C2.2 Atomic structure and the Periodic Table
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is an atom?
The smallest particle that can exist which are the building blocks of all matter
What is a neutral atom?
An atom that has no net electric charge because it has the same amount of protons and electrons
All elements in the periodic table are neutral atoms
Describe the structure of an atom
Made up of protons, electrons and neutrons
Protons and neutrons are located at the center of the atom called the nucleus
The nucleus has a positive charge
Electrons move around the nucleus in orbital paths called shells
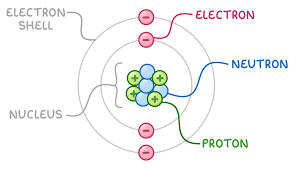
What is the location, relative mass and charge of the subatomic particles?
Protons:
Location: nucleus
Relative mass: 1
Charge: 1+
Neutrons:
Location: nucleus
Relative mass: 1
Charge: 0
Electrons:
Location: shells
Relative mass: 0 (negligible mass)
Charge: 1-
What is proton/atomic number?
The atomic number is the total number of protons in the nucleus
In neutral atoms, it is the number of electrons
Smaller than the atomic mass
Determines position of element on the periodic table
What is the nucleon/mass number?
The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom

How to find number of neutrons or protons in an atom?
Neutrons = Nucleon number - Proton number
Protons = Nucleon number - Neutron number
What does group number (vertical column) determine in the periodic table?
Number of valence electrons an element has
What does period number (horizontal row) determine in the periodic table?
Number of electron shells an element has
How many electrons can each electron shell hold?
First electron shell: 2
Second electron shell: 8
Third electron shell: 8
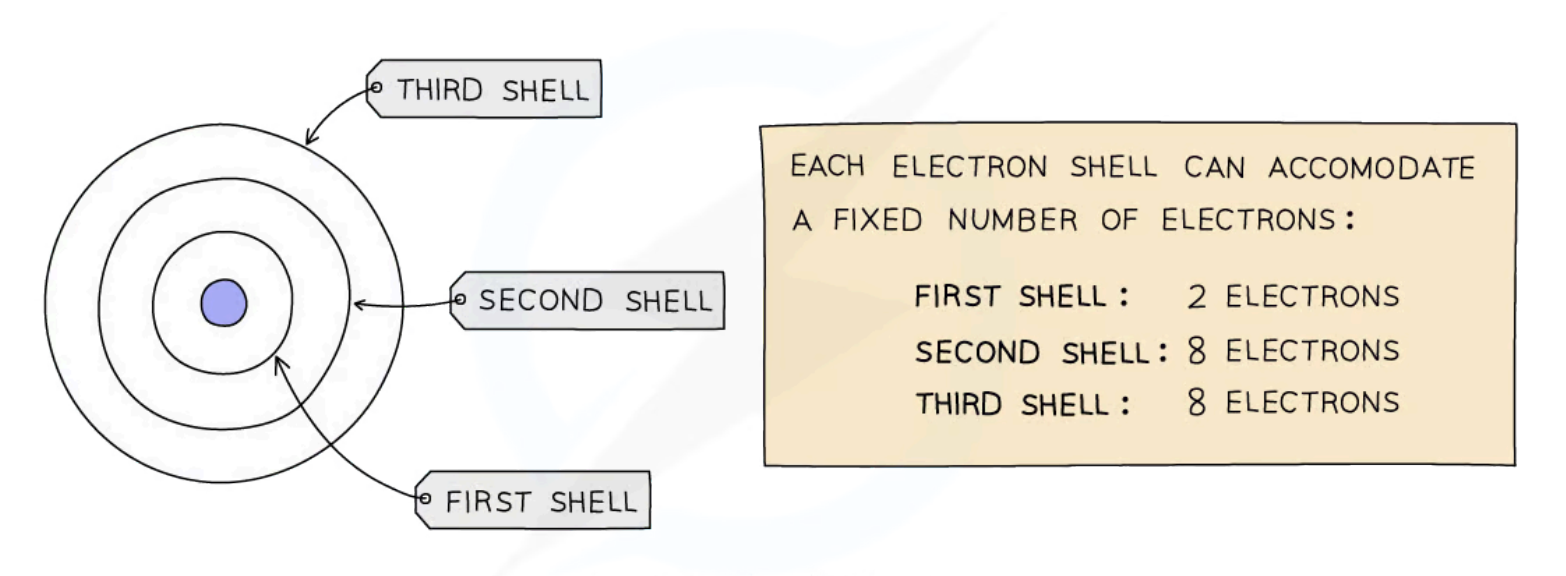
Determine the electronic configuration of elements with proton number 1 to 20
Proton number | Element (Symbol) | Shell Configuration |
1 | Hydrogen (H) | 1 |
2 | Helium (He) | 2 |
3 | Lithium (Li) | 2, 1 |
4 | Beryllium (Be) | 2, 2 |
5 | Boron (B) | 2, 3 |
6 | Carbon (C) | 2, 4 |
7 | Nitrogen (N) | 2, 5 |
8 | Oxygen (O) | 2, 6 |
9 | Fluorine (F) | 2, 7 |
10 | Neon (Ne) | 2, 8 |
11 | Sodium (Na) | 2, 8, 1 |
12 | Magnesium (Mg) | 2, 8, 2 |
13 | Aluminium (Al) | 2, 8, 3 |
14 | Silicon (Si) | 2, 8, 4 |
15 | Phosphorus (P) | 2, 8, 5 |
16 | Sulfur (S) | 2, 8, 6 |
17 | Chlorine (Cl) | 2, 8, 7 |
18 | Argon (Ar) | 2, 8, 8 |
19 | Potassium (K) | 2, 8, 8, 1 |
20 | Calcium (Ca) | 2, 8, 8, 2 |
Describe the characteristics of noble gases
Elements in group 8 are called the noble gases, and have a full outer shell of electrons
All noble gases are unreactive, since their full electron shell makes them stable
Atoms that are not noble gases want to reach a full configuration of electrons in the outer shell, so they bond with other atoms to get a full outer shell
Which are the diatomic elements in the periodic table?
Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Iodine, Chlorine, Bromine
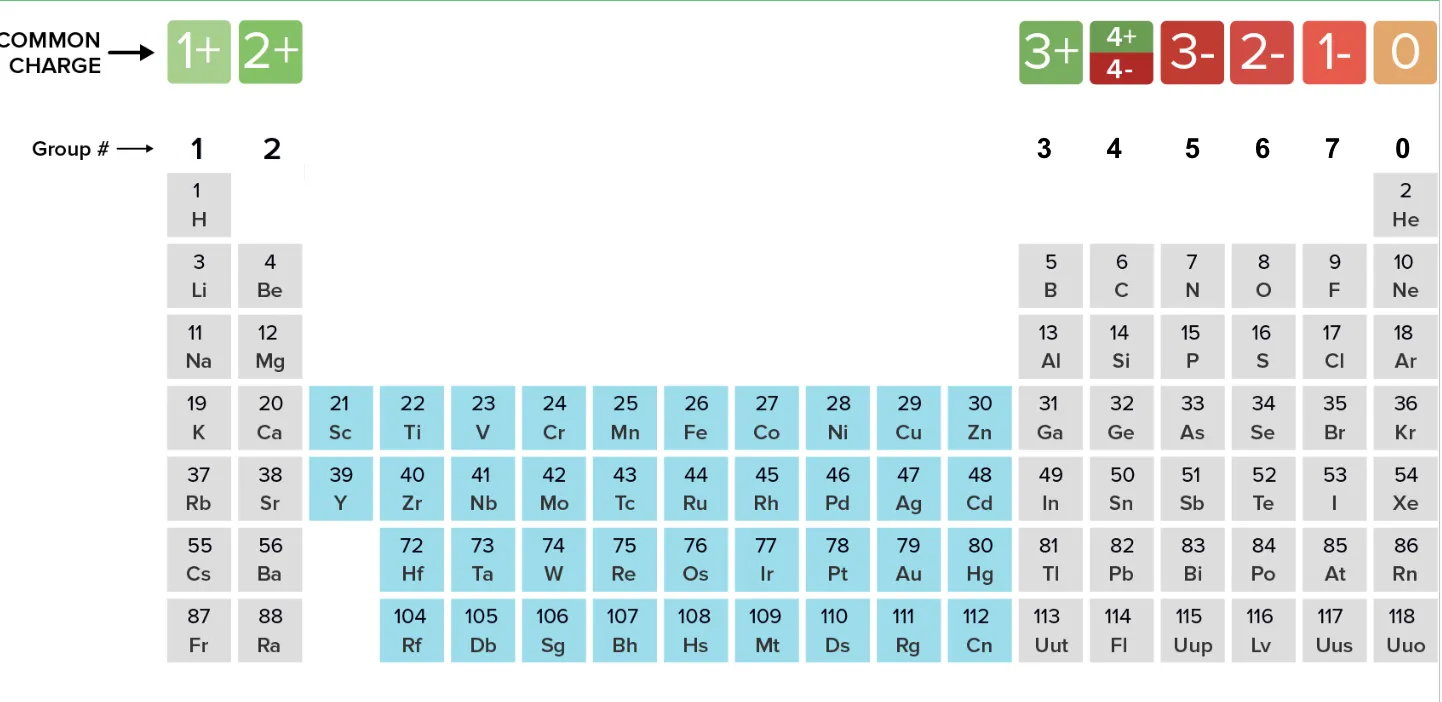
What is the charge of elements in group 1-7?
Group 1: 1+ (loses electron) - cation
Group 2: 2+ (loses electrons) - cation
Group 3: 3+ (loses electrons) - cation
Group 4: 4+ or 4- (depends on element)
Group 5: 3- (gains electrons) - anion
Group 6: 2- (gains electrons) - anion
Group 7: 1- (gains electron) - anion
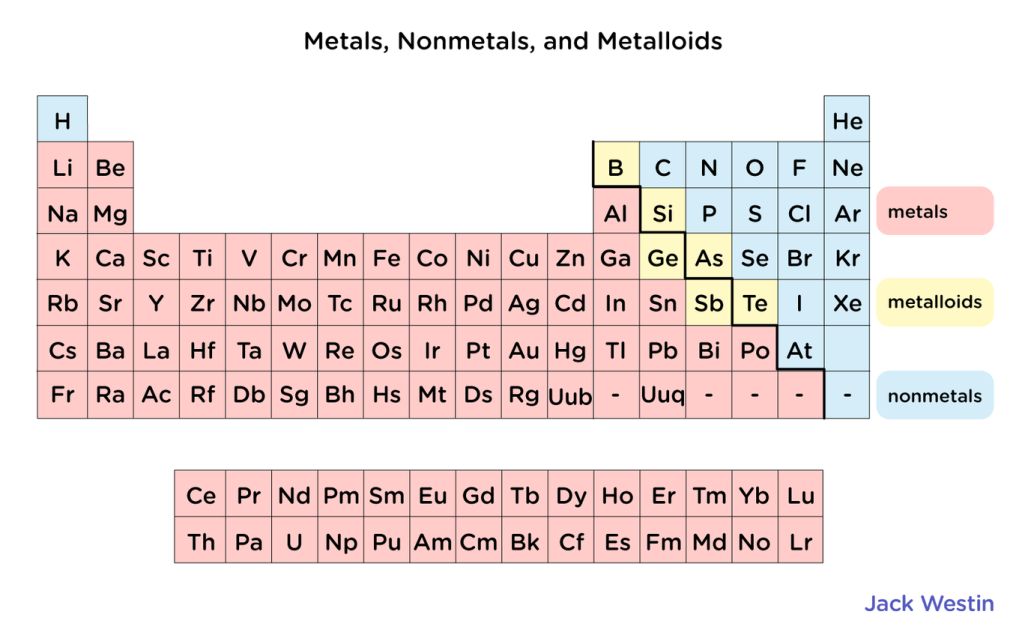
Where are metals and non-metals located in the periodic table?
What group is the halogens?
Group 7