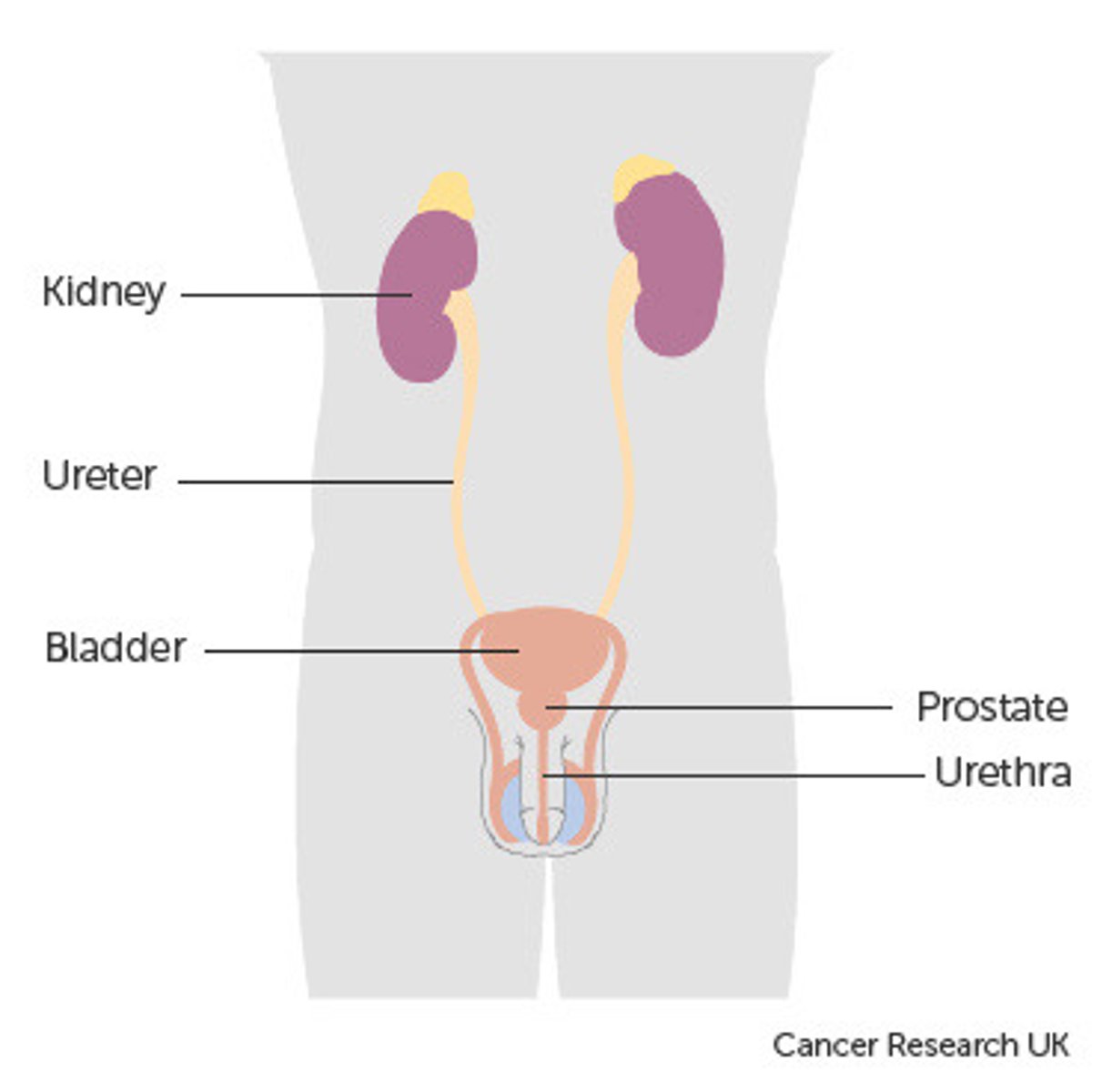
excretion
The removal of waste products from the body
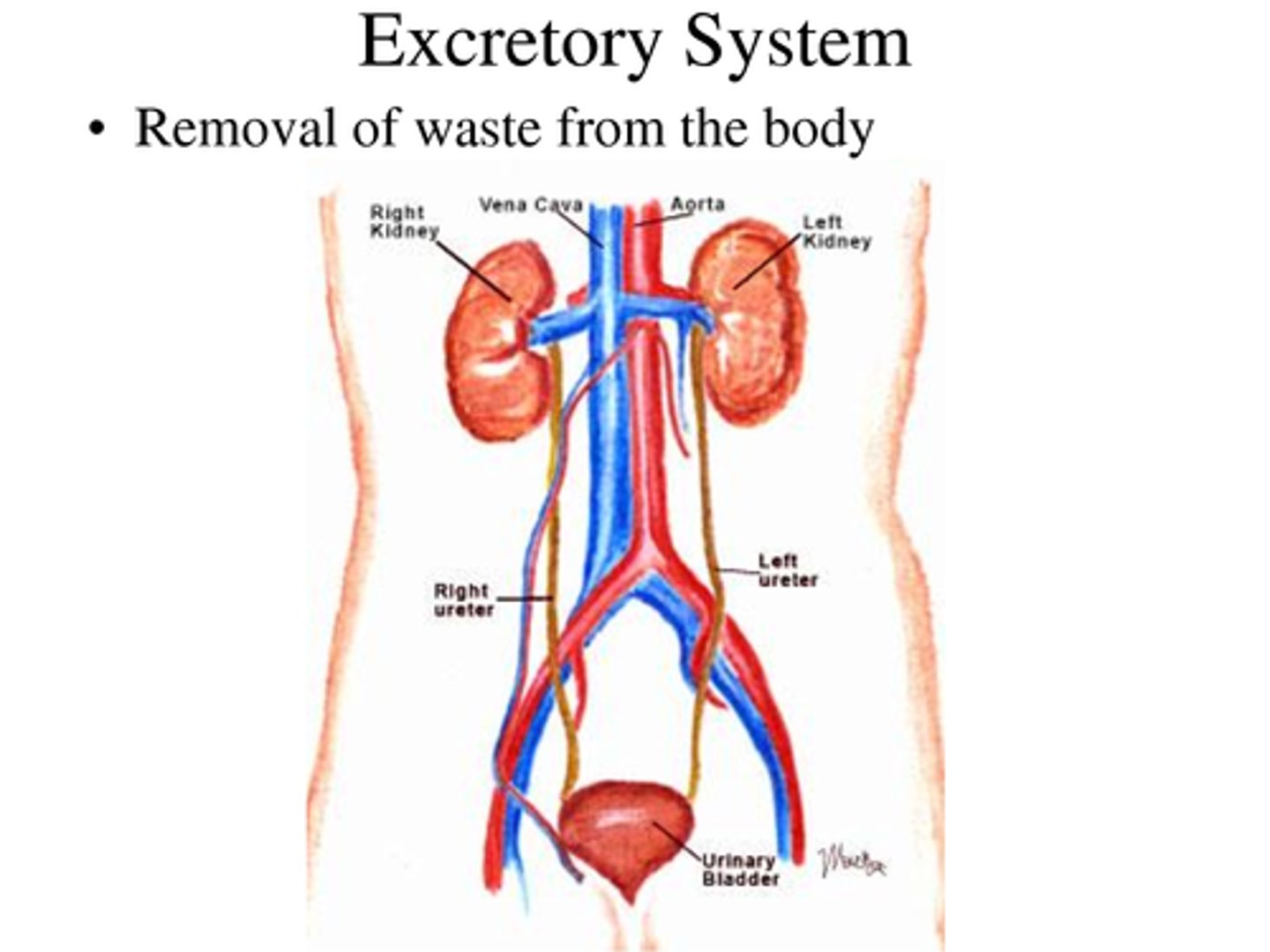
excretory system
The body system that gets rid of waste products
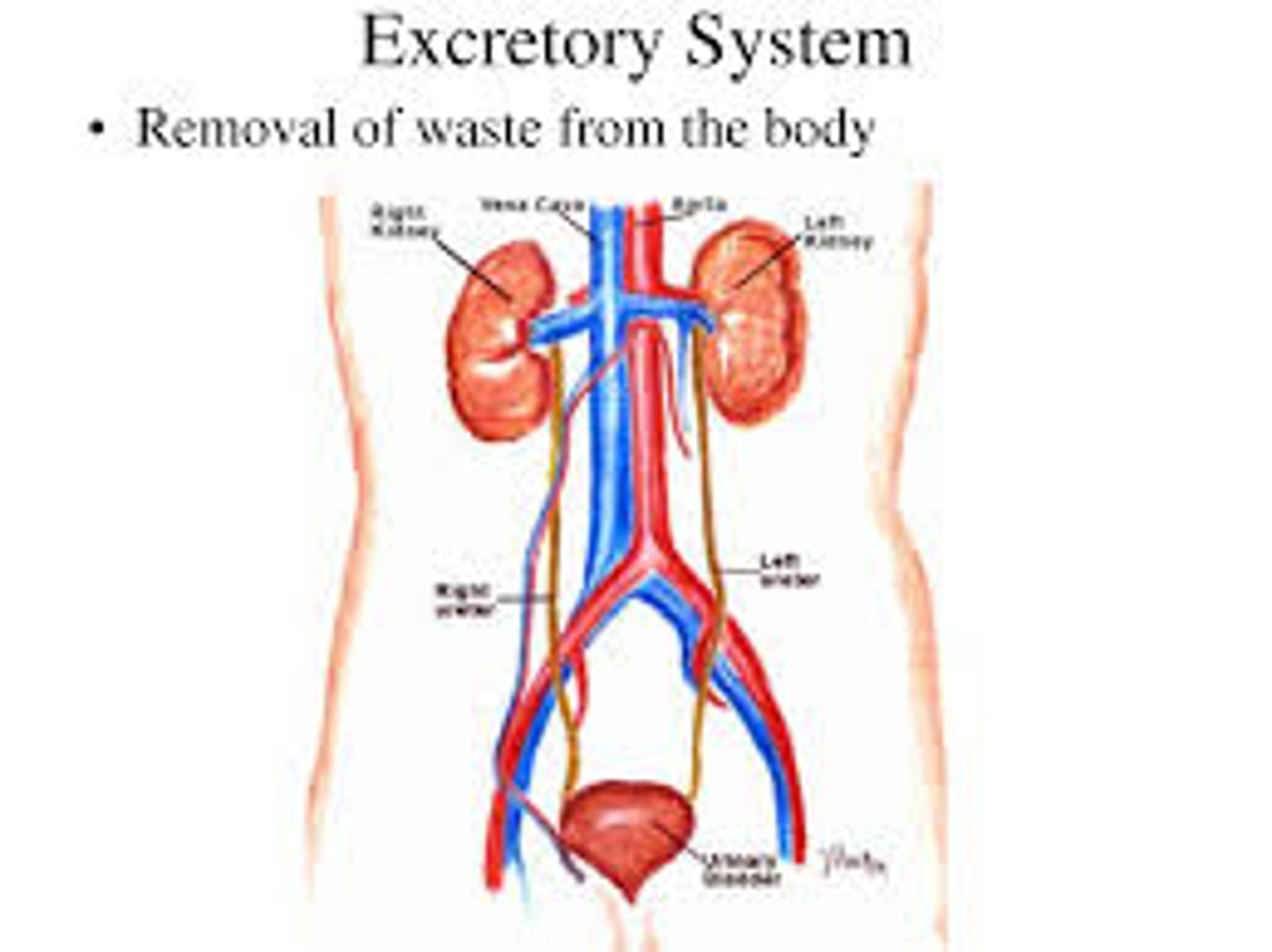
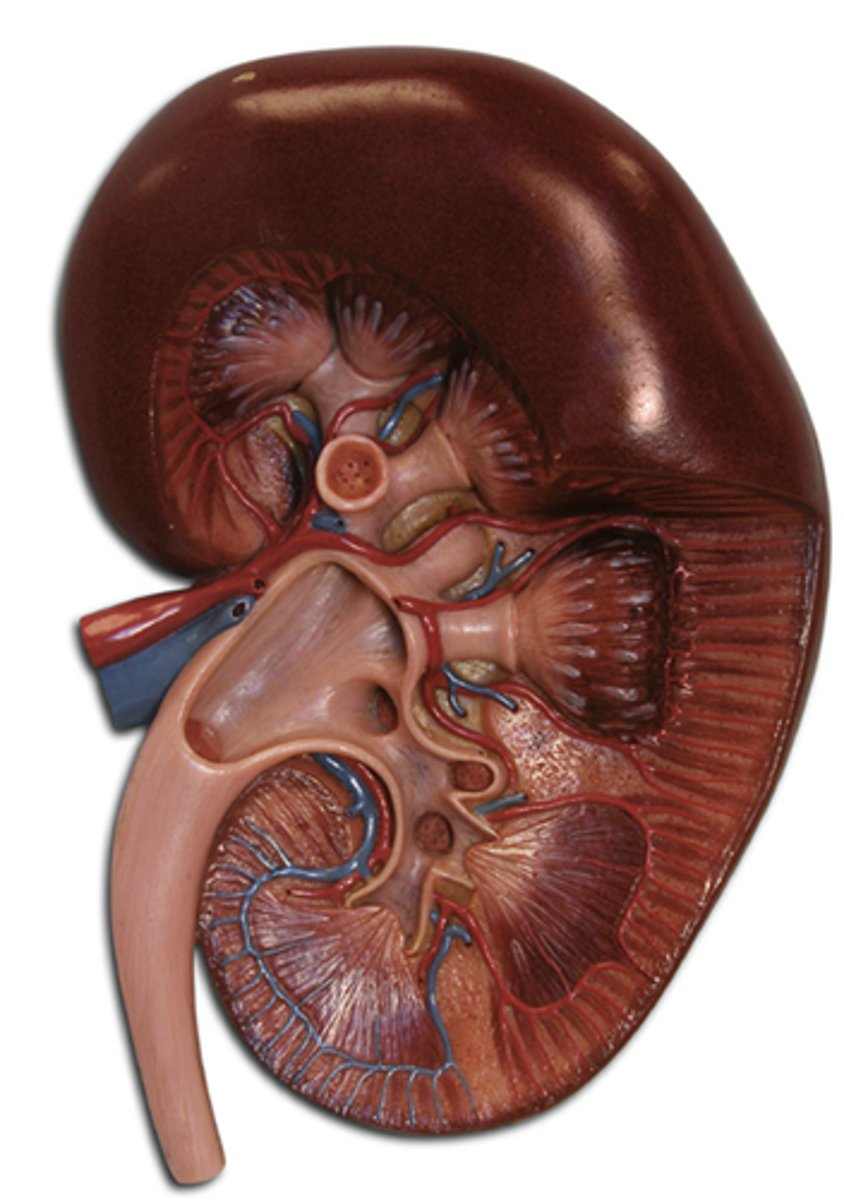
kidney
An organ that filters blood and excretes urine
ureter
A long tube that carries urine to the bladder
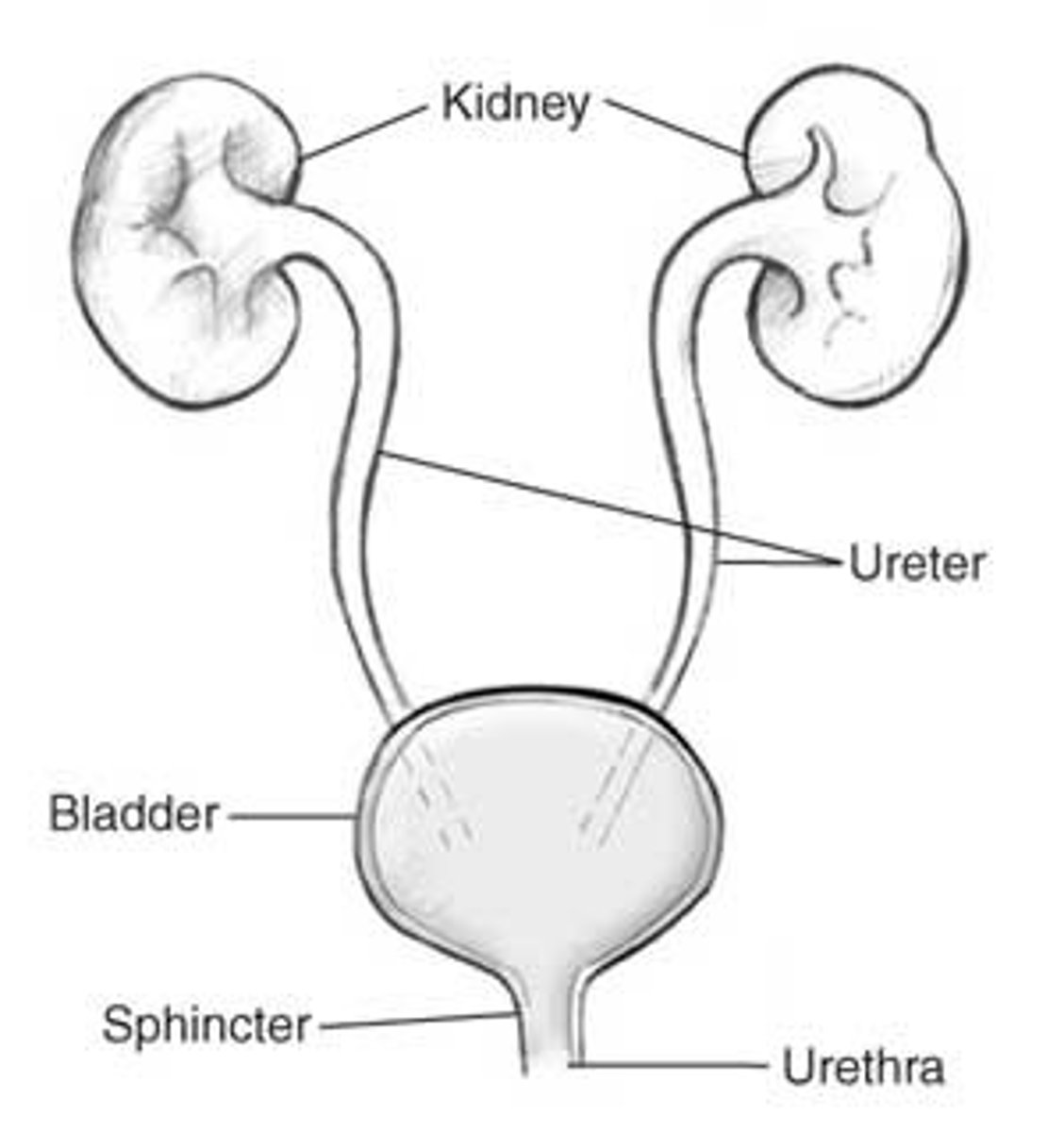
urethra
The tube that carries urine out of the body