geriatrics exam #3
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
urinary incontinence
involuntary leakage of urine
urinary incontinence prevalence
- more common with increasing age
- not normal part of aging
- urgency UI, MC type in geriatrics
- women more common, 70% NH residents
- men vs women 1:3 until age 85, then 1:1
- men increased due to prostate surgeries
increase urinary incontinence risk
- UTI (may be presentation)
- skin breakdown
- falls
urinary incontinence screen
all older pts w ROS, esp women
urgency incontinence
- strong/sudden need to void, difficult to postpone
- leakage preceded by or assoc w urgency
- need to "rush" to the toilet
stress incontinence
- leakage w effort, exertion, sneezing, or coughing
- failure of sphincter mech w cough, laugh, sneeze, or physical activity
- severe sphincter damage, uninhibited detrusor contraction
mixed incontinence
urgency and stress incontinence sx
overflow incontinence (nonspecific)
inability to completely empty
incontinence evaluation
- labs: first obtain UA, culture if UTI sx
- imaging
incontinence management
- pts often overestimate impact and invasiveness of treatment
- ask about pts concerns regarding tx
- behavior treatments (1st line)
- weight loss (only evidence based lifestyle intervention)
refer incontinence pts if
- acute onset of UI and suprapubic, lower ab, and or pelvic pain
- red flag for underlying neuro or neoplastic dz
- should prompt quick referral to neuro/uro/gyn
Ms. J, who is 82 years old, complains of urine leakage while playing golf. This has gotten worse over the past year, and she rarely makes it through 9 holes without feeling like she needs to "run into the bushes and go." Leakage is usually small volume, but causes her extreme embarrassment because she is afraid she will smell of urine. She has tried limiting caffeine in the morning before she golfs and avoiding drinking water while playing, to no effect. She also tried "those Kegeler" exercises in the past without success. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation for Ms. J?
bladder training
3 multiple choice options
which of the following is true about tolterodine (detrol)
it has greater risk of adverse effects w its twice daily formulation
3 multiple choice options
The daughter of a 79-year-old woman notes that her mother, who has dementia and lives with her, is wetting herself when she attends her new day program. Program staff have requested that "something be done" as she is requiring a clothes change nearly every time she is there. She cannot describe the circumstances of leakage, saying "it just comes." Leakage is uncommon at home. Her medications include donepezil and acetaminophen. Physical examination is normal. Initial treatment approach will require intervention by
which of the following?
day program staff
3 multiple choice options
An 82-year-old man, Mr. A, complains of worsening nocturia, occurring four times per night. His other lower urinary tract symptoms are slow stream, occasional urgency, and
urgency-related leakage once weekly. Medical problems include poorly controlled hypertension, diastolic heart failure, hyperlipidemia, osteoarthritis, and prediabetes. His
medications include lisinopril 20 mg daily, metoprolol succinate 75 mg daily, atorvastatin 10 mg daily, metformin 500 mg twice daily, hydrocodone-acetaminophen as needed, and aspirin 81 mg daily. Amlodipine 5 mg daily was recently added by his cardiologist. On review of systems, Mr. A complains that nocturia is causing daytime fatigue, and he is more constipated. Physical examination is notable for blood pressure 162/83 mmHg, heart rate 60 beats per minute, clear lungs, soft abdomen, enlarged prostate, and 21 pretibial edema. Your next step in management should be:
stop amlodipine and increase lisinopril
3 multiple choice options
constipation
- infrequent passage of stool
- generally <3 BMs/wk
fetal incontinence
involuntary loss of liquid or solid stool
fecal incontinence history
- use pt oriented term and obtain focused hx on frequency, consistency, other sx
- helps excludes primary and secondary cases
- sx of persistent N/V and abd pain, broaden DD and eval, esp for intestinal obstruction
new constipation and FI sx <6 months should always prompt eval for warning signs such as
- hematochezia
- + fecal occult blood test
- obstructive bowel sx
- acute onset of constipation
- constipation refractory to tx
- weight loss >10 lbs
- change in stool caliber
- fam hx of colon CA or IBD
- new onset constipation/diarrhea w/o evidence of potential primary cause
fecal incontinence imaging
- abd radiographs 1st, may show stool retention
- rarely need specialized testing but there are options
constipation treatment
- eval and address secondary causes
- slow transit & prevention: pt edu, dietary, drug therapies
- dyssynergic: biofeedback, relaxation, suppository. treat this first
constipation pharmacologic treatments
- cholestyramine
- bulking agents (stool softener) often first line
- stool softeners and emollients, lubrication effects
- osmotic lax promote secretion of water into intestinal lumen by osmosis (NO CKD or CHF)
fecal impaction
- large amt of stool in rectum
- abd radiograph if suspect impaction is beyond reach
- digital disimpaction and colon evac
- refer to surg if abd tenderness +/- bleeding, could be perf or ischemia
incontinence associated dermatitis
- involvement of perineal area can occur from wetness & moisture from pads or other forms
- skin barrier cream recommended to help prevent & tx erythema and maceration
which treatment has some evidence for improving constipation and fecal incontinence
stool softeners
3 multiple choice options
common secondary causes of constipation in older adults include which of the following
all of the above
3 multiple choice options
constipation in older adults may result from many factors. which of the following is not considered a common contributing factor to constipation in older adults
obesity
3 multiple choice options
risk factors assoc with constipation in older women are
all of these
3 multiple choice options
the first step in developing a treatment strategy for a physically active pt with constipation symptoms that are not caused by other potential causes is to
recommend higher fiber and water intake
3 multiple choice options
T or F: supplemental fiber treatment can improve symptoms related to constipation and FI
true
over the counter milk of magnesia and polyethylene glycol improve constipation by
promoting secretion of water into the intestinal lumen
3 multiple choice options
male sexuality with aging
- frequency and prevalence of sexual activity decreases, sexual interest remains
- ED not normal aging. MC sexual problem of older men
- ED related to low testosterone, mental health, lack of partner attraction, neuro&vasc dz MC
psychogenic ED
MC cause if sleep assoc erections or erections w masturbation
ED evaluation
- PE: attention to sx of vascular, neuro, or endocrine dz
- labs: vascular dz or disorders suggested by PE, serum T if low libido and no other sx
ED treatment
- 5 phospho inhibitors 1st line
- sildenafil or vardenafil
- low initial dose in men suspected of neurogenic ED
- poor response suggests vasculogenic ED
female sexual dysfunction pelvic exam
- try to localize source of pain
- tender pelvic floor muscles are a sign of high tone pelvic floor dysfxn
- refer to PT specializing in pelvic floor muscle dysfxn
vulvovaginal atrophy treatment
local/topical estrogen
low libido w/o identifiable cause may respond to T, but it is
not FDA approved
what is the MC cause of ED in older men
atherosclerosis
3 multiple choice options
A 70-year-old woman reports sexual pain with deep penetration only. What is the most likely cause of her problem?
high tone pelvic floor dysfunction
3 multiple choice options
which is the most reasonable first step in the treatment of older men with ED
sildenafil
3 multiple choice options
A 72-year-old woman reports vaginal dryness that interferes
with coitus. Her medical history includes type 2 diabetes,
hypertension, and osteoarthritis. Medications are glyburide,
chlorthalidone, and acetaminophen. What would be your first
step in therapy?
stop chlorthalidone
3 multiple choice options
peripheral vascular disease risk factors
- 90% have hx of CAD
- smoking
- advanced age
does absence of a bruit rule out a carotid disease
no
hollenhorst plaques
cholesterol microemboli in retinal arterioles from plaque embolization
carotid stenosis diagnosis
- duplex US initially
- angiography gold standard
carotid stenosis screening
- asymptomatic pts >60 yo w 1+ risk factors
- HTN, CAD, smoker, 1st degree relative w CVA
- if will be undergoing a planned CABG
abdominal aortic aneurysm
- degenerative dz of aorta, progressive remodeling of arterial walls, possible rupture
- increase in vessel diameter by >50%, usually >3-5 cm
- MC in men >65 yo
- common presenting sx: abd pain radiating to back, pulsatile abd mass
abdominal aortic aneurysm risk factors
- smoking
- advanced age
- CAD
- hx of CVA
ultrasound AAA screening
- men 65+ w smoking hx
- men 55+ w fam hx of AAA
- women 65+ w smoking hx and or fam hx of AAA
AAA PE and diagnosis
- abdomen may have tender, pulsatile mass
- US ideal for screening
- CT of abdomen for measuring and pre op
AAA treatment
- elective surgery: 5-5.5 cm in men, 4.5-5 cm in women
- urgent: increase 0.5 cm in 6 mo, increase 1 cm in 12 mos regardless of size
PAD/PVD screening
- >60 yo w 1 or more risk factors
- HTN, CAD, smoker, 1st relative w stroke hx
- if undergoing planned CABG
PAD/PVD MC presentation
- claudication or cramping of LE muscle w ambulation
- calves or buttocks relieved w 10 mins cessation of activity
PAD/PVD diagnostics
- doppler by segmental arterial pressure & ABI
- US initial study to ID
- CT contrast angio for accurate
- peripheral catheter based angio gold standard
PAD/PVD walking program
30 min walk 3x/wk can 2x or 3x max walking distance in pts w LE arterial dz & outcomes comparable to iliac angio & stenting
which of the following is true regarding lower extremity peripheral artery disease
the ABI is an easy to perform office based procedure that is rapid and reliable for diagnosing PAD
3 multiple choice options
with regard to endovascular versus open aortic aneurysm repair, which of the following is false
open repair results in a threefold increase in operative mortality
2 multiple choice options
relative contraindications for performance of carotid stenting include which of the following
age >80 yrs
3 multiple choice options
4 point dermatologic description
- anatomic distribution
- lesion configuration
- primary lesion and color
- secondary change if present
stasis dermatitis
- caused by venous insufficiency
- acquired venous incompetence, saphenous vein grafting, or prior thromboembolism
- often misdiagnosed as bilateral leg cellulitis
seborrheic dermatitis
- frequently on scalp, eyebrows, forehead, nasolabial folds, central chest, axilla
- affect 10% of population
- etiology not clear, exuberant inflammatory response to malassezia yeast
rosacea
- inflammation exacerbated by vasodilatory responses to triggers (UV light, stress, spicy)
- papulopustular eruption of nose/cheeks, ruddy cheeks & nose, bulbous nose
- topical steroids can make worse
A 90-year-old balding farmer who is otherwise healthy and active has diffuse pink, rough scaly papules on his scalp. Which of the following statements is most correct about his condition?
one-quarter may spontaneously regress, esp with aggressive sun protection
3 multiple choice options
A 70-year-old patient has scattered nummular plaques with thick scale on his shins that are extremely pruritic. He also has very dry skin. Skin scraping is negative for dermatophyte. He had already completed a course of oral antifungal medication prescribed to him by an urgent care physician. Assuming this is nummular eczema, which of the following topical medication and vehicle is the best choice?
triamcinolone 0.1% ointment
3 multiple choice options
A 65-year old man is hospitalized with sudden onset chest pain and discharged after a negative cardiac workup. He comes to your office with itchy and painful pink bumps without scale along the left sternum and the left flank that abruptly stop at the midline, where he thinks electrical leads were placed. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
empiric valacyclovir
3 multiple choice options
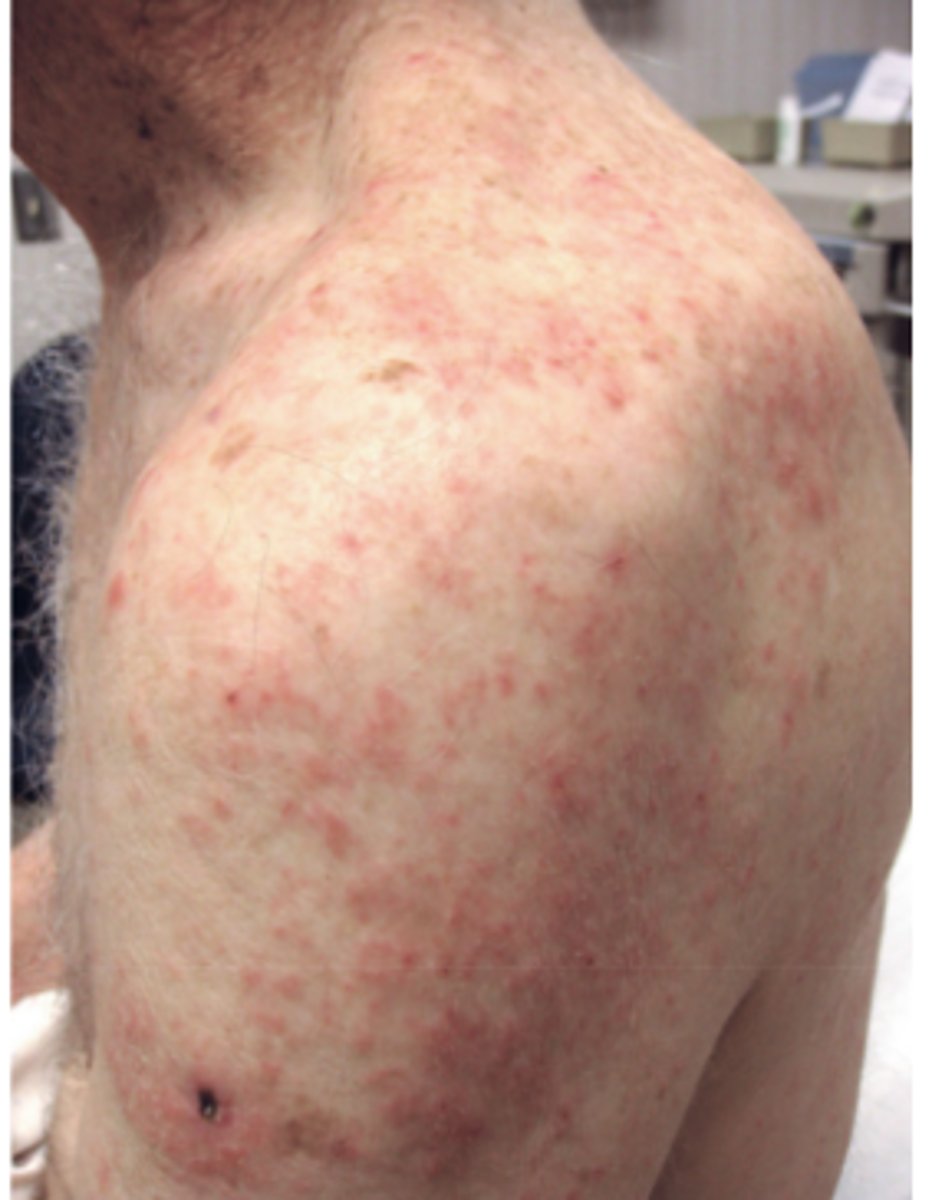
what is the primary lesion in the photo
papule
3 multiple choice options
largest category of psychiatric DO in older adults
depression
elderly depression risk factors
- chronic medical illness
- loss of a loved one
- relocation
- disability
- social isolation
elderly pts with depression are more likely to have what kind of complants
somatic complaints (mainly GI) or illness anxiety, & irritability, rather than guilt or low self-esteem
subsyndromal depression
- AKA minor depression in DSM-V
- often present w comorbid chronic illness leading to functional decline
- more prevalent with advancing age
persistent depressive DO (PDD)
- AKA dysthymic disorder
- more chronic, less severe form of MDD
- unlikely to occur in late late; may persist from midlife into late life
subsyndromal depression symptoms unique to elderly
- somatic complaints primarily HI
- complaints out of proportion to illness
- timing of new or worsening physical complaints and onset of stressor
- hypochondriasis
- agitation
- may deny emotional disturbance; instead, reports multiple of physical sx
PDD symptoms (2 or more)
- poor appetite or overeating
- sleep disturbance
- low energy or fatigue
- difficulty w concentration
- indecisiveness
- feelings of hopelessness
- low self esteem
normal grief and bereavement
- effect on functioning differentiates normal process from psychopathology
- normal grief does not, or only minimally impairs funtion
complicated grief
- protracted, severe form
- strong feelings of anger or bitterness
- feelings of emptiness
- persistent longing to be with the loved one
- recurring intrusive thoughts about the loss
- reclusiveness from family and friends
- PCBD if >=12 mos, prolonged grief DO 6 mos
depression is a risk factor for
dementia, stroke
what should you always order for acute onset depressive sx in the elderly
UA
which of the following is not a risk factor for late-life depression
family history of depression
3 multiple choice options
which of the following is not a side effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in older adults
increase in suicidal ideation
3 multiple choice options
you want to start pharmacologic treatment for depression
in an older patient who is taking numerous medications.
You are concerned about drug-drug interactions. Which of
the following antidepressants is the least likely to cause
such an interaction?
citalopram
3 multiple choice options
which of the following groups has the highest rate of suicide in the elderly
white males
3 multiple choice options
the remission rate of depressed pts who are 65 yrs and older to initial antidepressant treatment is
30%
3 multiple choice options
PCP role in elder abuse
- among least likely to report abuse to adult protective services
- you are a provider, not an investigator
- your job is to look for and report, not prove or disprove
- if you suspect abuse, report to local authorities
elder abuse victim risk factors
- advanced age (80+)
- poor health
- dependent for basic ADLs, functional dependence
- cognitive impairment
- mental illness
- financial dependency
- combative behavior
elder abuse perpetrator risk factors
- financial dependence on victim
- increase in caregiver responsibilities
- depression/mental illness
- alcohol and or drug dependence
- shared living arrangement
elderly abuse evaluation
- examined alone, away from family or caregivers
- direct questing by PCP in caring, nonthreatening manner
- home environment and safety issues should be evaluated
- inciting factors, frequency, type of abuse
- delay seeking tx, confusing injury causes, hx of suspicious incidents or doctor shopping
elderly abuse PE
- full skill assessment for bruising, burns, tenderness, abrasions. look in hidden areas
- weight loss, hygiene
- hx of fractures
- GYN eval may be necessary
- cognitive evaluation
suspect caregiver burnout when caregiver
- complains about pt
- blames pt for situations out of their control
risk factors for elder abuse include all of the following except
chronic diseases
3 multiple choice options
risk factors for elder mistreatment include all except
financial independence of the caregiver
3 multiple choice options
barriers to detecting elder mistreatment include all, except
the tendency for many older adults to falsely claim they are being abused
3 multiple choice options
subtypes of elder mistreatment include
all of these
3 multiple choice options
3rd most prevalent psych DO among elderly men surpassed only by dementia and anxiety
alcoholism
alcohol use
- at least 1 drink in past 30 days
- binge: 5+ drinks on same occasion
- heavy: 5+ drinks on same occasion for 5+ days in the past 30 days
- moderate use: 1 or more drinks/day
- heavy use: 2 or more drinks/day
- excessive use: 3 or more drinks/day
4 classification patterns for elderly pts w alcoholism
- chronic
- intermittent
- late onset (after 65), 1/3
- reactive (after stressor)
- chronic and intermittent almost all early onset, 2/3
most age appropriate depression screening tool for elderly
geriatric MAST
elderly alcohol use lab testing
- blood alc levels
- most useful: GGT, elevated in excessive drinkers
- MCV
- CDT
alcohol use meds
- disulfiram
- naltrexone (reduces craving)
- acamprosate
the diagnosis and treatment of alcohol dependency is best facilitated by using the model that defines alcoholism as a
disease
3 multiple choice options